Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Acids and Bases
Hochgeladen von
thabo0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
155 Ansichten4 SeitenAcids and bases can be identified using litmus paper tests. Acids turn litmus paper red and bases turn litmus paper blue. Common acids include lemon juice and vinegar, while common bases include sodium hydroxide, bicarbonate of soda, and toothpaste. Acids and bases have a variety of uses, such as toothpaste neutralizing acids in the mouth to prevent tooth decay and bicarbonate of soda neutralizing bee stings.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
science
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenAcids and bases can be identified using litmus paper tests. Acids turn litmus paper red and bases turn litmus paper blue. Common acids include lemon juice and vinegar, while common bases include sodium hydroxide, bicarbonate of soda, and toothpaste. Acids and bases have a variety of uses, such as toothpaste neutralizing acids in the mouth to prevent tooth decay and bicarbonate of soda neutralizing bee stings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
155 Ansichten4 SeitenAcids and Bases
Hochgeladen von
thaboAcids and bases can be identified using litmus paper tests. Acids turn litmus paper red and bases turn litmus paper blue. Common acids include lemon juice and vinegar, while common bases include sodium hydroxide, bicarbonate of soda, and toothpaste. Acids and bases have a variety of uses, such as toothpaste neutralizing acids in the mouth to prevent tooth decay and bicarbonate of soda neutralizing bee stings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
ACIDS AND BASES
Acid
- a substance that turns blue litmus paper red
- has a sour taste
- soluble in water and form an acidic solution
- very corrosive
- examples, hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, nitric acid, citric acid
Bases
- a substance that reacts with an acid to give a neutral solution
- turns red litmus paper blue
- react with acids and remove the sour taste
- some bases dissolve in water to form an alkaline solution
- bases that dissolve in water are called alkalis
- examples sodium hydroxide, ammonia, sodium carbonate
Neutral substances
- substances that are neither acidic nor basic
- have no effect on litmus paper
Litmus paper test for acids and bases
- a litmus paper changes between red and blue
- a blue litmus paper turns red in the presence of an acid
- a red litmus paper turns blue in the presence of a base
Experiment : to investigate the effect of acids and bases on litmus paper
Method
Dip a litmus paper in a solution of the following substances and record
observations
Results
Substance Red litmus paper Blue litmus paper Type of substance
Sodium hydroxide Turns blue No effect alkali
Lemon juice No effect Turns red acid
Colgate Turns blue No effect alkali
Bicarbonate of Turns blue No effect alkali
soda
Tap water No effect No effect neutral
Handy andy Turns blue No effect alkali
Vinegar No effect Turns red acid
Properties of acids and bases
Acids and bases can be strong or weak
Strong acids and bases are very corrosive and dangerous e. sulphuric
acid, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide
These cause serious burns
In the labs, we use dilute acids dissolved in water
Weak acids are for example citric acid found in citrus fruits, acetic acid in
vinegar and these are not dangerous
Weak bases are for example the bases found in toothpaste, bicarbonate
of soda and detergents
Uses of acids and bases
i. Acids formed in the mouth by bacteria cause tooth decay. The
alkali in toothpaste removes the acids preventing tooth decay
ii. Our stomachs contain hydrochloric acid needed for digestion of
food. A person with excess acid in the stomach takes anti acids
which contain an alkali that removes the excess acids
iii. The acid in a bee sting can be neutralised by bicarbonate of soda
iv. The alkaline sting of a wasp can be neutralised using vinegar
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Acids, Bases, & Salts: Presentation by Navaneeth.S VII DDokument14 SeitenAcids, Bases, & Salts: Presentation by Navaneeth.S VII DSantu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACIDICDokument5 SeitenACIDICNitesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids & Bases (New) Ntse Module Class 6Dokument16 SeitenAcids & Bases (New) Ntse Module Class 6arya starkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids Bases and Salts-Handout: Subject: Science Class ViiDokument4 SeitenAcids Bases and Salts-Handout: Subject: Science Class ViiKavyaranjan “Ranju”Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Acids Bases and SaltsDokument4 Seiten2 Acids Bases and SaltsRounak BasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Alkalis NotesDokument10 SeitenAcids and Alkalis NotesNurulAinMatAronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and BasesDokument6 SeitenAcids and Basesstyleofuniverse06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and AlkalisDokument33 SeitenAcids and AlkalisLubna ErumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Holiday HomeworkDokument25 SeitenChemistry Holiday HomeworkManisha GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Bases and SaltDokument8 SeitenAcid Bases and SaltKhyati kothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salts and AcidsDokument15 SeitenSalts and Acidsmuhammad irtazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are AcidsDokument4 SeitenWhat Are AcidsruthlynhenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases, and Salts 1Dokument13 SeitenAcids, Bases, and Salts 1Ramadas BhiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids Bases and SaltsDokument55 SeitenAcids Bases and Saltsgeorgy shibuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids & AlkalisDokument37 SeitenAcids & AlkalisSevenzsciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Alkalis - PPTX Form 2Dokument9 SeitenAcids and Alkalis - PPTX Form 2NITIASSWARENoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemicals Acids&BasesDokument7 SeitenChemicals Acids&BasesRishi GovindaHarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 5 Acid Bases and Salts 2Dokument16 SeitenCH 5 Acid Bases and Salts 2Khoa Hoa Nguyen Thi Thu TrangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Bases & SaltDokument16 SeitenAcid Bases & SaltKK patel0% (1)
- Acids and Alkalis: Learning ObjectivesDokument16 SeitenAcids and Alkalis: Learning ObjectivesYayang NuggrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 2 Acids and AlkalisDokument17 SeitenSection 2 Acids and AlkalismaahaeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- F2 Chapter 6 Acid and AlkaliDokument6 SeitenF2 Chapter 6 Acid and AlkaliMei Shuen CheamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACIDS, BASES & MIXTURES - Full NoteDokument18 SeitenACIDS, BASES & MIXTURES - Full NoteGabbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Base and SaltsDokument3 SeitenAcids, Base and SaltsGeorgia SimmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases and Salts NotesDokument4 SeitenAcids, Bases and Salts NotesMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7A50% (2)
- SBA #15 - Acids & BasesDokument4 SeitenSBA #15 - Acids & BaseslucyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 2 Chapter 6 Acid and AlkaliDokument28 SeitenForm 2 Chapter 6 Acid and AlkaliNurul Husna50% (4)
- F2 C6: Acids & AlkaliDokument3 SeitenF2 C6: Acids & AlkaliJas 408Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 5 Acid Bases and Salts 1Dokument24 SeitenCH 5 Acid Bases and Salts 1shubhamsing0403Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch12 Kitabcd Class 8 MSBHSE Science NotesDokument6 SeitenCh12 Kitabcd Class 8 MSBHSE Science NotesONE CLICK COMPUTERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and AlkalisDokument34 SeitenAcids and AlkalisMoh AmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and AlkalisDokument16 SeitenAcids and Alkalispoorv1235570Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9.1 Common Acids and AlkalisDokument3 Seiten9.1 Common Acids and AlkalisKitty CheungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqua Regia or "Kingly Water" and Has The Ability To Dissolve GoldDokument6 SeitenAqua Regia or "Kingly Water" and Has The Ability To Dissolve GoldMaRiz BalitaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AcidsDokument4 SeitenAcidsNIdhi GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 2: 5.5 Acid and AlkaliDokument38 SeitenScience Form 2: 5.5 Acid and AlkalinurafziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDokument6 SeitenAcids, Bases and SaltsPranav ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids & BasesDokument38 SeitenAcids & BasesMeltem YorgancıNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 7 Ch5 Notes AcidsDokument6 SeitenClass 7 Ch5 Notes Acidsclass7science iisjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDokument31 SeitenAcids, Bases and Saltssmi_santhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDokument11 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 2 Acids, Bases and Saltsmilind dhamaniyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7E Acids and Alkalis: Name: .Dokument21 SeitenUnit 7E Acids and Alkalis: Name: .irene9tan9ailianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 2 Chapter 6 Acid and AlkaliDokument28 SeitenForm 2 Chapter 6 Acid and AlkaliammyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science RevisionDokument3 SeitenScience Revisionfaizy moukaddemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid, Bases and SaltDokument8 SeitenAcid, Bases and SaltAbdul Raheem UlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Material For ChemistryDokument7 SeitenStudy Material For ChemistryBHADRANoch keine Bewertungen
- AcidsDokument3 SeitenAcidsYash Ardeshna100% (1)
- 7E Acids and AlkalisDokument10 Seiten7E Acids and AlkalisMikey Mcfc PetersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Alkalis Final PDFDokument19 SeitenAcids and Alkalis Final PDFCristina CarcedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 2 ACID AND ALKALI SHORTS NOTESDokument27 SeitenForm 2 ACID AND ALKALI SHORTS NOTESShahrul HisyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and BasesDokument37 SeitenAcids and BasesAnthony MandizividzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids Bases and SaltsDokument72 SeitenAcids Bases and SaltsHarshita bhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- YT Acid Base and Salt 1Dokument77 SeitenYT Acid Base and Salt 1reyanshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 7 - Acids and AlkalisDokument26 SeitenGrade 7 - Acids and AlkalisKolade Fatai OpeyemiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Base SaltDokument14 SeitenAcid Base Saltshineblade99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Part One Dictionary: Grow Your Vocabulary, #28Von EverandChemistry Part One Dictionary: Grow Your Vocabulary, #28Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual of Formulas - Recipes, Methods & Secret ProcessesVon EverandManual of Formulas - Recipes, Methods & Secret ProcessesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Homemade Soda Recipes: Ultimate Soda Cookbook for Making Refreshing & Tasty Homemade SodasVon EverandHomemade Soda Recipes: Ultimate Soda Cookbook for Making Refreshing & Tasty Homemade SodasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature-Time GraphsDokument5 SeitenTemperature-Time GraphsthaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- S D ' C H S: T Ominic S Hishawasha IGH ChoolDokument8 SeitenS D ' C H S: T Ominic S Hishawasha IGH ChoolthaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements Compounds and MixturesDokument10 SeitenElements Compounds and MixturesthaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of Descriptive EssayDokument4 SeitenDefinition of Descriptive EssaythaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- ShonaDokument2 SeitenShonathabo100% (1)
- Multiple ChoiceDokument16 SeitenMultiple ChoicethaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDokument12 SeitenZimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelthaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDokument24 SeitenZimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelthabo100% (2)
- Skintec Price List 2019Dokument2 SeitenSkintec Price List 2019Melieza Melody Ampan100% (1)
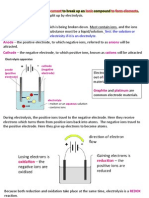
- IGCSE Chemistry - ElectrolysisDokument11 SeitenIGCSE Chemistry - ElectrolysisChemistryKlipz97% (34)
- ChemDokument3 SeitenChemAlquino Heart RubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSC Sem 2 Unit 1.1Dokument13 SeitenMSC Sem 2 Unit 1.1almas shaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- NeopreneDokument48 SeitenNeoprenest_calvoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transition Metal Test JC2 - 2020Dokument4 SeitenTransition Metal Test JC2 - 2020Allan GunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids Bases and Salt Preparations 2 MSDokument8 SeitenAcids Bases and Salt Preparations 2 MSal katerjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed Bed GasifiersDokument56 SeitenFixed Bed GasifiersYan LaksanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersDokument19 SeitenSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersChinWynn.com94% (16)
- MDEA PropertiesDokument9 SeitenMDEA PropertiescacardonarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSE Stage 1 2016 17 Solution NSEC Code C322 v1Dokument29 SeitenNSE Stage 1 2016 17 Solution NSEC Code C322 v1Chirayu VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Features: Securon ® 540Dokument2 SeitenProduct Features: Securon ® 540raju_hosssenNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Matter???: Pure Substance MixtureDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Matter???: Pure Substance MixtureArdelynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Toothpaste Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12Dokument20 SeitenAnalysis of Toothpaste Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12Prakhar Joshi100% (1)
- LSD SynthDokument10 SeitenLSD SynthBill644Noch keine Bewertungen
- Isomerism - Final (NUCLEUS EDUCATION)Dokument19 SeitenIsomerism - Final (NUCLEUS EDUCATION)Pankaj MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zwitterion On Mishaps and Tragedies in Making MDMADokument2 SeitenZwitterion On Mishaps and Tragedies in Making MDMAinvitacionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gama de Solventes Alifaticos en ChileDokument9 SeitenGama de Solventes Alifaticos en ChileFelipe OtarolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEM01A1 - EXP A5 ANSWER SHEET 2019 Fillable PDFDokument7 SeitenCEM01A1 - EXP A5 ANSWER SHEET 2019 Fillable PDFmaccusf0% (1)
- Investigatory Project ChemistryDokument12 SeitenInvestigatory Project ChemistryAnonymous LgH4EmNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDokument9 Seiten16 Introduction To Organic Chemistryizabel0% (1)
- Benzyl Alcohol: 2. Physical PropertiesDokument10 SeitenBenzyl Alcohol: 2. Physical PropertiesniteshacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (PHAR 3 LAB) Preparation #14 - Strong Iodine SolutionDokument1 Seite(PHAR 3 LAB) Preparation #14 - Strong Iodine SolutionSebastian Moron100% (4)
- CoversionDokument12 SeitenCoversionSunil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- List INN 08february2012 PDFDokument128 SeitenList INN 08february2012 PDFMarisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas or Vapor Specific Heat Capacity TableDokument2 SeitenGas or Vapor Specific Heat Capacity TableDominic LibradillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Ceramics: Part 3: MME 467 Ceramics For Advanced ApplicationsDokument15 SeitenStructure of Ceramics: Part 3: MME 467 Ceramics For Advanced ApplicationsMd. Rafiqul IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Requirements For Discharge of Trade Effluent Into The Public SewersDokument6 SeitenRequirements For Discharge of Trade Effluent Into The Public Sewersalfador_yxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolation of RNA and Uv MeasurementDokument4 SeitenIsolation of RNA and Uv MeasurementJairish Keith GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DocxDokument7 SeitenDocxJasmin YangNoch keine Bewertungen