Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
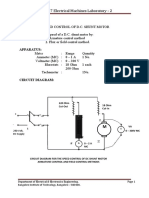
Electrical Machines Laboratory - 2: AIM: To Determine The Efficiency of The D.C. Machine by Conducting Swineburne's
Hochgeladen von
sanjuOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Electrical Machines Laboratory - 2: AIM: To Determine The Efficiency of The D.C. Machine by Conducting Swineburne's
Hochgeladen von
sanjuCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Electrical Machines Laboratory - 2
EXPT No:
DATE:
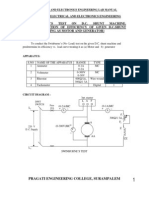
SWINEBURNE’S TEST ON D.C. MACHINE
AIM: To determine the efficiency of the d.c. machine by conducting Swineburne's
test.
APPARATUS:
Ammeter (MC) 0-5AI 1 No.
0-1 A 1 No.
Voltmeter (MC) 0 - 300 V 1 No.
0-30 V 1 No.
Rheostats 18 Ohms 1 No.
200 Ohms 1 No.
Tachometer 1 No.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS:
Swineburne’s Test:
0–5A
A MC
+ -
220 Ohm
18 Ohm
Cut-Out
Cut-In
+
+ Z
V
A
V 0 – 300V
-
- MC
230 Volt,
S M
DC Supply ZZ
+
AA
If A 0–2A
-
MC
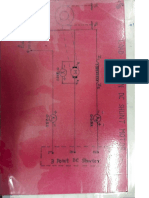
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM FOR THE SWINEBURNE’S TEST ON DC SHUNT MOTOR
Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Page 1
Bangalore Institute of Technology, Bangalore – 560 004
Electrical Machines Laboratory - 2
Lamp Load
+
0 – 10 A A LAMP LOAD
MC -
A
- +
S V
V 0 – 15V
230 Volt,
DC Supply - MC
AA
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF ARMATURE RESISTANCE
PROCEDURE: For Swinburne’s Test:
1. Connections are made as shown in the circuit diagram.
2. The name plate details of the motor are noted down.
2. With 18 Ohm rheostat in the cut-in position, 200 Ohm rheostat in cut-out position,
supply switch S1 is closed
3. The motor is brought to its rated speed by cutting out 18 Ohm rheostat and if
necessary cutting in the 200 Ohm rheostat.
4. The meter readings are taken in the tabular column. The rheostats are brought back
to their initial positions and the supply switch is opened.
For the measurement of Armature Resistance:
1. Connections are made as shown in the circuit diagram.
2. With load switches open, the supply switch S1 is closed.
3. A load is applied and the meter readings are noted down in the tabular column.
4. The load is reduced and the supply switch is opened.
Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Page 2
Bangalore Institute of Technology, Bangalore – 560 004
Electrical Machines Laboratory - 2
OBSERVATIONS:
NAME PLATE DETAILS
Rated voltage :
Rated Current :
Field Current :
Rated Speed :
Rating :
TABULAR COLUMNS:
SWINBURNE’S TEST
Speed, V0 I0 If
N rpm Volts Amps Amps
Armature Resistance
S. No. V I Resistance. Ra = V/ I
Volts Amps
1
2
3
Average resistance
CALCULATIONS:
No load input = V0 I0
No load armature current , Ia0 = I0 - If
Field copper loss = V0 If
No load armature copper loss = Ia02 Ra
Constant losses of the machine = V0 I0 - Ia02 Ra
Efficiency of the machine as motor:
Copper losses at full load = Iafl2 Rafl
Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Page 3
Bangalore Institute of Technology, Bangalore – 560 004
Electrical Machines Laboratory - 2
Where Iafl is the full load armature current = I - If
and Rafl = Ra X 1.25
𝐹𝑢𝑙𝑙 𝑙𝑜𝑎𝑑 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡−𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑒𝑠𝑠
Efficiency at full load =
𝐹𝑢𝑙𝑙 𝑙𝑜𝑎𝑑 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡
2
𝑉𝐼 − 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑠 − 𝐼𝑎𝑓𝑙 𝑅𝑎𝑓𝑙 − 𝑉𝐼𝑓
=
𝑉𝐼
Efficiency at full load, x
2
𝑥𝑉𝐼 − 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑠 − 𝑥 2 𝐼𝑎𝑓𝑙 𝑅𝑎𝑓𝑙 − 𝑉𝐼𝑓
=
𝑥𝑉𝐼
Efficiency of the machine as generator:
Copper losses at full load = Iafl2 Rafl
Where Iafl is the full load armature current = I + If
and Rafl = Ra X 1.25
𝐹𝑢𝑙𝑙 𝑙𝑜𝑎𝑑 𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡
Efficiency at full load =
𝐹𝑢𝑙𝑙 𝑙𝑜𝑎𝑑 𝑜𝑢𝑝𝑢𝑡+𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑠
𝑉𝐼
= 2
𝑉𝐼 + 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑠 + 𝐼𝑎𝑓𝑙 𝑅𝑎𝑓𝑙 + 𝑉𝐼𝑓
Efficiency at full load, x
𝑥𝑉𝐼
= 2
𝑥𝑉𝐼 + 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 𝑙𝑜𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑠 + 𝑥 2 𝐼𝑎𝑓𝑙 𝑅𝑎𝑓𝑙 + 𝑉𝐼𝑓
Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Page 4
Bangalore Institute of Technology, Bangalore – 560 004
Electrical Machines Laboratory - 2
The efficiencies of the machine as a motor and as generator is to be calculated
for different values of x (x is varied from 0 to 1) and are to be tabulated.
S.No. Load Efficiency of Efficiency of
Motor generator
1 0.1
2 0.2
3 0.3
4 0.4
5 0.5
6 0.6
7 0.7
8 0.8
9 0.9
10 1.0
GRAPHS: Following graphs are to be plotted from the calculations:
1. Load – Efficiency curve for motor
2. Load – Efficiency curve for generator.
Expected Shape for the graphs: The load – efficiency curves for motor and
generator will have the following shape.
Efficiency
Generator
Motor
Load
RESULT: Student should discuss the result – should discuss why the efficiency
of the generator is more than that of motor.
Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Page 5
Bangalore Institute of Technology, Bangalore – 560 004
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Load Test On DC Shunt MotorDokument6 SeitenLoad Test On DC Shunt Motorsanju0% (1)
- Speed Control of DC MotorDokument4 SeitenSpeed Control of DC MotorsanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee2259 LMDokument90 SeitenEe2259 LMPradeep KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment Beyond Syllabus Experiment - 14: 15eel38 Electrical Lab - IDokument6 SeitenExperiment Beyond Syllabus Experiment - 14: 15eel38 Electrical Lab - IsanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment - 12: Power Angle Curve of Syncronous MachineDokument3 SeitenExperiment - 12: Power Angle Curve of Syncronous MachinesanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEE Lab For Ist YearsDokument32 SeitenBEE Lab For Ist YearsMutya BalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines-II Lab ManualDokument52 SeitenElectrical Machines-II Lab Manualsai100% (1)
- Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering: List of Experiments SL - No Name of The Experiment Page NoDokument51 SeitenDepartment of Electrical and Electronics Engineering: List of Experiments SL - No Name of The Experiment Page Nosuresh270Noch keine Bewertungen
- Field Test On DC Series MotorDokument6 SeitenField Test On DC Series MotorsanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE8311 Electrical Machines Lab - 1 Manual PDFDokument67 SeitenEE8311 Electrical Machines Lab - 1 Manual PDFkrishnandrk100% (2)
- Bee Lab Manual R19Dokument25 SeitenBee Lab Manual R19Sudharshan ChennupalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment - 10Dokument7 SeitenExperiment - 10sanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Machine LabDokument4 Seiten2 Machine LabManoj GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECS LAB Manual - For Students PDFDokument40 SeitenECS LAB Manual - For Students PDFmirehoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEE492C Electrical Machines and Measurement LabDokument12 SeitenPEE492C Electrical Machines and Measurement LabRaqib ChohdharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines - Ii Lab Manual: Anurag College of EngineeringDokument82 SeitenElectrical Machines - Ii Lab Manual: Anurag College of Engineeringshehryar khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE Lab Manual 2019 FINAL-1Dokument30 SeitenPE Lab Manual 2019 FINAL-1stephan dsilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual: Power ElectronicsDokument23 SeitenLab Manual: Power Electronicsprakhar yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Em-I LAB MANUALDokument52 SeitenEm-I LAB MANUALSukanya MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swinburns'S Test On D.C Shunt MachineDokument15 SeitenSwinburns'S Test On D.C Shunt MachineharimadhavareddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM - II LabDokument45 SeitenEM - II LabHarimadhavareddy YenireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Speed Control of DC Shunt MotorDokument4 Seiten05 Speed Control of DC Shunt MotorTadikala SomyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp.2 - No-Load and Blocked Rotor Test On A Three-Phase Squirrel Cage InductionDokument4 SeitenExp.2 - No-Load and Blocked Rotor Test On A Three-Phase Squirrel Cage InductionMasood RizviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Em Lab-II ManualDokument45 SeitenEm Lab-II Manualrkadiraj701150% (4)
- Single Ehase Hrans Foxmer 0-1n y - Single Phase AC. NolthmetesDokument3 SeitenSingle Ehase Hrans Foxmer 0-1n y - Single Phase AC. NolthmetesShah Tanishq RiteshkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt GeneratorDokument10 SeitenOpen Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt Generatorramniwas123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Objective: - To Perform Open Circuit (OC) & Short Circuit (SC) Test On Single Phase Transformer andDokument5 SeitenObjective: - To Perform Open Circuit (OC) & Short Circuit (SC) Test On Single Phase Transformer andJehan zaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2Dokument5 SeitenLab 2Cassandra Chrystel CalicdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC6361 Lab ManualDokument214 SeitenEC6361 Lab ManualPackirisamy NavaneethakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machine-Ii Lab ManualDokument33 SeitenElectrical Machine-Ii Lab ManualTauhidul Haque100% (1)
- Exp MachinesDokument8 SeitenExp MachinesAngelina JolieNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE Manual 2017-18Dokument49 SeitenPE Manual 2017-18sandeep sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductor - Experiment PDFDokument116 SeitenSemiconductor - Experiment PDFMuthu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.AC Phase Control Using SCRDokument8 Seiten5.AC Phase Control Using SCRabcdefgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp-7 OC & SC TestDokument7 SeitenExp-7 OC & SC TestVamsi RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Machines Manual-1Dokument38 SeitenDC Machines Manual-1sarikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEE Lab ManualDokument21 SeitenBEE Lab ManualRaviranjan ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE6512-Electrical Machines LaboratoryDokument82 SeitenEE6512-Electrical Machines LaboratoryGopinath B L NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM-I LAB-finalDokument114 SeitenEM-I LAB-finalHarimadhavareddy YenireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEE Lab ManualDokument17 SeitenBEE Lab ManualDr-Ahmed ElkoranyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CascadedDokument4 SeitenCascadedshruthisankar4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Swinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)Dokument24 SeitenSwinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)pragatinareshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt GeneratorDokument5 SeitenOpen Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt Generatorramniwas123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines Lab ManualDokument50 SeitenElectrical Machines Lab ManualRajKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines Laboratory - 2Dokument7 SeitenElectrical Machines Laboratory - 2sanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 ExperimentsDokument100 Seiten3 ExperimentsSaravanan T YNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Practical Experiments 14-15Dokument23 SeitenElectrical Practical Experiments 14-15आयुष शुक्लNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load Test On Single Phase TransformerDokument22 SeitenLoad Test On Single Phase TransformerNamrajit Dey0% (1)
- DCMT .AnDokument47 SeitenDCMT .AnastridyoungtheoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee694 Power Electronics Lab Manual PDFDokument24 SeitenEe694 Power Electronics Lab Manual PDFSabeeh HasnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aim of The Experiment:: Sl. No. Name of Apparatus Specification QuantityDokument4 SeitenAim of The Experiment:: Sl. No. Name of Apparatus Specification QuantityDevansh MankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No 2Dokument7 SeitenExperiment No 2Krishnaa SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beee Lab ManualDokument36 SeitenBeee Lab ManualChanduVarmaKalidindiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ReportDokument17 SeitenLab ReporttivendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Compound Generator LoadtestDokument4 SeitenDC Compound Generator LoadtestsagrvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines Lab 1 Electrical MacDokument153 SeitenElectrical Machines Lab 1 Electrical MacOladimeji OluwaseunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Em-Ii ExperimentDokument19 SeitenEm-Ii Experimentprince rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines Laboratory - 2Dokument7 SeitenElectrical Machines Laboratory - 2sanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18ELE24 QP Code: A Summer Semester (preparatory-II) B, Tech Programme Examination Aug-2019 Basic Electrical Engineering Time: 3hrs Max Marks: 100Dokument2 Seiten18ELE24 QP Code: A Summer Semester (preparatory-II) B, Tech Programme Examination Aug-2019 Basic Electrical Engineering Time: 3hrs Max Marks: 100sanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Provisional Result: Make Up Exam August - 2019 ExaminationDokument1 SeiteProvisional Result: Make Up Exam August - 2019 ExaminationsanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project 1ST PDFDokument3 SeitenProject 1ST PDFsanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18ELE24 QP Code: A Summer Semester (preparatory-III) B, Tech Programme Examination Aug-2019 Basic Electrical Engineering Time: 3hrs Max Marks: 100Dokument2 Seiten18ELE24 QP Code: A Summer Semester (preparatory-III) B, Tech Programme Examination Aug-2019 Basic Electrical Engineering Time: 3hrs Max Marks: 100sanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQS On CoronaDokument4 SeitenMCQS On CoronasanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Provisional Result: Summer Exam August - 2019 ExaminationDokument1 SeiteProvisional Result: Summer Exam August - 2019 ExaminationsanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Difference Between The Puncture and The Flashover of An Insulator - QuoraDokument3 SeitenWhat Is The Difference Between The Puncture and The Flashover of An Insulator - QuorasanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Basic EleDokument2 SeitenMCQ Basic ElesanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Basic EleDokument6 SeitenMCQ Basic ElesanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Questions Bank Module-2 Single Phase Ac CircuitsDokument5 SeitenMultiple Choice Questions Bank Module-2 Single Phase Ac CircuitssanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Electronics Lab (As Per Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) Scheme)Dokument2 SeitenDigital Electronics Lab (As Per Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) Scheme)sanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Swinburne's Test - Advantages, Disadvantages & Limitations - Circuit GlobeDokument17 SeitenWhat Is Swinburne's Test - Advantages, Disadvantages & Limitations - Circuit GlobesanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Students QuestionsDokument6 SeitenStudents QuestionssanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- View Answer / Hide AnswerDokument6 SeitenView Answer / Hide AnswersanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank Power Generation Transmission and Distribution (18EE42)Dokument2 SeitenQuestion Bank Power Generation Transmission and Distribution (18EE42)sanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No:3: AIM: To Plot The V-I Characteristics of A PN Junction Diode in Both ForwardDokument3 SeitenExperiment No:3: AIM: To Plot The V-I Characteristics of A PN Junction Diode in Both ForwardsanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment: 5: AIM: Study of CB & CE Characteristics of Transistor TheoryDokument5 SeitenExperiment: 5: AIM: Study of CB & CE Characteristics of Transistor TheorysanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 & 2: The Function of A Moderator Is To A) Absorb The Part of The Kinetic Energy of The NeutronsDokument21 SeitenModule 1 & 2: The Function of A Moderator Is To A) Absorb The Part of The Kinetic Energy of The NeutronssanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faculty of Engineering and Technology (Co-Education)Dokument4 SeitenFaculty of Engineering and Technology (Co-Education)sanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt No 2Dokument4 SeitenExpt No 2sanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt 4Dokument4 SeitenExpt 4sanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- em Lab1Dokument1 Seiteem Lab1sanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mesuring InstrumentsDokument22 SeitenMesuring InstrumentssanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- USN Marks Present / Absent: Practical / Laboratory / Project / Viva Voce / Term Paper See - Marks SheetDokument1 SeiteUSN Marks Present / Absent: Practical / Laboratory / Project / Viva Voce / Term Paper See - Marks SheetsanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt No 1Dokument5 SeitenExpt No 1sanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faculty of Engineering & Technology, (Co-Education) Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering III Semester Supplementary Project Topic ListDokument4 SeitenFaculty of Engineering & Technology, (Co-Education) Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering III Semester Supplementary Project Topic ListsanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sharnbasva University, Kalaburagi: Guide Name SL No USN Student NameDokument8 SeitenSharnbasva University, Kalaburagi: Guide Name SL No USN Student NamesanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Electronics Lab (As Per Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) Scheme)Dokument2 SeitenDigital Electronics Lab (As Per Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) Scheme)sanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Electronics Lab Equipments and Quantity RequiredDokument2 SeitenDigital Electronics Lab Equipments and Quantity RequiredsanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Measurement of Human Body Temperature OnDokument9 SeitenAutomatic Measurement of Human Body Temperature OnsanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input CircuitsDokument34 SeitenInput Circuitsvadithya1515Noch keine Bewertungen
- EE 466/586 VLSI Design: School of EECS Washington State University Pande@eecs - Wsu.eduDokument18 SeitenEE 466/586 VLSI Design: School of EECS Washington State University Pande@eecs - Wsu.eduPhạm Đức ThuậnNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A MOSFET - Basics, Working Principle & ApplicationsDokument3 SeitenWhat Is A MOSFET - Basics, Working Principle & ApplicationsKimberly Camacho CatubigNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09N03LADokument9 Seiten09N03LAMihai GaneaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dielectric Constant, Tan Delta & Resistivity of Ester Oils As Insulating Oils in TransformerDokument7 SeitenDielectric Constant, Tan Delta & Resistivity of Ester Oils As Insulating Oils in Transformertaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDokument28 SeitenBasic Electronic ComponentsJafar ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Rad PrimerDokument58 SeitenGen Rad PrimerkgskgmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigatory Project On LDRDokument17 SeitenInvestigatory Project On LDRMradul DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON PLAN in Scienc GRADE-5Dokument12 SeitenLESSON PLAN in Scienc GRADE-5Jessebel RecillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Does Your Capacitor WorkDokument51 SeitenHow Does Your Capacitor WorkVishal MahireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Observe Science Magazine 1st EditionDokument31 SeitenObserve Science Magazine 1st Editionapi-408725114Noch keine Bewertungen
- EC302Dokument20 SeitenEC302api-3853441Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ha-Relays: Cost Saving Subminiature PC Board RelaysDokument3 SeitenHa-Relays: Cost Saving Subminiature PC Board Relaysjuan echeverryNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Generator Ee301Dokument16 SeitenDC Generator Ee301Fred S. RickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 21: Electric Charge and Electric FieldDokument30 SeitenChapter 21: Electric Charge and Electric FieldLam NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ddugjy TS of HT AB CableDokument7 SeitenDdugjy TS of HT AB CableJaks JaksNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Project On Blinker Circuit: BY Jatin Gola Xii Sc. ADokument11 SeitenA Project On Blinker Circuit: BY Jatin Gola Xii Sc. AJatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: K.kalyani ADDRESS: D/o K.s.v.veeraswamy Phone - 8143696170Dokument4 SeitenName: K.kalyani ADDRESS: D/o K.s.v.veeraswamy Phone - 8143696170Kalyani KowtarapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Power Rectifier Diodes - 5SYA 2029Dokument9 SeitenHigh Power Rectifier Diodes - 5SYA 2029Paola LainesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode Equivalent Circuits: R BiasDokument3 SeitenDiode Equivalent Circuits: R Biaseric labordoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microwave PresentationDokument49 SeitenMicrowave PresentationPawan YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives and Plan For Igcse PhysicsDokument17 SeitenObjectives and Plan For Igcse PhysicsCarole ThamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TMP 86 FDDokument5 SeitenTMP 86 FDFrontiersNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIT 501 Smart Digital Insulation TesterDokument2 SeitenAIT 501 Smart Digital Insulation TesterAnkadi Sikari ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Failure Analysis of Aluminum Wires in All Aluminum Alloy Conductors - AAAC PDFDokument20 SeitenFailure Analysis of Aluminum Wires in All Aluminum Alloy Conductors - AAAC PDFqaqc peleburanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of HF Wideband Power Transformers: Application NoteDokument23 SeitenDesign of HF Wideband Power Transformers: Application NoteAlexandr SemenkoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Схема усилителя magnat - bull - power - 2200Dokument7 SeitenСхема усилителя magnat - bull - power - 2200Александр ГоршеневNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductor Devices Are Electronic Components That Exploit The Electronic Properties of Semiconductor MaterialsDokument3 SeitenSemiconductor Devices Are Electronic Components That Exploit The Electronic Properties of Semiconductor MaterialsNuwan SameeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT CP 1 (T) Calibration of RTDDokument4 SeitenCAT CP 1 (T) Calibration of RTDAmar Singh100% (1)
- Automatic Lamp Using Transistor & LDR - Class 12 Physics Investigatory Project Free PDF Downl..Dokument20 SeitenAutomatic Lamp Using Transistor & LDR - Class 12 Physics Investigatory Project Free PDF Downl..Babu Lal100% (1)