Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Treatment Protocol For Confirmed COVID-19 Infection: A. Version 9 Recommendation Changes
Hochgeladen von
CristianAltunaSotomayorOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Treatment Protocol For Confirmed COVID-19 Infection: A. Version 9 Recommendation Changes
Hochgeladen von
CristianAltunaSotomayorCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Treatment Protocol for confirmed COVID-19 Infection
A. Version 9 recommendation changes:
1. Ritonavir + Lopinavir (Kaletra) was removed from treatment protocol as monotherapy but it was
kept as part of combination therapy for patients in ICU with pneumonia.
2. Convalescent plasma will be the treatment option for pregnant females with pneumonia
3. Reactive terminology was introduced for CT values > 30.
4. Cut off for CT value to be considered as non-infectious is > 30.
5. For patients with Reactive CT value > 30 upon diagnosis there is no need for repeat testing
unless symptoms suggestive of C0VID-19 infection developed.
6. Patients who are defined as cured and still needs hospitalization for various reasons, can be
transferred to non COVID facilities and they are considered noninfectious with no further
isolation precautions apart from standard precautions.
7. For asymptomatic patients with Reactive RT-PCR with CT value > 30 requiring
surgery/procedure:
For emergency surgery/procedure then it can be done with full PPE( Gown, gloves,
N95 mask, face shield /goggles )
For non-emergency (Elective) surgery/procedure postpone for at-least 1 week with
repeat testing then surgery/procedure can be performed unless CT value is ≤ 30.
8. All patients with symptoms suggestive of C0VID-19 infection should be evaluated to rule out
active disease regardless of the CT value and if emergency surgery/procedure is required then
full PPE (Gown, gloves, N95 mask, face shield /goggles) should be applied.
9. Alternatives to dexamethasone were added
10. Disposition of COVID 19 Positive Patient algorithm was added
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
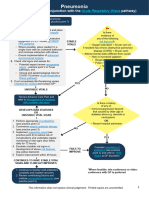
B. Treatment Algorithm:
Asymptomatic patients
with or without risk No treatment is
factors including recommended
pregnant women
Symptomatic patients
Mild URTI infection for
all adult patients Non ICU pneumonia ICU pneumonia with
Non ICU pneumonia ICU pneumonia
including pregnant with pregnency pregnency
women
Antibiotics +Kaletra+Ribavirin +
Interferon +Dexamethasone
Antibiotics +Favipiravir ± Antibiotics + convalescent plasma
Antibiotics + convalescent plasma or +
Dexamethasone
Symptomatic ±
Antibiotics +Favipiravir +interferon Dexamethasone
treatment Dexamethasone + Dexamethasone
consider Tocilizumab and consider Tocilizumab if indicated
consider Tocilizumab if indicated
convalescent plasma if indicated
consider Tocilizumab and
convalescent plasma if indicated
C. General information:
1- The purpose of the protocol is to assist physicians and healthcare providers in management of patients
with confirmed COVID-19 infection.
2- Those recommendations are based on case series, registered and observational trials and recent
publications and available data on patients with MERS CoV, SARS and COVID-19 infections.
3- To date there is no approved vaccine against COVID-19 infection
4- Strict infection control measures should be maintained all the time.
D. Collection of swabs: (Table 1)
1- Strict infection control measures should be maintained all the time.
2- Samples should be collected in negative pressure room (if not available single room with HEPA FILTERS)
3- Staff should wear full personal protective equipment PPE (Gown, gloves, N95 mask, face shield (goggles))
4- Combined Nasopharyngeal/ Oropharyngeal swab is recommended.
5- Lower respiratory specimen is preferred when the patient is intubated.
6- Airborne / contact isolation is recommended
7- Confirmed cases can be cohorted in case of shortage of single isolation rooms
8- For further information contact your infection control practitioner.
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
E. Collection of other laboratory diagnostic tests: (Table 2)
1- Request CBC, CMP, CRP, Respiratory panel including COVID-19 PCR for all cases with confirmed
pneumonia, Chest X-ray as baseline investigations.
2- Request electrocardiogram (ECG) for all patients.
3- QuantiFERON test for patient whom will be started on Tocilizumab.
4- Repeat other blood tests if indicated and for patients in ICU.
5- CT Chest if clinically indicated
6- Appropriate PPE should be applied during laboratory investigation (specimen collection and transport)
performing ECG and radiological investigations.
F. Supportive therapy and monitoring:
1- No evidence linking NSAIDS to COVID-related clinical deterioration. This has not been proven clinically to
date, so we cannot make a recommendation for or against their use at this time.
2- American Heart Association, the Heart Failure Society of America and the American College of
Cardiology all recommend that ACE inhibitors or ARBs be continued in people who have an indication for
these medications We do not currently routinely recommend stopping these agents
3- Continue statins if already prescribed if no contraindications and can be prescribed if it is indicated ,
take precautions in patients with elevated Liver enzymes
4- Postexposure Prophylaxis for Healthcare Workers: There is currently no proven role for post exposure
prophylaxis for people with a known COVID-19 exposure. They should monitor themselves for appearance
of symptoms for another14-days.
5- Monitor for drug -drug interactions (consult with your clinical pharmacist)
6- Give supplemental oxygen therapy immediately to patients with COVID-19 and respiratory distress,
hypoxemia, or shock. Initiate oxygen therapy at 5 L/min and titrate flow rates to reach target SpO2 ≥90%
in non-pregnant adults and SpO2 ≥92-95 % in pregnant patients.
7- All areas where patients with COVID-19 are cared for should be equipped with pulse oximeters,
functioning oxygen systems and disposable, single-use, oxygen-delivering interfaces (nasal cannula,
simple face mask, and mask with reservoir bag). Use contact precautions when handling contaminated
oxygen interfaces of patients with COVID-19 infection.
8- Use conservative fluid management in patients with COVID-19 when there is no evidence of shock.
9- Give empiric antimicrobials to treat all likely pathogens causing secondary bacterial infection in COVID-
19 patients. Give antimicrobials within one hour of initial patient assessment for patients with sepsis.
According to HMC local protocol (CG 10015)
10- Systemic corticosteroids for treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia is recently found to decrease mortality in
patient with evidence of Cytokine Release Storm (CRS), patients’ needs oxygen and respiratory support.
(recovery trial)
11- Closely monitor patients with COVID-19 for signs of clinical deterioration, such as rapidly progressive
respiratory failure and sepsis, and apply supportive care interventions immediately.
12- Understand the patient’s co-morbid condition(s) to tailor the management of critical illness and
appreciate the prognosis. Communicate early with patient and family.
13- Home recovery advice for cured patients if required:
Download Ehteraz application, activate it and check your status on regular basis
Stay at home
Don’t allow visitors into your house
In the event of a medical emergency call 999.
Your caregiver should wear a facemask and gloves every time he or she enters your room and
should dispose of the mask and gloves and wash their hands immediately after leaving the room.
A distance of at least one-two meter shall always be maintained between you and others.
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
14- Home isolation advice for active COVID-19 cases in the community (if applicable):
Download Ehteraz application, active it and check your status on regular basis
Stay at home in a separate room to other family members, preferably one with an en-suite
bathroom, and ensure proper and regular ventilation
Avoid any direct contact with other family members
Don’t allow visitors into your house
Use your phone if you need to contact anyone else in the house
Ask others - a family member or friend - to run errands for you like buying food or medicine
You must not leave your house. In the event of a medical emergency call 999.
Only one member of the family should be allowed to provide care to you. Your caregiver should
wear a facemask and gloves every time he or she enters your room and should dispose of the
mask and gloves and wash their hands immediately after leaving the room.
A distance of at least one-two meter shall always be maintained between you and your
caregiver.
15- patient can be discharge home If: Appendix 1
For hospitalized patients:
1. Resolution of the fever for > 3 days without use of antipyretic medication.
Plus
2. Improve respiratory symptoms (supplementary oxygen not required for at least 48 hrs.)
Plus
3. Improving Pulmonary Imaging (if repeated)
Plus
4. One negative RT- PCR tests from Naso-oropharyngeal swab after 10 days of symptom
onset
Or
One Inconclusive RT- PCR tests from Naso-oropharyngeal swab after 10 days of symptom
onset.
Or
One Reactive result with CT Value > 30 after 10 days of symptom onset.
If the swab is positive and CT value ≤ 30 repeat swab weekly till become Negative /Inconclusive
/Reactive.
For asymptomatic/mild symptomatic patients in isolation facilities Patient can be discharged
home after:
1. After 14 days from diagnosis (first RT-PCR positive result) and minimum 5 days from
resolution of symptoms if present, whichever is longer
Notes:
1. There will be no need for testing prior to discharge to confirm recovery unless the patient
had vulnerable population at home like household ≥ 60 years, immunocompromised
patients then swab will be repeated before discharge and he/she can be discharged
home if RT-PCR is negative or inconclusive or Reactive with CT value results > 30 , If the
swab is positive and CT value ≤ 30 patient will be kept in isolation facility to complete total
21 days from the first positive results, then can be discharge home without the need for
retesting.
2. For pneumonia patients transferred from hospitals and had previous positive RT-PCR with
CT value results ≤ 30 repeat another RT-PCR before discharge at day14.
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
3. For patients who are asymptomatic with Reactive CT value > 30 upon diagnosis can go
home with home recovery for 1 week from the first RT-PCR positive result.
4. For patients with Reactive CT value > 30 upon diagnosis there is no need for repeat testing
unless symptoms suggestive of C0VID-19 infection developed.
5. For patients who are defined as cured and still needs hospitalization for various reasons,
they can be transferred to non COVID facilities and they are considered noninfectious with
no further isolation precautions apart from standard precautions are needed.
6. For asymptomatic patients with Reactive RT-PCR with CT value > 30 requiring
surgery/procedure:
For emergency surgery/procedure then it can be done with full PPE( Gown, gloves, N95
mask, face shield /goggles )
For non-emergency (Elective) surgery/procedure postpone for at-least 1 week and
repeat testing, then surgery/procedure can be performed unless CT value is ≤ 30.
7. All patients with symptoms suggestive of C0VID-19 infection should be evaluated to rule
out active disease regardless of the CT value and if emergency surgery/procedure is
required then full PPE (Gown, gloves, N95 mask, face shield /goggles) should be applied.
N.B: in all those conditions the patient should be asymptomatic or at least 5 days passed from
resolution of COVID-19 symptoms
16- For case definition please see Appendix 2
17- For Medication related consideration please see Appendix 3
18- For COVID-19 infection in special population please see Appendix 4
19- All patients admitted patients with COVID-19 should be evaluated for the risk of VTE and receive standard
prophylactic/therapeutic anticoagulation with LMWH/ Unfractionated heparin if no contraindications, D-
Dimer based protocol was established in some centers see Appendix 5
20- QTc Screening to Identify Patients at Increased Risk: Patients admitted with COVID-19 are likely to have
longer baseline QTc and have higher potential arrhythmic risks as a result of the metabolic and
physiologic sequelae of their illness, and a typically greater burden of comorbid disease. However, given
the risk of Covid-19 hospitalized and critically ill patients may also derive the most benefit from potentially
effective therapies. The goal of QTc screening in this setting is not to identify patients whom are not
candidates for therapy, but to identify those who are at increased risk for torsade de pointes (TdP) so
aggressive counter measures may be implemented for prediction of drug-associated QT prolongation
among hospitalized patients see Appendix 6
21- Favipiravir patient drug information Appendix 7
22- Dexamethasone alternatives see Appendix 8
23- Disposition of COVID 19 Positive Patient Appendix 9
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
With or without Risk factors for severe disease (Table 3)
Admit the patient to isolation facility for observation
No treatment is recommended
Strict infection control measures should be maintained all the time.
With or without risk factors for severe disease (Table 3)
For patients with no risk factors Admit the patient to isolation facility for observation
No treatment is recommended
Strict infection control measures should be maintained all the time.
To be evaluated by obstetrician.
1. Positive COVID-19 PCR with Uncomplicated Upper Respiratory Tract Infection (URTI) (for definition see Table 4)
Admit the patient to Isolation Facility/ COVID Hospital upon physician decision
Strict infection control measures should be maintained all the time.
+
Symptomatic treatment
2. Treatment protocol for Pregnant females with Positive COVID-19 PCR with Uncomplicated Upper Respiratory
Tract Infection
Admit the patient to Isolation Facility/ COVID Hospital upon physician decision
Strict infection control measures should be maintained all the time.
+
Symptomatic treatment
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
3. Treatment protocol for COVID-19 Pneumonia (Documented pneumonia in CXR/CT scan) (for definition see Table 5)
Admit the patient to COVID Hospital
Strict infection control measures should be maintained all the time.
Start
Antibiotic * IV/PO As per local CAP guidelines for 7 days#
+
Favipiravir @ PO 1600 mg/dose twice a day on the first day; followed
by 600 mg/dose twice a day for 7 days
±
Dexamethasone $ PO/IV PO 6 mg Daily for 10 days
IV 8 mg Daily for 10 days
±
Tocilizumab For patients with evidence of cytokine release syndrome IV Initial dose of 4–8 mg/kg infused over more than 60
(Table 8) minutes. If initial dose not effective, may administer
second dose (in same dosage as initial dose) after 12
hours. No more than 2 doses should be given;
maximum single dose is 800 mg and not to be
infused in the same line with other medications
±
Consider Convalescent Plasma Infusion (Table 9) IV 2 units of CP. Each unit of plasma (200 -250 ml) will be
given over 2 h with an interval of 1 h between the
two units. Can be repeated if indicated.
Add Oseltamivir 75 mg po bid if co-infection with influenza virus is confirmed
*Antibiotic can be switched to PO if the patient is clinically stable
#Management of community acquired pneumonia (cap) in immuno-competent adults (CG 10015)
@ potential teratogenic and other side effects of the drug should be explained fully for the patients
$ Dexamethasone use for patients whom need Oxygen, respiratory support or evidence of Cytokine Release Storm
4. Treatment protocol for Pregnant females with COVID-19 Pneumonia
Admit the patient to COVID-19 Hospital
Strict infection control measures should be maintained all the time.
Start
Antibiotic * IV/PO As per local CAP guidelines for 7 days #
+
Convalescent Plasma Infusion (Table 9) IV 2 units of CP. Each unit of plasma (200 -250 ml)
will be given over 2 h with an interval of 1 h
between the two units. Can be repeated if
indicated
±
Dexamethasone $ PO/IV PO 6 mg Daily for 10 days
IV 8 mg Daily for 10 days
±
Tocilizumab For patients with evidence of cytokine IV IV infusion: initial dose of 4–8 mg/kg infused over
release syndrome (Table 8) more than 60 minutes. If initial dose not
effective, may administer second dose (in same
dosage as initial dose) after 12 hours. No more
than 2 doses should be given; maximum single
dose is 800 mg and not to be infused in the
same line with other medications
Add Oseltamivir 75 mg po bid if co-infection with influenza virus is confirmed
*Antibiotic can be switched to PO if the patient is clinically stable
# Management of community acquired pneumonia (cap) in immuno-competent adults (CG 10015)
$ Dexamethasone use for patients whom need Oxygen, respiratory support or evidence of Cytokine Release Storm
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
5. Treatment protocol for COVID-19 pneumonia requiring Intensive care (Septic shock/ARDS) for definition see
(Tables 6,7)
Admit the patient to ICU in COVID-19 Hospital, Strict infection control measures should be maintained all the time.
Start
Option 1 Option 2
Favipiravir* PO1600 mg/dose twice a day on the first day;
Ritonavir + Lopinavir (Kaletra) 500mg PO BID for 10 days followed by 600 mg/dose twice a day for 10 days
+
+ IFN-α2a (Pegasys®) Subcutaneously 180 μg weekly for 2
Ribavirin PO 2.4 g orally as a loading dose followed by 1.2 g BID to weeks
be started 24 hours after loading dose for 10 days. Or Or
Interferon beta-1b Subcutaneously 8 MIU on alternative
+ days for 3 doses
IFN-α2a (Pegasys®) Subcutaneously 180 μg weekly for 2 weeks
Or
Interferon beta-1b Subcutaneously 8 MIU on alternative days for 3
doses
+
Antibiotics @ IV As per local CAP guidelines #
+
Dexamethasone IV 8 mg Daily for 10 days
±
Tocilizumab For patients with evidence of cytokine release IV Initial dose of 4–8 mg/kg infused over more than 60 minutes.
syndrome (Table 8) If initial dose not effective, may administer second dose (in
same dosage as initial dose) after 12 hours. No more than 2
doses should be given; maximum single dose is 800 mg and
not to be infused in the same line with other medications
±
Consider Convalescent Plasma Infusion (Table 9) IV
2 units of CP. Each unit of plasma (200 -250 ml) will be given
over 2 h with an interval of 1 h between the two units. Can
be repeated if indicated
Oseltamivir 75 mg po bid can be added if co-infection with influenza virus is suspected /confirmed
* potential teratogenic and other side effects of the drug should be explained fully for the patients
@Antibiotic can be switched to PO if the patient is clinically stable
#Management of community acquired pneumonia (cap) in immuno-competent adults (CG 10015)
6. Treatment protocol for COVID-19 pneumonia requiring Intensive care (Septic shock/ARDS) in pregnant females
Admit the patient to ICU in COVID Hospital, Strict infection control measures should be maintained all the time.
Start
Antibiotics * IV As per HMC CAP guidelines#
+
Dexamethasone $ IV 8 mg Daily for 10 days
+
Convalescent Plasma Infusion (Table 9) IV 2 units of CP. Each unit of plasma (200 -250 ml) will be given over 2 h
with an interval of 1 h between the two units. Can be repeated if
indicated
±
Tocilizumab For patients with evidence of cytokine IV IV infusion: initial dose of 4–8 mg/kg infused over more than 60 minutes.
release syndrome (Table 8) If initial dose not effective, may administer second dose (in same
dosage as initial dose) after 12 hours. No more than 2 doses should be
given; maximum single dose is 800 mg and not to be infused in the
same line with other medications
Oseltamivir 75 mg po bid can be added if co-infection with influenza virus is suspected /confirmed
*Antibiotic can be switched to PO if the patient is clinically stable
# Management of community acquired pneumonia (cap) in immuno-competent adults (CG 10015)
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Table 1: SAMPLE COLLECTON AND INFECTION CONTROL MEASURES
1- Samples should be collected in negative pressure room (if not available room with HEPA FILTERS)
2- Staff should wear full personal protective equipment PPE (Gown, gloves, N95 mask, face shield (goggles)
3- Combined nasopharyngeal/ oropharyngeal swab is recommended
4- Lower respiratory specimen is preferred when the patient is intubated.
5- Airborne / contact isolation is recommended
6- Confirmed cases can be cohorted in case of shortage of single isolation rooms
Table 2: Laboratories recommended for hospitalized patients with confirmed or suspected COVID-19
Baseline investigation CBC with diff (esp. total lymphocyte count)
Complete metabolic panel
CPK (creatine kinase)
Ferritin/CRP
D-Dimer
LDH
ECG
HBV serologies (HepBsAb, HepBcAb, and HepBsAg)
HCV antibody
HIV 1/2 Ab/Ag
In case of confirmed pneumonia full respiratory viral panel is recommended
Recommended follow up labs: CBC with diff (esp. total lymphocyte count)
Complete metabolic panel
CPK (creatine kinase)
Ferritin/CRP
Routine blood cultures (2 sets)
If clinically indicated: For acute kidney injury, send urinalysis and spot urine protein: creatinine
Procalcitonin
IL-6
QuantiFERON test for patient who will be started on Tocilizumab.
Anti X-a
Radiology Chest X-ray
CT chest if clinically indicated
Table 3: Risk factors for severe disease
Epidemiological Vital Signs Labs
1. Older adults Age > 55 1. Respiratory rate > 24 1. D-dimer > 1 mg/L
2. Patients of all ages with underlying medical breaths/min 2. CPK > twice upper limit of
2. Heart rate > 125 beats/min Normal
conditions, particularly if not well controlled,
3. SpO2 ≤ 94 % on ambient air 3. CRP > 100
including:
4. PaO2/FiO2 < 300 mmHg 4. LDH > 245 U/L
Patients with chronic lung disease or moderate 5. Elevated troponin
to severe asthma
6. Admission absolute
Patients who have serious heart conditions lymphocyte count < 0.8
Diabetes with HbA1c > 7.6% 7. Ferritin > 500 ug/L
History of hypertension
Patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing
dialysis
Patients with liver disease
3. immunocompromised patients, including cancer
treatment, smoking, bone marrow or organ
transplantation, immune deficiencies, poorly
controlled HIV or AIDS, and prolonged use of
corticosteroids and other immunosuppressants
4. Use of biologics
5. Obese patients (body mass index [BMI] ≥ 30
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Table 4: Definition of Uncomplicated upper respiratory tract viral infection:
Definition of Uncomplicated upper respiratory tract viral infection:
Patients with uncomplicated upper respiratory tract viral infection, may have non-specific symptoms such as fever, cough,
sore throat, nasal congestion, malaise, headache, muscle pain or malaise. The elderly and immunosuppressed may
present with atypical symptoms. These patients do not have any signs of dehydration, sepsis or shortness of breath.
Table 5: Definition of Pneumonia:
Definition of Pneumonia:
Mild pneumonia Patient with pneumonia and no signs of severe pneumonia.
Severe Adolescent or adult: fever or suspected respiratory infection, plus one of:
pneumonia - respiratory rate > 30 breaths/min
- severe respiratory distress, or SpO2 < 90% on room air
N.B: CURB65 and/or PSI can be used to assess pneumonia severity
Table 6: Definition of Sepsis &Septic shock
Definition of Sepsis &Septic shock
Sepsis Life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to suspected or proven infection,
with organ dysfunction. Signs of organ dysfunction include altered mental status, difficult or fast breathing, low
oxygen saturation, reduced urine output, fast heart rate, weak pulse, cold extremities or low blood pressure,
skin mottling, or laboratory evidence of coagulopathy, thrombocytopenia, acidosis, high lactate or
hyperbilirubinemia.
Septic shock Persisting hypotension despite volume resuscitation, requiring vasopressors to maintain MAP ≥65 mmHg and
serum lactate level >2 mmol/L.
Table 7: Definition of ARDS
Definition of ARDS
Berlin Definition of ARDS requires that all the following criteria be present for diagnosis:
●Respiratory symptoms must have begun within one week of a known clinical insult, or the patient must have new or worsening
symptoms during the past week.
●Bilateral opacities must be present on a chest radiograph or computed tomographic (CT) scan. These opacities must not be
fully explained by pleural effusions, lobar collapse, lung collapse, or pulmonary nodules.
●The patient's respiratory failure must not be fully explained by cardiac failure or fluid overload. An objective assessment (eg,
echocardiography) to exclude hydrostatic pulmonary edema is required if no risk factors for ARDS are present.
●A moderate to severe impairment of oxygenation must be present, as defined by the ratio of arterial oxygen tension to fracti on
of inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2). The severity of the hypoxemia defines the severity of the ARDS:
•Mild ARDS – The PaO2/FiO2 is >200 mmHg, but ≤300 mmHg, on ventilator settings that include positive end-expiratory pressure
(PEEP) or continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) ≥5 cm H2O.
•Moderate ARDS – The PaO2/FiO2 is >100 mmHg, but ≤200 mmHg, on ventilator settings that include PEEP ≥5 cm H2O.
•Severe ARDS – The PaO2/FiO2 is ≤100 mmHg on ventilator settings that include PEEP ≥5 cm H2O.
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Table 8: Guidance for Tocilizumab prescription:
Studies indicate advanced stage disease responses to β-Coronaviruses including COVID-19 have a high IL-6 cytokine signature.
Send serum IL-6 level prior to giving first dose of Tocilizumab
Tocilizumab is currently under investigation for use in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-associated pulmonary
complications with elevated IL-6 levels at this time, safety and efficacy have not been established and information specific to
pregnancy has not been located. Risk and benefits should be discussed with the patients /family prior to medication administration
Establish clinical status to COVID-19 Determine treatment intervention
Grade 1 – mild reaction No treatment
Grade 2 – moderate reaction, Send for serum IL-6
fever, need for IVF (no
hypotension), mild oxygen
requirement
Grade 3 – severe, liver test Send for serum IL-6; consider Tocilizumab , if no effect can repeat x 2 more
dysfunction, kidney injury, IVF for doses 12 hours apart; if no response, consider low dose corticosteroids
resuscitation, low dose
vasopressor, supplemental oxygen
(high flow, BiPAP, CPAP)
Grade 4 – life threatening, Send for serum IL-6; consider Tocilizumab if no effect can repeat x 2 more
mechanical ventilation, high dose doses 12 hours apart; consider corticosteroid
vasopressor
(adopted and based on the Penn CRS criteria)
N.B: Use for confirmed COVID-19 cases guided by IL-6 level should be prescribed by infectious disease consultant, QuantiFERON test
Indication criteria for Use of Laboratory Parameters also Tocilizumab Exclusion Criteria of Patient:
Tocilizumab supportive of cytokine storm ( one
or more of the following):
Extensive and bilateral lung Serum IL-6 > 10 x upper normal The inflammatory markers criteria should be in
disease and severely ill patients limit (Reference range ≤ 7 context of IL-6 along with other markers
with elevated IL-6 level pg/mL) mentioned below :
Alternatively, High levels of d- Ferritin >300 ug/L (or surrogate) Active TB
dimer and / or CRP/ or ferritin with doubling within 24 hours AST / ALT values higher than 5 times the normal
and / or fibrinogen progressively Ferritin >600 ug/L at levels.
increasing. presentation Neutrophil value lower than 500 cells / mm3
Worsening of respiratory LDH >250 U/L Platelets value lower than 50,000 cells /mm3
exchanges such as to require non- Elevated D-dimer (>1 mg/L) Complicated diverticulitis or intestinal perforation
invasive or invasive support from High CRP Skin infection in progress (e.g.
ventilation dermohypodermatitis not controlled by antibiotic
therapy)
Immunosuppressive anti-rejection therapy
Confirmed systemic bacterial & or fungal infection
(i.e. Bacteremia with pathogenic bacteria,
fungemia)
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Table 9: Recommendations for Investigational COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma:
Patient inclusion Criteria Laboratory confirmed COVID-19
Patients with ARDS (any severity) with or without septic shock / multiple organ
dysfunction
Age ≥to 18 years.
Patient/family member to provide informed consent
Patient exclusion Criteria Negative RT-PCR from respiratory secretions or blood within 48 h prior to
assessment of eligibility.
History of allergic reaction to blood or plasma products.
Medical conditions in which receipt of 500 mL intravascular volume may be
detrimental to the patient (e.g. actively decompensated congestive heart failure).
Severe multi-organ failure, hemodynamic instability.
Other documented uncontrolled infection.
Severe DIC needing factor replacement, FFP, cryoprecipitate.
Expected survival for ≤ 48 hours
Donor inclusion criteria 1- Prior diagnosis of COVID-19 documented by a laboratory test
2- Complete resolution of symptoms at least 28 days prior to donation
OR
3- Complete resolution of symptoms at least 14 days prior to donation AND Negative
results for COVID-19 either from one or more nasopharyngeal swab specimens or by
a molecular diagnostic test from blood
4- Male donors, female donors who have not been pregnant or female donors who
have been tested since their most recent pregnancy and results interpreted as
negative for HLA antibodies (if needed)
Defined SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing Defined SARS-CoV2 neutralizing antibody titers, if testing can be conducted
antibody titers (optimally greater than 1:80)
NOTE: If neutralizing antibody titers cannot be obtained in advance, consider storing
a retention sample from the convalescent plasma donation for determining antibody
titers later.
• COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma, Fresh Frozen, should be frozen within 8 hours after collection, stored at -18C◦ or colder and have an expiration date
one year from the date of collection
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Appendix 1: patient discharge criteria:
Hospitalized patients Patients in isolation facilities ( asymptomatic /mild
symptomatic )
Resolution of the fever for >3 days without use of antipyretic After 14 days from diagnosis (first RT-PCR positive result) and
medication. minimum 5 days from resolution of symptoms, whichever is longer.
Plus
Improve respiratory symptoms (not required oxygen x 4 8 hrs.)
Plus Notes
Improving Pulmonary Imaging ( if repeated )
Plus 1. There will be no need for testing prior to discharge to
One negative RT- PCR tests from Naso-oropharyngeal swab after confirm recovery unless the patient had vulnerable
10 days of symptom onset population at home like household ≥ 60 years,
immunocompromised patients then swab will be repeated
Or
before discharge and he/she can be discharged home if
One Inconclusive RT- PCR tests from Naso-oropharyngeal swab
RT-PCR is negative or inconclusive or Reactive with CT
after 10 days of symptom onset.
value results > 30 , If the swab is positive and CT value ≤ 30
patient will be kept in isolation facility to complete total 21
Or days from the first positive results, then can be discharge
One Reactive result with CT > Value 30 home without the need for retesting.
Notes :If the swab is positive and CT value ≤ 30 repeat swab 2. For pneumonia patients transferred from hospitals and
weekly till Negative /Inconclusive /Reactive had previous positive RT-PCR with CT value results ≤ 30
repeat another RT-PCR before discharge at day 14.
3. For patients who are asymptomatic with Reactive CT value
> 30 upon diagnosis can go home with home recovery for
1 week from the first RT-PCR positive result.
4. In all those conditions the patient should be asymptomatic
or at least 5 days passed from resolution of COVID-19
symptoms.
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Appendix 2: CASE DEFINITIO
Suspected case (requires diagnostic testing) Probable case Confirmed case
1. Acute respiratory tract infection (Sudden onset of the Suspected case + inconclusive Laboratory-confirmed infection,
following: fever ≥37.8C and/or cough and/or shortness of COVID-19 test regardless of signs and
breath) symptoms
+
No other etiology that fully explains the clinical presentation
particularly if he/she lives or works in area reporting recent local
transmission of COVID-19.
OR
Close contact with a confirmed or probable COVID-19 case
within ≤14 days prior to onset of symptoms
OR
Recent travel within the previous 14 days
OR
History of residence in country reporting local transmission of
COVID 19 Disease.
2. Severe acute respiratory infection (fever ≥37.8C and/or
at least one sign / symptoms of respiratory diseases (e.g: cough,
fever, shortness of breath)
+
Requiring hospitalization
+
No other etiology that fully explains the clinical presentation
3. Individuals present with any acute respiratory illness
including older adults (55 years or more) and individuals with
chronic medical conditions and/or an immunocompromised
state that may put them at higher risk for poor outcomes (e.g.,
diabetes, heart disease, receiving immunosuppressive
medications, chronic lung disease, chronic kidney disease,
cancer) regardless of travel history
4. Cluster case (2 or more cases with fever of 37.8 and/or
respiratory symptoms in a small area such as families, offices,
school room etc. within 2 weeks
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Appendix 3: COVID-19 Medications Information:
Lopinavir/Ritonavir (LPV/r) (Kaletra)
Baseline investigations ECG (Increase PR and QTc interval)
LFT
Monitoring recommendations Follow up LFT
Follow up ECG is recommended (Use with caution in these with cardiac conduction
abnormalities or when used with other medication that have similar effect).
Monitor for bleeding especially if used concurrently with some anticoagulant and
anti-platelets.
Most common side effects GI Symptoms (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea)
Increase liver enzymes.
Increase PR and QTc interval.
Drug-Drug interaction Major Drug-Drug interaction (especially with anti-arrythmia, anticoagulant, anti-
platelets, Domperidone)
Oseltamivir
Common side GI side effects (Diarrhea, Nausea, vomiting),
effects/contraindication To reduce Nausea, administer with food.
CNS symptoms (delirium and abnormal behavior)
Drug-Drug interaction No major Drug-Drug interaction
Dose adjustment Needs dose adjustment based on renal function
Tocilizumab
Baseline investigations Consider QuantiFERON test
CBC
LFT
Lipid profile
Most common side effects Injection site reaction
Infusion related reaction
Increase Liver enzymes (AST, ALT, ALP and T-bilirubin)
Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia
Drug-Drug interaction Caution with other immune suppressive medication and live attenuated vaccines
Pregnancy Considerations Post marketing data have not shown an increased rate of congenital malformations
or a pattern of specific malformations following in utero exposure to tocilizumab.
At this time, safety and efficacy have not been established and information specific to
pregnancy has not been located.
Informed consent is required
Breast-Feeding Considerations Tocilizumab is present in breast milk and in the serum of one infant at birth following
in utero exposure, concentrations rapidly decreased and were not detectable by 4
weeks of age.
Concentrations of tocilizumab are expected to be limited in breast milk due to large
molecular weight. Also, because tocilizumab is unlikely to be absorbed via the infant
gastrointestinal tract, use of tocilizumab may be considered in breastfeeding women
Interferon
Baseline investigations CBC
LFT
Monitoring recommendations CBC , Platelet count
LFT
Monitor for flu-like symptoms, allergic or anaphylactic reactions, injection-site
reactions,
Most common side effects Cardiovascular: Peripheral edema
Dermatologic: Skin rash
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain
Genitourinary: Urinary urgency
Hematologic & oncologic: Leukopenia , lymphocytopenia , neutropenia
Hepatic: Increased serum alanine aminotransferase (>5x baseline)
Nervous system: Ataxia , chills , headache , hypertonia , insomnia , pain
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Asthenia , myalgia
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Respiratory: Flu-like symptoms
Miscellaneous: Fever
Drug-Drug interaction Cladribine: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Interferons (Beta). Specifically,
the risk for lymphopenia may be increased. Risk X: Avoid combination
Zidovudine: Interferons may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Zidovudine.
Interferons may decrease the metabolism of Zidovudine. Risk C: Monitor therapy
Favipiravir
Baseline investigations CBC
LFT
Uric acid
Pregnancy test for females in childbearing age
Monitoring recommendations Follow up CBC
Follow up LFT
Follow up Uric acid
Most common side effects Anemia
Increase Liver enzymes
Testis toxicity
Teratogenic ( contraindicated in pregnancy )
For women of childbearing age (effective contraception is advised) and sexually
active men (use condoms and NO unprotected sexual intercourse with pregnant
women) for at least 7 days after the end of the treatment.
Potential teratogenic and other side effects of the drug should be explained fully for
the patients and should be documented in the patient EMR.
Drug-Drug interaction Pyrazinamide: Favipiravir may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Pyrazinamide.
Specifically, the risk for increased uric acid concentrations may be increased. Risk C:
Monitor therapy
Repaglinide: CYP2C8 Inhibitors (Weak) may increase the serum concentration of
Repaglinide. Risk C: Monitor therapy
Ribavirin
Baseline investigations CBC
Renal function test ( contraindicated if Crcl <50 ml/min stop the drug)
Pregnancy test for females in childbearing age
Monitoring recommendations Monitor for any symptoms or signs of hemolysis. RBV may cause hemolysis especially
in patients with impaired renal function, older age, high dose per body weight and
female gender).
Renal function test
Most common side effects Dermatologic: Alopecia ,dermatitis, diaphoresis , pruritus , skin rash ,xeroderma
Endocrine & metabolic: hyperuricemia,
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain, decreased appetite, diarrhea , dyspepsia , nausea
,vomiting.
Hematologic & oncologic: Anemia , hemolytic anemia , lymphocytopenia ,
neutropenia;
Hepatic: Hyperbilirubinemia
Nervous system: Anxiety ,depression, dizziness , emotional lability, fatigue, headache
insomnia, irritability ,nervousness
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Arthralgia ,myalgia .
Respiratory: Cough , dyspnea , flu-like symptoms , pharyngitis , sinusitis
Miscellaneous: Fever , chills
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Drug-Drug interaction Azathioprine: Ribavirin (Systemic) may increase serum concentrations of the active
metabolite(s) of Azathioprine. Management: Consider using alternative agent(s)
when possible. When these drugs are used in combination, monitor patients closely
for signs/symptoms of myelosuppression. Risk D: Consider therapy modification
Cladribine: Agents that Undergo Intracellular Phosphorylation may diminish the
therapeutic effect of Cladribine. Risk X: Avoid combination
Didanosine: Ribavirin (Systemic) may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Didanosine.
Risk X: Avoid combination
Interferons (Alfa): May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Ribavirin (Systemic).
Hemolytic anemia has been observed. Risk C: Monitor therapy
Vitamin K Antagonists (eg, warfarin): Ribavirin (Systemic) may diminish the
anticoagulant effect of Vitamin K Antagonists. Risk C: Monitor therapy
Zidovudine: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Ribavirin (Systemic). Specifically,
the risk/severity of anemia may be increased. Management: Due to significantly
increased risk of anemia, consider even closer monitoring for anemia than routinely
recommended for ribavirin. Alternative therapies should be considered when
clinically possible, particularly for patients with other risk factors. Risk D: Consider
therapy modification
Management of RBV induced For patients with no cardiac disease, ribavirin can be held/stop if hemoglobin levels
Hemolytic anemia <10 g/dL.
*check with your clinical pharmacist
Appendix 4: COVID-19 in special population:
Pregnancy Consult obstetrician
The use of therapeutic agents should be guided by individual risk-benefit analysis
Do not use statins
Pregnant women with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 infection should be treated
with supportive therapies as described above, considering the physiologic adaptations
of pregnancy.
Emergency delivery and pregnancy termination decisions are challenging and based
on many factors: gestational age, maternal condition, and fetal stability. Consultations
with obstetric, neonatal, and intensive care specialists (depending on the condition of
the mother) are essential.
CXR and CT scan Chest can be performed if clinically indicated and after patient
consent with appropriate shield
Tocilizumab is currently under investigation for use in the treatment of coronavirus
disease 2019 (COVID-19)-associated pulmonary complications with elevated IL-6 levels
at this time, safety and efficacy have not been established and information specific to
pregnancy has not been located. Risk and benefits should be discussed with the
patients /family prior to medication administration
People living with HIV Avoid LPV/r monotherapy in people with HIV
If IgG <400 Consider IVIG at dose of 25 grams x 1 (unclear benefit)
Consult transplant and transplant ID teams
Heart/Liver/Kidney Transplant Consider decreasing Tacrolimus/Cyclosporine by 50%,
Recipients Stop Mycophenolate and Azathioprine in kidney/liver transplant patients and reduce
dose by 50% in heart transplant patients.
For Kidney transplant patients approximate target Tacrolimus level 3-5 ng/ml,
Cyclosporine level target 25-50 ng/ml.
Critical illness – in liver and kidney – stop all immunosuppressants except for
Prednisone if they are on it at baseline
Lung transplant recipients Consult transplant and transplant ID teams
No change to usual immunosuppression (avoids high levels, tailor to patient)
For all those in ICU or with lower respiratory tract disease (most inpatients): pulse
Methylprednisolone 125mg IV q 12 hours
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Appendix 5: Anti- coagulation use in COVID-1 positive patients:
- Adopted from HMGH local protocol for Management of Anticoagulation in COVID19 pneumonia patients admitted to Intensive Care
Unit May 2020
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Appendix 6: For prediction of drug-associated QT prolongation among hospitalized patients (Tisdale score)
Risk Factors Points
Age ≥68 y 1
Female sex 1
Loop diuretic 1
Serum K+ ≤3.5 mEq/L 2
Admission QTc ≥450 ms 2
Acute MI 2
≥2 QTc-prolonging drugs 6
sepsis 3
Heart failure 3
One QTc-prolonging drug 3
Calculated score
Maximum Risk Score 21
Low risk = ≤6 points
Moderate risk = 7-10 points
High-risk = ≥11 points
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Appendix 7: Favipiravir patient drug information:
Avigan© Favipiravir
IMPORTANT INFORMATION YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT YOUR MEDICATION
Medication Brand Name Avigan©
Medication Generic Name Favipiravir
Purpose This is an anti-viral medication which inhibits virus replication and it is used for COVID-19 in
many countries
How to take it Take 8 tablets at once, two times on day one, then take 3 tablets at once two times per day
from day 2 to day 7-10
For how long 7-10 days is the treatment duration
Important - This medication causes early embryonic death and teratogenicity, so it is not given to
women known or suspected to be pregnant
- Lactating women should stop lactation during treatment
- When given to sexually active men precautions should be used up to 7 days after
treatment is completed
Call your doctor If you noticed any of the following side effects:
- Skin rash
- Bruises
- Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting
- Blood in urine
- Visual abnormalities
- Vertigo
- Anything that is abnormal
أفيغان © فافيبيرافير
معلومات هامة يجب عليك معرفتها عن هذا الدواء
©أفيغان االسم التجاري للدواء
فافيبيرافير االسم العلمي للدواء
هذا الدواء له خصائص مضادة للفيروسات ويعمل على منع تكاثر الفيروس ويستخدم الغرض من استخدام الدواء
في العديد من البلدان19 لكوفيد
3 ثم تناول، مرتين في اليوم األول من العالج، أقراص في المرة الواحدة8 تناول كيفية أخذ العالج
أقراص في المرة الواحدة مرتين في اليوم من اليوم الثاني إلى اليوم السابع إلى العاشر
أيام10 -7 مدة العالج
لذلك ال يتم إعطاؤه، قد يتسبب هذا الدواء في اإلجهاض والتشوهات الخلقية للجنين- ملحوظة هامة
للنساء في سن الحمل قبل الفحص وتأكيد عدم الحمل
يجب على النساء المرضعات التوقف عن الرضاعة أثناء فترة العالج-
عند إعطاء الرجال النشطين جنسيا يجب استخدام االحتياطات الالزمة لمنع الحمل-
أيام بعد االنتهاء من مدة العالج7 لمدة تصل إلى
:إذا الحظت أي من اآلثار الجانبية التالية يجب عليك إبالغ الطبيب
الطفح الجلدي-
كدمات-
الغثيان والقيء, آالم في البطن-
وجود دم في البول-
عدم وضوح في الرؤية-
الشعور بالدوخة-
أي عرض غير طبيعي وال يتعلق بالمرض-
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Appendix 8: Alternatives to dexamethasone include:
Drug Route Dose
Hydrocortisone IV 50 mg q8hrs (or q6h for refractory shock)
Methylprednisolone IV 30mg Once Daily
Prednisone PO 40mg Once Daily
Appendix 9: Disposition of COVID 19 Positive Patient
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
References:
1. Efficacy and Safety of Hydroxychloroquine for Treatment of Pneumonia Caused by 2019-nCoV (HC-nCoV) - Full
Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov.
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04261517?cond=SARS+%28Severe+Acute+Respiratory+Syndrome%29&draw
=5 (accessed March 16, 2020).
2. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized
clinical trial. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents .Available online 20 March 2020, 105949
3. Fei Zhou, Ting Yu*, Ronghui Du*, Guohui Fan, Ying Liu*, ----_Zhibo Liu, Jie Xiang, Yeming Wang, Bin Song, Xiaoying
Gu, Lulu Guan, Yuan Wei,Hui Li, Xudong Wu, Jiuyang Xu, Shengjin Tu, Yi Zhang, Hua Chen, Bin Cao Clinical course
and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study.
http://www.thelancet.com/ published online March 9 ,2020
4. A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Clinical Study of Antiviral Therapy in the 2019-nCoV Pneumonia - Full Text
View - ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04255017?draw=2 (accessed March 16, 2020).
5. Randomized, open-label, controlled trial for evaluating of the efficacy and safety of Baloxavir Marboxil,
Favipiravir, and Lopinavir-Ritonavir in the treatment of novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) patients Chinese
Clinical Trial Register (ChiCTR) - The world health organization international clinical trials registered organization
registered platform. http://www.chictr.org.cn/showprojen.aspx?proj=49065 (accessed March 16, 2020).
6. A Multi-centre, Double-blinded, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial on the Efficacy and Safety of Lopinavir /
Ritonavir Plus Ribavirin in the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov.
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00578825 (accessed March 16, 2020).
7. Effective Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Patients with Tocilizumab. Xiaoling Xu, Mingfeng Han, Tiantian Li, Wei Sun,
Dongsheng Wang, Binqing Fu, Yonggang Zhou, Xiaohu Zheng, Yun Yang, Xiuyong Li, Xiaohua Zhang, Aijun Pan,
Haiming Wei ..PNAS May 19, 2020 117 (20) 10970-10975; first published April 29, 2020
8. Rand Alattar ,Tawheeda B. H. Ibrahim ,Shahd H. Shaar, Shiema Abdalla,Kinda Shukri ,Joanne N. Daghfal
,Mohamed Y. Khatib ,Mohamed Aboukamar ,Mohamed Abukhattab ,Hussam A. Alsoub ,Muna A. Almaslamani,
Ali S. Omrani. Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019
.J Med Virol. 2020;1–8. Journal of Medical Virology DOI: 10.1002/jmv.25964
9. Songping Cui Shuo Chen Xiunan Li Shi Liu Feng Wang Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in patients with
severe novel coronavirus pneumonia First published:09 April 2020 https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.14830
10. M. Cellina, G. OlivaDepartment of Radiology, Ospedale Fatebenefratelli, ASST Fatebenefratelli Sacco, Piazza
Principessa Clotilde Acute pulmonary embolism in a patient with COVID-19 pneumonia 3, 20121, Milano, Italy
Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging
11. F.A. Kloka,M.J.H.A. Kruipb,N.J.M. ,van der Meerc,M.S.Arbousd, D.A.M.P.J.Gommerse,K.M. Kantf,F.H.J.
Kapteina,J.van Paassend,M.A.M.Stalsa,M.V. Huismana,1,H. Incidence of thrombotic complications incritically ill
ICU patients with COVID-19 . Endemane, Thromb Res. 2020 Apr 10 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013
12. Alexander T. Cohen, M.D., Theodore E. Spiro, M.D., Harry R. Büller, M.D., Lloyd Haskell, M.D., Dayi Hu, M.D., Russell
Hull, M.B., B.S., Alexandre Mebazaa, M.D., Geno Merli, M.D., Sebastian Schellong, M.D., Alex C. Spyropoulos, M.D.,
and Victor Tapson, M.D .Rivaroxaban for Thromboprophylaxis in Acutely Ill Medical Patients ,N. engl j med 368;6
nejm.org february 7, 2013
13. Tisdale JE, Jayes HA, Kingery JR, et al . Development and validation of a risk score to predict QT interval
prolongation in hospitalized patients. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2013;6:479-487.
14. Timothy F. Simpson, Richard J. Kovacs, Eric C. Stecker, ‘Ventricular Arrhythmia Risk Due to Hydroxychloroquine-
Azithromycin Treatment For COVID-19’. Am Coll Cardiol.(2020)
15. Wu C-I, PostemaPG, ArbeloE, Behr ER, BezzinaCR, Napolitano C, RobynsT, Probst V, Schulze-Bahr E, RemmeCA,
Wilde AAM, SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19 and inherited arrhythmia syndromes, Heart Rhythm (2020)
16. John R. Giudicessi, Peter A. Noseworthy, Paul A. Friedman, Michael J. Ackerman, 2020 ‘Urgent Guidance for
Navigating and Circumventing the QTc Prolonging and Torsadogenic Potential of Possible Pharmacotherapies for
COVID-19.
17. COVID-19 Treatment QT Adverse Effects Management Pathway prepared by al-khor hospital Clinical Pharmacy
team
18. National health commission of Republic of china guideline for diagnosis & treatment of COVID19 Pneumonia
version 6, version 7 http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2020-02/19/content_5480958.htm
Prepared by HMC CDC COVID-19 Scientific Committee (Doha-Qatar), version 9 (01/07/2020)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CAP Guidance 2020 Revision Final UpdatedDokument11 SeitenCAP Guidance 2020 Revision Final UpdatedNeerajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guideline For The Management of Community-Acquired PneumoniaDokument11 SeitenGuideline For The Management of Community-Acquired PneumoniaCarlos VSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recommended Doses of IVERMECTINDokument3 SeitenRecommended Doses of IVERMECTINRonald LunasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSMFM Guidelines On Common Practices Amid Covid 19Dokument8 SeitenPSMFM Guidelines On Common Practices Amid Covid 19Kismet LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gui Iia Uk PDFDokument2 SeitenGui Iia Uk PDFluckevNoch keine Bewertungen
- COVID-19 InterimGuidelines Treatment ENGDokument24 SeitenCOVID-19 InterimGuidelines Treatment ENGHouda LaatabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- COVID-19 InterimGuidelines Treatment ENGDokument25 SeitenCOVID-19 InterimGuidelines Treatment ENGMartin PaturlanneNoch keine Bewertungen
- COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines: Clinical ManagementDokument6 SeitenCOVID-19 Treatment Guidelines: Clinical ManagementPetra SpringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Management Guidelines For Suspected or Confirmed COVID 19 Infection in Adults Version 4 April 2023 MOH NUGDokument94 SeitenClinical Management Guidelines For Suspected or Confirmed COVID 19 Infection in Adults Version 4 April 2023 MOH NUGFrozenboy. 1993Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary InfectionsDokument16 SeitenPulmonary InfectionsFawad AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Case Studies of COVID-19 in PregnancyDokument29 SeitenSample Case Studies of COVID-19 in PregnancyAbdibaset Mohamed AdenNoch keine Bewertungen
- COVID-19 ER Clinical Pathway: Registration or Triage NurseDokument2 SeitenCOVID-19 ER Clinical Pathway: Registration or Triage NurseBassam AlqadasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dialysis Guide 2012Dokument12 SeitenDialysis Guide 2012nadhifNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIP COVID-19 Webinar Slides Key Considerations FinalDokument49 SeitenFIP COVID-19 Webinar Slides Key Considerations FinalCahyuni Saputri YusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics - A Rational ApproachDokument49 SeitenAntibiotics - A Rational ApproachMohammad AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care of Patient With Covid 19Dokument32 SeitenCritical Care of Patient With Covid 19Anonymous Kv0sHqFNoch keine Bewertungen
- POGS-PSMFM Interim Guidelines On Labor and Delivery For COVID EditedDokument20 SeitenPOGS-PSMFM Interim Guidelines On Labor and Delivery For COVID EditedMacky YongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory SlidesDokument40 SeitenRespiratory SlidesmaheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009-10-16 Current Antiviral Recommendations For Influenza TreatmentDokument2 Seiten2009-10-16 Current Antiviral Recommendations For Influenza Treatmenttamiprior5294Noch keine Bewertungen
- The British Society For Rheumatology Biologic DMARD Safety Guidelines in Inflammatory Arthritis-Executive SummaryDokument38 SeitenThe British Society For Rheumatology Biologic DMARD Safety Guidelines in Inflammatory Arthritis-Executive SummaryNathania Nadia BudimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orthopaedic Infection in Adults UHL GuidelineDokument10 SeitenOrthopaedic Infection in Adults UHL GuidelineFadlu ManafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio Preboard 1 NP 1 IntensiveDokument10 SeitenRatio Preboard 1 NP 1 IntensiveKonstantin Konstantius50% (2)
- Tuberculosis Management Guidelines and Associated DENTAL Management GuidelinesDokument11 SeitenTuberculosis Management Guidelines and Associated DENTAL Management GuidelinesAbdul AkhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inbound 9171532219273535705Dokument6 SeitenInbound 9171532219273535705MichelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2002 Guidelines For The Use of Antimicrobial Agents in Neutropenic Patients With CancerDokument23 Seiten2002 Guidelines For The Use of Antimicrobial Agents in Neutropenic Patients With CancerzuricatitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Roachs Introductory Clinical Pharmacology 10th North American Edition Susan M FordDokument9 SeitenTest Bank For Roachs Introductory Clinical Pharmacology 10th North American Edition Susan M FordAnthonyRogersydtfp100% (62)
- Pneumonia: Recent Evidence Based UpdatesDokument30 SeitenPneumonia: Recent Evidence Based UpdatesAli AzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Hiv AidsDokument28 SeitenManagement of Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Hiv AidsUtkarsh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid-19, Sars Cov-2Dokument8 SeitenCovid-19, Sars Cov-2siti lailatul mahmudahNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAQs On COVID-19 From AIIMS e-ICUsDokument3 SeitenFAQs On COVID-19 From AIIMS e-ICUsrakeshambasanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic PolicyDokument38 SeitenAntibiotic Policysapphiresalem9Noch keine Bewertungen
- COVID 19 MG Protocol FinalDokument13 SeitenCOVID 19 MG Protocol FinalajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid-19 Summary Guidance #8: Treatment Guidelines and Medicines To Be StockedDokument1 SeiteCovid-19 Summary Guidance #8: Treatment Guidelines and Medicines To Be Stockedbenny christantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- COVID-19 Antiviral TX Guidance 4-22-2020Dokument23 SeitenCOVID-19 Antiviral TX Guidance 4-22-2020Lydia IsaacNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFORMATION SHEET 1. - Risk Categorisation Guidelines: Protection Against The Specified Infectious Diseases Is RequiredDokument4 SeitenINFORMATION SHEET 1. - Risk Categorisation Guidelines: Protection Against The Specified Infectious Diseases Is RequiredjacksonzchenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis (PTB) : CausesDokument11 SeitenPulmonary Tuberculosis (PTB) : CausesFrancis Xavier S. MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid-19 Infection in Pregnancy: Dr. Asmita Pantha 3 Year Resident Department of OBGYN KusmsDokument61 SeitenCovid-19 Infection in Pregnancy: Dr. Asmita Pantha 3 Year Resident Department of OBGYN Kusmsshrinkhala bhattaraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- COVID-19 Guidelines For Renal Dialysis: 10 February 2022Dokument19 SeitenCOVID-19 Guidelines For Renal Dialysis: 10 February 2022zulfiqarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adult Outpatient Treatment Recommendations - Antibiotic Use - CDCDokument4 SeitenAdult Outpatient Treatment Recommendations - Antibiotic Use - CDCEdward LaurentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumonia: Anas Bahnassi PHDDokument26 SeitenPneumonia: Anas Bahnassi PHDyasmine abdelkarimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.CD Control Program: RD RDDokument18 Seiten1.CD Control Program: RD RDKen Mark CatubigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screenshot 2020-03-20 at 08.25.44 PDFDokument10 SeitenScreenshot 2020-03-20 at 08.25.44 PDFMiguel Angel Palacios FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Factor PneumoniaDokument6 SeitenRisk Factor Pneumoniaali subchanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultra Low Dose Rituximab in Refractory Pemphigus VulgarisDokument19 SeitenUltra Low Dose Rituximab in Refractory Pemphigus VulgarisSamhitha Reddy AkepatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Treat CovidDokument2 SeitenHow To Treat Covidwahida amalia100% (1)
- Janssen COVID-19 Vaccine (Johnson & Johnson) : Vaccine Preparation and Administration SummaryDokument3 SeitenJanssen COVID-19 Vaccine (Johnson & Johnson) : Vaccine Preparation and Administration SummaryJohn Alex SelorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDT007Dokument110 SeitenEDT007mahchusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recent TB Treatment GuidelinesDokument28 SeitenRecent TB Treatment GuidelinesDr venkatesh jalluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Surgical Care For House OfficersDokument22 SeitenHandbook of Surgical Care For House OfficersDeep SleepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Surgical Care For House OfficersDokument20 SeitenHandbook of Surgical Care For House OfficersCharity AtsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHC Intra Abdominal GuidelinesDokument13 SeitenSHC Intra Abdominal GuidelinesNguyễn Mạnh CườngNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Protocol of Infection Control For Mechanical Thrombectomy in Possible COVID-19 Patients: Tokai University COVID-19 ManualDokument5 SeitenA Protocol of Infection Control For Mechanical Thrombectomy in Possible COVID-19 Patients: Tokai University COVID-19 ManualMartha OktaviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antimicrobial Therapy and Its Modification After Diagnostic Test InterpretationDokument29 SeitenAntimicrobial Therapy and Its Modification After Diagnostic Test Interpretationeka kemala sariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tamil Nadu Treatment Guidelines PDFDokument8 SeitenTamil Nadu Treatment Guidelines PDFsekarchand33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inflammation ReviewerDokument17 SeitenInflammation ReviewerAinee MeuvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Print 2Dokument7 SeitenPrint 2ridawahyuni09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Monkeypox Protocol - V1.0 (2047833421)Dokument5 SeitenMonkeypox Protocol - V1.0 (2047833421)Syed AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Good Health in the Tropics: Advice to Travellers and SettlersVon EverandGood Health in the Tropics: Advice to Travellers and SettlersNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!Von EverandNCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- COVID-19 Mortality Review in Malaysia & Updates on Clinical Management of COVID-19Von EverandCOVID-19 Mortality Review in Malaysia & Updates on Clinical Management of COVID-19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Naberhuis 2017Dokument8 SeitenNaberhuis 2017CristianAltunaSotomayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correia M 2018Dokument11 SeitenCorreia M 2018CristianAltunaSotomayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sulo S Et Al. Hospital Nutrition Care Informs Potential Cost-Savings For HealthcareDokument6 SeitenSulo S Et Al. Hospital Nutrition Care Informs Potential Cost-Savings For HealthcareCristianAltunaSotomayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8JULIO COVID19 Sanford GuideDokument7 Seiten8JULIO COVID19 Sanford GuideCristianAltunaSotomayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ehaa575 PDFDokument79 SeitenEhaa575 PDFPatricia MarceloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corazón DerechoDokument326 SeitenCorazón DerechoCristianAltunaSotomayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sharad Coaching: Sense Organs 1 Marks QuestionsDokument8 SeitenSharad Coaching: Sense Organs 1 Marks QuestionsArnav AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDI 5000 Transducer ListingDokument6 SeitenHDI 5000 Transducer ListingjackxrdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Appraisal QuestionnaireDokument5 SeitenHealth Appraisal QuestionnaireSteveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebral Palsy Practice Essentials: Signs and SymptomsDokument11 SeitenCerebral Palsy Practice Essentials: Signs and SymptomsTahsinur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MICROBIO 1.5 PATHOGENESIS OF BACTERIAL INFECTION (Dr. Lim)Dokument3 SeitenMICROBIO 1.5 PATHOGENESIS OF BACTERIAL INFECTION (Dr. Lim)Patricia Elena ManaliliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Establishing The Mechanism of Supraventricular Tachycardia in The Electrophysiology LaboratoryDokument15 SeitenEstablishing The Mechanism of Supraventricular Tachycardia in The Electrophysiology LaboratorySamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Amenorrhea Is Failure of Menses To Occur by One of The FollowingDokument13 SeitenPrimary Amenorrhea Is Failure of Menses To Occur by One of The FollowingMuhammad Ilyas AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing in Sindroame CoronarieneDokument11 SeitenNursing in Sindroame CoronarieneAdriana StanciuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Virology NotesDokument13 SeitenIntro To Virology NotesSpongebob Squarepants100% (1)
- Troxipide vs. Rabeprazole in The Treatment of GastritisDokument8 SeitenTroxipide vs. Rabeprazole in The Treatment of GastritisZuventusHealthcareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treatment (PDQ®) - National Cancer InstituteDokument135 SeitenChildhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treatment (PDQ®) - National Cancer Institutealejandro1122100% (1)
- Classification of Endometriosis: Birmingham, AlabamaDokument2 SeitenClassification of Endometriosis: Birmingham, AlabamaAsela SubhasingheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crossword Puzzle of Systems in Human BodyDokument13 SeitenCrossword Puzzle of Systems in Human BodyAgra Haydar AllamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sar CodesDokument6 SeitenSar CodesnitkolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kode Icd XDokument8 SeitenKode Icd Xraniasyahcandra67% (6)
- ENT MCQ (Not Answered)Dokument75 SeitenENT MCQ (Not Answered)mohamed mowafeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EndometriumDokument15 SeitenEndometriumfadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Hep BDokument4 SeitenDrug Study Hep BSawada TsunayoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dialog AnamnesisDokument2 SeitenDialog AnamnesisMona Ahmd100% (1)
- Tooth Whitening What We KnowDokument12 SeitenTooth Whitening What We KnowTerrence ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robbins Pathology - Chapter 3 TransDokument18 SeitenRobbins Pathology - Chapter 3 Transnath nath100% (7)
- Glycofilm - Solabia USA - 2011Dokument7 SeitenGlycofilm - Solabia USA - 2011Danielle BarkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Infectious DiseasesDokument6 SeitenPediatric Infectious DiseasesZllison Mae Teodoro MangabatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of The Childbearing WomanDokument122 SeitenAssessment of The Childbearing WomanLaurisse April Necesito100% (1)
- Hormone Therapy and Castration Resistance of Prostate CancerDokument420 SeitenHormone Therapy and Castration Resistance of Prostate CancerDiego RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolasi, Identifikasi Dan Uji Sensitivitas Antibiotik Terhadap Pasteurella Multocida Asal Sapi Yang Dipotong Di Rumah Pemotongan Hewan Oeba KupangDokument9 SeitenIsolasi, Identifikasi Dan Uji Sensitivitas Antibiotik Terhadap Pasteurella Multocida Asal Sapi Yang Dipotong Di Rumah Pemotongan Hewan Oeba KupangSekar ArumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 78-Article Text-145-1-10-20191205Dokument7 Seiten78-Article Text-145-1-10-20191205nisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipid Profile TestDokument2 SeitenLipid Profile TestPrateek KanadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mephentermine Abuse For Stamina, Resulting in Mania - A Case ReportDokument4 SeitenMephentermine Abuse For Stamina, Resulting in Mania - A Case Reportgaurav sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bronchial Asthma: Harun ElçiçekDokument54 SeitenBronchial Asthma: Harun ElçiçekFiras Ali100% (2)