Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Philippine Literature Pre-Limenaries MT 2A
Hochgeladen von
Jerica Mae GabitoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Philippine Literature Pre-Limenaries MT 2A
Hochgeladen von
Jerica Mae GabitoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PHILIPPINE LITERATURE PRE-LIMENARIES MT 2A
INTRODUCTION TO LITERATURE d. Magazine
What is Philippine Literature o collection of articles regarding the
lifestyle of man
Literature
e. Oration
Comes from litera (Latin) which means o a formal treatment of a subject and
letters is intended to be spoken in public
Anything that gives you information f. Anecdote
Oral o a brief story, revealing account of
Oldest type of literature an individual person or an incident
What are the Types and Forms? 2. Poetry: based on the interplay of words
and rhythm. It often employs rhyme and
Types of Literature:
meter (a set of rules governing the number
1. Written and arrangement of syllables in each line)
2. Oral
Narrative
3. Visual - symbols
a. Epic
Forms of Literature:
o a narrative poem about
1. Prose: so-called "ordinary writing" — made supernatural powers possessed by
up of sentences and paragraphs, without heroes and heroines
any metrical (or rhyming) structure. o should be written in verse
Fiction - literature created from the b. Ballad
imagination, not presented as fact, though it may o a poem with harmony and rhythm,
be based on a true story or situation usually referred to as a song
a. Myth accompanying a dance
o story about gods and goddesses c. Metrical tale
b. Legend o is written in verse and can be
o story about the origin of a place or classified either a ballad or metrical
a thing romance
c. Novel o deals with the emotions or phase
o a long narrative divided into several of life and the story is told in a
chapters and usually taken from simple, straightforward and
true-to-life events realistic manner
d. Short story Lyric
o an organized plot usually with a a. Awit or Song
single impression o A lyric poem with 12 syllables, with
e. Fable melodious harmony and rhythm of
o story that uses animals as a guitar or banduria
characters and with moral lesson b. Sonnet
f. Parable o A poem consisting of 14 iambic
o story used by Jesus in teaching the pentameter lines
Good News c. Ode
g. Plays o A lyrical poem praising or glorifying
o presented on stage, divided into an event or individual, describing
acts and each act has many scenes nature intellectually as well as
o One-act play emotionally
Non-Fiction - literature based in fact d. Elegy
a. Essays o a lament for the dead
o expresses a viewpoint or opinion of e. Psalms (Dalit)
a writer about a particular problem o A song praising God or the Virgin
or event Mary and containing a Philosophy
b. Biography of life
o life story of a person written by f. Folksongs (Awiting Bayan)
another person o Short poems intended to be sung
c. News with common themes: love,
o collection of articles about various despair, grief, doubt, joy, hope and
current events sorrow
g. Corridos (Kuridos)
PHILIPPINE LITERATURE PRE-LIMENARIES MT 2A
o Have measured of eight syllables o developing and with many sided
and usually recited t a martial beat personalities that change, for
Drama – there is a heavy plot better or worse, by the end of the
story (gru from despicalble me)
a. Comedy
Static – stereotype, have one or two
o a theatrical play with a happy
characteristics that never change and are
ending
emphasized (cersie by game of thrones)
b. Tragedy
o involves a hero struggling mightily The Plot
against dynamic forces involves How the author arranges events to
death or ruin without success or develop his basic idea
satisfaction It is the sequence of events in a story or
c. Melodrama play
o usually used in musical plays with The plot is planned, logical series of events
the opera having a beginning, middle and end
d. Farce Short story usually has one plot so it can be
o is an exaggerated comedy read in one sitting
e. Social Poems a. Introduction/Exposition
o either purely comic or tragic and The beginning of the story where the
pictures the life of today characters and the setting is revealed
Elements of a Story b. Rising action
Characters This is where the events in the story
there are two meanings for the word character become complicated and the conflict in the
the person in a work of fiction story is revealed
o Protagonist – a character clearly events between the introductions and
central of the story with all major climax
events having some importance to c. Climax
him/her This is the highest point of interest and the
o Antagonist – the opposite of the turning point of the story
main character The reader wonders what will happen next:
o Confidante – the sidekick of either the conflict will be resolved or not?
the protagonist and antagonist A three-fold phenomenon:
o Foil - someone whose personality 1. The main character receives an
and values fundamentally clash information
with the protagonist’s (culprit of 2. Accepts this information (realizes it bur
the problem) does not necessarily agree with it)
o Background – they are not given 3. Acts on this information (makes a
lines but they are present in the choice that will determine whether or
scene not he/she gains his objective)
The characteristics of a person
d. Falling action
Characterization
The events and complications begin to
information that the author gives the resolve themselves
reader about the characters themselves. The reader knows what has happened next
He may reveal a character in several ways: and if the conflict was resolved or not
o His/her physical appearance Events between climax and denouement
o What he/says, thinks, feels and
e. Denouement - (resolution, end of the
dreams
problem)
o What he /she does or does not do
o What others say about him/her and This is the final outcome or untangling of
how others react to him/ her events in the story
Characters are convincing if they are consistent, Story endings
motivated and life-like a. Open Ending – the reader is given
individual the freedom to end the story
o round, many sided and complex b. Happy Ending –
personalities (batman) c. Tragic Ending – doesn’t necessary
Dynamic mean that the character dies
literally
PHILIPPINE LITERATURE PRE-LIMENARIES MT 2A
d. Fairy Ending – “and they live Can be identified when the story is done
happily ever after” a) Guilt and innocence
e. Surprise Ending b) Courage and fear
Setting c) Conflict
d) Alienation
a. Time - time of the day, year or elapsed time
e) Romance
b. Atmosphere - mood, climate, environment
c. Place
i. Locale - broad categories (country,
state, region, city and town, as well
as to more specific locales such as a
neighborhood, street, house or
school
ii. geography
iii. man-made geography
Point of View
a. Innocent eye - child
b. Stream of consciousness – thoughts of
character
c. First person - pronoun
d. Third person omniscient – limited/
omniscient (following the character)
Omniscient Limited
o The author tells the story in third
person.
o We know only what the character
knows and what the author allows
him/her to tells us.
o We can see the thoughts and
feelings od characters if the author
chooses to reveal them to us
Omniscient Objective
o The author tells the story in third
person.
o It appears as though a camera is
following the characters going
anywhere, and recording only what
is seen and heard there is no
comment on the characters or their
thoughts.
o No interpretations are offered.
o The reader is placed in the position
of spectator without the author
there to explain.
o The reader has to interpret events
on his own
Conflict
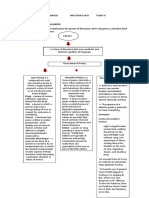
a) Man vs. Man (External)
b) Man vs. Nature (External)
c) Man vs. Supernatural (External)
d) Man vs. Society (External)
e) Man vs. Self (Internal)
Themes
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- GEC13Dokument2 SeitenGEC13bench karl bautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2: General Types and Forms of Literature: A. Prose Fiction B. Poetry C. Drama D. Nonfiction ProseDokument4 SeitenLesson 2: General Types and Forms of Literature: A. Prose Fiction B. Poetry C. Drama D. Nonfiction ProseMelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 2 Handout For 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDokument5 SeitenWeek 1 2 Handout For 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldShyna SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Types of Literature: 1. ProseDokument6 Seiten2 Types of Literature: 1. ProseChard ApdujanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReviewerDokument4 SeitenReviewerJoshua TorrecampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of LiteratureDokument1 SeiteClassification of LiteratureKhirtz Angel AlcantaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21st Reviewer Japanese To AmericanDokument5 Seiten21st Reviewer Japanese To Americanleanielpayos911Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lit ReviewerDokument13 SeitenLit ReviewernellielumanglasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21ST L4 Types of PoetryDokument1 Seite21ST L4 Types of PoetryDenise Nicole T. LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIT101Dokument20 SeitenLIT101luxasuhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Literature: Ricardo Conag Mikee Sanchez Kyle Bañados Lorimel GellicaDokument11 SeitenIntroduction To Literature: Ricardo Conag Mikee Sanchez Kyle Bañados Lorimel GellicaMikee SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prose Poetry Hand OutDokument2 SeitenProse Poetry Hand OutIyah Xyza VenturaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Daily Bread - LiteratureDokument3 SeitenOur Daily Bread - LiteratureRemigio ArguillesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lit ReviewerDokument11 SeitenLit Reviewerljarcangel0324Noch keine Bewertungen
- NON-FICTION - A Prose Writing That: Prose Is Derived From The Latin Prosa Which LiterallyDokument4 SeitenNON-FICTION - A Prose Writing That: Prose Is Derived From The Latin Prosa Which LiterallyJomir Kimberly DomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- C GELIT02 PrelimsDokument9 SeitenC GELIT02 PrelimsKarl LintanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PoetryDokument3 SeitenPoetryBenjamin Maenard R. FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PoetryDokument3 SeitenPoetryf.evilla106Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prose and PoetryDokument30 SeitenProse and Poetrynvze9990% (1)
- 21 StrevDokument8 Seiten21 StrevJohn Carl SalavarriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English 400 WorksheetDokument4 SeitenEnglish 400 WorksheetBaby Mae Bonghanoy MaribaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21st Literature ReviewerDokument5 Seiten21st Literature Reviewer12humssmichael.alfaro.kristineNoch keine Bewertungen
- LITDokument4 SeitenLITMarivica DagunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generaltypes of LiteratureDokument4 SeitenGeneraltypes of LiteratureJohanna CadeteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Day 1 ReviewersDokument12 Seiten1st Day 1 Reviewerschristian austriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Literature 101Dokument8 SeitenPhilippine Literature 101MarkAlcazar100% (1)
- Florante at Laura Ibong AdarnaDokument9 SeitenFlorante at Laura Ibong AdarnaKristin Joy AbalosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 Material Reading and Writing Unit 1 Introduction To Reading, Writing, and Thinking Strategies Lesson 1Dokument3 SeitenWeek 1 Material Reading and Writing Unit 1 Introduction To Reading, Writing, and Thinking Strategies Lesson 1Bea FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 LectureDokument2 SeitenWeek 2 LectureThiel Aeden GloriosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LiteratureDokument72 SeitenLiteratureRhain CongayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Because, It Has The Magical Ability To Pull Us inDokument4 SeitenBecause, It Has The Magical Ability To Pull Us inJebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To LiteratureDokument25 SeitenIntroduction To LiteratureAyeisha ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21clpw ReviewerDokument8 Seiten21clpw ReviewerpatNoch keine Bewertungen
- CREATIVE WRITING Types PF ProseDokument3 SeitenCREATIVE WRITING Types PF ProseJeff CahulaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phil Lit - Introduction IIDokument3 SeitenPhil Lit - Introduction IIJessica AbuqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Monochromatic Simple The Minimalist Presentation TemplateDokument21 SeitenGreen Monochromatic Simple The Minimalist Presentation TemplateTimmmyyy 27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Literature (From Latin Litterae (Plural) Letter) Is The Art of Written Work, and Is Not Confined To PublishedDokument4 SeitenLiterature (From Latin Litterae (Plural) Letter) Is The Art of Written Work, and Is Not Confined To PublishedLaica RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Damasco Michelle Ann LIT 2 MID YEAR CLASS Activity 1Dokument4 SeitenDamasco Michelle Ann LIT 2 MID YEAR CLASS Activity 1Mimi DamascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handoutcreative WritingDokument3 SeitenHandoutcreative WritingSteffanie OlivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature (From Latin Litterae (Plural) Letter) Is The Art of Written Work, and Is Not Confined ToDokument4 SeitenLiterature (From Latin Litterae (Plural) Letter) Is The Art of Written Work, and Is Not Confined ToDanstan Ferrolino Genova II100% (1)
- Divisions of LiteratureDokument3 SeitenDivisions of LiteratureJullianne Micaell CarlayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phillit 2Dokument79 SeitenPhillit 2Gelo BertulfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1.2 Literary Genres: Genres of Poetry: Arellano UniversityDokument22 SeitenLesson 1.2 Literary Genres: Genres of Poetry: Arellano UniversityHUMSS 23 - Yñigo James D. AñabezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification and Definition of Literary TypesDokument47 SeitenClassification and Definition of Literary TypesWarren Valiente100% (1)
- Literary GenresDokument5 SeitenLiterary GenresJoshrael SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- World Literature: Anna Marie M. Alonzo, Maied InstructorDokument32 SeitenWorld Literature: Anna Marie M. Alonzo, Maied InstructorSUPPLYOFFICE EVSUBCNoch keine Bewertungen
- POETRY MODULE 9 (Ans)Dokument14 SeitenPOETRY MODULE 9 (Ans)PUTIAN, REYNA MARIE ANTONETTE S.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Literature: Literary StandardsDokument4 SeitenLiterature: Literary StandardsLhea IldefonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Literature StudentsDokument18 SeitenIntroduction To Literature StudentsKAYERAVEN MORANTENoch keine Bewertungen
- LIKEDokument7 SeitenLIKEGlen LubricoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of LiteratureDokument2 SeitenTypes of LiteraturemariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson No. 3: Text Types and StructuresDokument51 SeitenLesson No. 3: Text Types and StructuresshinNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Reviewer: Grade 8 1 Quarter ExaminationDokument4 SeitenEnglish Reviewer: Grade 8 1 Quarter ExaminationLester Marquin MattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Its Divisions and Other ConcernsDokument7 SeitenLiterature Its Divisions and Other Concernswonieshi lomlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literary GenresDokument4 SeitenLiterary GenresEugene Salazar100% (1)
- Module 4 Classification and Types of LiteratureDokument5 SeitenModule 4 Classification and Types of LiteratureSter CustodioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wesleyan: Module 1: Review Introduction To Literature Week 1 & 2 I. Learning OutcomesDokument11 SeitenWesleyan: Module 1: Review Introduction To Literature Week 1 & 2 I. Learning OutcomesPokpak LimarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edelt 104 Lesson 1 4 CompilationDokument14 SeitenEdelt 104 Lesson 1 4 CompilationRhea BermejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIT Division of Literature and Literary ApproachesDokument3 SeitenLIT Division of Literature and Literary ApproachesMari LeianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me - As The Object Can Also Refer To Measuring A Single Ability, Attribute, Construct, or SkillDokument7 SeitenMe - As The Object Can Also Refer To Measuring A Single Ability, Attribute, Construct, or SkillJerica Mae GabitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life and Works of RizalDokument4 SeitenLife and Works of RizalJerica Mae GabitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Chemistry Lecture Pre-Limenaries MT 2ADokument10 SeitenAnalytical Chemistry Lecture Pre-Limenaries MT 2AJerica Mae GabitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Globalization: The Contemporary World Preliminaries Page - 1Dokument6 SeitenGlobalization: The Contemporary World Preliminaries Page - 1Jerica Mae GabitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMLS Reviewer For Midterms PDFDokument14 SeitenPMLS Reviewer For Midterms PDFJerica Mae GabitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMLS Reviewer For Midterms PDFDokument14 SeitenPMLS Reviewer For Midterms PDFJerica Mae GabitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TFG Gaso NuriaDokument58 SeitenTFG Gaso NuriaSinae DaseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Epic and Mock EpicDokument3 SeitenDifference Between Epic and Mock EpicGeetanjali Joshi75% (4)
- KrumbacherDokument82 SeitenKrumbacherbiemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Night SweatsDokument2 SeitenNight SweatsLeonard KithaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionsDokument78 SeitenContemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionsRheena-Ann DupaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emily DickinsonDokument166 SeitenEmily DickinsonJeremyCohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Early Purges WorksheetDokument9 SeitenThe Early Purges Worksheetjohnmelhughes596150% (2)
- The Evolution of Poetry (Assignment and Rubric)Dokument2 SeitenThe Evolution of Poetry (Assignment and Rubric)Anonymous oichxpcbNoch keine Bewertungen
- GreekLyricPoetry 10107921 PDFDokument505 SeitenGreekLyricPoetry 10107921 PDFDenis DiaconuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 - Egyptian Love PoemsDokument9 SeitenWeek 2 - Egyptian Love PoemsthuybonginNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 4Dokument32 SeitenYear 4Dian Nurmala WulansariNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK3ENG10Dokument5 SeitenWEEK3ENG10JC ManioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20Dokument10 Seiten20Alka KujurNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Does Owen Portray The Impact of War in 'Anthem For Doomed Youth'Dokument3 SeitenHow Does Owen Portray The Impact of War in 'Anthem For Doomed Youth'kaitlnwalllaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT English Year 4Dokument26 SeitenRPT English Year 4skppasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mockboard ReviewerDokument74 SeitenMockboard ReviewerJoerico Enriquez100% (1)
- Croosing The BarDokument2 SeitenCroosing The BarnikkilyceeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peso Ancestral ResumenDokument7 SeitenPeso Ancestral Resumenafdmjphtj100% (1)
- The Ant and The CricketDokument10 SeitenThe Ant and The CricketDiya LokeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- LITERATURE CLASS - Sonnet Composed Upon Westminster BridgeDokument6 SeitenLITERATURE CLASS - Sonnet Composed Upon Westminster Bridgedale2741830Noch keine Bewertungen
- EFL Journal (10.2) 6.00 PM PDFDokument134 SeitenEFL Journal (10.2) 6.00 PM PDFCeline Jibu MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sonnet 116 & Sonnet 29: By: William ShakespeareDokument24 SeitenSonnet 116 & Sonnet 29: By: William ShakespeareMicah ElaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christine Reynier-Virginia Woolf's Ethics of The Short Story (2009) .29-46Dokument18 SeitenChristine Reynier-Virginia Woolf's Ethics of The Short Story (2009) .29-46Zorana SimićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beowulf NotesDokument5 SeitenBeowulf NotesEduardo La RosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appropriate PedagogyDokument14 SeitenAppropriate PedagogyBelenVetteseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linguistic Deviation in Literary Style: A Stylistic AnalysisDokument10 SeitenLinguistic Deviation in Literary Style: A Stylistic AnalysisInzan NarifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yeats SymbolismDokument32 SeitenYeats SymbolismJoão Luís GuimarãesNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Speech: Milton's Grand StyleDokument3 SeitenFirst Speech: Milton's Grand StyleWahab speaksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sonnet 116Dokument3 SeitenSonnet 116Daniel UsadelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Core: Language Arts Standards, Grade 2Dokument4 SeitenCommon Core: Language Arts Standards, Grade 2api-335623629Noch keine Bewertungen