Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cost Classification PDF
Hochgeladen von
lakshmi aparna yelganamoni0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
30 Ansichten14 SeitenThe document outlines key cost categories for a manufacturing firm, including direct materials, direct labor, manufacturing overhead, marketing costs, and administrative costs. Manufacturing overhead includes indirect materials, indirect labor, and other costs like depreciation and utilities. It also discusses classification of costs as variable or fixed, and how total, per-unit, and average costs change within a relevant range of production.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Cost_Classification_15797785035787779425e2981c79293b.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document outlines key cost categories for a manufacturing firm, including direct materials, direct labor, manufacturing overhead, marketing costs, and administrative costs. Manufacturing overhead includes indirect materials, indirect labor, and other costs like depreciation and utilities. It also discusses classification of costs as variable or fixed, and how total, per-unit, and average costs change within a relevant range of production.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
30 Ansichten14 SeitenCost Classification PDF
Hochgeladen von
lakshmi aparna yelganamoniThe document outlines key cost categories for a manufacturing firm, including direct materials, direct labor, manufacturing overhead, marketing costs, and administrative costs. Manufacturing overhead includes indirect materials, indirect labor, and other costs like depreciation and utilities. It also discusses classification of costs as variable or fixed, and how total, per-unit, and average costs change within a relevant range of production.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 14
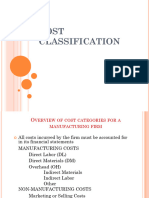
COST CLASSIFICATION
OVERVIEW OF COST CATEGORIES
FOR A MANUFACTURING FIRM
All costs incurred by the firm must be accounted for in
its financial statements
MANUFACTURING COSTS
Direct Labor (DL)
Direct Materials (DM)
Overhead (OH)
Indirect Materials
Indirect Labor
Other
NON-MANUFACTURING COSTS
Marketing or Selling Costs
Administrative Costs
MANUFACTURING COSTS
1. Direct Materials (DM)
Materials that are consumed in the manufacturing
process and physically incorporated in the finished
product
Materials whose cost is sufficiently large to justify the
record keeping expenses necessary to trace the costs to
individual products
MANUFACTURING COSTS
2. Direct Labor (DL)
Labor time that is physically traceable to the
products being manufactured
Labor time whose cost is sufficiently large to justify
the record keeping expenses necessary to trace the
costs to individual products
Example:
Direct labor for manufacturing Honda Accords
Line workers, robot operators, painters, assembly
workers
MANUFACTURING COSTS
3. Manufacturing Overhead (OH)
All of costs of manufacturing excluding direct materials and
direct labor
a. Indirect Materials (IM) – Materials, used in the
manufacturing of products, which are difficult to trace to
particular products in an economical way
Glue, nails, cleaning supplies
b. Indirect Labor (IL) – Labor, used in the manufacturing of
products, which is difficult to trace to particular products in
an economical way
Wages for maintenance workers, factory supervisor’s
salary
MANUFACTURING COSTS
C. All other types of manufacturing overhead
Depreciation on machinery, depreciation on
factory building, factory insurance, utilities for
factory
NON-MANUFACTURING COSTS
1. Marketing or Selling Costs – Costs incurred in
securing orders from customers and providing
customers with the finished product
Sales commissions, costs of shipping products to
customers, storage of finished goods
2. Administrative Costs – Executive, organizational,
and clerical costs that are not related to
manufacturing or marketing
CEO’s salary, cost of controller’s office,
depreciation on administrative building.
CLASSIFICATION EXERCISE
Classify the following cost items
Depreciation on factory building
Depreciation on office equipment
Paper used in textbook production
Paper used in central office computer
Wages paid to assembly line workers
Maintenance cost for machines
COSTS RELATED TO DECISION MAKING
Opportunity Costs - costs when taking one action requires
giving up the opportunity to earn profits from a different
action
Nike Inc. has limited production capacity. What would be
Nike’s opportunity cost of accepting a special order from
the military for combat boots?
If Nike accepts the special order, they may not be able to
produce enough product for other sales. So, Nike would
lose the profit from the other sale.
VARIABLE AND FIXED COSTS
Variable Costs – costs that change proportionately (in total) with the
activity level within a relevant range of activity
Fixed Costs – costs that do not change in total as activity level
changes within a relevant range of activity
Example: Publishing a magazine
Variable costs Fixed Costs
Cost of paper Rent on building
Cost of ink Salaries to reporters
Sales Commissions Depreciation on printing equipment
Cost of lubricants for machine
TOTAL VARIABLE AND FIXED COSTS
Total Variable Cost Total Fixed Cost
Number of units Number of units
VARIABLE AND FIXED COSTS PER UNIT
Per Unit Variable Cost Per Unit Fixed Cost
Number of units Number of units
RELEVANT RANGE
The range of activity within
which the firm’s cost structure
(i.e. variable cost per unit and
total fixed cost) remains
unchanged
In particular, a "fixed" cost is
Total Fixed Cost
likely to remain fixed only within
a relevant range of activity
ABC Company constructs a
budget within a relevant
revenue range of no more than
$20 million. If actual sales were
to exceed that amount, then
ABC would need to construct a
new manufacturing facility.
Relevant Range Number of units
TOTAL COSTS
To get total costs you need to add variable costs and
fixed costs
Total Cost
Fixed costs
The Slope is the
variable cost per
unit
Number of units
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Rocky Road: The Irish Economy Since The 1920s by Cormac Ó'GrádaDokument256 SeitenRocky Road: The Irish Economy Since The 1920s by Cormac Ó'GrádazoomtardNoch keine Bewertungen
- TNB E.HandbookDokument65 SeitenTNB E.Handbookbrad100% (2)
- Costs - Concepts and Classification: JmcnncpaDokument37 SeitenCosts - Concepts and Classification: JmcnncpaMari Mar100% (1)
- C1 A Perspective On EntrepreneurshipDokument35 SeitenC1 A Perspective On EntrepreneurshipWilnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Mitchell Fixing The EconomyDokument21 Seiten3 Mitchell Fixing The EconomyJuliethM.LópezArboledaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Classifications ADokument16 SeitenCost Classifications A22je0766Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 02 - MADokument23 SeitenChapter - 02 - MAMaithri Vidana KariyakaranageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost AccountancyDokument27 SeitenCost AccountancyManohar GrewalNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFenDokument68 SeitenPDFenby ScribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accountancy 2203 Review Workshop Sindhu BalaDokument27 SeitenAccountancy 2203 Review Workshop Sindhu BalaAnna Mae SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CostDokument27 SeitenCostAbid AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Cost Categories For A Manufacturing FirmDokument26 SeitenOverview of Cost Categories For A Manufacturing FirmbiarrahsiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Sheet P&SDokument41 SeitenCost Sheet P&SJishnuPatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- COST Lesson 2Dokument4 SeitenCOST Lesson 2Christian Clyde Zacal Ching0% (1)
- Acctg 135Dokument27 SeitenAcctg 135yanc.hellosolarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inventory: COST OF PRODUCTIONDokument104 SeitenInventory: COST OF PRODUCTIONHAFIZ MUHAMMAD UMAR FAROOQ RANANoch keine Bewertungen
- BMT1009 Production and Operations Management BMT1009 Production and Operations ManagementDokument37 SeitenBMT1009 Production and Operations Management BMT1009 Production and Operations ManagementYash PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1b - Cost Concepts and Terminology - 14sept06Dokument31 Seiten1b - Cost Concepts and Terminology - 14sept06Zaid AnsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMT1009 Production and Operations Management: Unit-IIDokument37 SeitenBMT1009 Production and Operations Management: Unit-IIKartik ChaturvediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Cost Sheet (Unit Costing)Dokument102 SeitenChapter 1: Cost Sheet (Unit Costing)Rimsha HanifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Costs - Concepts and ClassificationsDokument5 SeitenCosts - Concepts and ClassificationsCarlo B CagampangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Costing NotesDokument48 SeitenCosting NotesOckouri BarnesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting 2Dokument5 SeitenAccounting 2jessicaong2403Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 03Dokument16 SeitenCH 03Xinjie MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost ClassificationDokument30 SeitenCost ClassificationnehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting For Manufacturing OperationsDokument49 SeitenAccounting For Manufacturing Operationsgab mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finacial and Managerial Act Chapter 5-7Dokument59 SeitenFinacial and Managerial Act Chapter 5-7solomon asefaNoch keine Bewertungen
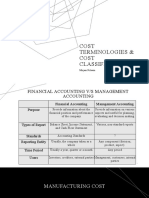
- Cost Terminologies & Cost Classification: Mirjam NilssonDokument13 SeitenCost Terminologies & Cost Classification: Mirjam NilssonHitesh JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Accounting Discussion Set 1Dokument17 SeitenManagerial Accounting Discussion Set 1julsmlarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument10 SeitenChapter 2Aklil TeganewNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - Cost Concepts and ClassificationsDokument31 Seiten5 - Cost Concepts and ClassificationsAlyssa TolcidasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - Managerial Cost Concepts and Cost Behaviour AnalysisDokument53 SeitenChapter 2 - Managerial Cost Concepts and Cost Behaviour AnalysisPRAkriT POUdeLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes and Summary in Product Costing With QuizzerDokument12 SeitenNotes and Summary in Product Costing With QuizzerCykee Hanna Quizo LumongsodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 01 - Cost AccountingDokument56 SeitenLecture 01 - Cost Accountingdia_890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument7 SeitenChapter 1yebegashetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2Dokument3 SeitenTopic 2CLAUDIA RUIZ CUEVAS SAINZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Accounting Concepts: Prof. Dr. Farid MoharamDokument90 SeitenCost Accounting Concepts: Prof. Dr. Farid Moharammohamed el kadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 02Dokument40 SeitenCH 02lyonanh289Noch keine Bewertungen
- A.3. Cost ClassificationsDokument57 SeitenA.3. Cost ClassificationsTiyas KurniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pertemuan 1-Akuntansi Biaya OKDokument15 SeitenPertemuan 1-Akuntansi Biaya OKZahrotul MillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction Cost Concepts Terms and BehaviorDokument43 SeitenIntroduction Cost Concepts Terms and BehaviorZACARIAS, Marc Nickson DG.Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1491820614costing by CA Jitender Singh (Overhead, Labour, Material, Marginal, Ratio, Machine Hour RateDokument311 Seiten1491820614costing by CA Jitender Singh (Overhead, Labour, Material, Marginal, Ratio, Machine Hour RateRam IyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 2 IIMDokument24 SeitenClass 2 IIMRahul BharadwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 7 - Absorption & Marginal CostingDokument8 SeitenTopic 7 - Absorption & Marginal CostingMuhammad Alif100% (5)
- Cost Concept and Classification of CostDokument31 SeitenCost Concept and Classification of CostRujean Salar AltejarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument17 SeitenChapter 2Ngọc Minh Đỗ ChâuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Hilton 10th Instructor NotesDokument10 SeitenChapter 2 Hilton 10th Instructor NotesKD MV100% (1)
- Cost Terms, Concepts and Classification Session 2 2018 For UploadingDokument19 SeitenCost Terms, Concepts and Classification Session 2 2018 For UploadingSohaib ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Cost Management ConceptsDokument7 SeitenBasic Cost Management ConceptsImadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualifying Exam (Cost)Dokument48 SeitenQualifying Exam (Cost)ysaelll03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Term Associated With CostDokument6 SeitenTerm Associated With Costaashir chNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOTES - CHAPTER II - Cost Accounting and ControlDokument11 SeitenNOTES - CHAPTER II - Cost Accounting and ControlHanna CasasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost HandoutDokument31 SeitenCost HandoutTilahun GirmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Terms, Concepts, and ClassificationDokument27 SeitenCost Terms, Concepts, and ClassificationParadise VillageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absorption and Variable Costing: Types of Product Costing MethodDokument2 SeitenAbsorption and Variable Costing: Types of Product Costing MethodKuya ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Units, Cost Classification and Profit Reporting: Lesson 3Dokument41 SeitenCost Units, Cost Classification and Profit Reporting: Lesson 3Kj NayeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Accounting: Introduction To Cost Accounting Lecture-1 Jameel A Khan HakroDokument35 SeitenCost Accounting: Introduction To Cost Accounting Lecture-1 Jameel A Khan Hakrokashif aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Analysis of Any Product or ServiceDokument27 SeitenCost Analysis of Any Product or ServiceAayushiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN #2 - CVP AnalysisDokument5 SeitenCN #2 - CVP AnalysisRen EyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Costing TheoryDokument5 SeitenCosting TheoryShaji KuttyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brewer 8e PPT Ch01 TDokument54 SeitenBrewer 8e PPT Ch01 TJuan Camilo IdarragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Terms, Concepts, and Classifications: UAA - ACCT 202 Principles of Managerial Accounting Dr. Fred BarbeeDokument41 SeitenCost Terms, Concepts, and Classifications: UAA - ACCT 202 Principles of Managerial Accounting Dr. Fred BarbeeBlerim HalimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageVon EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- For Module - 1 (Part 1) PDFDokument48 SeitenFor Module - 1 (Part 1) PDFlakshmi aparna yelganamoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Written Class Notes B PDFDokument14 SeitenHand Written Class Notes B PDFlakshmi aparna yelganamoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Sheet 2 A PDFDokument3 SeitenTutorial Sheet 2 A PDFlakshmi aparna yelganamoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Economics & FinanceDokument21 SeitenEngineering Economics & Financelakshmi aparna yelganamoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Accounting: Breakeven AnalysisDokument27 SeitenManagement Accounting: Breakeven Analysislakshmi aparna yelganamoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classical Mechanics Electrodynamics 8Dokument8 SeitenClassical Mechanics Electrodynamics 8lakshmi aparna yelganamoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies (Part I)Dokument1 SeiteAssignment 2 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies (Part I)lakshmi aparna yelganamoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salary Advance PolicyDokument4 SeitenSalary Advance PolicySumit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apocado and Garcia CaseDokument3 SeitenApocado and Garcia CaseJohn Roel VillaruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Labor LawsDokument2 SeitenIntroduction To Labor LawsErdanlove DielNoch keine Bewertungen
- What The Western Cape Government Is Doing To Tackle Youth UnemploymentDokument2 SeitenWhat The Western Cape Government Is Doing To Tackle Youth Unemploymentapi-146640615Noch keine Bewertungen
- Employer-Employee RElationshipDokument172 SeitenEmployer-Employee RElationshipJust a researcherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progress and Poverty - Henry GeorgeDokument344 SeitenProgress and Poverty - Henry GeorgetherootsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Plan: Operations ManagerDokument14 SeitenManagement Plan: Operations Manager弗朗兹Noch keine Bewertungen
- Contract SEIUDokument97 SeitenContract SEIUWashington ExaminerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zero Based BudgetingDokument6 SeitenZero Based Budgetingchetan_shirasi2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge GCE Economics Year 1 NotesDokument45 SeitenCambridge GCE Economics Year 1 NotesEm Wade100% (1)
- Entrepreneurship Development ProgrammesDokument17 SeitenEntrepreneurship Development Programmeskalapusky_141065268Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Minimum Wages Act 1948Dokument34 SeitenThe Minimum Wages Act 1948Ihsan Ullah Himmat B-124100% (1)
- Chapter 2Dokument14 SeitenChapter 2preetikagoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12-Variable Pay and Executive Compensation: Multiple ChoiceDokument28 SeitenChapter 12-Variable Pay and Executive Compensation: Multiple ChoiceDyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Theory of WageDokument6 SeitenModern Theory of Wagegazal1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Best Long-Term Incentive PlanDokument34 SeitenBest Long-Term Incentive PlanQuant TradingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project On NaregaDokument20 SeitenProject On NaregalkovijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recruitment AgreementDokument5 SeitenRecruitment AgreementTricia GrafiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLA Foxconn-And-Apple Report AppendixDokument244 SeitenFLA Foxconn-And-Apple Report AppendixventurebeathkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2007 Year End OverviewDokument28 Seiten2007 Year End OverviewLmoorjaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bankard Vs NLRC G.R. No. 171664Dokument7 SeitenBankard Vs NLRC G.R. No. 171664Karen HaleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature of Human Resource ManagementDokument20 SeitenNature of Human Resource ManagementXzArina DulduLaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA1 First TestDokument14 SeitenMA1 First TestMishael MAKE-UP100% (1)
- WC 206Dokument1 SeiteWC 206jeffdandelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument39 SeitenChapter 3Ashwin vk100% (1)
- Jan - 18 - Staff SalaryDokument21 SeitenJan - 18 - Staff Salarym.kannaiyanNoch keine Bewertungen