Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Case Study ON: Saint James Academy
Hochgeladen von
Yna Marie GutierrezOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Case Study ON: Saint James Academy
Hochgeladen von
Yna Marie GutierrezCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Saint James Academy
Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
CASE STUDY
ON
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS
A Case Study Presented to the
Faculty of Senior High School Department
Saint James Academy
Ibaan, Batangas
In Partial Fulfilment
of the Requirements for
General Biology
ESEO, Mark Angelo G.
2020
Oblates of saint joseph schools
Saint James Academy
Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
I. Introduction
This case study with focus and discuss one of the diseases that can be present or
happen in circulatory or cardiovascular system, this is stems includes the veins heart
arteries and capillaries. The circulatory system is responsible in the blood circulation
throughout the body in order to transport nutrients and oxygen period. Lymphatic system
is also part of circulatory system because telling transport fats and eliminate bacteria. It is
beneficial for our body because it also fights off disease also it Is responsible in
maintaining a normal body temperature and provides the right chemical balance to
provide body's homeostasis. In short circulatory system contributes lot for us to live but
what if there is a problem on it? What if one of the major organ in circulatory system fails
to develop perfectly from the time that the patient was born?
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a medical condition in which ductus arteriosus fails
to close after birth. Ductus arteriosus or known as ductus botalli act as a connecting
bridge between the aorta and the pulmonary artery, it is a persistent opening between the
two major blood vessels leading from the heart (mayoclinic, 2020). In a developing fetus
the lungs are not fully functional, not breathing for taking up oxygen yet so it is not
needed to have a bunch of blood via this is pulmonary arteries through the lungs instead,
it can come via pulmonary arteries and then go via this ductus arteriosus so that via aorta,
it can go to the rest of the body. When a baby was born, it starts to breath, so the fluids in
the lungs will come out when the baby starts to cry and the blood can come to the lungs
without the oxygen and then it will go back to the heart with oxygen. Normally, the
ductus arteriosus (DA) closes after the birth to stop the blood flow but there are some
cases wherein it fails to close and that call Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA). Patent is a
Latin word which means "open" so PDA means Open Ductus Arteriosus. What will
happen if there’s an open hole? So in this case, the blood that are supposedly flow
properly didn’t happen, the blood will continuously flow from the aorta into the lungs
this means that the nutrients from the blood are not able to receive by the body it goes
back to the heart instead.
Oblates of saint joseph schools
Saint James Academy
Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
II. Medical History
Patent Ductus Arteriosus is a kind of congenital heart defect. Congenital heart defects
are the most common type of birth defect. The defects can involve the walls of the heart,
the valves of the heart, and the arteries and veins near the heart. They can disrupt the
normal flow of blood through the heart. The blood flow can slow down, go in the wrong
direction or to the wrong place, or be blocked completely (MedlinePlus, 2019)
Congenital heart defects arise from problems early in the heart's development but there's
often no clear cause. Genetic factors might play a role. The doctors make use of physical
and different heart test to diagnose different Congenital diseases.
As part of the study, the researcher interviewed a patient who was diagnosed of
having Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Patient X is a 8 year old girl born on April 13,
2011, at birth noted to have a good cry, good suck and activity, the researcher
interviewed the patient parents for much accurate and correct information. According to
her mother, after she gave birth the pediatrician advised them that they should look for a
cardiologist because of the present of heart murmur (an unusual sound heard between
heartbeats) on their child. Patient X undergo her first 2-D ECHO w/CFDS one month
after she was born, the examination has 8 different remark, congenital heart disease and
patent ductus arteriosus 0.37 cm and PG of 33.4 mmHg was included on the remarks,
signed by a medical professional. August 14, 2013, patient X undergo for another 2-D
ECHO w/ CFDS, the result shows an increase of .03 cm on her Patent Ductus Arteriosus,
from 0.37cm to 0.4 cm. Only patient X has (PDA) among her family. Patient X heart beat
faster than a normal individual and has a weak immune system but she’s still free to eat
anything she want according to her mother. July 11, 2016 patient X has been admitted in
Philippine Heart Center in East Avenue, Quezon City with a final diagnosis of Congenital
Heart Disease, PDA,CoA.
Oblates of saint joseph schools
Saint James Academy
Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
III. Laboratory
The following images shows the patient X laboratory result during her check up,
consultation and different heart examinations.
IV. Anatomy and Physiology
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) occurs in our circulatory system particularly
in our heart. Circulatory system is a network consisting of blood, blood
vessels, and the heart. This network supplies tissues in the body with oxygen
and other nutrients, transports hormones, and removes unnecessary waste
products.
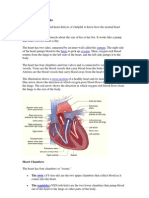
child's heart is a muscle about the size of his or her fist. It works like a pump and
beats about 100,000 times a day. The heart has two sides, separated by an inner
wall called the septum. The right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs to pick
up oxygen. Then, oxygen-rich blood returns from the lungs to the left side of the
heart, and the left side pumps it to the body.
The illustration shows a cross-section of a healthy heart and its inside structures.
Oblates of saint joseph schools
Saint James Academy
Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
The ductus arteriosus is a blood vessel that connects a baby's aorta and pulmonary
artery while the baby is in the womb. This connection allows blood to be pumped
from the right side of the heart straight to the aorta, without stopping at the lungs for
oxygen.
While a baby is in the womb, only a small amount of his or her blood needs to go to
the lungs. This is because the baby gets oxygen from the mother's bloodstream.
After birth, the baby is no longer connected to the mother's bloodstream. The baby's
blood must now go to his or her own lungs to get oxygen. Normally, as the baby
begins to breathe on his or her own, the pulmonary artery opens to allow blood into
the lungs, and the ductus arteriosus closes.
Once the ductus arteriosus closes, blood leaving the right side of the heart no longer
goes straight to the aorta. First, it goes through the left and right pulmonary arteries
and through the lungs to pick up oxygen. Then, the oxygen-rich blood returns to the
left side of the heart and is pumped out to the rest of the body.
If the ductus arteriosus doesn't close after birth as it should, it's called a patent
ductus arteriosus (PDA). A PDA allows blood to flow directly from the aorta into the
pulmonary artery and to the lungs. This extra amount of blood flowing into the lungs
strains the heart and increases blood pressure in the lung's arteries.
The abnormal opening causes too much blood to circulate to the baby's lungs and heart.
Untreated, the blood pressure in the baby's lungs might increase (pulmonary
hypertension) and the baby's heart might enlarge and weaken. Some risk factors of
having this kind of disease for a newborn baby are Premature birth, Family history
and other genetic conditions, Rubella infection during pregnancy The rubella virus
Oblates of saint joseph schools
Saint James Academy
Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
crosses the placenta and spreads through the baby's circulatory system, damaging blood
vessels and organs, including the heart, born at a high altitude, and being female
because PDA is most common in girls. Here are some of the signs and symptoms of a
baby that has a large Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) a bounding (strong and
forceful) pulse, fast breathing, not feeding well, shortness of breath, sweating
while feeding, tiring very easily and poor growth.
kidney is a bean-shaped organ that clear harmful substance in your body by
filtering your blood. It is like a water purification plant that helps clean the drinking water
for a city. It also regulates pH, volume, pressure, osmolality as well as produce
hormones. The kidneys are located between the T12 and L3 vertebrae, and they're
partially protected by ribs 11 and 12- which are the floating ribs. The kidneys are roughly
the size of a fist and are retroperitoneal, meaning they sit behind the peritoneal membrane
alongside the vertebral column. Like all solid organs, kidneys are enclosed in a fibrous
capsule that provides protection. The right kidney is pushed down by the liver so its sits
slightly lower that the left kidney.
In the middle of each kidney there is an indentation that forms the renal hilum.
This is the entry and exit point for the ureter renal artery and renal vein, lymphatics, and
nerves go into and come out of the kidney. The continuous pale outer tissues of the
kidney are known as the renal cortex, which surrounds the inner renal medulla. The shape
and interaction of the renal medulla and cortex cause the medulla to take on triangular
shapes known as renal pyramids.
Oblates of saint joseph schools
Saint James Academy
Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
Found within the renal cortex and medulla is the nephron, the kidney’s
microscopic functioning unit. The nephron serves as the body’s filter and removes toxins
and wastes from the blood. Each kidney has roughly 1.25 million nephrons that total a
length of more than 145 km. The nephron has two primary structures: the renal corpuscle
and the renal tubule. The renal corpuscle (in the cortex) filters blood at the glomerulus
into Bowman’s capsule. The glomerulus is a capillary network and is enveloped by
Bowman’s capsule, which is the start of the nephron’s waste collection system. The two
are separated by a thin epithelial wall. It is within the glomerulus where the blood
pressure forces fluid and dissolved solutes out of an arteriole and into Bowman’s capsule.
The fluid and solutes forced from the blood are called filtrate and drain into the proximal
convoluted tubule. Damage to the barrier between the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule
will lead to Chronic Kidney Disease.
Oblates of saint joseph schools
Saint James Academy
Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
V. Pathophysiology
Secondary Hypertension
↓
Arteriosclerotic lesions of the afferent and efferent arterioles
↓
Falling glomerular filtration rate
Decrease capability of the kidneys to excrete waste products
Due to hypertension, there are lesion to the afferent and efferent arterioles
decreasing the effectiveness of the filtration of blood in the glomerular that leads to the
decrease capability of the kidney to properly excrete waste products. Chronic kidney
disease is initially described as diminished renal reserve or renal insufficiency, which
may progress to renal failure (end-stage renal disease). Initially, as renal tissue loses
function, there are few noticeable abnormalities because the remaining tissue increases its
performance (renal functional adaptation).
Oblates of saint joseph schools
Saint James Academy
Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
VI. Pharmacologic Treatment/ Surgical Treatment
Depending on the underlying cause, some types of kidney disease can be treated.
Often, though, chronic kidney disease has no cure. Treatment usually consists of
measures to help control signs and symptoms, reduce complications, and slow
progression of the disease. For treating complication, treatments may include:
High blood pressure medications.
Medications to lower cholesterol levels.
Medications to treat anemia.
Medications to relieve swelling.
Medications to protect your bones.
A lower protein diet to minimize waste products in your blood
If your kidneys can't keep up with waste and fluid clearance on their own and you
develop complete or near-complete kidney failure, you have end-stage kidney disease. At
that point, you need dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Dialysis artificially removes waste products and extra fluid from your blood when
your kidneys can no longer do this. In hemodialysis, a machine filters waste and excess
fluids from your blood. In peritoneal dialysis, a thin tube (catheter) inserted into your
abdomen fills your abdominal cavity with a dialysis solution that absorbs waste and
excess fluids. After a period of time, the dialysis solution drains from your body, carrying
the waste with it.
A kidney transplant involves surgically placing a healthy kidney from a donor
into your body. Transplanted kidneys can come from deceased or living donors. You'll
need to take medications for the rest of your life to keep your body from rejecting the
new organ. You don't need to be on dialysis to have a kidney transplant.
Oblates of saint joseph schools
Saint James Academy
Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
VII. Palliative Care/ Rehabilitation
With a serious illness like chronic kidney disease, a palliative care should be
offered. Palliative care is a specialized type of medical care that can help people living
with CKD by alleviating pain, other symptoms and stress at the same time they are
receiving treatment to cure their disease. The goal of palliative care is to improve quality
of life for both the patient and the family. Palliative care puts control back in the hands
of the patient and family, and it can extend patients’ lives.”
When a person has a CKD, they already know that they need to take special care
of their body. Managing care and treatment for kidney disease can be a round-the-clock
effort that can put enormous physical and emotional strain on both the patient and the
family. A palliative care offer people with CKD an extra layer of support.
Manage pain and other conditions related to CKD. Palliative care is provided
alongside curative treatment. A palliative care team will work to provide relief from
conditions related to kidney disease, including high blood pressure, heart disease,
diabetes, and kidney failure.
Help with communication with other doctors and evaluating treatment options
Palliative care can help make critical decisions about treatment options including dialysis
and kidney transplant. The palliative care team can help the patient understand and decide
whether to go on dialysis.
Explain what to expect throughout the illness. The palliative care team will spend
as much time to help a patient and his/her family members to better understand the
condition and treatments.
Help a patient cope with worry, stress or depression. The burden of CKD and
kidney failure can be heavy. Palliative care provides emotional support for both patients
Oblates of saint joseph schools
Saint James Academy
Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
and their families. The palliative care team can often provide additional therapies,
including massages, talk therapy, and relaxation techniques, to ease emotional and
spiritual stress.
VIII. References
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/patent-ductus-arteriosus/symptoms-
causes/syc-20376145
https://medlineplus.gov/congenitalheartdefects.html
https://www.khanacademy.org/science/high-school-biology/hs-human-body-systems/hs-the-
circulatory-and-respiratory-systems/a/hs-the-circulatory-system-review
Oblates of saint joseph schools
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MCN Board Exam QuestionsDokument14 SeitenMCN Board Exam QuestionsStephannie Miranda100% (1)
- Cardiac Rehabilitation GuidelineDokument57 SeitenCardiac Rehabilitation GuidelineCarolina Pereira100% (1)
- Ncm09: Pedia: Erjen Alexandria M. Sia Bsn2BDokument12 SeitenNcm09: Pedia: Erjen Alexandria M. Sia Bsn2BErjen Alexandria SiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atrial Septal DefectDokument7 SeitenAtrial Septal DefectRis Amy AyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study ON: University of Perpetual Help System Cauayan City, IsabelaDokument27 SeitenCase Study ON: University of Perpetual Help System Cauayan City, Isabelaliam0831Noch keine Bewertungen
- About The Heart and Blood Vessels Anatomy and Function of The Heart ValvesDokument4 SeitenAbout The Heart and Blood Vessels Anatomy and Function of The Heart ValvesdomlhynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patent Ductus ArteriosusDokument6 SeitenPatent Ductus ArteriosusnidyaparasayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 - Semiotics of Cardiovascular Disorders. Semiotics of Congenital Hert Diseases in Children.Dokument30 Seiten12 - Semiotics of Cardiovascular Disorders. Semiotics of Congenital Hert Diseases in Children.Omowunmi KadriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atrial Septal DefectDokument5 SeitenAtrial Septal DefectalmorsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Research Paper TopicsDokument6 SeitenCardiovascular Research Paper Topicsgvym06g6100% (1)
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)Dokument19 SeitenPatent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)putri avriantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Askep PdaDokument44 SeitenAskep Pdaririn2942Noch keine Bewertungen
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) : What Is It?Dokument2 SeitenPatent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) : What Is It?Putri Ria AriyantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How The Heart Works: Septum Lungs OxygenDokument22 SeitenHow The Heart Works: Septum Lungs OxygenSuzan IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tricuspid AtresiaDokument5 SeitenTricuspid AtresiaCassyDelaRosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TuGaS Cardi0Dokument13 SeitenTuGaS Cardi0winfrey2207Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Ventricular Septal DefectDokument2 SeitenWhat Is A Ventricular Septal DefectKARAN MOHANANINoch keine Bewertungen
- Anak PDFDokument2 SeitenAnak PDFGheavita Chandra DewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0419 Hospi LabDokument11 Seiten0419 Hospi LabbiancaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conginital Heart DiseaseDokument19 SeitenConginital Heart DiseaseSanthosh.S.UNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patent Ductus ArteriosusDokument49 SeitenPatent Ductus Arteriosusarchana vermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System Research PaperDokument6 SeitenCirculatory System Research Papergbjtjrwgf100% (1)
- Research of ASDDokument3 SeitenResearch of ASDJennifer FinnaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System Dr. Eman Badr 2020Dokument182 SeitenCardiovascular System Dr. Eman Badr 2020Amina DinarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetralogy of FallotDokument5 SeitenTetralogy of FallotCharity OaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ateneo de Zamboanga University College of Nursing NCM 103 DeliverablesDokument6 SeitenAteneo de Zamboanga University College of Nursing NCM 103 DeliverablesNoelle HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Heart DiseasesDokument55 SeitenCongenital Heart DiseasesFaheem BasharatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus: Patient InformationDokument4 SeitenPatent Ductus Arteriosus: Patient InformationPamela JumpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital AnomaliesDokument26 SeitenCongenital AnomaliesMaria VisitacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 13 CongenitalHeartDefectDokument4 SeitenCH 13 CongenitalHeartDefectCarlo TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper On The Human HeartDokument5 SeitenResearch Paper On The Human Heartfysfs7g3100% (1)
- Research Paper About HeartDokument6 SeitenResearch Paper About Heartafnlamxovhaexz100% (1)
- Pediatric Patent Ductus ArteriosusDokument12 SeitenPediatric Patent Ductus Arteriosusabirami_murugesuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transposition of The Great Arteries What Is Transposition of The Great Arteries (TGA) ?Dokument5 SeitenTransposition of The Great Arteries What Is Transposition of The Great Arteries (TGA) ?Kenzi A HasyaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVSD - Revised VersionDokument3 SeitenAVSD - Revised Versiondr_IstiqlalMiftahulJannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Ventricular Septal DefectDokument2 SeitenWhat Is A Ventricular Septal DefectKARAN MOHANANINoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Forensic Pathology: Limits and ControversiesDokument191 SeitenPediatric Forensic Pathology: Limits and Controversieschrisr310Noch keine Bewertungen
- Midterms Group 5Dokument25 SeitenMidterms Group 5Karina MadriagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Heart DefectDokument12 SeitenCongenital Heart Defectsangkularosmina837Noch keine Bewertungen
- Child Nursing Care of The High-Risk Newborn To Maturity: I. PrematurityDokument392 SeitenChild Nursing Care of The High-Risk Newborn To Maturity: I. PrematuritydaisibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)Dokument12 SeitenAtrial Septal Defect (ASD)anggiehardiyantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 23 59 1 PBDokument6 Seiten23 59 1 PBrazgriz1412Noch keine Bewertungen
- Activity No. 3, Cardiovascular Sys.Dokument3 SeitenActivity No. 3, Cardiovascular Sys.Mariel CaylanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fetal CirculationDokument19 SeitenFetal CirculationAlozie PrestigeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Heart DiseasesDokument6 SeitenCongenital Heart DiseasesMox SwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHD CaseDokument5 SeitenCHD CaseChristineAlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transposition of Great Artery: 1. AbstractDokument7 SeitenTransposition of Great Artery: 1. AbstractA. Fajar AprianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TiKa TaKa PediatricsDokument86 SeitenTiKa TaKa PediatricsEmad MerganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus ClosureDokument7 SeitenPatent Ductus Arteriosus ClosureDard TongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Heart DefectDokument10 SeitenCongenital Heart DefectShubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Heart Disease 1223958712449685 9Dokument58 SeitenCongenital Heart Disease 1223958712449685 9RinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) ?: Autosomal Recessive, With Variable ExpressionDokument3 SeitenWhat Is A Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) ?: Autosomal Recessive, With Variable ExpressionpilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atrial Septal DefectDokument3 SeitenAtrial Septal Defectsyahid_unsriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tumbang KabehDokument57 SeitenTumbang KabehArif WicaksanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial HeartDokument10 SeitenArtificial HeartPrathyushaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atrial Septal Defect - A ReviewDokument5 SeitenAtrial Septal Defect - A ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 9 Student Handout2021 I - TaggedDokument12 SeitenUNIT 9 Student Handout2021 I - TaggedNia AvellanedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Heart Diseases, A Simple Guide to these Medical ConditionsVon EverandCongenital Heart Diseases, A Simple Guide to these Medical ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of TermsDokument5 SeitenDefinition of TermsYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- September 8Dokument7 SeitenSeptember 8Yna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Korean 1 23Dokument1 SeiteKorean 1 23Yna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Korean 1 23Dokument1 SeiteKorean 1 23Yna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Korean 1 23Dokument1 SeiteKorean 1 23Yna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- COURSE, DIVERSIFIED, CPD, Unti ETHICSDokument8 SeitenCOURSE, DIVERSIFIED, CPD, Unti ETHICSYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- HBJKDokument16 SeitenHBJKHealthene Joy Familara AlesnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architectural Interiors - Self StudyDokument5 SeitenArchitectural Interiors - Self StudyYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arc-2101, Gutierrez-PlumbingDokument3 SeitenArc-2101, Gutierrez-PlumbingYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isaac Newton Was One of The Most Important Figures in The History of ScienceDokument2 SeitenIsaac Newton Was One of The Most Important Figures in The History of ScienceYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity #1, My Personal SpaceDokument14 SeitenActivity #1, My Personal SpaceYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arc-2101 Gutierrez PurcomDokument1 SeiteArc-2101 Gutierrez PurcomYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arc-2101 - Gutierrez, Yna Marie - Act.2Dokument8 SeitenArc-2101 - Gutierrez, Yna Marie - Act.2Yna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isaac Newton Was One of The Most Important Figures in The History of ScienceDokument2 SeitenIsaac Newton Was One of The Most Important Figures in The History of ScienceYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- IHATEDJDokument1 SeiteIHATEDJYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Korean N Japan DraftDokument29 SeitenKorean N Japan DraftYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Metamorphosis of The Philippine ConstitutionDokument24 SeitenThe Metamorphosis of The Philippine ConstitutionYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arraya Tower: KUWAIT CITY, KUWAIT 2,297,800 SF / 213,470COMPLETION 2012Dokument14 SeitenArraya Tower: KUWAIT CITY, KUWAIT 2,297,800 SF / 213,470COMPLETION 2012Yna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erwteewev TF I Hate This SadlymdljaldpakdaDokument5 SeitenErwteewev TF I Hate This SadlymdljaldpakdaYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architectural Interiors: Client ProfileDokument8 SeitenArchitectural Interiors: Client ProfileYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Korean 1 23Dokument1 SeiteKorean 1 23Yna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mema InfoDokument1 SeiteMema InfoYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Korean 1 23Dokument1 SeiteKorean 1 23Yna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- TR 1Dokument3 SeitenTR 1Yna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Dolphin Safe": A Deceptive LabelDokument2 Seiten"Dolphin Safe": A Deceptive LabelYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Folk Beliefs in Construction: Old Beliefs Mostly Influence The Design of A House in Filipino ArchitectureDokument13 SeitenFolk Beliefs in Construction: Old Beliefs Mostly Influence The Design of A House in Filipino ArchitectureYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Dolphin Safe": A Deceptive LabelDokument2 Seiten"Dolphin Safe": A Deceptive LabelYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Dolphin Safe": A Deceptive LabelDokument2 Seiten"Dolphin Safe": A Deceptive LabelYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Dolphin Safe": A Deceptive LabelDokument2 Seiten"Dolphin Safe": A Deceptive LabelYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete and PlasticsDokument14 SeitenConcrete and PlasticsYna Marie GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 1st Periodical TestDokument4 SeitenScience 9 1st Periodical TestKebu Yen100% (1)
- Marieb ch11bDokument28 SeitenMarieb ch11bapi-229554503Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ajr 16 16449Dokument9 SeitenAjr 16 16449Lbc CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventricular Septal DefectDokument6 SeitenVentricular Septal DefectYannah Mae EspineliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Almaghrabi Cardio ExaminationDokument22 SeitenAlmaghrabi Cardio ExaminationSagit Nauman81Noch keine Bewertungen
- TesteDokument589 SeitenTesteJose Wo Oliveira SobrinhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inner SmileDokument1 SeiteInner SmileIon ConstantinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiotronic MedicationsDokument13 SeitenCardiotronic MedicationsTee WoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Beat Monitoring SystemDokument40 SeitenHeart Beat Monitoring System27051977Noch keine Bewertungen
- IPD - KardiologiDokument124 SeitenIPD - KardiologiAnis BonitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Assessment CataractDokument12 SeitenPhysical Assessment CataractEries Lacanlale LumbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Worksheet For Science Quiz 2 Grade 4Dokument3 SeitenRevision Worksheet For Science Quiz 2 Grade 4randah A.HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suz 183Dokument29 SeitenSuz 183Benny Chris TantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yyyyy Y YDokument49 SeitenYyyyy Y YSiva Nantham100% (1)
- The Deaths and Side Effects of Toxic Covid Vaccines!Dokument56 SeitenThe Deaths and Side Effects of Toxic Covid Vaccines!Francisco100% (1)
- Reading 1Dokument5 SeitenReading 1Buiducanh BuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Lead EKG Interpretation PDFDokument251 Seiten12 Lead EKG Interpretation PDFRobert So JrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1985-Cardiac Adaptations To Chronic ExerciseDokument28 Seiten1985-Cardiac Adaptations To Chronic ExerciseJavier Mora BaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated - Prioritization of ProblemsDokument1 SeiteUpdated - Prioritization of ProblemsKaycelyn JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pastest FOP PDFDokument2.947 SeitenPastest FOP PDFKyaw Zin HtetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Physiology of Cardiac Repolarization: Nerbonne, Jeanne M., and Robert S. KassDokument49 SeitenMolecular Physiology of Cardiac Repolarization: Nerbonne, Jeanne M., and Robert S. Kassrizki sundusiasihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dhapnia Heart Rate ExperimentDokument10 SeitenDhapnia Heart Rate ExperimentDinesha Sudarshani LiyanageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Bedah Thorax 2Dokument15 SeitenJournal Bedah Thorax 2Novia LarasatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of King's Theory of Goal Attainment in Miocard Infarct PatientDokument34 SeitenApplication of King's Theory of Goal Attainment in Miocard Infarct PatientYulis HatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACLS AlgorithmDokument12 SeitenACLS AlgorithmwildionNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Practise Exam Answers - 2019Dokument10 SeitenECG Practise Exam Answers - 2019Ronak SinaeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport in HumansDokument6 SeitenTransport in HumansSadiaNoch keine Bewertungen