Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
USCP Lesson 4 (Anthropology, Political Science, and Sociology)
Hochgeladen von
Andrei0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
342 Ansichten2 SeitenAnthropology studies humans and human cultures through four fields: physical, cultural, biological, and linguistic anthropology. Political science focuses on power dynamics within government and society. Sociology seeks to understand social phenomena and relationships by examining impersonal social forces. Social change occurs through invention, discovery, and diffusion of new ideas and technologies. Political change includes more open and participatory government. Cultural change alters cultural traits and structures, such as the rise of transnational families and impact of technologies like Facebook.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
USCP lesson 4 (Anthropology, Political Science, and Sociology)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenAnthropology studies humans and human cultures through four fields: physical, cultural, biological, and linguistic anthropology. Political science focuses on power dynamics within government and society. Sociology seeks to understand social phenomena and relationships by examining impersonal social forces. Social change occurs through invention, discovery, and diffusion of new ideas and technologies. Political change includes more open and participatory government. Cultural change alters cultural traits and structures, such as the rise of transnational families and impact of technologies like Facebook.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
342 Ansichten2 SeitenUSCP Lesson 4 (Anthropology, Political Science, and Sociology)
Hochgeladen von
AndreiAnthropology studies humans and human cultures through four fields: physical, cultural, biological, and linguistic anthropology. Political science focuses on power dynamics within government and society. Sociology seeks to understand social phenomena and relationships by examining impersonal social forces. Social change occurs through invention, discovery, and diffusion of new ideas and technologies. Political change includes more open and participatory government. Cultural change alters cultural traits and structures, such as the rise of transnational families and impact of technologies like Facebook.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Lesson # 4
THE ESSENCE OF ANTHROPOLOGY, POLITICAL SCIENCE AND SOCIOLOGY
Anthropology is the study of human beings and their ancestors.
Importance of anthropology:
Anthropology produces knowledge about what makes people different from one another and
what they all share in common.
Four fields of anthropology:
1. Physical anthropology – focus on humans as biological organism.
2. Cultural anthropology – investigates the contrasting ways groups of humans think, feel,
and behave.
3. Biological anthropology – tries to recover information about human cultures – usually
from the past – by studying material samples, skeletal remains, and settlements.
4. Linguistic anthropology – studies the nature of languages – communication systems by
which cultures are maintained and passed on to succeeding generations.
Political Science is the body of knowledge relating to the study of the state and government. It
primarily focuses on the ‘power’ that plays a crucial part in the struggle in which the individuals
and their group may be found involved according to their capability and degree of interest at all
levels – local, regional, national and international.
Sociology is considered the science of society and social behavior, which is viewed as an
aggregate (kabuuan) of individuals.
It seeks to discover the general principles underlying (hindi agad nakikita o nakatago) all social
phenomena and social relationship and to establish laws of change and growth in social sciences.
For instance, many consider suicide as a personal thing but a sociologist looks at it differently by
examining the various impersonal social forces at work in such a destructive act.
SOCIAL, POLITICAL and CULTURAL CHANGE
Social change refers to variations (konting pagkakaiba) or modifications (pagbabago) in the
patterns of social organization, of sub-groups within a society, or of the entire society itself.
There are three causes of social change:
1. Invention
2. Discovery
3. Diffusion
1. Invention is often defined as a new combination or a new use of existing knowledge. It
produces mechanical objects, ideas, and social patterns that reshape society to varying
degrees. It can be classified into:
a. Material inventions (example: mobile phone, airplane)
b. Social inventions (example: alphabet, texting, jejemon)
2. Discovery, on the other hand, takes place when people reorganized existing elements of the
world they had not noticed before or learned to see in a new way. A discovery is also an
addition to the store of verified knowledge.
3. Diffusion refers to the spread of culture traits from one group to another. It creates changes
as cultural elements spread from one society to another through trade, migration, and mass
communication.
Political change includes all categories of change in the direction of open, participatory, and
accountable politics.
Examples:
1. Youth awareness and active participation during election process.
2. The emergence of civil society groups as “pressure groups” during crises in
Philippine politics.
Cultural change refers to all alterations affecting new traits or trait complexes, to change in a
culture’s content and structure.
Examples:
1. Transnational families – one parent, or both parents are contracted to live and work in
another country away from their love ones.
2. Facebook – this technology has radically transformed worldwide interaction.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- UCSP - 3rd and 4th Quarter ExamDokument20 SeitenUCSP - 3rd and 4th Quarter ExamDE MATA, Anneka Kristana H.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Culture, Society and Politics: Justice Emilio Angeles Gancayco Memorial High SchoolDokument3 SeitenUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics: Justice Emilio Angeles Gancayco Memorial High SchoolHarito GtjajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Are You Ready To Listen and Learn?Dokument34 SeitenAre You Ready To Listen and Learn?mariel obradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 UCSPDokument26 SeitenModule 3 UCSPRaiza CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - Emergence of The Social ScienceDokument2 SeitenModule 1 - Emergence of The Social SciencejessafesalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDokument2 SeitenUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsRichmond Jake AlmazanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics (Grade 11/12) : Let Us DiscoverDokument6 SeitenUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politics (Grade 11/12) : Let Us DiscoverJohn Asher FajardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Written Tests in UCSPDokument1 SeiteWritten Tests in UCSPRuel LlagosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Human Cultural Variations Social Differences Social Change and Political IdentitiesDokument29 SeitenLesson 1 Human Cultural Variations Social Differences Social Change and Political IdentitiesReyna RodelasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 19 Religion & Belief System AminismDokument3 SeitenTopic 19 Religion & Belief System AminismMarilyn DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDokument12 SeitenCurriculum Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsChem C. CandaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dll-Ucsp - 12 TVL-GDokument4 SeitenDll-Ucsp - 12 TVL-GMALOU ELEVERA100% (1)
- Chapter 1 (Ucsp)Dokument34 SeitenChapter 1 (Ucsp)AzeLuceroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson I - Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDokument10 SeitenLesson I - Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsBrylkit MonteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ucsp Module 2Dokument47 SeitenUcsp Module 2Khatorsxe Imba100% (2)
- Importance of Artifacts in Interpreting Social, Cultural, Political and Economic ProcessesDokument9 SeitenImportance of Artifacts in Interpreting Social, Cultural, Political and Economic ProcessesAnecita L. Calamohoy46% (13)
- Name: - Grade&Sec: Date: - Score: - I. Read The Statements Below Carefully and Encircle The Letter of Your Choice. NO ERASURESDokument5 SeitenName: - Grade&Sec: Date: - Score: - I. Read The Statements Below Carefully and Encircle The Letter of Your Choice. NO ERASURESJade Til-adanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education Bureau of Learning Delivery Teaching and Learning DivisionDokument11 SeitenDepartment of Education Bureau of Learning Delivery Teaching and Learning DivisionAira Joyce Nepomuceno CuaternoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UCSP Q1 Mod9 ConformityAndDeviance v5Dokument14 SeitenUCSP Q1 Mod9 ConformityAndDeviance v5Rey Mark Racelis MarabelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ucsp Q1 W3 PPTDokument21 SeitenUcsp Q1 W3 PPTVan Harold SampotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ucsp & PPG QuizDokument1 SeiteUcsp & PPG QuizJOEL D. BATERISNANoch keine Bewertungen
- Empirical-Analytical Approaches in The Social SciencesDokument28 SeitenEmpirical-Analytical Approaches in The Social SciencesLeejarde Jardeliza Mahanlud0% (1)
- UcspDokument23 SeitenUcspFrancis Mico AndayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Cultural VariationsDokument17 SeitenHuman Cultural VariationsKenneth SalivioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Culture Society and Politics Quarter 1: Week 1 - Module 1Dokument15 SeitenUnderstanding Culture Society and Politics Quarter 1: Week 1 - Module 1Angelica Robles AmaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior High School Department Summative Test in Understanding Culture, Society and Politics 12Dokument3 SeitenSenior High School Department Summative Test in Understanding Culture, Society and Politics 12Aurea BodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide 4 (UCSP) : Conformity and DevianceDokument12 SeitenStudy Guide 4 (UCSP) : Conformity and DevianceAl Cheeno AnonuevoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UCSP Test QuestionDokument2 SeitenUCSP Test QuestionJohn Lorenze Valenzuela0% (1)
- Pangasinan Division II Manaoag National High School - SHSDokument6 SeitenPangasinan Division II Manaoag National High School - SHSMark Anthony GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conformity and DevianceDokument10 SeitenConformity and DevianceRonalyn CajudoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 1 SLM UCSP 3Dokument46 SeitenQuarter 1 SLM UCSP 3Lorinel MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Becoming A Member of SocietyDokument31 SeitenBecoming A Member of SocietyDa Ya NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Culture, Society and Politics: Chapter 1. The Birth and Growth of The Social SciencesDokument68 SeitenUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics: Chapter 1. The Birth and Growth of The Social SciencesTishailoshaina Naje0% (1)
- Gonzales, Christopher Shane M. EAPP ASS. #3Dokument2 SeitenGonzales, Christopher Shane M. EAPP ASS. #3Christopher Shane GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Culture, Society and Politics: Performance Tasks (Fourth Quarter - Second Semester)Dokument24 SeitenUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics: Performance Tasks (Fourth Quarter - Second Semester)Jhon Keneth Namias100% (1)
- HUMSS 11-Structural FunctionalisDokument4 SeitenHUMSS 11-Structural FunctionalisRochelle Beatriz MapanaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity-Sheet-AS in UCSP 2nd Quarter Sources of Social and Cultural ChangeDokument3 SeitenActivity-Sheet-AS in UCSP 2nd Quarter Sources of Social and Cultural ChangeQuarentai Siete LptNoch keine Bewertungen
- Andrea C. Lanip, LPT Clarisa Z. Reyes, LPT Roma Jane Catillo, LPTDokument8 SeitenAndrea C. Lanip, LPT Clarisa Z. Reyes, LPT Roma Jane Catillo, LPTDaniela TulipanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philo ReviewerDokument4 SeitenPhilo Reviewermonzonjomar6Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2Q Exam - UCSPDokument5 Seiten2Q Exam - UCSPRizza Joy Sariego EsplanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UCSP Chapter 5-Lesson 1Dokument37 SeitenUCSP Chapter 5-Lesson 1Jed Farrell100% (1)
- Understanding Culture, Society & Politics: Quarter 1 - Week 1Dokument14 SeitenUnderstanding Culture, Society & Politics: Quarter 1 - Week 1Michael JunioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gender and Gender Roles: Cultural Variations and Social Differences ObjectiveDokument24 SeitenGender and Gender Roles: Cultural Variations and Social Differences ObjectiveMarvie Cayaba GumaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics / Pre-First QuarterDokument5 SeitenUnderstanding Culture, Society, and Politics / Pre-First QuarterKim Kathleen ArizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP - LESSON 2 - Historical Context of The Emergence of Disciplines in Social SciencesDokument3 SeitenDLP - LESSON 2 - Historical Context of The Emergence of Disciplines in Social SciencesFaith SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UCSP Quarter 2 Module 7: Social InequalitiesDokument15 SeitenUCSP Quarter 2 Module 7: Social InequalitiesThinthin Araque100% (2)
- Cultural Variation Ethnocentrism and Cultural RelativismDokument19 SeitenCultural Variation Ethnocentrism and Cultural RelativismPrincess Rona Alcantara0% (1)
- Concept of CultureDokument40 SeitenConcept of CultureKaren Mae SibalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explain The Context Content Processes and ConsequencesDokument23 SeitenExplain The Context Content Processes and ConsequencesYhrl Yieshua Igdalino100% (1)
- LEC 2 - (WEEK 2) Human Cultural Variation, Social Differences, and Political IdentitiesDokument36 SeitenLEC 2 - (WEEK 2) Human Cultural Variation, Social Differences, and Political IdentitiessheelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Becoming A Member of SocietyDokument5 SeitenBecoming A Member of SocietyPelayo ElyzherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Socialization and The Assertion of Agency: Session 7 - 1 Grading Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDokument13 SeitenSocialization and The Assertion of Agency: Session 7 - 1 Grading Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsmineNoch keine Bewertungen
- UCSP Lesson 1 Handout - Manifestations of Human Variations Through Cultural Diversity, Social Differences and Political IdentitiesDokument2 SeitenUCSP Lesson 1 Handout - Manifestations of Human Variations Through Cultural Diversity, Social Differences and Political IdentitiesLeah Joy Valeriano-QuiñosNoch keine Bewertungen
- A UCSP Q1M6 Teacher Copy Final LayoutDokument25 SeitenA UCSP Q1M6 Teacher Copy Final LayoutKarylle Joy DumalaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior High Schoool: Division of Zamboanga Del SurDokument2 SeitenSenior High Schoool: Division of Zamboanga Del SurNadineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 7 UCSPDokument19 SeitenModule 7 UCSPRaiza Cabrera0% (1)
- Social Organization UCSP 11Dokument4 SeitenSocial Organization UCSP 11Venus IsarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 9 The Study of Culture, Society, and PoliticsDokument3 SeitenTopic 9 The Study of Culture, Society, and PoliticsMarilyn Dizon100% (1)
- Ucsp Module 101Dokument60 SeitenUcsp Module 101Joshua CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Info-Online - Miami.edu-Fuzzy Logic Timothy J Ross Solution ManualDokument5 SeitenInfo-Online - Miami.edu-Fuzzy Logic Timothy J Ross Solution ManualAndrei0% (2)
- Government of Tamil Nadu Directorate of Technical Education: Content/uploads/2020/04/dote-E-Lecture PDFDokument1 SeiteGovernment of Tamil Nadu Directorate of Technical Education: Content/uploads/2020/04/dote-E-Lecture PDFAndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Funtional RequirementsDokument2 SeitenFuntional RequirementsAndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuzzy Logic With Engineering Applications Third Edition Solution ManualDokument3 SeitenFuzzy Logic With Engineering Applications Third Edition Solution ManualAndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
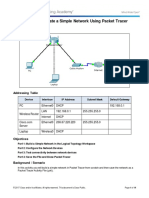
- 2.1.1.5 Packet Tracer - Create A Simple Network Using Packet TracerDokument14 Seiten2.1.1.5 Packet Tracer - Create A Simple Network Using Packet TracerNico Elicaño100% (2)
- Finally Power DiodeDokument8 SeitenFinally Power DiodeAndrei50% (2)
- Presentation 2Dokument7 SeitenPresentation 2AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR11Dokument5 SeitenPR11AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Observing Plant and Animal CellsDokument3 SeitenObserving Plant and Animal CellsAndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Forms and Changes TESTDokument9 SeitenEnergy Forms and Changes TESTAndrei100% (2)
- The Perception of THE Grade 11 Students in Joining School Organization in Notre Dame of Trece Martires City - Docx (RESEARCH)Dokument6 SeitenThe Perception of THE Grade 11 Students in Joining School Organization in Notre Dame of Trece Martires City - Docx (RESEARCH)AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gender & Development: By: Sheila Mae Rosali D.N. LavapieDokument22 SeitenGender & Development: By: Sheila Mae Rosali D.N. LavapieMichelle GensayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module in Carbohydrates PDFDokument19 SeitenModule in Carbohydrates PDFAndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gadmae 130328015140 Phpapp01Dokument68 SeitenGadmae 130328015140 Phpapp01Valladolid WCPDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthsatmosphere 130422102150 Phpapp02Dokument32 SeitenEarthsatmosphere 130422102150 Phpapp02Suresh ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- USCP Lesson 3 (Politics)Dokument2 SeitenUSCP Lesson 3 (Politics)AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- USCP Lesson 10 (Conformity and Deviance)Dokument2 SeitenUSCP Lesson 10 (Conformity and Deviance)AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- USCP Lesson 5a (Ethnocentrism and Cultural Relativism)Dokument1 SeiteUSCP Lesson 5a (Ethnocentrism and Cultural Relativism)AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- USCP Lesson 11 (Religion and Belief Systems) MyDokument5 SeitenUSCP Lesson 11 (Religion and Belief Systems) MyAndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- USCP Lesson 7 (Human Dignity)Dokument3 SeitenUSCP Lesson 7 (Human Dignity)AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- USCP Lesson 8 (Groups) StudentsDokument1 SeiteUSCP Lesson 8 (Groups) StudentsAndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- USCP Lesson 5 (Ethnocentrism and Cultural Relativism)Dokument1 SeiteUSCP Lesson 5 (Ethnocentrism and Cultural Relativism)AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Creat Gold From WaterDokument1 SeiteHow To Creat Gold From WaterAndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- USCP Lesson 3 (Politics)Dokument2 SeitenUSCP Lesson 3 (Politics)AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- USCP Lesson 2 (Society)Dokument3 SeitenUSCP Lesson 2 (Society)AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- USCP Lesson 1 (Culture)Dokument1 SeiteUSCP Lesson 1 (Culture)AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phil Pol 3 (The Concept of Power) Students'Dokument2 SeitenPhil Pol 3 (The Concept of Power) Students'AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phil Pol 4 (States, Nations, and Globalization) Students'Dokument3 SeitenPhil Pol 4 (States, Nations, and Globalization) Students'AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phil Pol 2 (Political Ideologies) Students'Dokument2 SeitenPhil Pol 2 (Political Ideologies) Students'AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Task 2Dokument4 SeitenNew Task 2api-301265993100% (1)
- Lo5. Contribute To Workplace InnovationDokument6 SeitenLo5. Contribute To Workplace Innovationrobelyn veranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Integrated English 2018-2019Dokument11 SeitenMid Integrated English 2018-2019hasna azzuhaira100% (2)
- Otl545 Module 6 CT TemplateDokument5 SeitenOtl545 Module 6 CT Templateapi-446537912Noch keine Bewertungen
- B3 G1 AimlDokument27 SeitenB3 G1 Aimldihosid99100% (1)
- Project Management Chapter 4 Pinto-1Dokument43 SeitenProject Management Chapter 4 Pinto-1Saleem-alone AbroNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Bremen-Groningen Online Workshops On Multimodality 2020 - 2021Dokument6 SeitenThe Bremen-Groningen Online Workshops On Multimodality 2020 - 2021cecirennieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kolbs CycleDokument3 SeitenKolbs CycleMarlon B. OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training and Developing Employees: Global Edition 12eDokument41 SeitenTraining and Developing Employees: Global Edition 12eĐàm Quang Thanh TúNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 3 Models of Semantic MemoryDokument7 SeitenTop 3 Models of Semantic Memoryaaminafarooq321Noch keine Bewertungen
- Book Effective Teaching and Learning English For Spesific PURPOSE - PDFDokument117 SeitenBook Effective Teaching and Learning English For Spesific PURPOSE - PDFAbdulghafur HadengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extracting Terminology With SimilisDokument6 SeitenExtracting Terminology With SimilisAdil AlharthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Literature Using Localized Instructional MaterialsDokument10 SeitenTeaching Literature Using Localized Instructional MaterialsAnde Hernandez-CalipsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identification of Noun, Adjective, Verb, Adverb 2 For PDFDokument22 SeitenIdentification of Noun, Adjective, Verb, Adverb 2 For PDFmukeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Holy Fire III Reiki: by Illiam Ee andDokument17 SeitenIntroduction To Holy Fire III Reiki: by Illiam Ee andAlberto100% (1)
- Q3 Tos English 8Dokument1 SeiteQ3 Tos English 8gayle badorayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Population Vs SampleDokument5 SeitenPopulation Vs Sampleronald bantuganNoch keine Bewertungen
- WorkSheet 1 Unit 5Dokument8 SeitenWorkSheet 1 Unit 5Omar MestraNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Language Student SBA GuideDokument34 SeitenEnglish Language Student SBA GuideAmelia PitterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planning CommentaryDokument9 SeitenPlanning Commentaryapi-443510939Noch keine Bewertungen
- "The Effect of Time Management in Reducing Stress AmongDokument7 Seiten"The Effect of Time Management in Reducing Stress AmongLyvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social AwarenessDokument11 SeitenSocial AwarenessBhumika BiyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active and Passive Voice and Exercise 1 of Language BookletDokument3 SeitenActive and Passive Voice and Exercise 1 of Language BookletEmily Wyatt-MinterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication in Social WorkDokument2 SeitenCommunication in Social WorkOly Marian100% (4)
- Unit1 Lesson 2Dokument1 SeiteUnit1 Lesson 2Raizah Salva CambarihanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teste Diagnostico de Ingles 5o AnoDokument3 SeitenTeste Diagnostico de Ingles 5o AnoCentro De Explicações CentroBookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emp Unit-1 Communication SkillsDokument14 SeitenEmp Unit-1 Communication SkillsSaraswathi GopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching On Spiritual Care. ASSETDokument7 SeitenTeaching On Spiritual Care. ASSETjanuar rizqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elijah Joseph O. Guzman: Saint Louis UniversityDokument6 SeitenElijah Joseph O. Guzman: Saint Louis UniversityzanibabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distinguishing and Classifying Individual Schizophrenic ChildDokument58 SeitenDistinguishing and Classifying Individual Schizophrenic Childbhupal reddyNoch keine Bewertungen