Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Protective Relays: 1. Visual and Mechanical Inspection
Hochgeladen von
Honeylyn IgnacioOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Protective Relays: 1. Visual and Mechanical Inspection
Hochgeladen von
Honeylyn IgnacioCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Protective relays
1. Visual and Mechanical Inspection
1. Compare equipment nameplate data with drawings and specifications.
2. Inspect relays and cases for physical damage. Remove shipping restraint material.
3. Verify the unit is clean.
4. Tighten case connections. Inspect cover for gasket seal. Clean cover glass. Inspect shorting
hardware, connection paddles and or knife switches. Remove any foreign materials from the
case. Verify target reset.
5. Inspect relay for foreign material, particularly in disk slots of the damping and electromagnets.
6. Verify contact clearance and spring bias. Inspect spiral spring convolutions. Inspect disk and
contacts for freedom of movement and correct travel. Verify tightness of mounting hardware
and connections. Burnish contacts. Inspect bearing and/or pivots.
2. Electrical tests
1. Perform insulation resistance test on each circuit to frame. Determine from the manufacturer’s
published data the allowable procedures for this test for solid state and microprocessor-based
relays.
2. Inspect targets and indicators.
1. Determine pickup and dropout of electromechanical targets.
2. Verify operation of all light-emitting diode indicators.
3. Set contrast for liquid-crystal display readouts.
3. Functional Operation
1. 2/62 timing relay
1. Determine time delay
2. Verify operation of instantaneous contacts.
2. 21 Distance Relay
1. Determine maximum reach.
2. Determine maximum torque angle.
3. Determine offset.
4. Plot impedance circle.
3. 24 Volts/Hertz Relay
1. Pickup frequency at rated voltage.
2. Determine pickup frequency at a second voltage level.
3. Determine time delay.
4. 25 Sync Check relay
1. Determine closing zone at rated voltage
2. Determine maximum voltage differential that permits closing at zero degree.
3. Determine live line, live bus, dead line, and dead bus set points.
4. Determine time delay
5. Verify dead bus/live line, dead line/live bus and dead bus/dead line control functions.
5. 27 Under voltage relay
1. Determine dropout voltage.
2. Determine time delay
3. Determine the time delay at a second point on the timing curve for inverse time relays.
6. 32 Directional Power Relays
1. Determine minimum pickup at maximum torque angle.
2. Determine closing zone.
3. Determine maximum torque angle.
4. Determine time delay
5. Verify the time at a second point on the timing curve for inverse time relays.
6. Plot the operating characteristic.
7. 40 Loss of Field (Impedance ) relay
1. Determine maximum reach.
2. Determine maximum torque angle.
3. Determine offset.
4. Plot impedance circle.
8. 46 Current Balance Relay
1. Determine pickup of each unit.
2. Determine percent slope.
3. Determine time delay
9. 46N Negative Sequence Current Relay
1. Determine negative sequence alarm level
2. Determine negative sequence minimum trip level
3. Determine maximum time delay
4. Verify two points on the (I2)2 curve
10. Phase Sequence or Phase Balance Voltage Relay
1. Determine the positive sequence voltage to close the normally open contact.
2. Determine the positive sequence voltage to open the normally close contact (under
voltage trip)
3. Verify negative sequence trip.
4. Determine time delay to close the normally open contact with sudden application of 120
percent of pickup.
5. Determine time delay to close the normally close contact upon removal of voltage when
previously set to rated system voltage.
11. 49R Thermal Replica Relay
1. Determine time delay at 300 percent of setting
2. Determine a second point on the operating curve.
3. Determine pickup
12. 49T Temperature (RTD) Relay
1. Determine trip resistance
2. Determine reset resistance
13. 50 Instantaneous Overcurrent Relay
1. Determine pickup
2. Determine dropout
3. Determine time delay
14. 51 Time Overcurrent
1. Determine tripping pickup
2. Determine time delays at two points on the time current curve.
15. 55 Power Factor Relay
1. Determine tripping angle.
2. Determine time delay.
16. 59 Overvoltage Relay
1. Determine overvoltage pickup
2. Determine time delay to close the contacts with sudden application of 120 percent of
pickup.
17. 60 Voltage Balance Relay
1. Determine voltage difference to close the contacts with one source at rated voltage.
2. Plot the operating curve for the relay.
18. 63 Transformer Sudden Pressure Relay
1. Determine rate-of-rise or the pickup level of suddenly applied pressure in accordance
with manufacturer’s specifications.
2. Verify operation of the 63 FPX seal-in circuit.
3. Verify trip circuit to remote breaker.
19. 64 Ground Detector Relay
1. Determine maximum impedance to ground causing relay pickup.
20. 67 Directional Overcurrent Relay
1. Determine directional unit minimum pickup at maximum torque angle.
2. Determine closing zone.
3. Determine maximum torque angle.
4. Plot operating characteristics.
5. Determine overcurrent pickup.
6. Determine overcurrent unit time delay at two points on the time current curve.
21. 79 Reclosing Relay
1. Determine time delay for each programmed reclosing interval.
2. Verify lockout for unsuccessful reclosing.
3. Determine reset time
4. Determine close pulse duration.
5. Verify instantaneous overcurrent lockout.
22. 81 Frequency Relay
1. Verify frequency set points.
2. Determine time delay
3. Determine under voltage cut-off.
23. 85 Pilot Wire Monitor
1. Determine overcurrent pickup.
2. Determine undercurrent pickup.
3. Determine pilot wire ground pickup level.
24. 87 Differential
1. Determine operating unit pickup.
2. Determine the operation for each restraint unit.
3. Determine slope.
4. Determine harmonic restraint.
5. Determine instantaneous pickup.
6. Plot operating characteristics for each restraint.
4. System Tests
1. Function tests.
1. Verify that each of the relay contacts performs its intended function in the control scheme
including breaker trip tests, close inhibit tests, and alarm functions. Refer to Section 8.0.
2. In service monitoring.
After the equipment is initially energized, measure magnitude and phase angle of all inputs and
compare to expected values.
5. Test Values
1. When not otherwise specified, use manufacturers recommended tolerance.
2. When critical test points are specified, the relay should be calibrated to those points even
though other test points maybe out of tolerance.
ATS-2003.84
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Electrical Characterization of Organic Electronic Materials and DevicesVon EverandElectrical Characterization of Organic Electronic Materials and DevicesNoch keine Bewertungen
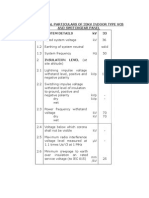
- National Transmission & Despatch Company (NTDC) Limited Pakistan High Voltage and Short Circuit Lab, RawatDokument16 SeitenNational Transmission & Despatch Company (NTDC) Limited Pakistan High Voltage and Short Circuit Lab, RawatAhmad Ali0% (1)
- People Oriented Innovation and DevelopmentDokument28 SeitenPeople Oriented Innovation and DevelopmentshivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Files For YouDokument66 SeitenFiles For YouGi BoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCR700 enDokument24 SeitenLCR700 enTrần Dương Nhật HuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sanwa LCR700Dokument24 SeitenSanwa LCR700Shanon RustoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog & Digital Electronics-14 PDFDokument68 SeitenAnalog & Digital Electronics-14 PDFanuthNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Transformer-ProtectionDokument42 Seiten7 Transformer-Protectionmuaz_aminu1422Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Circuits2 - BMI LabDokument59 SeitenBasic Circuits2 - BMI LabkaranipgrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molded Recloser: User'S ManualDokument24 SeitenMolded Recloser: User'S Manualjulitssa SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLSX - Tu 274Dokument8 SeitenTLSX - Tu 274Hùng MeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTDC Internship ReportDokument17 SeitenNTDC Internship ReportMuhammad Mohsin AbbasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PotM 02 2021 Medium Voltage Breaker Testing ENUDokument5 SeitenPotM 02 2021 Medium Voltage Breaker Testing ENUkegiw15659Noch keine Bewertungen
- CADPHI Test ProceduresDokument7 SeitenCADPHI Test ProceduresJay F. KuizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Executive SummaryDokument33 SeitenExecutive Summaryanandshekhar1885Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11-12 Break Characteristic Tester MSGK-E ManualDokument23 Seiten11-12 Break Characteristic Tester MSGK-E ManualwubinhappydayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mwedc Lab ManualDokument74 SeitenMwedc Lab ManualAllanki Sanyasi RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14vortex Manual PDFDokument83 Seiten14vortex Manual PDFphong dauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 2Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 2FRANCIS BALTAZARNoch keine Bewertungen
- HZ7411 Circuit Breaker Analyzer-User ManualDokument23 SeitenHZ7411 Circuit Breaker Analyzer-User ManualMạnh Nguyễn VănNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System Protection SlidesDokument59 SeitenPower System Protection SlidessajedarefinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20EE504-PE Lab ManualDokument59 Seiten20EE504-PE Lab Manual20EUEE018 - DEEPAK. MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Methods For Dry Type TransformersDokument5 SeitenTest Methods For Dry Type TransformersCihan YasarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rili Paul Casper M. BMC Worksheet 2Dokument4 SeitenRili Paul Casper M. BMC Worksheet 2FRANCIS BALTAZARNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARES Manual V5.0.1en PDFDokument103 SeitenARES Manual V5.0.1en PDFbundang syarifullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scope of WorkDokument3 SeitenScope of WorkShah Aizat RazaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Test Procedures (31121016-000-Gap-00023-000)Dokument155 SeitenAll Test Procedures (31121016-000-Gap-00023-000)Zeeshan Hashmi100% (1)
- 33kV Breaker SpecDokument19 Seiten33kV Breaker SpecBala KumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Testing: Test Order Type of Test Reading Measured inDokument7 SeitenElectrical Testing: Test Order Type of Test Reading Measured inMegan ChaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansi - Scte 44 2010 Test Method For DC Loop ResistenceDokument7 SeitenAnsi - Scte 44 2010 Test Method For DC Loop ResistenceYung SangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Inspection ProcedureDokument17 SeitenElectrical Inspection Proceduredidi sudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- WS2 BMC ...........Dokument3 SeitenWS2 BMC ...........FRANCIS BALTAZARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Em-2 Lab ManualDokument9 SeitenEm-2 Lab Manualsomnath banerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amprobe AC68C User ManualDokument52 SeitenAmprobe AC68C User ManualMiguel CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.LT PanelDokument42 Seiten7.LT PanelDhivagar Namakkal100% (1)
- Basic Electrical Machines (Eceg132) Laboratory Manual: Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringDokument158 SeitenBasic Electrical Machines (Eceg132) Laboratory Manual: Department of Electrical and Computer EngineeringRonan Rojas100% (1)
- PSP Lab ManualDokument21 SeitenPSP Lab Manualakhil100% (1)
- Electrical Inspection ProcedureDokument21 SeitenElectrical Inspection ProcedurebernardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dgca Feb 2014 - Paper 2Dokument8 SeitenDgca Feb 2014 - Paper 2Manish MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dry Type Transformer Testing ManualDokument23 SeitenDry Type Transformer Testing Manualyalewlet tarekeggnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 400 KV Switchyard Testing ScheduleDokument2 Seiten400 KV Switchyard Testing ScheduleBedabyas_dehury100% (2)
- MS2108A English ManualDokument24 SeitenMS2108A English ManualiconeykregNoch keine Bewertungen
- MFJ 269 CalibrationDokument7 SeitenMFJ 269 CalibrationclistenesrosasNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEO Orals On Marine Electro Technology Function 5Dokument19 SeitenMEO Orals On Marine Electro Technology Function 5Rajeev ValunjkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Device Manual (NEC-354) : Department of Electronics & Communication EngineeringDokument58 SeitenElectronics Device Manual (NEC-354) : Department of Electronics & Communication EngineeringE-Biz NetworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commissioning of Electrical EquipmentDokument5 SeitenCommissioning of Electrical Equipmentburaqtech49Noch keine Bewertungen
- MFJ MFJ-269 Ant Analyser Calibration PDFDokument0 SeitenMFJ MFJ-269 Ant Analyser Calibration PDFchaparalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tadano Load Sensor Repair ManualDokument11 SeitenTadano Load Sensor Repair ManualRaja SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- BKR Timing TestDokument11 SeitenBKR Timing TestNaveedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aq SerieDokument76 SeitenAq Serieharold_anilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual ECE132Dokument42 SeitenLab Manual ECE132intustan lee100% (8)
- MAS345Dokument31 SeitenMAS345Abrahan CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Babani 265 More Advanced Uses of The MultimeterDokument98 SeitenBabani 265 More Advanced Uses of The Multimeterpkrajni100% (3)
- 3 HV Sub Station Maint - Tranasformer Part2Dokument121 Seiten3 HV Sub Station Maint - Tranasformer Part2matshah9889Noch keine Bewertungen
- Meterk MK6000 True RMS Clamp MeterDokument28 SeitenMeterk MK6000 True RMS Clamp MeterAlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansi Scte 04-2007Dokument9 SeitenAnsi Scte 04-2007liuyx866Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12 FDP 11 Ec 306 Electronics Circuits Lab TotalDokument459 Seiten12 FDP 11 Ec 306 Electronics Circuits Lab Totalkrish104411Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics—From Theory Into Practice: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesVon EverandElectronics—From Theory Into Practice: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Analog Circuit Techniques: With Digital InterfacingVon EverandAnalog Circuit Techniques: With Digital InterfacingNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASME SEC IX - Welding Procedure and PerfDokument44 SeitenASME SEC IX - Welding Procedure and Perfstefanie_1980100% (2)
- ASME SEC IX - Welding Procedure and PerfDokument44 SeitenASME SEC IX - Welding Procedure and Perfstefanie_1980100% (2)
- Emergency Shower and Eyewash Station: Your Security IS MY PromiseDokument2 SeitenEmergency Shower and Eyewash Station: Your Security IS MY PromiseHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICAM - Toolkit - V1-0 FDDDokument22 SeitenICAM - Toolkit - V1-0 FDDHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notice of Readiness of Mechanical Completion: Pasar CorporationDokument12 SeitenNotice of Readiness of Mechanical Completion: Pasar CorporationHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Copper Telluride Tank (TK-V32) PDFDokument4 SeitenCopper Telluride Tank (TK-V32) PDFHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformers, Liquid-Filled: 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionDokument4 SeitenTransformers, Liquid-Filled: 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformers, Dry Type, Air-Cooled, Low Voltage, SmallDokument2 SeitenTransformers, Dry Type, Air-Cooled, Low Voltage, SmallHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Breakers, Air, Insulated-CaseMolded-CaseDokument3 SeitenCircuit Breakers, Air, Insulated-CaseMolded-CaseHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformers, Liquid-Filled: 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionDokument4 SeitenTransformers, Liquid-Filled: 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switches-Air, Low VoltageDokument2 SeitenSwitches-Air, Low VoltageHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switchgears and Switchboard AssembliesDokument3 SeitenSwitchgears and Switchboard AssembliesHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrument Transformers: 1. 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionDokument2 SeitenInstrument Transformers: 1. 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformers, Liquid-Filled: 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionDokument4 SeitenTransformers, Liquid-Filled: 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformers, Dry Type, Air-Cooled, LargeDokument4 SeitenTransformers, Dry Type, Air-Cooled, LargeHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switches Air, Medium - and High Voltage, OpenDokument3 SeitenSwitches Air, Medium - and High Voltage, OpenHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformers, Liquid-Filled: 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionDokument4 SeitenTransformers, Liquid-Filled: 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Breakers, Air, Medium-VoltageDokument3 SeitenCircuit Breakers, Air, Medium-VoltageHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrument Transformers: 1. 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionDokument2 SeitenInstrument Transformers: 1. 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cables, Medium and High VoltageDokument4 SeitenCables, Medium and High VoltageHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Breakers, Air, Low-Voltage PowerDokument3 SeitenCircuit Breakers, Air, Low-Voltage PowerHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Switchers: 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionDokument3 SeitenCircuit Switchers: 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Breakers SF6: 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionDokument3 SeitenCircuit Breakers SF6: 1. Visual and Mechanical InspectionHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taran Preet Singh (Ms12044)Dokument23 SeitenTaran Preet Singh (Ms12044)Honeylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide NanoparticlesDokument17 SeitenSynthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide NanoparticlesHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aligning of Seawater Pump Motor (Pu-W84)Dokument40 SeitenAligning of Seawater Pump Motor (Pu-W84)Honeylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mercury PoisoningDokument38 SeitenMercury PoisoningHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lead PoisoningDokument20 SeitenLead PoisoningHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide NanoparticlesDokument17 SeitenSynthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide NanoparticlesHoneylyn IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- POWER LAB Manual PDFDokument82 SeitenPOWER LAB Manual PDFHamda KhalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternating Current Field Measurement Level 1 Course (ACFM L1)Dokument357 SeitenAlternating Current Field Measurement Level 1 Course (ACFM L1)susheel100% (2)
- 330 ManualDokument83 Seiten330 Manualgedeus8072Noch keine Bewertungen
- Discharge Lamps EV. DHLS EVZDokument8 SeitenDischarge Lamps EV. DHLS EVZapptilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wavepackets and Dispersion: 1 Wave PacketsDokument8 SeitenWavepackets and Dispersion: 1 Wave PacketsRaphael BaltarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Leakage FieldDokument13 SeitenMagnetic Leakage FieldNjkt CADNoch keine Bewertungen
- QS Um 354GB GB WW 1104-3Dokument202 SeitenQS Um 354GB GB WW 1104-3NhậtQuangNguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classical Dynamics: Example Sheet 3: A Ab B ADokument3 SeitenClassical Dynamics: Example Sheet 3: A Ab B A김승수Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class:7 Subject: Science Topic: Electric Current and Its EffectsDokument24 SeitenClass:7 Subject: Science Topic: Electric Current and Its EffectsManpreet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Test Distance Relay 7SA522 PDFDokument55 SeitenHow To Test Distance Relay 7SA522 PDFBalaji100% (1)
- A More Exact Linear FMCW Radar Signal Model For Simultaneous Range-Velocity EstimationDokument5 SeitenA More Exact Linear FMCW Radar Signal Model For Simultaneous Range-Velocity EstimationRobert MujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC-DC - Fabrication 2Dokument191 SeitenAC-DC - Fabrication 2VinayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- EI 550 ManualDokument110 SeitenEI 550 Manualgiorg_dan-1100% (1)
- US7676053Dokument12 SeitenUS7676053Morena SlpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Flywheel Based Energy Storage SystemsDokument6 SeitenReview of Flywheel Based Energy Storage SystemsCRISTIANO NICCOLO GERONIMO100% (1)
- Mechanical Vibrations by V.P. Singh PDFDokument131 SeitenMechanical Vibrations by V.P. Singh PDFmayilsvhec70% (10)
- Cold Fusion Mechanism of Bond CompressionDokument9 SeitenCold Fusion Mechanism of Bond CompressionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load-Independent Proportional Valve Type PVG 120: CatalogueDokument24 SeitenLoad-Independent Proportional Valve Type PVG 120: CataloguemagzigioNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB - Electrical Transmission and Distribution Reference BookDokument853 SeitenABB - Electrical Transmission and Distribution Reference BookEduardo Antunes da Luz100% (11)
- Cherry E Series: General Purpose Double Pole SwitchesDokument1 SeiteCherry E Series: General Purpose Double Pole SwitchesMilton UrrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Value Based Questions Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter PDFDokument39 SeitenPhysics Value Based Questions Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter PDFMohammad HuzaifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of A TransformerDokument3 SeitenParts of A TransformerCoreen ElizaldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micom p139 Over Current RelayDokument4 SeitenMicom p139 Over Current Relayanoop_jan139885100% (1)
- Eaton 066166 EMT6 en - GBDokument3 SeitenEaton 066166 EMT6 en - GBSiva RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial MEP1553 - Insulation CoordinationDokument4 SeitenTutorial MEP1553 - Insulation CoordinationSharin Bin Ab GhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Question Bank Fo RMV Unit V Continuous Systems 06 05 2018 Additional PDFDokument4 Seiten05 Question Bank Fo RMV Unit V Continuous Systems 06 05 2018 Additional PDFNABIL HUSSAIN0% (1)
- Dahlander WindingDokument1 SeiteDahlander WindingSreekanth Raveendran50% (2)
- Basic PhysicsDokument140 SeitenBasic PhysicsdeepakaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- AN001-Control Design of 100-kW PMSM DriveDokument9 SeitenAN001-Control Design of 100-kW PMSM DriveRudhi KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen