Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Final Exam Reviewer: Math 17
Hochgeladen von
Dondee Sibulo Alejandro0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten2 SeitenOriginaltitel
Final_Exam_Reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten2 SeitenFinal Exam Reviewer: Math 17
Hochgeladen von
Dondee Sibulo AlejandroCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Math 17
Final Exam Reviewer
Factoring Polynomials Rational exponents
If n is a positive integer greater than 1, and a is a real number, then if √
is a real number
⁄
√
⁄
√
If m and n are positive integers that are relatively prime, and a is a real
number, then if √ is a real number
⁄ ⁄ ⁄
√
⁄ ⁄ ⁄
√
If m and n are positive even integers and a is a real number, then
Absolute Value ⁄ | | ⁄
| | {
√ {
| |
| | { If m and n are positive integers that are relatively prime, and a is a real
number and , then if √ is a real number
Pythagorean Theorem ⁄
⁄
Integer Exponents Properties of Logarithmic Functions Quadratic Equation
If n and m are positive integers and iff √
a and b are real numbers, then If u and v are positive
numbers, and n is any real number, then
To complete the square of ,
Add
Nature of roots
(i) : roots are real and equal
(ii) : roots are real and unequal
(iii) : roots are imaginary and
unequal
Radicals The Principal Square Root of a Composite Function
If a and b are real numbers, Negative Number (f ᵒ g)(x) = f (g(x))
√ √ √ If p is a positive number, then the Where the domain of f ᵒ g is the set of all
√ principal square root of –p, denoted by numbers x in the domain of g such that
√ g(x) is in the domain of f .
√ √ , is defined by
Where both and if n is even √ √
Even Function. A function f is said to be
an even function if for every x in the
Inequalities Function Operations
If a, b, and c are real numbers and domain of f, .
Given the functions f and g:
(i) if and , then Odd Function. A function f is said to be
(i)
an odd function if for every x in the
(ii) if then (ii)
domain of f, .
(iii) if then (iii)
(iv) if and , then (iv) ⁄ ⁄
Extreme Values of a Quadratic
(v) if and , then
Function , where
(vi) if , In each case the domain of the resulting
| | function consists of those values of x
| | or common to the domains of f and g. In
(vii) | | | | | | case (iv), the values of x for which g(x) =
| | 0 are excluded.
| |
| |
(ix) | | | | | |
Midpoint Formula Equation of a Circle with center at
and radius r Distance between two points
|̅̅̅̅̅̅| √
Equations of a line Remainder Theorem. If P(x) is a polynomial and r is a real
number, then if P(x) is divided by x – r, the remainder is P(r).
Factor Theorem. If P(x) is a polynomial and r is a real
a = x-intercept b = y-intercept number, then P(x) has x – r as a factor if and only if P(r) = 0.
The Eight Fundamental Trigonometric Identities
2 distinct nonvertical lines l1 and l2 with slopes m1 and m2 are
Vertical-line Test. The graph of a function can be intersected
by a vertical line in at most one point.
0° 30° 45° 60° 90° 180° 270° 15° 75°
Radian Measure ⁄ ⁄ ⁄ ⁄ ⁄ ⁄ ⁄
0 ⁄ √ ⁄ √ ⁄ 1 0 √ √ ⁄ √ √ ⁄
1 √ ⁄ √ ⁄ ⁄ 0 0 √ √ ⁄ √ √ ⁄
0 √ ⁄ 1 √ 0 √ √
√ 1 √ ⁄ 0 0 √ √
1 √ ⁄ √ 2 √ √ √ √ )
2 √ √ ⁄ 1 √ √ ) √ √
Sum and Difference Identities Special Reduction Formulas If are the angles of any triangle, and
a, b, and c are, respectively, the measures of the
sides opposite these angles, then
( )
( )
( )
Double-Measure and Half-Measure Identities Product to Sum Identities
Sum to Product Identities
√ √
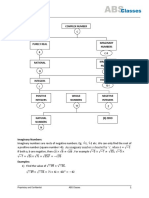
√ Absolute Value of a Complex Number
| | √
Polar Form of nth Roots of Complex Numbers
| | If z is a nonzero complex number, where and
If n is a positive integer, then z has exactly n distinct nth roots given
then by
⁄
[ ]
Where k is 0, 1, …, n – 1.
De Moivre’s Theorem
If n is any integer, then
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- @StudyTime - Channel Maths-4Dokument12 Seiten@StudyTime - Channel Maths-4Sipra PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polynomials ExplainedDokument12 SeitenPolynomials ExplainedSipra PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan IX MATHS 2020 CompressedDokument30 SeitenLesson Plan IX MATHS 2020 CompressedHimanhsu60% (5)
- Class 7 Maths Formula Chapter 9Dokument2 SeitenClass 7 Maths Formula Chapter 9KANAPATHI MURUGANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Numbers & Functions in 40 CharactersDokument8 SeitenComplex Numbers & Functions in 40 CharactersVĩnh PhongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Numbers and Euclid's Division AlgorithmDokument28 SeitenReal Numbers and Euclid's Division AlgorithmbgmiytNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Numbers Class 10 + Integrated PYQsDokument28 SeitenReal Numbers Class 10 + Integrated PYQsKhushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math ReviewDokument31 SeitenMath ReviewTrecy Jane RicabordaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Numbers and Rational Numbers FoundationDokument1 SeiteReal Numbers and Rational Numbers FoundationPrakruthi LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Converse: P Q P Q Q PDokument12 SeitenConverse: P Q P Q Q PxddddNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scan 30 Jan 2023Dokument16 SeitenScan 30 Jan 2023Sherissa HiralallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hecate SlidesCarnivalDokument14 SeitenHecate SlidesCarnivalAngelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 2Dokument4 SeitenMathematics 2redaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Number Systems: This Chapter IncludesDokument50 SeitenNumber Systems: This Chapter IncludesAtharv AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conditions That Make A Quadrilateral A ParallelogramDokument10 SeitenConditions That Make A Quadrilateral A ParallelogramJaSOn WaNiWanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Clinic Gr11 ENGDokument42 SeitenMaths Clinic Gr11 ENGPriyanka KanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Clinic Gr12 ENG SmartPrep v1.0 1 PDFDokument69 SeitenMaths Clinic Gr12 ENG SmartPrep v1.0 1 PDFNakeisha Jesse Napallatan50% (6)
- Ilovepdf - Merged 1Dokument59 SeitenIlovepdf - Merged 1satyajeetkumar7085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra Class 8 (Zambak) - Zambak Publishing PDF Fraction (Mathematics) Rational NumberDokument1 SeiteAlgebra Class 8 (Zambak) - Zambak Publishing PDF Fraction (Mathematics) Rational NumberAisha MedetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Numbers: Express Square Roots, Plot on Plane, Add & MultiplyDokument12 SeitenComplex Numbers: Express Square Roots, Plot on Plane, Add & MultiplyJea Mae G. BatiancilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- App FDokument6 SeitenApp FRamsha TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modal Verbs - FunctionsDokument4 SeitenModal Verbs - FunctionsRevalia MonicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aug 3 2015 Principal RootDokument3 SeitenAug 3 2015 Principal RootGlen Kristopher SenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bilinear Interpolation: Y) On A Rectilinear 2D GridDokument3 SeitenBilinear Interpolation: Y) On A Rectilinear 2D GridReinaldo Chohfi Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Proposition LogicDokument5 SeitenProposition LogicJoshua D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- QA - Classification of NumbersDokument3 SeitenQA - Classification of NumberschaostheoristNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematic GemsDokument1 SeiteMathematic GemsGREEN BOXNoch keine Bewertungen
- General MathDokument12 SeitenGeneral MathdarlingggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Contributions To The Foundations of Set TheoryDokument9 SeitenTwo Contributions To The Foundations of Set TheoryDietethiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comp1012 (2015)Dokument16 SeitenComp1012 (2015)FoxyDee Tsugi NoMaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.5 Exploring The Effect of Degree On Polynomial FunctionsDokument4 Seiten1.5 Exploring The Effect of Degree On Polynomial FunctionsDa'veon Ramsay-EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary 3-6Dokument1 SeiteSummary 3-6jkl jklNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homomorphisms of Groups 3Dokument65 SeitenHomomorphisms of Groups 3JAHANZAIBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 Mathematics 2018-19 PDFDokument7 SeitenClass 10 Mathematics 2018-19 PDFgulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 2018 - 2019: Scheme of Work / Term Wise Syllabus BreakupDokument7 SeitenMathematics 2018 - 2019: Scheme of Work / Term Wise Syllabus BreakupgulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Y5 Y6 Properties of Shapes AnglesDokument1 SeiteY5 Y6 Properties of Shapes AnglesOscar MasindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Areas of Mathematics Glossary of Areas of Mathematics: See Also: andDokument12 SeitenAreas of Mathematics Glossary of Areas of Mathematics: See Also: andrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elementary AlgebraDokument9 SeitenElementary AlgebraSrikant AcharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- @StudyTime - Channel Maths-13Dokument12 Seiten@StudyTime - Channel Maths-13Sipra PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathsclinic Smartprep Gr11 Eng 3Dokument45 SeitenMathsclinic Smartprep Gr11 Eng 3lulamangwenya67Noch keine Bewertungen
- Domain and Range of FunctionDokument15 SeitenDomain and Range of FunctionBuela, Lance GabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real NumbersDokument6 SeitenReal NumbersRatinder SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math221 Fall2019 Lecture2 Locical Compound Statements Part1 v22Dokument135 SeitenMath221 Fall2019 Lecture2 Locical Compound Statements Part1 v22eesha shahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Numbers 2Dokument26 SeitenComplex Numbers 2Unexpected TheoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- QA - SurdsDokument6 SeitenQA - SurdschaostheoristNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Equations Reference Sheet: Equation of A LineDokument1 SeiteLinear Equations Reference Sheet: Equation of A LineNoor FarhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Number SystemsDokument6 SeitenNumber SystemsPranav ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are P-Adic Numbers? What Are They Used For?Dokument6 SeitenWhat Are P-Adic Numbers? What Are They Used For?Arvey Sebastian Velandia Rodriguez -2143414Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math Live Class Notes - 9f5b9f77 Ceeb 4591 A0c6 E71d003b4655Dokument94 SeitenMath Live Class Notes - 9f5b9f77 Ceeb 4591 A0c6 E71d003b4655priya kurienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Reviewer Second QuarterDokument6 SeitenMath Reviewer Second Quarterwjohn6182Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pontryagin, L.S. Amer. Math So Transl. (1955), 95-110 - Edit 1Dokument1 SeitePontryagin, L.S. Amer. Math So Transl. (1955), 95-110 - Edit 1BetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadrature Shapes: Square TriangleDokument2 SeitenQuadrature Shapes: Square TriangleAyah FNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLARITO - BPA-1B - Math Languange and SymbolsDokument3 SeitenCLARITO - BPA-1B - Math Languange and SymbolsAngelica May ClaritoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Clinic Gr12 ENG SmartPrep v1.2 1Dokument69 SeitenMaths Clinic Gr12 ENG SmartPrep v1.2 1Matsiri ImmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 3 - Linear RegressionDokument9 SeitenLec 3 - Linear Regression14 Asif AkhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Mathematics Applied To Wireless Rev21Dokument122 Seiten1-Mathematics Applied To Wireless Rev21Randy DookheranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 7 Rational NumbersDokument15 SeitenClass 7 Rational NumbersSMKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rosmaina 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 391 012064Dokument10 SeitenRosmaina 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 391 012064Dondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physico-chemical Characteristics of the Queen Pineapple CultivarDokument2 SeitenPhysico-chemical Characteristics of the Queen Pineapple CultivarDondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISE DevelopingFXTradingStrategy 021108 PDFDokument63 SeitenISE DevelopingFXTradingStrategy 021108 PDFDondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphing Trig Functions PDFDokument4 SeitenGraphing Trig Functions PDFMark Abion ValladolidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Definition of The Derivative PDFDokument15 SeitenUnit 2 Definition of The Derivative PDFDondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphing Trig Functions PDFDokument4 SeitenGraphing Trig Functions PDFMark Abion ValladolidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adding and Subtracting Radical ExpressionsDokument2 SeitenAdding and Subtracting Radical ExpressionsJera ObsinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asnwers-1 2 PDFDokument1 SeiteAsnwers-1 2 PDFDondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Study Resource Was: Math 17 Finals - 1Dokument2 SeitenThis Study Resource Was: Math 17 Finals - 1Dondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- IFCMarketsBook PDFDokument12 SeitenIFCMarketsBook PDFDondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand BookDokument79 SeitenHand BookumeshnihalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trading 101 BasicsDokument3 SeitenTrading 101 BasicsNaveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tri Go No Me Tri ADokument396 SeitenTri Go No Me Tri Aslanas_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- LE1 Sample Exam 2 PDFDokument1 SeiteLE1 Sample Exam 2 PDFHanalit ZafraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements, CMPDS, Mix Ws PDFDokument4 SeitenElements, CMPDS, Mix Ws PDFDean JezerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Teacher: Date: Score:: Multiplying With Powers of TenDokument1 SeiteName: Teacher: Date: Score:: Multiplying With Powers of TenDondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equation of A Line WorksheetDokument11 SeitenEquation of A Line WorksheetAra HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Style Questions: GuidanceDokument12 SeitenExam Style Questions: GuidanceLynseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ooo Mdas Integers Foursteps Positive 001Dokument2 SeitenOoo Mdas Integers Foursteps Positive 001api-314809600Noch keine Bewertungen
- Order of OperationsDokument2 SeitenOrder of OperationsDondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1-1 Otec 2Dokument109 SeitenA1-1 Otec 2Dondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Order of OperationsDokument2 SeitenOrder of OperationsDondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rankine Cycle Alejandro Cabico MadjilonDokument109 SeitenRankine Cycle Alejandro Cabico MadjilonDondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upcat Reviewer Practice Test 1Dokument27 SeitenUpcat Reviewer Practice Test 1Michelle Panganduyon100% (1)
- Rankine Cycle Alejandro Cabico MadjilonDokument109 SeitenRankine Cycle Alejandro Cabico MadjilonDondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Brake Disc and CalliperDokument32 SeitenAutomotive Brake Disc and CalliperDondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alejandro - Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC)Dokument45 SeitenAlejandro - Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC)Dondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 Master BuilderDokument6 Seiten09 Master BuilderDondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Charge and Electric FieldDokument5 SeitenElectric Charge and Electric FieldDondee Sibulo AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- W Wor Orks Ksho Hop 08 P08 Iintrod Ntroductio Uction To Proce N To Process Ss O Opt Ptim Imiza Izati Tion On Iin NG Gams Ams® ®Dokument29 SeitenW Wor Orks Ksho Hop 08 P08 Iintrod Ntroductio Uction To Proce N To Process Ss O Opt Ptim Imiza Izati Tion On Iin NG Gams Ams® ®franko2422Noch keine Bewertungen
- Policy Analysis ProcessDokument9 SeitenPolicy Analysis ProcesswubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRE 377 Research Methods: Qualitative Research - Lecture Outline (4 Sessions) Session Topics / Learning OutcomesDokument15 SeitenBRE 377 Research Methods: Qualitative Research - Lecture Outline (4 Sessions) Session Topics / Learning OutcomesKinming PoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths 3 SyllabusDokument2 SeitenMaths 3 SyllabusShashwat TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ma034 RPDokument9 SeitenMa034 RPkamal kannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronbach'S Alpha: Case Processing SummaryDokument21 SeitenChronbach'S Alpha: Case Processing SummaryJakie UbinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul3 DEA 4Dokument14 SeitenModul3 DEA 4Rahardjo TriNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comparison of Two Linear Algebra BooksDokument3 SeitenA Comparison of Two Linear Algebra BooksAnton Van WykNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 3 Stat IDokument24 SeitenUNIT 3 Stat INasri IBRAHIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTH 201 Business Mathematics-I - BBADokument2 SeitenMTH 201 Business Mathematics-I - BBAAbdul RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Enhancement FrequencyDokument50 Seiten04 Enhancement FrequencyButta RajasekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 305 Systems Dynamics Course SyllabusDokument1 SeiteME 305 Systems Dynamics Course SyllabusSylvester JemigbeyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving arithmetic, geometric, and other sequence problemsDokument1 SeiteSolving arithmetic, geometric, and other sequence problemsAnonymous 1kqMBf2Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10.6 - Surface Integrals FDokument21 Seiten10.6 - Surface Integrals FKrishna ChaituNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing The Difference Between Means, Variances, and ProportionsDokument53 SeitenTesting The Difference Between Means, Variances, and ProportionsaswardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2-Demand ForecastingDokument36 SeitenCHAPTER 2-Demand ForecastingJohn TuahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of The Parareal AlgorithmDokument24 SeitenApplications of The Parareal AlgorithmTina BargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Measures of VariabilityDokument24 SeitenChapter 5 Measures of VariabilityjessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Economics in A Global Economy: Linear ProgrammingDokument18 SeitenManagerial Economics in A Global Economy: Linear ProgrammingArif DarmawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Systems Questions for Competitive ExamsDokument11 SeitenControl Systems Questions for Competitive Examssrinu247Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1A - Differential EquationsDokument4 SeitenAssignment 1A - Differential EquationsAlina KenyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 19 - Network AnalysisDokument36 SeitenLab 19 - Network AnalysisUno de MadridNoch keine Bewertungen
- 348 - 38835 - BA101 - 2017 - 4 - 1 - 1 - A7 Calculus1 Fall 2017-Dr. Mostafa ElogailDokument5 Seiten348 - 38835 - BA101 - 2017 - 4 - 1 - 1 - A7 Calculus1 Fall 2017-Dr. Mostafa ElogailAyman Hesham El-AttarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra II Unit 7 StatisticsDokument14 SeitenAlgebra II Unit 7 Statisticsapi-287816312Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Assemblies Their Design Manufacture and Role in Product Development PDFDokument573 SeitenMechanical Assemblies Their Design Manufacture and Role in Product Development PDFIsmael Naranjo Veléz100% (1)
- Basic Data Analysis: Descriptive StatisticsDokument23 SeitenBasic Data Analysis: Descriptive Statisticsamul65Noch keine Bewertungen
- Variational PrinciplesDokument61 SeitenVariational Principlesnickthegreek142857Noch keine Bewertungen
- Estimation of Parameters of The Makeham Distribution Using The Least Squares MethodDokument11 SeitenEstimation of Parameters of The Makeham Distribution Using The Least Squares MethodhenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Work Statistics and MethodsDokument4 SeitenSocial Work Statistics and MethodsDennis Mohammed100% (1)
- AP Calculus AB Exam: Section I Practice QuestionsDokument18 SeitenAP Calculus AB Exam: Section I Practice QuestionsDSaulBNoch keine Bewertungen