Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Gases and Vapors
Hochgeladen von
Khristel PenoliarOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Gases and Vapors
Hochgeladen von
Khristel PenoliarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
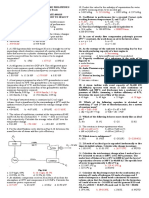
Chemical Engineering Calculations 1
Problem Set 2 Gases, Vapors and Saturation
Name: ____________________________________
1. (a) What is the vapor pressure of i) water at 80°F ii) n-octane at 250oC iii) n-pentane at 120oC
iv) mercury at 200oC. (b) What is the boiling point of i) benzene at 30 in. Hg ii) water at 100 mm Hg iii)
toluene at 4 atm iv) propane at 50 psig.
2. Given that at 10 mm Hg glycerol boils at 167.20C and at 760 mm Hg, 290oC, calculate the constants A and B
in the equation: log(VP)= A - B/(C+T) where VP is the vapor pressure in mm Hg, T is the temperature in
K and C=230. What is the vapor pressure of glycerol at 200°C?
3. The atm pressure varies with elevation according to the equation : P= 29.92 -0.00111h: where P IS the
pressure in inches Hg and h is the altitude in ft. What is the elevation where water boils at 95 oC?
4. A liquid mixture at 0oC consists of 30% ethane, 40% propane and 30% butane. Find the composition of the
vapor mixture in equilibrium with this liquid. What is the total equilibrium pressure? Apply Raoult’s Law.
5. A gaseous mixture of 61% n-hexane, 25% n-octane and 13% n- decane is at a temperature of 50oC. Find the
equilibrium pressure and the composition of the liquid in equilibrium with the mixture.
6. What is the total pressure exerted by a liquid-vapor system in equilibrium if the liquid phase consists of 30%
propane, 10% butane, 30% pentane, 10% hexane and 4% heptane at a temperature of 12 oC?
7. A liquid mixture of 50% mole n-butane and 50% mole n-pentane at 60 oC and total pressure of 2600 mm Hg.
At equilibrium, find the composition of both the liquid and vapor phases. What fraction of the original liquid
was vaporized. If the mixture is heated further to 80°C what is the resulting pressure?
8. (a) What is the bubble point (T) of a liquid mixture of 45% toluene and 55% benzene at a pressure of 1000
mm Hg? What is the composition of the first vapor formed? (b) What is the dew point of a gaseous mixture
of 45% toluene and 55% benzene at a pressure of 1000 mm Hg. What is the composition of the liquid
formed?
9. A liquid mixture consists of 40% n-pentane and 60% n-hexane by mole. It is placed in a closed container
and is heated to 100oC and a pressure of 3.5 atm. What is the resulting composition of the vapor and liquid
phases in equilibrium? What % of the original liquid is vaporized?
10 The composition of Liquefied Petroleum Gas(LPG) is 0.5% ethane, 0.1 % acetylene, 16.4% propane, 2.1%
ethylene, 74% butane and 6.9% butene, If the room temperature is at 30oC,what is the pressure inside the
tank and the composition of the gas that first issues from this mixture.
11. (a) Calculate the composition by volume and by weight of air that is saturated with water vapor at a
pressure of 755 torrs and a temperature of 14°C. (b) Calculate the composition by volume and by weight of
CO2 that is saturated with water vapor at the conditions of part (a).
12. Nitrogen is saturated with benzene vapor at a temperature of 280 oC and a pressure of 0.9875 bar.
Calculate the composition of the mixture, expressed in the following terms. (a) % by vol (b) % by wt
(c) Grains benzene/m3 of mixture (d) kg benzene/kg N2 (e) kgmols benzene/kgmol N2.
13. CO2 contains 0.055 kg-mol of water vapor per kg mol dry CO 2 at a temperature of 33oC and a total pressure
of 755 mm Hg. Calculate: (a) relative saturation (b) % saturation of the mixture
(c) temperature to which the mixture must be heated in order that the relative saturation shall
be 35%.
14. A mixture of benzene and air at 36 0C and 100 kPa is found to have a dew point of 16 oC. Calculate its: (a)
composition by volume (b) kg-mol benzene/kg-mol air (c) wt benzene/wt air.
P=100 kPa=750.06 mmHg
A=6.89272; B=1203.531 ; C=219.888
B 1203.531
log 10 ( Pobenzene ) = A− =6.89272−
T +C 16 +219.888
Pobenzene =61.74 mmHg
Pobenzene =Pbenzene=61.74 mmHg
Pair =750.06 mmHg−61.74 mmHg=688.32 mmHg
a.)
% by vol=% by mol=% by pressure
61.74 mmHg
%mo l benzene= ×100=8.23 %
750.06 mmHg
688.32mmHg
%mo l air = ×100=91.77 %
750.06 mmHg
b.) Basis: 100 kg-mol mixture
kg−mol benzene 8.23 kg−mol kg−mol benzene
= =0.08968
kg−mol air 91.77 kg−mol kg−mol air
c.)
78.11kg
8.23 kg−mol ×
wt benzene 1 kg−mol kg benzene
= =0. 2148
wt air 28.97 kg kg air
91.77 kg−mol ×
1 kg−mol
15. A flue gas on a wet basis contains 10% CO2, 1 % CO, 5% O2, 5% H2O and 79% N2. It is at 190oC and 750 torr.
To what temperature should it be cooled to make it saturated with water vapour keeping the total
pressure constant?
P=750 torr=750 mmHg
x C O =0.1 ; x CO =0.01 ; x O =0.05 ; x H O=0.05; x N =0.79
2 2 2 2
P H O =x H O P o
2 2
PH O
x H O= 2
2
P
P H O =( 0.05 ) ( 750 mmHg )=375 mmHg
2
P H O =PoH O =375 mmHg
2 2
B
log 10 ( PoH O )= A−
2
T +C
B
T= −C
A−log 10 ( P oH 2 O)
A=8.140191; B=1810.94 ; C=244.485
1810.94
T= −244.485=80.86 o
8.140191−log 10 ( 375 )
16. A N2-acctone gas mixture consist of 20% acetone and 80% N 2. The mixture is made by bubbling dry N2 gas
through acetone. Thus the N2 becomes saturated with acetone. The pressure is at 755 mm Hg. At what
temperature is the bubbling made?
17. 250 grams of steam is injected into a large enclosed container containing 55 kg air. If the temperature is at.
2SoC and pressure 120 kPa, calculate: (a) relative humidity (b) molal humidity
(c) humidity (d) % humidity (e) dew point.
18. A gas-vapor mixture consisting of benzene and N 2 at a total pressure of 800 mm Hg and 45 0C has a %
saturation of 65%. (a) What is the dew point and % relative saturation of the gas mixture (b) If the mixture
is heated to 700oC, what is its relative saturation and dew point with total pressure maintained at 800 mm
Hg (c) Up to what pressure can the mixture be compressed without condensing any of the benzene if the
temperature is kept at 450C?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsVon EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- PS5 Gases-and-Vapors SaturationDokument2 SeitenPS5 Gases-and-Vapors SaturationLizvel Keith TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05-Chem Eng Tools 2016Dokument11 Seiten05-Chem Eng Tools 2016Hazel Raditya MizumareruNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEPARATIONSDokument13 SeitenSEPARATIONSR ZoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Docslide - Us - Stoic Solution To Problems PDFDokument61 SeitenDocslide - Us - Stoic Solution To Problems PDFGleden UmayamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Fuels Problem SetDokument1 SeiteSolid Fuels Problem SetCaseyJaneAguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHECALC Sample ProblemsDokument7 SeitenCHECALC Sample ProblemshulyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChE Calculations 2Dokument7 SeitenChE Calculations 2niezajanepatna100% (2)
- Checal2 LauritoDokument1 SeiteChecal2 LauritoGarcia RaphNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 322 - Gaseous Fuel ProblemsDokument26 SeitenCHE 322 - Gaseous Fuel ProblemsDanice LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Che219 Case1 Gaseous and LiquidDokument9 SeitenChe219 Case1 Gaseous and LiquidMargaret FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- AA - CHE312 - Chemical CalculationsDokument37 SeitenAA - CHE312 - Chemical CalculationsLizvel Keith TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gaseous FuelsDokument5 SeitenGaseous FuelsShane PatulotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Lab ReportDokument5 SeitenChapter 1 Lab ReportJabin Sta. TeresaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5Dokument18 SeitenLecture 5Sandra MacatangayNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChoppiDokument12 SeitenChoppiSarah Sanchez100% (1)
- Che Calc 2 Unit 1 PDFDokument31 SeitenChe Calc 2 Unit 1 PDFJerico Hercules MutiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics Exam 2015 20161 For Students1Dokument1 SeiteThermodynamics Exam 2015 20161 For Students1Alvin Salmingo100% (1)
- Distillation 2Dokument3 SeitenDistillation 2roxette100% (2)
- ReviewerDokument11 SeitenReviewerApril Joyce RaymundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaporation Sample Solved ProblemsDokument19 SeitenEvaporation Sample Solved ProblemsZeny Naranjo100% (2)
- PS Checalc 2 PrelimsDokument10 SeitenPS Checalc 2 PrelimsPrincess Janine CatralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head Losses in An Abrupt and Smoothly Contoured Change of Direction of Flow of Fluid PDFDokument30 SeitenHead Losses in An Abrupt and Smoothly Contoured Change of Direction of Flow of Fluid PDFChali HaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 312 Problem Set #2Dokument4 SeitenCHE 312 Problem Set #2rkz93Noch keine Bewertungen
- 14-Plant Design-Ans Key-Master FileDokument22 Seiten14-Plant Design-Ans Key-Master FilePaul Philip LabitoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checal 2 Quiz 1Dokument3 SeitenChecal 2 Quiz 1JamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium Homework SolutionsDokument30 SeitenEquilibrium Homework SolutionsGrissel De Aquino Villanueva80% (10)
- Gas AbDokument14 SeitenGas AbJackielyn EugenioNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC3Dokument33 SeitenCC3Kitty Last50% (2)
- Heat and Mass Transfer ReviewerDokument4 SeitenHeat and Mass Transfer ReviewerDianne VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 7 Abst, Intro, and AtqDokument6 SeitenExp 7 Abst, Intro, and AtqChali HaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4.ADokument20 SeitenChapter 4.ABendaud bataborNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forstudents Mar4Dokument4 SeitenForstudents Mar4RawlinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phychem 1 Review 1 Sept 2015Dokument2 SeitenPhychem 1 Review 1 Sept 2015Jupert Jasser AbellanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH E 2111/L: Chemical Engineering Calculations 2: Midterm Quiz #2Dokument1 SeiteCH E 2111/L: Chemical Engineering Calculations 2: Midterm Quiz #2CYBER DOMINGONoch keine Bewertungen
- AssigDokument2 SeitenAssigZakwan0% (1)
- Drying ProblemDokument5 SeitenDrying ProblemStephanie Torrecampo Delima100% (2)
- Crystallizations QuestionsDokument4 SeitenCrystallizations Questionsengr2021Noch keine Bewertungen
- ML ML ML N ML N ML N ML N: Appendix B Calculations & ComputationsDokument14 SeitenML ML ML N ML N ML N ML N: Appendix B Calculations & ComputationshaanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drying ExamplesDokument6 SeitenDrying ExamplesIsabelNoch keine Bewertungen
- (AdU Special Topics) PhyChm and ChEThermo ProblemsDokument4 Seiten(AdU Special Topics) PhyChm and ChEThermo ProblemsRyan MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 322 - Gaseous Fuel Problems PDFDokument26 SeitenCHE 322 - Gaseous Fuel Problems PDFDanice LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Fuels W:oDokument3 SeitenSolid Fuels W:oShane PatulotNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChE127 NUNEZ Assignment1Dokument1 SeiteChE127 NUNEZ Assignment1John Patrick Sanay NunezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indiabix SummaryDokument6 SeitenIndiabix SummaryMayNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChE 135 HQRUV Laboratory Manual v2Dokument52 SeitenChE 135 HQRUV Laboratory Manual v2gol12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Constant Rate and Constant Pressure FiltrationDokument2 SeitenConstant Rate and Constant Pressure FiltrationCece SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 511A Compilation 2 3 M F PDFDokument164 SeitenCHE 511A Compilation 2 3 M F PDFMaame Efua NeizerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Assessment #1 PDFDokument1 SeiteSummative Assessment #1 PDFCYBER DOMINGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Mccabe-Thiele MethodDokument7 SeitenMccabe-Thiele MethodBlessy GabaynoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam CheCalc 02Dokument2 SeitenFinal Exam CheCalc 02Christine FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem e Thermo Chapter 1 SolnDokument5 SeitenChem e Thermo Chapter 1 SolnBernice Go100% (1)
- Diaz Solid FuelsDokument20 SeitenDiaz Solid Fuelshoneylet tayactac100% (2)
- Chpter Four Fluid DynamicDokument33 SeitenChpter Four Fluid DynamicabdulqadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orca Share Media1567598084691Dokument10 SeitenOrca Share Media1567598084691Kobe AcobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - 6 Chemical Engineering Principles - Ii Self-Assessment Tests (Sats) Section-4.1Dokument7 SeitenAssignment - 6 Chemical Engineering Principles - Ii Self-Assessment Tests (Sats) Section-4.1Ali Hamza ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atk2 1 2014Dokument34 SeitenAtk2 1 2014Zakiyah Kamto IrfinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chee Assignment 1Dokument13 SeitenChee Assignment 1TSHEGOFATSO GOTSILENGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Exhaust Gas C C CDokument3 SeitenCommon Exhaust Gas C C CKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2: Sulfur and Its Compounds: Burning of Raw Sulfur Roasting of Pyrites Production of Sulfuric AcidDokument6 SeitenModule 2: Sulfur and Its Compounds: Burning of Raw Sulfur Roasting of Pyrites Production of Sulfuric AcidKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1 Common Integrals: Algebraic FunctionsDokument12 SeitenPart 1 Common Integrals: Algebraic FunctionsKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 de Priester ChartDokument4 Seiten1 de Priester ChartKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Statistics 2017Dokument6 SeitenBasic Statistics 2017Khristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Statistics 2018Dokument6 SeitenBasic Statistics 2018Khristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction Stoichiometry: Engineering CalculationsDokument17 SeitenReaction Stoichiometry: Engineering CalculationsKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 3: Metals & CorrosionDokument7 SeitenExperiment 3: Metals & CorrosionKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chinese EnglishDokument12 SeitenChinese EnglishKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng2015 Quiz 1 ReviewerDokument4 SeitenEng2015 Quiz 1 ReviewerKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1: Statistics and Data Handling in Analytical ChemistryDokument16 SeitenActivity 1: Statistics and Data Handling in Analytical ChemistryKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Ways of Studying Before Exams: How Do The These Principles Work Together in Relation To A Family?Dokument1 SeiteEffective Ways of Studying Before Exams: How Do The These Principles Work Together in Relation To A Family?Khristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water: Its Properties and Purification: Ust Chemical Engineering DepartmentDokument13 SeitenWater: Its Properties and Purification: Ust Chemical Engineering DepartmentKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gases and Vapors (Part 1)Dokument2 SeitenGases and Vapors (Part 1)Khristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENG201 M4.3: Electrochemistry Practice ProblemsDokument2 SeitenENG201 M4.3: Electrochemistry Practice ProblemsKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 2: Basic Techniques & Numeracy in Analytical Chemistry LaboratoryDokument26 SeitenActivity 2: Basic Techniques & Numeracy in Analytical Chemistry LaboratoryKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Intro To Vector Analysis PDFDokument33 Seiten1-Intro To Vector Analysis PDFKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Motion in One Dimension PDFDokument43 Seiten2-Motion in One Dimension PDFKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Middle Period Literary WorksDokument5 SeitenMiddle Period Literary WorksKhristel Penoliar0% (1)
- Phil. Lit. During Spanish ColonizationDokument8 SeitenPhil. Lit. During Spanish ColonizationKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 PhysChem - May 2022 - W - AnsDokument5 SeitenTest 1 PhysChem - May 2022 - W - Ansmarc jacobs davisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Olevel NotesDokument42 SeitenHeat Olevel NoteskimbugweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 (2) - Energy Balances On Reactive Systems 2Dokument23 SeitenLecture 5 (2) - Energy Balances On Reactive Systems 2Gee DevilleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Che 314: Heat TransferDokument5 SeitenChe 314: Heat TransferMason LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Conditioning of AuditoriumsDokument14 SeitenAir Conditioning of AuditoriumsKalyana SundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 RadiationDokument26 SeitenModule 5 RadiationskyyyxsageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics HeatDokument6 SeitenPhysics Heatsiba padhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Entropy and The Second Law of Thermodynamics: 5.1 Reversible and Irreversible ProcessesDokument20 Seiten5 Entropy and The Second Law of Thermodynamics: 5.1 Reversible and Irreversible ProcessesLexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 PDFDokument145 SeitenChapter 2 PDFOscar Espinosa BonillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workbook - EquilibriumDokument57 SeitenWorkbook - EquilibriumBruce Walker100% (1)
- 6.0 Chemical EquilibriumDokument105 Seiten6.0 Chemical EquilibriumTasya KassimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 1 Chapter 7 HeatDokument12 SeitenForm 1 Chapter 7 HeatajakazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capítulo 2 - IncroperaDokument33 SeitenCapítulo 2 - IncroperaCaio MunizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alfa Laval Heating and Cooling Hub Air-Conditioning and Chillers BrochureDokument6 SeitenAlfa Laval Heating and Cooling Hub Air-Conditioning and Chillers BrochureEmmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L8 MCQS Chapter-1Dokument13 SeitenL8 MCQS Chapter-1niggsNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVAC System Selection Report Appendices Appendix A ExtractDokument25 SeitenHVAC System Selection Report Appendices Appendix A ExtractArman Ul Nasar100% (1)
- Physics HSSC 1 Paper II-4Dokument16 SeitenPhysics HSSC 1 Paper II-4Qudsia AbrarNoch keine Bewertungen
- States of Matter and Phase Changes WorksheetDokument2 SeitenStates of Matter and Phase Changes WorksheetCaryl Ann C. Sernadilla100% (1)
- Forms of Energy 2Dokument16 SeitenForms of Energy 2cecilia b. guillen50% (2)
- Cibse Solar AcDokument11 SeitenCibse Solar Acdhananjay176Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Air Conditioning and Ventilation System For A Multi Storey Office BuildingDokument5 SeitenDesign of Air Conditioning and Ventilation System For A Multi Storey Office BuildingIppiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duhok Polytechnic University Petrochemical Department Second Stage Physical ChemistryDokument6 SeitenDuhok Polytechnic University Petrochemical Department Second Stage Physical Chemistrylya AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Law of Thermodynamics 1Dokument16 SeitenSecond Law of Thermodynamics 1Lone KnightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Chillers PDFDokument26 SeitenIntroduction To Chillers PDFValar MorghulisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theoretical and Experimental Analysis of Liquid Flooded CompressiDokument622 SeitenTheoretical and Experimental Analysis of Liquid Flooded CompressiTao YeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics of Non-Isothermal Sorption PDFDokument8 SeitenKinetics of Non-Isothermal Sorption PDFali105Noch keine Bewertungen
- 06 PP T235 CoolingDokument29 Seiten06 PP T235 CoolingEzhil ArasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 - ACA-1A - Physical Chemistry - Class XIthDokument13 Seiten2019 - ACA-1A - Physical Chemistry - Class XIthYash DhokeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretation - Chemistry Enthalpy of CombustionDokument5 SeitenInterpretation - Chemistry Enthalpy of CombustionKim ThaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3 PDFDokument2 SeitenTutorial 3 PDFyatiNoch keine Bewertungen