Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
N M (Joules) FT LB Newton LB M FT: Inhinyero Review Center
Hochgeladen von
Angelo PlumosOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
N M (Joules) FT LB Newton LB M FT: Inhinyero Review Center
Hochgeladen von
Angelo PlumosCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
REVIEW – HYDRAULICS AND GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
Base Units and Unit Pressures
Englis
Unit of Measure SI
h
𝑚 𝑓𝑡
Acceleration
𝑠2 𝑠2
Area 𝑚2 𝑓𝑡 2
Energy N ·m P: pressure gage
ft ·lb
(Joules) Pabs: absolute pressure
Force Newton lb (If pressure is not specified, assume
Length m ft gage)
Mass kg Slug
Area Moment of Pabs = P + 1 atm
𝑚4
Inertia 𝑓𝑡 4
1 atm = 14.7 psi = 101.3 kPa
Momentum 𝑚 lb·s The pressure head in meters of a
𝑘𝑔 ·
𝑠 specified fluid:
𝑙𝑏
Power watts ft · 𝑷
𝑠 𝒉=
𝑙𝑏 𝜸
Pressure Pa Given two fluids A and B, the pressure
𝑓𝑡 2
head is:
Time s s
𝑺𝑮𝑨
𝑚 𝑓𝑡 𝒉𝑩 = 𝒉
Velocity 𝑺𝑮𝑩 𝑨
𝑠 𝑠
Other Formula:
Volume 𝑚3 𝑓𝑡 3 𝑊𝑒𝑖𝑔ℎ𝑡
N ·m Unit weight: 𝛾 = = 𝜌𝑔
𝑉𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒
Work ft ·lb
(Joules) Density: 𝜌 =
𝑀𝑎𝑠𝑠
𝑉𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒
𝛾 𝜌
Specific Gravity: 𝑆𝐺 = =
Manometers: 𝛾𝑤 𝜌𝑤
An instrument for measuring the pressure 𝑁 𝑘𝑔
𝛾𝑤 = 9810 𝜌𝑤 = 1000
acting on a column of fluid, especially 𝑚3 𝑚3
𝛾
one with a U-shaped tube of liquid. (For gases): 𝑆𝐺 =
𝛾𝑎𝑖𝑟
𝑁
For a differential manometer, 𝛾𝑎𝑖𝑟 = 12
𝑚3
Typical Specific Gravity Values:
Freshwater = 1.0
Seawater = 1.03
Oil = 0.80
Mercury = 13.6
Relationship of density, pressure and
density for air and other gases.
𝑃 = ρRT
Where:
P = absolute pressure
ρ = density of gas
R = gas constant
T = temperature in Kelvin or Rankine
Σpressures, P = γh
Sample Problems:
1. One slug is equivalent to how many
kg?
2. What is the mass density of fresh
water in slugs per cubic foot?
INHINYERO REVIEW CENTER
REVIEW – HYDRAULICS AND GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
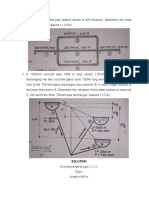
3. A body has a mass P) at A and B is water and the specific
𝑚
of 1.5 slugs in a place where 𝑔 = 9.81 2 , gravity of mercury is 13.6.
𝑠
what is the mass in slugs where 𝑔 =
𝑚
9.78 2 ?
𝑠
4. A liquid in a 1.31 m3 container has a
mass of 1345 kg.
a. What is its mass density?
b. What is its specific gravity?
c. What is its gravity force?
5. A reservoir of glycerine has a mass
of 1200 kg and a volume of 0.952 cu. M.
Find its:
a. weight
b. density
c. specific weight 13. Find the pressure at A.
d. specific gravity
e. specific volume
6. The specific gravity of certain oil
is 0.82. Calculate its:
a. specific weight in lb/ft3
b. specific weight in kN/m3
c. mass density in slugs/ft3
d. mass density in kg/m3
7. A volume of water weighs about 9.75N.
Calculate its mass in kilograms.
8. If an object has a mass of 22 kg at
sea level, what will be its weight at a
14. Covert 98 gpm to cms.
point where the acceleration due to
gravity is 9.75 m/s2? What will be its
mass at that point? 15. Oil is flowing in a 0.1 m Φ pipe at
3.5 m/s.
9. A man weighs 70 kg. What is his a. What is the discharge in cms?
weight in lb and in N? b. Find the flow rate in mgd
c. Find the weight flux in kN/s
10. The pressure gage in a given tank
reads 92 mmHg. Determine the equivalent 16. A gas is under pressure of 25 bar
height of column of oil, sg = 0.84. absolute at 40 degree celcius.
a. Compute the pressure in kPa
11. CE Board May 1998. A pressure gauge b. Compute the gage pressure
at elevation 8m at the side of a tank c. Compute the gas constant R in
containing a liquid reads 80 kPa. m2/s2K if it has a unit weight of 360
Another gauge at elevation 3m. reads 120 N/m3
kPa. Compute the following:
a. specific weight of the fluid
b. density of the fluid
c. specific gravity of the fluid
12. A U tube manometer measures the
pressure difference between two points A
and B in a liquid. The U tube contains
mercury (fluid Q). Calculate the
difference in pressure if h =1.5 m, h2 =
0.75 m and h1 = 0.5 m. The liquid (fluid
INHINYERO REVIEW CENTER
REVIEW – HYDRAULICS AND GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
a. Calculate the total force of the
water on the gate
Total Hydrostatic Pressures: b. How far is the said force from
A. Plane Surfaces the vertex measured along the gate?
c. What normal force must be applied
at the vertex of the gate to open it?
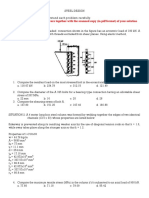
2. A vertical rectangular gate on the
face of the dam is 2 m wide and 4 m
high. The upper edge is 3 m below the
water surface.
a. Find the total force of water on
the gate
b. How far is the said force from
the bottom of the gate?
c. If the gate is hinged at top, how
much horizontal force applied at the
bottom is needed to open it?
𝑭 = 𝜸𝒉̅𝑨
at c.p. (total hydrostatic pressure on 3. From the liquid surface, determine
plane area A subjected to liquid) the distance of the center of pressure
The distance between the centroid (c) of the following:
and center of pressure (c.p.) along the a. A triangle of base b and height d
body is called eccentricity (e). as vertical and submerged in a liquid
̅𝑰 with its vertex at the liquid surface.
𝒆= b. A circular area of diameter d and
𝑨𝒚 ̅
submerged in a liquid. Its upper edge
̅
𝒉 – distance of the coincides with the liquid surface.
350-mm
centroidriser pipe the
below c. A vertical semi-circular area of
eliquid surface on the diameter d and radius r is submerged
vertical (m) and has its diameter in a liquid
𝒚̅ – distance of the surface.
3.6 m centroid below the
liquid surface along the 4. Tank abcd is 2.4 m wide and 6 m
body (m) long.
𝑰̅ –
b c
a. Compute the magnitude of the force on
moment water wall ab
of 1.8 m b. Find the location of the force from
the bottom
c. Total force in the bottom of the
inertia of A with respect to its tank
a
centroidal axis (m4)
d
B. Curved Surfaces
P = total hydrostatic pressure on a
curved surface
𝑃 = √𝑃ℎ 2 + 𝑃𝑣 2
𝑷𝒉 - horizontal component; total
hydrostatic pressure on plane area “A”
which is the projection of the curved
surface on the vertical
Sample Problems: ̅A (projected area)
𝑷𝒉 = 𝜸𝒉
1. A triangular gate with a horizontal
base 1.2 m long and an altitude of 1.8 m
is inclined 45° from the vertical with
the vertex pointing upward. The hinged
horizontal base of the gate is 2.7 m
below the water surface.
INHINYERO REVIEW CENTER
REVIEW – HYDRAULICS AND GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
b. Determine the angle of the
Liquid above Surface resultant force of water with respect
to the horizontal
2. Curve “mn” shown is a quarter circle
with radius of 5 m. For a length of 3 m
perpendicular to the paper, determine:
a. The horizontal force acting on the
curve
b. The vertical force acting on the
curve
c. The total force on the curve
𝑷𝒗 - vertical component; weight of liquid
whose volume is traced by moving the
curve vertically upward until the liquid
surface (prolongation)
𝑷𝒗 = 𝜸𝑽𝒐𝒍
Liquid below Surface
3. Curve wall ABC is a quarter circle 9ft
into the paper.
a. Compute the horizontal hydrostatic
force on the wall
b. Compute the vertical hydrostatic
Sample Problems:
force on the wall.
1. The face of the 50-m long dam shown
c. Compute the line of action (angle
is a quarter circle with radius 20 m.
from the horizontal) of the resultant
force.
a. Calculate the vertical component of
the force of water on the dam
INHINYERO REVIEW CENTER
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- UntitledDokument19 SeitenUntitledRojane FloraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inhouse Practice Problems - RCD-Column - Without AnswersDokument1 SeiteInhouse Practice Problems - RCD-Column - Without AnswersAndrea Sochayseng SolijonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis For ShearDokument20 SeitenDesign and Analysis For Shearhonesto reynaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 12Dokument6 SeitenQuiz 12John Taylor BernasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q P A Q 1600 4 (4) Q 100 Kpa: SolutionDokument8 SeitenQ P A Q 1600 4 (4) Q 100 Kpa: SolutionFrancis John BuacNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEE330 - Influnece Lines PDFDokument9 SeitenCEE330 - Influnece Lines PDFAvijit SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Econ. - ANNUITYDokument35 SeitenEngineering Econ. - ANNUITYNikolai VillegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Problem 4.1: Free-Body DiagramDokument4 SeitenSample Problem 4.1: Free-Body DiagramAlbert MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refresher Module 04 - M6 - Intermodal Transportation SystemDokument1 SeiteRefresher Module 04 - M6 - Intermodal Transportation SystemKiki Do youNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces On Curved Surfaces 1Dokument13 SeitenForces On Curved Surfaces 1Yours PamoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friction ProblemsDokument4 SeitenFriction ProblemsDaniel PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- M05 - SEC 5 Solution (131331) For FB PostingDokument11 SeitenM05 - SEC 5 Solution (131331) For FB PostingRimar LiguanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Engineering & ConstructionDokument13 SeitenStructural Engineering & ConstructionREX AMPONGANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic of The Philippines: Exam 2Dokument4 SeitenRepublic of The Philippines: Exam 2Jan Jan AnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics: Measure of Central Tendency MeanDokument25 SeitenStatistics: Measure of Central Tendency MeanjlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moren - MODULE 3 - Beams-ColumnDokument18 SeitenMoren - MODULE 3 - Beams-ColumnJoshua Espanto MorenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignDokument40 SeitenCe0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignjerichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials 1 DiscussionDokument36 SeitenStrength of Materials 1 DiscussionsadonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE Review - Steel Design Problems SolvedDokument3 SeitenCE Review - Steel Design Problems SolvedLemuel TeopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determine Water Surface Elevation and Pipe Discharge PowerDokument4 SeitenDetermine Water Surface Elevation and Pipe Discharge PowerDiecon Irish ArboledaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Quiz Problems To Be MadeDokument16 SeitenFinal Quiz Problems To Be MadeRyan ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maximum Stresses On A Pole Subjected To Combined LoadingsDokument2 SeitenMaximum Stresses On A Pole Subjected To Combined LoadingsShiela GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural design problems and solutionsDokument6 SeitenStructural design problems and solutionsPaulo ValderamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mata Deseree Plate 7Dokument9 SeitenMata Deseree Plate 7Diecon Irish ArboledaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem No: 1: Submitted ToDokument4 SeitenProblem No: 1: Submitted ToLight HouseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Square FootingDokument9 SeitenSquare FootingFrancis Ko Badongen-Cawi Tabaniag Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- 14.3332013AtterbergLimitsData BlankDokument18 Seiten14.3332013AtterbergLimitsData BlankMewnEProwtNoch keine Bewertungen
- RC 3Dokument4 SeitenRC 3Mayya BonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingDokument1 SeitePreboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingAngelice Alliah De la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Achievement Exam ReviewDokument12 SeitenEngineering Achievement Exam ReviewJade Paul D. BesanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Problem 1Dokument14 SeitenSample Problem 1Fritz Luzon100% (1)
- Assignment - 1Dokument3 SeitenAssignment - 1chritNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersDokument1 SeiteRCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersArwin VillegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrau Geotech Focusproblems3 2019Dokument7 SeitenHydrau Geotech Focusproblems3 2019kimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Correlation Engineering CorrelationDokument8 SeitenEngineering Correlation Engineering CorrelationMarbel PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 EllipseDokument42 SeitenLesson 4 EllipseANGEL GWYNET RIEGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Struct Nov2019Dokument4 SeitenStruct Nov2019ryanmikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering MechanicsDokument4 SeitenEngineering MechanicsDonna MelgarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tos1 MidtermDokument2 SeitenTos1 MidtermMa.Zyra M. DascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HydraulicsDokument12 SeitenHydraulicsMugiwara Sparrow0% (1)
- Total Hydrostatic Pressure: P Ha I e AyDokument2 SeitenTotal Hydrostatic Pressure: P Ha I e AyJocelyn CabarlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tos 1Dokument5 SeitenTos 1Allyanna Elise Diam100% (1)
- NSCP Code: Specificatio N ScoreDokument17 SeitenNSCP Code: Specificatio N ScoreMarco SatomeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Steel Design for Tension MembersDokument62 SeitenPrinciples of Steel Design for Tension MembersTyrone PaulinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cebu University CE Review 3 quiz on structural steel designDokument3 SeitenCebu University CE Review 3 quiz on structural steel designNikki Marie G OclaritNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Engineering Education Achievement Exam CDokument9 SeitenCollege of Engineering Education Achievement Exam CJade Paul D. BesanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Design INSTRUCTION: Read and Understand Each Problem CarefullyDokument3 SeitenSteel Design INSTRUCTION: Read and Understand Each Problem CarefullyRoma Raquepo RingorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feu Hydraulics PreboardDokument2 SeitenFeu Hydraulics PreboardEla Macabante100% (1)
- Steel 3Dokument3 SeitenSteel 3Mayya Bona100% (1)
- Steel Design 1Dokument26 SeitenSteel Design 1Gracielle NebresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotechnical Engineering - Ii (Foundation Engineering) : PilesDokument26 SeitenGeotechnical Engineering - Ii (Foundation Engineering) : PilesPascasio PascasioNoch keine Bewertungen
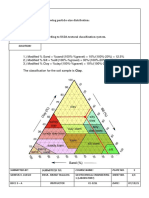
- Problems: 1. A Residential Urban Area Has The Following Proportions of Different Land Use: Roofs, 25Dokument1 SeiteProblems: 1. A Residential Urban Area Has The Following Proportions of Different Land Use: Roofs, 25TWICE TEUDOONGIENoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertical Stresses in Soil Mass - Part 1Dokument14 SeitenVertical Stresses in Soil Mass - Part 1AbbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tos 2Dokument3 SeitenTos 2Allyanna Elise DiamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nov 2021 CoachingDokument71 SeitenNov 2021 CoachingKenny CaluzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 7. Structural Design "CE Board Exam Nov. 1992Dokument1 SeiteProblem 7. Structural Design "CE Board Exam Nov. 1992AlvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- N M (Joules) FT LB Newton LB M FT: Inhinyero Review CenterDokument4 SeitenN M (Joules) FT LB Newton LB M FT: Inhinyero Review CenterPaulyne TuganoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of LiquidsDokument92 SeitenMechanical Properties of LiquidsRajuramNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Fluid Mechanics - Properties of Fluids PDFDokument10 Seiten1 Fluid Mechanics - Properties of Fluids PDFLucas VylxiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- For CMR Manually Issued Ecc To OnlineDokument1 SeiteFor CMR Manually Issued Ecc To OnlineAngelo PlumosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review - Hydraulics and Geotechnical Engineering Soil MechanicsDokument4 SeitenReview - Hydraulics and Geotechnical Engineering Soil MechanicsAngelo PlumosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1: General Information Reference No.:326263 Year:2022 Quarter: 1 Name of Plant: Philippine Red Cross NotesDokument10 SeitenModule 1: General Information Reference No.:326263 Year:2022 Quarter: 1 Name of Plant: Philippine Red Cross NotesAngelo PlumosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastery 3Dokument2 SeitenMastery 3Angelo PlumosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reinforced Concrete Design RefresherDokument5 SeitenReinforced Concrete Design RefresherMark Neil Delgaco Gastilo100% (2)
- MT3 SolutionDokument4 SeitenMT3 SolutionAngelo Plumos100% (1)
- App Form UMID 2013Dokument2 SeitenApp Form UMID 2013Адриан Убежище МоленьоNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Review - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringDokument12 SeitenReview - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringAngelo PlumosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating compound and simple curve dataDokument3 SeitenCalculating compound and simple curve dataMarc Dared Cagaoan50% (2)
- Fluid 10Dokument131 SeitenFluid 10subrahmanyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument12 SeitenChapter 1Angelo PlumosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Waste Management: An Overview of Key Concepts and ComponentsDokument43 SeitenSolid Waste Management: An Overview of Key Concepts and ComponentsAngelo PlumosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16-CONSERVATION OF LINEAR MOMENTUM - 01-TheoryDokument15 Seiten16-CONSERVATION OF LINEAR MOMENTUM - 01-TheoryRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Van Deemter EquationDokument19 SeitenVan Deemter EquationAsif AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Matematik Pertengahan Tahun Ting 5 Smksbu 2019 Kertas 1Dokument24 SeitenSoalan Matematik Pertengahan Tahun Ting 5 Smksbu 2019 Kertas 1ZULKFELI BIN ISMAIL AWANG MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- (TC31) IEC 60079-0 Edition 6.0 (2011-06-22)Dokument9 Seiten(TC31) IEC 60079-0 Edition 6.0 (2011-06-22)Shirish100% (1)
- MD (BD) - Lst-Cep-In-1001 Control System Io List Rev0 PDFDokument17 SeitenMD (BD) - Lst-Cep-In-1001 Control System Io List Rev0 PDFKook PengNoch keine Bewertungen
- LE13-038-R04a (TECHNICAL SHEET)Dokument83 SeitenLE13-038-R04a (TECHNICAL SHEET)Sermchart PakumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of A Chest Freezer - Optimum Design of An Evaporator CoilDokument15 SeitenDevelopment of A Chest Freezer - Optimum Design of An Evaporator CoilJss Aircond & ElectricalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17.1 17.3 Oscillations SHM and EnergyDokument26 Seiten17.1 17.3 Oscillations SHM and EnergyTruly SkunkedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doping SemiconductorsDokument4 SeitenDoping SemiconductorsPratheek UNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synchronous AlternatorsDokument31 SeitenSynchronous AlternatorsAndrew Lozgachev100% (1)
- LKPB Practice Test Four Section 1Dokument27 SeitenLKPB Practice Test Four Section 1Bintana CahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. 5 Overcurrent and Undercurrent Relay: ObjectiveDokument4 SeitenExperiment No. 5 Overcurrent and Undercurrent Relay: ObjectiveMian Tauseef100% (1)
- AC For Mechanical EngineeringDokument77 SeitenAC For Mechanical EngineeringHasen Yunne ShemsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument5 SeitenChapter 1Christian EduardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys 3106Dokument8 SeitenPhys 3106myo htetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics Speed and AccelerationDokument2 SeitenKinematics Speed and AccelerationAhmad OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM 2022 SEM 2 Mock AnsDokument2 SeitenSTPM 2022 SEM 2 Mock Ansm-4306022Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rechargeable Sealed Lead-Acid Battery: 12 Volt 18.0 Amp. HrsDokument2 SeitenRechargeable Sealed Lead-Acid Battery: 12 Volt 18.0 Amp. HrsJuan EsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFD analysis of a resistance muffler performanceDokument4 SeitenCFD analysis of a resistance muffler performanceMohammadreza NaghaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 44) API 653 Day 7 Book (1 To 52)Dokument53 Seiten44) API 653 Day 7 Book (1 To 52)SHAHIDALI100% (1)
- Sargent Welch TablaDokument2 SeitenSargent Welch Tablamimi57% (7)
- Concept of Settling PDFDokument25 SeitenConcept of Settling PDFkasara sreetejNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chip Formation: IntroductionDokument5 SeitenChip Formation: IntroductionDr.S.Ravi CITNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stal9781607500315 1088Dokument3 SeitenStal9781607500315 1088Tariq SufianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 7 Post Test Ratios and Proportions - QuizizzDokument7 SeitenGrade 7 Post Test Ratios and Proportions - QuizizzSadiah PratiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 PBDokument12 Seiten3 PBfaagoldfishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit No. 6: Mechanical SpringDokument61 SeitenUnit No. 6: Mechanical SpringGaurav JiwnaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment-1Dokument2 SeitenAssignment-1Rahul KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Power Electronic Converters - Electrical4uDokument3 SeitenAdvantages and Disadvantages of Power Electronic Converters - Electrical4uabhinawpratap singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main Switchboard Drawing (Praxis PMS)Dokument94 SeitenMain Switchboard Drawing (Praxis PMS)minpyitNoch keine Bewertungen