Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Publication RC - PosterModena - ITALY
Hochgeladen von
Dr RC MishraOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Publication RC - PosterModena - ITALY
Hochgeladen von
Dr RC MishraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
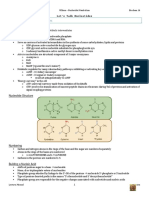
Solid Phase Synthesis of Substituted Adenine Phosphates as P2 Receptor Ligands
Ram Chandra Mishra, Diego Dal Ben, Catia Lambertucci, Floriana Rosa Portino, Rosaria Volpini, Sauro Vittori, Gloria Cristalli
Department of Chemical Sciences, University of Camerino,
Via S. Agostino 1, 62032 Camerino (MC) ITALY
Presenting Author E-mail: sauro.vittori@unicam.it
Purinergic (Purine and Pyrimidine) Receptors
Introduction ectonucleotidases
Adenosine kinase
The purinergic receptors are broadly classified into P1 and P2 receptor types. Adenosine is the ATP ADP AMP Adenosine
natural ligand of the P1 receptors, while corresponding nucleotide ATP is natural ligand for P2 class of
receptors (Figure 1). Many derivatives of the 9-ethyl adenine synthesized in our laboratory had shown UTP,UDP,UDP-glucose
to have very good binding affinities towards the P1 receptors.1,2
Other well known antagonists of the P1 receptors are the derivatives of natural xanthines, among
which caffeine and theophilline are of significance.3 These molecular skeletons with substitutions on
various positions have lead to the development of potent and selective P1 receptor antagonists.
P2Y1,2,11,12,13 A1 A2A A2B A3
P2X1-7
Moreover, phosphorylated analogues of these compounds, which are commonly known as ‘mini P2Y2,4,6,14
nucleotides, had shown high affinity for the P2 family of receptors, specifically the P2X subclass.3 P2 receptor family P1 receptors
Figure 1
Present Work The monophosphates derivatives were obtained by reaction with phosphorous oxychloride in
On all the above and for the development of new P2 receptor ligands, we were prompted to trimethylphosphate, under nitrogen stream at room temperature, according to the Yoshikawa method.
synthesize some substituted adenine phosphates, which would be prospective P2 receptor ligands. Phosphorylation on solid phase using Yoshikawa procedure did not work. We are modifying the conditions
to develop a method for solid phase phosphate synthesis. The preparation of the diphosphate and
To begin with, we used the 2,6-dichloropurine as the starting material, which was derivatized at
triphosphate (Hoard-Hott method) is outlined in Scheme 2.
various positions before being phosphorylated. The phosphorylation was done on these derivatives to
obtain the corresponding mono, di and tri phosphates; on the same time attempts were made to
obtain these molecules on solid support.
HN
l
NH2 POC 3 N
NH2 N TMP N
N
O OMe M N N Cl
N /DC HO
Rink Amine Linker R N OH POCl3
NH2 T FA
%
TMP N 30
N SP 3
O
Cross linked Solid Support R N N O P O NH
4
(Polystyrene with DVB) OMe OH
PF 70 & 73
O
Figure 2: Rink Amine Resin Bu3NH H2P2O3 (Bu3NH)2 H2P2O7
N N N N
The use of solid support in synthesis of organic compounds, also known as the SPOS (Solid NH2 NH2
Phase Organic Synthesis) has been beneficial in faster synthesis of various classes of
N N
compounds.4 In the present case we have applied the use of Rink Amine resin for the synthesis of N N
O O O O O
substituted adenine phosphate (mini nucleotides). R N N N
O P O P O R N O P O P O P O
O O O O O
Cl x 3 NH4
PF 72 & 75 x 4 NH4
N PF 71 & 74
N
PF 70, 71, 72 R = Cl,
TMP = Trimethyl Phosphate
Cl N N PF 73, 74, 75 R =-O(CH2)2Ph
Ri n
H kA
NH3 liq. min Scheme 2
1 DI eR
PE esin
NH2 A, HN
85 % DM
N F N Biological Activity
N N
30 % TFA/DCM
Cl N N Cl N N
H H 100
2 SP 2 1uM 50uM 500uM
4-Bromobutyl acetate
4-Bromobutyl acetate
K2CO3, DMF, 80 oC K2CO3, DMF, rt, 24h
75
1uM 50uM
NH2 12 % (3)
viable cells (%)
N 64 % (4)
N 50 500uM
N NH
Cl N OCOCH3 +4
30 % TFA/DCM N N
3 25
Ph Cl N N OCOCH3
en
et
hy SP 3
NH3/MeOH la
98 % m
in 0
e/
al NH3 in Dioxane T PF70 w T PF72 w T PF74 w
NH2 co T PF73 w
ho
l rt, 12h
N N
HN T = Transfected, W = Wild type
Cl N N OH
NH2 N N
N N
Cl N N OH
Figure 3
4
R N N OH
SP 4 Results/Conclusion
30 % TFA/DCM We have synthesized 2,9-disubstituted adenine mono, di and tri phosphates, and developed a method to
load on solid support and derivatize the 2,6-dichlopurine leading to the synthesis of key intermediate for
A 5, R = -O(CH2)2Ph, 79 % B the Solid phase synthesis of mini nucleotides.
6, R = -NH(CH2)2Ph, 77 %
With respect to conventional synthesis, solid phase strategy in the present study needed milder reaction
Scheme 1 conditions, yielded sufficiently pure products without chromatography. All the compounds were
characterized using spectroscopic and chromatographic (TLC, HPLC) techniques.
The synthetic strategy for the preparation of substituted adenines starts with the commercially Preliminary screening of synthesized adenine mininucleotides was performed on P2Y4 receptors,
available 2,6-dichloropurine. The traditional approach, as well as the solid phase approach, overexpressed in human neuroblastoma cells (Figure 3). The activity was compared with the same on wild
are described in Scheme 1. type cells. Compounds PF 70 and PF 74 showed slight cytoxicity, proving the interaction of these
compounds with P2Y4 receptors.
References
[1] Camaioni E; Di Francesco E; Vittori S; Volpini R.; Klotz K-N; Cristalli G. New substituted 9-alkylpurines as adenosine receptor ligands Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1998; 6: 523-533.
[2] Volpini R; Costanzi S; Lambertucci C; Vittori S; Martini C; Trincavelli M L; Klotz K-N; Cristalli G. 2- And 8-alkynyl-9-ethyladenines: Synthesis and biological activity at human and rat adenosines receptors Purinergic Signalling 2005; 1: 173-181.
[3] Fischer B; Yefidoff R; Major D T; Rutman-Halili I; Shneyvays V; Zinman T; Jacobson K A; Shainberg, A. Characterization of "Mini-Nucleotides" as P2X Receptor Agonists in Rat Cardiomyocyte Cultures. An Integrated Synthetic, Biochemical, and
Theoretical Study J. Med. Chem. 1999; 42: 2685-2696.
[4] Dörwald F. Z; Organic Synthesis on Solid Phase: Supports, Linkers, Reactions, Wiley-VCH, March 2000.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Purines, Pyrimidines and Nucleotides: And the Chemistry of Nucleic AcidsVon EverandPurines, Pyrimidines and Nucleotides: And the Chemistry of Nucleic AcidsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentacion EntenderDokument37 SeitenPresentacion EntenderJuan David Marin ChiguachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accepted Manuscript: Coordination Chemistry ReviewsDokument48 SeitenAccepted Manuscript: Coordination Chemistry ReviewsLuis Fancisco Alcaraz BlancasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NucleotidesDokument6 SeitenNucleotidesDianne Ignacio100% (1)
- Bis (zinc (II) -dipicolylamine) -functionalized sub-2 μm core-shell microspheres for the analysis of N-phosphoproteomeDokument12 SeitenBis (zinc (II) -dipicolylamine) -functionalized sub-2 μm core-shell microspheres for the analysis of N-phosphoproteomeTuyết HânNoch keine Bewertungen
- J Fob 2015 05 002Dokument10 SeitenJ Fob 2015 05 002ericktNoch keine Bewertungen
- De Furano A IndoleDokument9 SeitenDe Furano A IndolecristianlalindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dopamine Receptors: GlossaryDokument5 SeitenDopamine Receptors: Glossarytirasi1214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Perylene-3,4,9,10-Tetracarboxylic Acid Diimides: Synthesis, Physical Properties, and Use in Organic ElectronicsDokument22 SeitenPerylene-3,4,9,10-Tetracarboxylic Acid Diimides: Synthesis, Physical Properties, and Use in Organic ElectronicsMuhammad Faisal AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemical and Biophysical Research CommunicationsDokument4 SeitenBiochemical and Biophysical Research CommunicationsGiggly HadidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oyamada 2008Dokument5 SeitenOyamada 2008DAMNiningNoch keine Bewertungen
- GC Analysis of Pahs Using An Agilent J&W Factorfour Vf-17Ms Column With Ez-GuardDokument2 SeitenGC Analysis of Pahs Using An Agilent J&W Factorfour Vf-17Ms Column With Ez-GuardJean RisquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecules of HeredDokument82 SeitenMolecules of HeredTri Hiu AmborowatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem1b Ren NucleotideMetabDokument15 SeitenBiochem1b Ren NucleotideMetabKristine VanzuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Palladium Precatalyst Design and Its Applications in Cross-CouplingDokument27 SeitenPalladium Precatalyst Design and Its Applications in Cross-CouplingiammouliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21 - N Fixation PDFDokument7 Seiten21 - N Fixation PDFshubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Novabiochem: Derivatives For Enhancing Peptide SynthesisDokument4 SeitenNovabiochem: Derivatives For Enhancing Peptide SynthesisValentina D BrunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 53 110 PMR Apr06Dokument58 Seiten53 110 PMR Apr06Aziz BasyariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abbreviations and Symbols For Nucleic Acids, Polynucleotides, and Their ConstituentsDokument6 SeitenAbbreviations and Symbols For Nucleic Acids, Polynucleotides, and Their ConstituentsRickySaptarshi SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination Surface-Confined Derivatized With: of Surface Values of Molecules pH-Sensitive Pendant GroupsDokument3 SeitenDetermination Surface-Confined Derivatized With: of Surface Values of Molecules pH-Sensitive Pendant GroupsBoodeppa NatarajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Diphosphine Ligands Containing EthylDokument10 SeitenNew Diphosphine Ligands Containing EthylGI2015Noch keine Bewertungen
- Purine and Purinergic ReceptorsDokument10 SeitenPurine and Purinergic ReceptorsAdila BilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Tellurabenziporphyrin and Its PD (II) Complex: Sunit Kumar, Way-Zen Lee, and Mangalampalli RavikanthDokument4 SeitenSynthesis of Tellurabenziporphyrin and Its PD (II) Complex: Sunit Kumar, Way-Zen Lee, and Mangalampalli RavikanthPoonam Rajesh PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- C1AN15021ADokument8 SeitenC1AN15021AiprateekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 (Part 2)Dokument9 SeitenChapter 1 (Part 2)Hafiy DarwisyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adenosine Triphosphate PDFDokument7 SeitenAdenosine Triphosphate PDFFrancisco BecerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methoxy and Hydroxy Derivatives of 3,4-Dihydro-3 - (Di-N-Propylamino) - 2h-1-Benzopyrans - New Synthesis and Dopaminergic ActivityDokument8 SeitenMethoxy and Hydroxy Derivatives of 3,4-Dihydro-3 - (Di-N-Propylamino) - 2h-1-Benzopyrans - New Synthesis and Dopaminergic ActivityHamilton MorrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cpy in The Metabolism of DrugsDokument2 SeitenCpy in The Metabolism of DrugsAngie CeronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetrahedron Letters: Graziano Baccolini, Carla Boga, Camilla Delpivo, Gabriele MichelettiDokument5 SeitenTetrahedron Letters: Graziano Baccolini, Carla Boga, Camilla Delpivo, Gabriele MichelettiRiyadh RayhandhiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Communication - A Novel Synthesis of 3 4-Methylenedioxyphenyl-2-Propanone MDP2P From HelionalDokument3 SeitenShort Communication - A Novel Synthesis of 3 4-Methylenedioxyphenyl-2-Propanone MDP2P From HelionalMikel L.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Poster SubstratesDokument1 SeitePoster SubstratesDani VankovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference 1Dokument3 SeitenReference 1pathinfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijcb 53B (10) 1255-1262Dokument8 SeitenIjcb 53B (10) 1255-1262Alex WasabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDokument15 SeitenWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistskamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystengcomm: PaperDokument12 SeitenCrystengcomm: PaperMuhammad Al-HanafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- (BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 5 Nucleic Acid ChemistryDokument7 Seiten(BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 5 Nucleic Acid ChemistryJhun Lucky SadsadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inventi ImpactMMpepDokument7 SeitenInventi ImpactMMpeplitafsmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transaminases: Scheme 1 General Reaction Scheme For - Transaminase-Catalyzed Asymmetric Reductive AminationDokument38 SeitenTransaminases: Scheme 1 General Reaction Scheme For - Transaminase-Catalyzed Asymmetric Reductive Aminationbluedolphin7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Regenerative Role of The Red Phosphorus in The Couple HI/P'Dokument6 SeitenRegenerative Role of The Red Phosphorus in The Couple HI/P'spNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moree 1993Dokument10 SeitenMoree 1993xrovljolscjvmiszchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic AcidDokument9 SeitenNucleic AcidAmit AnirudhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purine NucleotideDokument61 SeitenPurine NucleotideMayalu123100% (1)
- Why Nature Chose Phosphates - F H Westheimer - 1987Dokument7 SeitenWhy Nature Chose Phosphates - F H Westheimer - 1987Antonio Vázquez MotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATP ADP Cycle Activity PDFDokument2 SeitenATP ADP Cycle Activity PDFFaustino, Jayreign MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highly Acidic BINOL-Derived Phosphoramidimidates and Their ApplicationDokument3 SeitenHighly Acidic BINOL-Derived Phosphoramidimidates and Their Applicationxuyijing2007comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transition-Metal-Catalyzed C-P Cross-Coupling ReactionsDokument26 SeitenTransition-Metal-Catalyzed C-P Cross-Coupling ReactionsMarius ConstantinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kopranenkov 1995Dokument18 SeitenKopranenkov 1995aleena.taufiq125Noch keine Bewertungen
- Polymeric Materials (Compatibility Mode)Dokument20 SeitenPolymeric Materials (Compatibility Mode)hkharshak065Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters: Scott R. Walker, Wanting Jiao, Emily J. ParkerDokument6 SeitenBioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters: Scott R. Walker, Wanting Jiao, Emily J. ParkerIsmael GuardiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Note On BCH 202Dokument16 SeitenLecture Note On BCH 202Muhammad LawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry - Metabolism of Purines and PyrimidinesDokument11 SeitenBiochemistry - Metabolism of Purines and PyrimidinesProjjal SanyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Molecular BiologyDokument15 Seiten3 - Molecular BiologyGoodone OneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tolmie Michael B 2001Dokument79 SeitenTolmie Michael B 2001Florian FischerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetamide-Modified Hyper-Cross-Linked Resin: Synthesis, Characterization, and Adsorption Performance To Phenol From Aqueous SolutionDokument9 SeitenAcetamide-Modified Hyper-Cross-Linked Resin: Synthesis, Characterization, and Adsorption Performance To Phenol From Aqueous SolutionAdel ZaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article On RifampinDokument47 SeitenArticle On RifampinShilpi PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficient Scavenging of PH P and PH Pdo With High-Loading Merrifield ResinDokument3 SeitenEfficient Scavenging of PH P and PH Pdo With High-Loading Merrifield ResinLy NgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02Dokument123 Seiten02กาญจนา นุ้ยนิ่งNoch keine Bewertungen
- Russian Journal of Organic Chemistry 2023, 59, 652-655Dokument4 SeitenRussian Journal of Organic Chemistry 2023, 59, 652-655NoimurNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role and ApplicationDokument12 SeitenThe Role and ApplicationÂn NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purine and Pyrimidine Nucleotide MetabolismDokument13 SeitenPurine and Pyrimidine Nucleotide Metabolism202210034Noch keine Bewertungen
- Noscapine: Derivatization For Optimization of Anticancer ActivityDokument16 SeitenNoscapine: Derivatization For Optimization of Anticancer ActivityDr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT - Cdri@yahoo - Co.in RP - Tripathi@cdri - Res.in: ST STDokument30 SeitenRPT - Cdri@yahoo - Co.in RP - Tripathi@cdri - Res.in: ST STDr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- CV Rptripathi 240111Dokument29 SeitenCV Rptripathi 240111Dr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV Rptripathi 210310Dokument29 SeitenCV Rptripathi 210310Dr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV Rptripathi 210310Dokument29 SeitenCV Rptripathi 210310Dr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication List - TableDokument3 SeitenPublication List - TableDr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jacobson SeminarDokument1 SeiteJacobson SeminarDr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orphan Drugs Doctoral SeminarDokument21 SeitenOrphan Drugs Doctoral SeminarDr RC Mishra100% (1)
- Lunar Eclipse 2008 August 16PDokument1 SeiteLunar Eclipse 2008 August 16PDr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amarnath TruthDokument17 SeitenAmarnath TruthDr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication RPT - MCR - TuberculosisDokument39 SeitenPublication RPT - MCR - TuberculosisDr RC Mishra100% (3)
- Publication List - PatentsDokument1 SeitePublication List - PatentsDr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication List - PosterDokument3 SeitenPublication List - PosterDr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication RC - BMC2Dokument12 SeitenPublication RC - BMC2Dr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication List - OralPresentationDokument1 SeitePublication List - OralPresentationDr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication RC - CCHTSDokument14 SeitenPublication RC - CCHTSDr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication RC - BMCLDokument5 SeitenPublication RC - BMCLDr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Glycosylated - Amino Hydroxamates As New Class of AntimalarialsDokument12 SeitenSynthesis of Glycosylated - Amino Hydroxamates As New Class of AntimalarialsDr RC MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling Fluid Contamination & TreatmentDokument109 SeitenDrilling Fluid Contamination & TreatmentjalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S2214785322053214 MainDokument4 Seiten1 s2.0 S2214785322053214 MainMaurya GyanprakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron Transport Chain PPT 5Dokument39 SeitenElectron Transport Chain PPT 5rohajira67% (3)
- Studies On Tribological Behaviour of Banana and Coir Hybrid Fiber Epoxy Reinforced CompositesDokument19 SeitenStudies On Tribological Behaviour of Banana and Coir Hybrid Fiber Epoxy Reinforced CompositesKirubhakaran KathiresanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICON SMART - Arya Rifan Syah - University of Lampung - Video PresentationDokument16 SeitenICON SMART - Arya Rifan Syah - University of Lampung - Video PresentationArya RifansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravimetric Analysis PDFDokument6 SeitenGravimetric Analysis PDFMourineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 2Dokument18 SeitenPresentation 2rayonneeemdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) : From Precursors To Thin Film StructuresDokument9 SeitenAtomic Layer Deposition (ALD) : From Precursors To Thin Film StructurestehtnicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silcone Glass Cloth Tech SheetDokument1 SeiteSilcone Glass Cloth Tech SheetOdo AsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes-MoleDokument15 SeitenLecture Notes-MoleKotyada ParthivNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rational Drug DesignDokument451 SeitenRational Drug DesignVIRAJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystals: Anti-Solvent Crystallization Strategies For Highly Efficient Perovskite Solar CellsDokument21 SeitenCrystals: Anti-Solvent Crystallization Strategies For Highly Efficient Perovskite Solar CellsGianluca J BravettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 8 Electrochemistry 8.1 Objectives: SKU3073 Chemistry Semester 1 2020/2021Dokument6 SeitenExperiment 8 Electrochemistry 8.1 Objectives: SKU3073 Chemistry Semester 1 2020/2021Maldini JosnonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Firas EPG RecyclingDokument26 SeitenFiras EPG RecyclingSuji Educational ServicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04-06-2020 - SR - LT - All - All INDIA - E-Test Series - Jee Main - MFT-02 - Key & Sol's (NjwnddnsnshsabhbDokument14 Seiten04-06-2020 - SR - LT - All - All INDIA - E-Test Series - Jee Main - MFT-02 - Key & Sol's (NjwnddnsnshsabhbSai GokulNoch keine Bewertungen
- N (G) - 2Nh (G) : StoichiometryDokument5 SeitenN (G) - 2Nh (G) : StoichiometryJaidenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Inorganic ChemistryDokument1 SeiteExperimental Inorganic ChemistryAkash AB OfficialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic EquilibriumDokument100 SeitenIonic EquilibriumShohom DeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZIMSEC O' Level Chemistry HandoutDokument120 SeitenZIMSEC O' Level Chemistry Handoutjacob t Ngwenya100% (10)
- Mcqs - Biochemistry - HPLC - PFMSG ForumDokument4 SeitenMcqs - Biochemistry - HPLC - PFMSG ForumArslan Bashir67% (3)
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokument9 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSanthiya SanjeeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.3 Procesos de Pulpeo - KraftDokument35 Seiten4.3 Procesos de Pulpeo - KraftMiguel MontielNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHemistry TEST 2 Mole Concept 4ADokument3 SeitenCHemistry TEST 2 Mole Concept 4AMinorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo Scientific Pierce Protein Ladders GuideDokument5 SeitenThermo Scientific Pierce Protein Ladders GuideBerniceTanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perspectives On The Agrochemical Industry and Agrochemical DiscoveryDokument6 SeitenPerspectives On The Agrochemical Industry and Agrochemical DiscoveryIxora MyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mil PRF 25567eDokument13 SeitenMil PRF 25567eAviasafe AviationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paut Inspection Report: Client Rfi NoDokument5 SeitenPaut Inspection Report: Client Rfi NoThiru Maran MasterscanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rates Practice Exam QuestionsDokument18 SeitenRates Practice Exam QuestionsisheanesuNoch keine Bewertungen
- XI CHANGFENG 2024 - Miscibility of Light Oil and Flue Gas Under Thermal ActionDokument8 SeitenXI CHANGFENG 2024 - Miscibility of Light Oil and Flue Gas Under Thermal Actionmilla kamilatuzzahrohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Manuals - Parr Instrument CompanyDokument7 SeitenInstruction Manuals - Parr Instrument CompanyMika SuominenNoch keine Bewertungen