Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
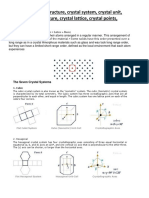
Types of Crystal Forms
Hochgeladen von
Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Types of Crystal Forms
Hochgeladen von
Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Types of Crystal Forms
Closed & Open Crystal Forms
Any grouping of crystal faces or facets that are arranged in the same symmetry is referred
to as a crystal's "form." There are approximately 48 unique crystal forms which are divided
into either "open," "closed Isometric," or "closed non-Isometric" form categories.
There are thirty closed Isometric, or closed non-Isometric forms, and eighteen open crystal
forms. Closed crystal forms are those groupings of facets that are related by symmetry,
and completely enclosing a volume of space.
Open Forms
The eighteen open-forms are those facet groupings that are related by symmetry, but do
not completely enclose a volume of space. A crystal with open-form faces also requires
some additional closed-form facets to complete a structure. Open-forms include:
• Pedion
• Pinacoid
• Dome
• Sphenoid
• Pyramid
• Prism
A Pedion is a flat face that is not parallel, or geometrically linked to any other faces. A
Pinacoid is composed of only two parallel faces, forming tabular crystals such as ruby. A
Dome is found in monoclinic and orthorhombic minerals.
Two intersecting faces that are caused by mirroring (topaz) commonly forms domes.
Sphenoids are found in monoclinic and orthorhombic minerals, and have two-fold
rotational axes. A Pyramid's multiple facets converge on a single crystallographic axis, and
pyramid forms are not possible on minerals from the isometric, monoclinic or triclinic
systems.
Open Hexagonal & Triangular Prisms
Prisms have a set of facets that run parallel to an axis of a crystal, yet never converge with
it. Quartz forms two sets of three sided prisms. Prisms are not possible in isometric or
triclinic minerals.
A Hexagonal (trigonal) prism is comprised of two hexagonal bases connected by a set of
six rectangular faces that run parallel to, and never converge with an axes in the crystal.
A triangular (trigonal) prism is comprised of two triangular bases connected by a set of
three rectangular faces that run parallel to, and never converge with an axes in the
crystal. This form is similar to a light-refracting 60º prism.
Closed Isometric Forms
There are several crystal forms in the cubic crystal system that are common in diamond,
garnet, spinel and other "symmetrical" gemstones. These forms include:
• Hexahedron (Pyrite)
• Octahedron (Diamond, Spinel)
• Tetrahedron (Tetrahedrite)
• Dodecahedron (Rhombic - Garnet)
• Hexoctahedron (Diamond)
A hexahedron (cube) has eight points, six faces, and twelve edges that are perpendicular
to each other, forming 90 degree angles. An octahedron has two four sided pyramids lying
base to base, and is totally symmetrical with no top, or bottom and has eight faces. A
tetrahedron has four equilateral triangular faces.
A dodecahedron has 12 faces and there are four types of dodecahedrons listed in order of
descending symmetry: 1. Symmetrical pentagonal (five edged polygons) dodecahedrons,
2. Asymmetrical (tetartoid) pentagonal dodecahedrons, 3. Delta (four edged polygons)
dodecahedrons, and 4. Rhombic dodecahedrons. A Hexoctahedron is a multi-faceted
dodecahedron with 48 triangular faces.
Closed Non-Isometric Forms
1. Hexagonal (Trigonal) Closed Forms
• Hexagonal Pyramid
• Hexagonal Bipyramid (Apatite)
• Dihexagonal bipyramid (Beryl)
• Hexagonal Trapezohedron
• Hexagonal Scalenohedron
• Tetrahexahedron
2. Tetragonal Closed Forms
• Tetragonal Disphenoid
• Tetragonal Scalenohedron
• Tetragonal Trapezohedron
• Tetragonal Trapezohedral Trisoctahedron
• Tetragonal Ditetragonal Bipyramidal (Rutile)
3. Rhombohedral Closed Forms
• Rhombohedral Trapezohedral (Quartz)
• Rhombohedral Hemimorphic (Tourmaline)
• Rhombohedral Holohedra (Calcite)
• Rhombohedral Dodecahedron (Garnet, Fluorite)
• Rhombohedral Trisoctahedron
4. Orthorhombic Closed Forms
• Rhombic Prism
• Rhombic Pyramid
• Rhombic Dipyramid
• Rhombic Hemimorphic
• Rhombic Sphenoid
• Rhombic Pyramid
5. Monoclinic Closed Forms
• Prism
• Monoclinic Clinopinacoid
6. Triclinic Closed Forms
• Prism
• Triclinic Dipyramid
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Paragenesis of OlivineDokument18 SeitenParagenesis of OlivineSyed Zaman100% (2)
- Crystallography Symmetry GuideDokument68 SeitenCrystallography Symmetry GuideMajid AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 48 Special Crystal Forms ExplainedDokument8 SeitenThe 48 Special Crystal Forms ExplainedCJPATAGANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal FormsDokument6 SeitenCrystal FormsLouise Victoria BeltranNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRYSTALLOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDEDokument24 SeitenCRYSTALLOGRAPHY STUDY GUIDEtoobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Seven Crystal SystemsDokument8 SeitenThe Seven Crystal SystemsArif Siddiquie50% (2)
- Nature's Geometry of Crystals/ Minerals, Quartz, RocksDokument24 SeitenNature's Geometry of Crystals/ Minerals, Quartz, Rocksyoungwarrior888Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Hexagonal Crystal System ExplainedDokument9 SeitenThe Hexagonal Crystal System ExplainedLaxmana GeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal SystemsDokument99 SeitenCrystal SystemsTristram KeatsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallographyand Mineralogy ShaltamiDokument106 SeitenCrystallographyand Mineralogy Shaltamiabhinandpradeep2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Crystal Forms and 32 Symmetry ClassesDokument5 SeitenIntroduction to Crystal Forms and 32 Symmetry ClassesKatrina BucudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 1 GEODokument3 SeitenHomework 1 GEOChristine Jane BarriosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallography and Mineralogy PresentationDokument106 SeitenCrystallography and Mineralogy PresentationDede TaufikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystals Systems PDFDokument56 SeitenCrystals Systems PDFAnonymous JIITRrEvoSNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeoDokument102 SeitenGeoseijuro0028Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0004Dokument11 SeitenWa0004Alusine Sheriff TommyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Square: Please Note The Differences Between The Definitions For US and UKDokument10 SeitenSquare: Please Note The Differences Between The Definitions For US and UKbobNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemgDokument2 SeitenChemgjuyjuyalcalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystalline Solid: - The Atoms in Crystalline Solid Matter Are Arranged in Regular Repeating Patterns - Eg-MetalDokument38 SeitenCrystalline Solid: - The Atoms in Crystalline Solid Matter Are Arranged in Regular Repeating Patterns - Eg-MetalKripa KattelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materi Ke 20 Jenis KristalDokument8 SeitenMateri Ke 20 Jenis KristalIzza AfkarimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallography DesignDokument45 SeitenCrystallography DesignAl JawadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2Dokument13 Seiten2rsrinivasavaradanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PolyhedronDokument15 SeitenPolyhedronIIRemmyII100% (1)
- 2023 Lect2-1 Physical Properties IDokument45 Seiten2023 Lect2-1 Physical Properties ITER ASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Temu Bual Dengan MuridDokument23 SeitenSoalan Temu Bual Dengan MuridJia Hui TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Structure and Crystal System: Source: Dave - Ucsc.edu/myrtreia/crystal - HTMLDokument10 SeitenCrystal Structure and Crystal System: Source: Dave - Ucsc.edu/myrtreia/crystal - HTMLJawehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystals 1 1Dokument22 SeitenCrystals 1 1ananavinceheroNoch keine Bewertungen
- MineralDokument85 SeitenMineralAsuncion TheaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Crystallography and Mineral Crystal SystemsDokument6 SeitenIntroduction to Crystallography and Mineral Crystal Systemsvictor mamani sencaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallography Unit 1Dokument70 SeitenCrystallography Unit 1addydavid85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Seminar Class 8Dokument14 SeitenMaths Seminar Class 8explorewithsrinikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three-Dimensional Symmetry: How Can We Put Dots On A Sphere?Dokument24 SeitenThree-Dimensional Symmetry: How Can We Put Dots On A Sphere?cikeirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Crystallography and Mineral Crystal Systems: Prof. Dr. Andrea Koschinsky Geosciences and AstrophysicsDokument28 SeitenIntroduction To Crystallography and Mineral Crystal Systems: Prof. Dr. Andrea Koschinsky Geosciences and AstrophysicsAhmad Maroof100% (1)
- Archemidian SolidsDokument22 SeitenArchemidian Solidspositron999100% (1)
- ShapesDokument11 SeitenShapesanissafeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument5 SeitenAssignmentXarOonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Crystal FormsDokument30 Seiten5 Crystal FormsGustavo AraújoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Systems GuideDokument9 SeitenCrystal Systems GuideAkhil Sai Krishna0% (1)
- Tessellation Shapes Fill PlaneDokument24 SeitenTessellation Shapes Fill PlaneShazwani AzizulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assigment Geometry Mte3103Dokument10 SeitenAssigment Geometry Mte3103asmidanoordinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MineralogyDokument15 SeitenMineralogyJESSA MAE PERUCHONoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Structure and Crystal SystemDokument15 SeitenCrystal Structure and Crystal SystemA common people Residence of JadavpurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal SystemDokument17 SeitenCrystal SystemRathnavel Ponnuswami100% (1)
- Seven Crystal SystemDokument15 SeitenSeven Crystal SystemJakeReynaldo29Noch keine Bewertungen
- All About CrystaDokument7 SeitenAll About CrystaGALVEZ, JOHN LEENARD T.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallography PDFDokument22 SeitenCrystallography PDFUsama IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- CrystallographyDokument25 SeitenCrystallographyAkhil Sai KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal - 1Dokument60 SeitenCrystal - 1Shivam SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology: - What Is A Mineral? - What Is A Gem? - What Is A Rock? - How Are These Formed?Dokument26 SeitenGeology: - What Is A Mineral? - What Is A Gem? - What Is A Rock? - How Are These Formed?OcZzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Forms and Systems GuideDokument3 SeitenCrystal Forms and Systems Guidekitkat retuerneNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURES GUIDEDokument22 SeitenCRYSTAL STRUCTURES GUIDE4e3w21qw33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Form, Zones, Crystal Habit: This Page Last Updated On 08-Sep-2008Dokument14 SeitenCrystal Form, Zones, Crystal Habit: This Page Last Updated On 08-Sep-2008api-19643403Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Geology & GeomorphologyDokument132 SeitenEngineering Geology & Geomorphologyhh ffhhNoch keine Bewertungen
- WK 14Dokument20 SeitenWK 14mariusreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Mineralogy and CrystallographyDokument64 SeitenPrinciples of Mineralogy and CrystallographyCamille RaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- GS1126 - 2 SKS Teori: Semester 1, 2014-2015Dokument24 SeitenGS1126 - 2 SKS Teori: Semester 1, 2014-2015Yudit SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Types of Crystal StructureDokument3 Seiten7 Types of Crystal StructureJR Deviente50% (4)
- Crystallography: The Study of Minerals and Rock Forming ElementsDokument104 SeitenCrystallography: The Study of Minerals and Rock Forming ElementsJason Doctolero Holgado100% (1)
- 5 CrystallographyDokument32 Seiten5 CrystallographyPrabhav DeujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beginning Optical Mineralogy Notes For Lab SectionDokument16 SeitenBeginning Optical Mineralogy Notes For Lab SectionVanessa Carolina100% (2)
- Gloria Light by Light 14Dokument1 SeiteGloria Light by Light 14Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Responsorial Psalm p1Dokument1 SeiteResponsorial Psalm p1Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psalm 118Dokument1 SeitePsalm 118Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lord of Salvation Part 2Dokument1 SeiteThe Lord of Salvation Part 2Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lord of Salvation Part 5Dokument1 SeiteThe Lord of Salvation Part 5Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lord, Have Mercy (Kyrie, Eleison) 1Dokument1 SeiteLord, Have Mercy (Kyrie, Eleison) 1Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gloria Light by Light 13Dokument1 SeiteGloria Light by Light 13Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lord of Salvation Part 4Dokument1 SeiteThe Lord of Salvation Part 4Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Watermark DraftDokument3 SeitenWatermark DraftFelichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance 32Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance 32Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Great Is Our God 1 PDFDokument1 SeiteGreat Is Our God 1 PDFFelichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance 31Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance 31Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Code On Sanitation of The PhilippinesDokument1 SeiteThe Code On Sanitation of The PhilippinesFelichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lord of Salvation Part 3Dokument1 SeiteThe Lord of Salvation Part 3Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christmas Caroling RequestDokument1 SeiteChristmas Caroling RequestFelichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance 29Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance 29Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance - 22Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance - 22Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance - 20Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance - 20Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance-28 PDFDokument1 SeiteMy Romance-28 PDFFelichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance 28Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance 28Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christmas Party 2016Dokument1 SeiteChristmas Party 2016Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance - 26Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance - 26Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance - 25Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance - 25Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance-28 PDFDokument1 SeiteMy Romance-28 PDFFelichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance - 27Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance - 27Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance - 23Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance - 23Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance - 19Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance - 19Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance - 17Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance - 17Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance - 24Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance - 24Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Romance - 21Dokument1 SeiteMy Romance - 21Felichi Dacumos BalajadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Pathophysiology of Hypoxemia and HypoxiaDokument15 SeitenOverview of Pathophysiology of Hypoxemia and HypoxiaMARY ANN CAGATANNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 F.Y.B.Sc - Chemistry PDFDokument22 Seiten11 F.Y.B.Sc - Chemistry PDFmalini PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- NQ-NQM Panelboards and Qonq Load Centers Information Manual 80043-712-06 Rev.02 06-2015 2 PiezasDokument144 SeitenNQ-NQM Panelboards and Qonq Load Centers Information Manual 80043-712-06 Rev.02 06-2015 2 PiezasNadia EspinozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outline 1. Background of Revision: JEITA CP-1104BDokument4 SeitenOutline 1. Background of Revision: JEITA CP-1104BkksdnjdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delay-Tolerant NetworksDokument66 SeitenDelay-Tolerant NetworksMegi YantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S2210803316300781 MainDokument8 Seiten1 s2.0 S2210803316300781 MainGilang Aji P. EmonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classified Advertisements from Gulf Times NewspaperDokument6 SeitenClassified Advertisements from Gulf Times NewspaperAli Naveed FarookiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDI-500 Specialized Crime Investigation and Legal MedicineDokument20 SeitenCDI-500 Specialized Crime Investigation and Legal MedicineCherry Len FaroniloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbine Stress EvaluatorDokument14 SeitenTurbine Stress EvaluatorsumitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiger 690 Conversion PDFDokument8 SeitenTiger 690 Conversion PDFGerardo Esteban Lagos RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fe in Black TeaDokument6 SeitenFe in Black TeaHerni Nur AeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabi - EE 5004 - Power ElectronicsDokument2 SeitenSyllabi - EE 5004 - Power ElectronicsKalum ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet ID FanDokument5 SeitenData Sheet ID FanrudiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 ESC Guidelines On EndocarditisDokument45 Seiten2009 ESC Guidelines On EndocarditisDaondy Friarsa SoehartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment #1: 1 HgjyygbykvrfDokument1 SeiteAssignment #1: 1 HgjyygbykvrfJuan Sebastian ArangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MACRO XII Subhash Dey All Chapters PPTs (Teaching Made Easier)Dokument2.231 SeitenMACRO XII Subhash Dey All Chapters PPTs (Teaching Made Easier)Vatsal HarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Edition February 2013: Ec2 Guide For Reinforced Concrete Design For Test and Final ExaminationDokument41 Seiten3 Edition February 2013: Ec2 Guide For Reinforced Concrete Design For Test and Final ExaminationDark StingyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd - Science-Second-Quarter-Week-1Dokument37 Seiten2nd - Science-Second-Quarter-Week-1Arlene AranzasoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CORRELATION AND LINEAR REGRESSIONDokument9 SeitenCORRELATION AND LINEAR REGRESSIONSANKET GANDHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Carta Psicrometrica PDFDokument2 SeitenCarta Psicrometrica PDFJuliethNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Wanna Be Yours Arctic Monkeys Love SongDokument3 SeitenI Wanna Be Yours Arctic Monkeys Love SongAndréia E NiltonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Guide For PpeDokument45 SeitenSolution Guide For PpeTrek Apostol57% (7)
- Technical PaperDokument6 SeitenTechnical PaperSIJO MONACHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammarism Ed Ing Adjectives Test 4 1189424Dokument2 SeitenGrammarism Ed Ing Adjectives Test 4 1189424Royal Stars Drama AcademyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Biostataplus Sbi2014-EDokument4 SeitenData Biostataplus Sbi2014-ELucila Milagros PinillosNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTE56004 Thru NTE56010 TRIAC, 15 Amp: FeaturesDokument2 SeitenNTE56004 Thru NTE56010 TRIAC, 15 Amp: FeaturesFreddy SarabiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stepan Pol BC 180Dokument2 SeitenStepan Pol BC 180Parag RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer Part Exchange Program: Product InformationDokument8 SeitenCustomer Part Exchange Program: Product InformationAdrian GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To Malabsorption (SANJAY)Dokument58 SeitenApproach To Malabsorption (SANJAY)Sanjay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nokia N97 User Guide: 9221217 Issue 2.0Dokument76 SeitenNokia N97 User Guide: 9221217 Issue 2.0Boris CavarNoch keine Bewertungen