Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Concept Map 2
Hochgeladen von
api-335772646Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Concept Map 2
Hochgeladen von
api-335772646Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
English
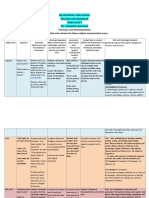
CONCEPT MAP Makin’ Myths: with reference to existing myths, legends and
explanations of the Sun, Earth and Moon, create your own
Maths story that explains how they came to be and their relationship
My daily routine: Complete a visual storyboard of your Religious Education / Spiritual Education to each other.
daily routine that is matched to timescales for the Plan, draft and publish imaginative, informative and persuasive
Sun and light: God made light on the first day but didn’t make the Sun and Stars until
rotation of Earth texts demonstrating increasing control over text structures and
the third day. Explore existing possible explanations for this and devise some of your
Tell time to the minute and investigate the relationship language features and selecting print,and multimodal elements
own.
between units of time (ACMMG062) appropriate to the audience and purpose (ACELY1682)
Traditional understandings of Sun, Earth and Moon: Study and compare contemporary
Measuring shadows: Measure the length of a stationary Poem/jingle: Create a poem or a jingle in a small group with
understandings of the Sun, Earth and Moon with those of various religions and cultures
schoolyard object at different points of the day using rhyme and rhythm that teaches the listener about Earth’s
such as Indigenous dream time stories, Christianity and mythology. Create a roleplay
metric units of length. rotation, the Sun and/or the moon. Perform for the class.
that demonstrates traditional understandings such as Ra (sun God) sailing across the sky.
Measure, order and compare objects using familiar Create texts that adapt language features and patterns
metric units of length, mass and capacity (ACMMG061) encountered in literary texts, for example characterisation,
Wanted: Spheres and Circles! Create a ‘wanted’ poster rhyme, rhythm, mood, music, sound effects and dialogue
for imperfect spheres (Moon and Earth) and circles Concept: Night and day Year: 3 (ACELT1791)
(Sun) that highlights key features/description of the Other activities: word walls, t-charts, KWL charts, exit tickets,
shape e.g. No corners, curved edge. Etc. Make models
Term: 3 Weeks: 1 – 3 of 10 week unit presentations, verbal recordings.
of three-dimensional objects and describe key features
(ACMMG063)
Earth’s shadow: Using black and coloured card, model Health & Physical Education
©The University of Notre Dame 2010 developed by C McGunnigle
Science / Technology & Enterprise
and represent half of Earth in shadow and half in light Shadow tag: played as either whole class or pairs, students try catch other students’ Chemistry: Make predictions about which of several
Model and represent unit fractions including 1/2, 1/4, shadows. Locomotor skills: run (ACPMP043) objects will melt/change in state first when left out in the
1/3, 1/5 and their multiples to a complete whole Sun Safety: Make links between the Sun’s position in the sky and the UV index. Teach the sun (e.g. icecream, iceblock, plastic etc). Observe and
(ACMNA058) importance of sun safety, protective clothing and sunscreen. compare results to predictions
Other links: Graphing, data collection and interpretation Sun damage experiment: create a controlled experiment with newspaper, paper and A change of state between solid and liquid can be caused
tissue paper. Have half of the materials exposed to the sun and the other half protected. by adding or removing heat (ACSSU046)
Come back in a few hours and observe the damage to the materials caused by the sun. Biology: Label and annotate a diagram of a flower and
Geography Actions in daily routines that promote health, safety and wellbeing (ACPPS036) highlight how it photosynthesizes and uses sunlight
Climate and weather: Colour in a word map, Living things can be grouped on the basis of observable
highlighting the main climatic zones of the History The Arts features and can be distinguished from non-living things
world. Link new understandings to Earth’s Historical understandings: Research various Visual arts (ACSSU044)
rotation on its axis and the effect it has on historical astronomers such as Plato, Galileo, Aboriginal shelters: Make a model of a traditional Southern 3D modelling: Create a 3D paper maiche model that
weather and the climatic zones. Aristotle and Nicolaus Copernicus and write a Australia Indigenous shelter out of twigs and leaves that takes demonstrates the movement and relative sizes of the
The difference between climate and weather, report on their understandings of the Earth, advantage of the Sun’s path and prevents the cold Southern wind Earth, Sun and Moon.
the main climatic zones of the world (e.g. Sun and Moon and how they came to their entering. Monitor and adjust. Develop and communicate ideas using labelled drawings
equatorial, tropical, arid, temperate) and the conclusions. Exploration of artwork from other cultures, such as styles and and appropriate technical terms (WATPPS17)
similarities and differences between the Chinese New Year and Moon Festivals: Create symbols of Indigenous Australian and Asian cultures Australian Sun: The light and heat given off by the Sun is
climates of different places (ACHASSK068) a calendar year for Earth’s cycle around the (ACAVAM110) very hot in Australia, too hot for some of our crops!
Indigenous seasons: Study and compare the Sun and another for Lunar months, highlight Media Arts Design a system that can be used by our farmers to
six Aboriginal Australian seasons and match and discuss they are different as they are News reporting: combine images and text with voice over to reduce the sun that is cost effective.
them and their defining characteristics to the based off different cycles. create a news story reporting on breaking news: That scientists Create a sequence of steps to solve a given task
four-season system typically used. The historical origins and significance of have discovered that the Earth rotates the Sun. (WATPPS16)
Seasons: Annotate an image of the world to celebrations and commemorations in other Exploration of how sequenced images, audio and text can be Types of food and fibre produced in different
show what season it is for the rest of the places around the world (e.g. Bastille Day in used to tell a story or convey a message (ACAMAM058) environments, cultures or time periods, including the
globe when it is summer in Australia. France, Independence Day in the USA; and Dance/drama equipment used to produce or prepare them
The location of Australia's neighbouring those observed in Australia, such as Chinese Create a performance piece/representation of our solar system (ACTDEK012)
countries and their diverse natural New Year, Christmas Day, Diwali, Easter, which demonstrates the relative size and movement of the Earth, OR
characteristics and human characteristics Hanukkah, the Moon Festival, Ramadan) Sun and Moon. Create an anti-UV greenhouse using the provided
(ACHASSK067) (ACHASSK065) Exploration, improvisation and selection of movement ideas to materials
create a dance that has a narrative structure (ACADAM005) Select, and safely use, appropriate components with
given equipment to make a solution (WATPPS18)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Unit Planner Teacher/Team: Sarah Contin: Understanding-Learning OutcomesDokument15 SeitenUnit Planner Teacher/Team: Sarah Contin: Understanding-Learning Outcomesapi-405445275Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edtpa Lesson Plan Guide LPG Carter 2Dokument5 SeitenEdtpa Lesson Plan Guide LPG Carter 2api-653779848Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science: Planning Document University of Notre DameDokument13 SeitenScience: Planning Document University of Notre Dameapi-450567526Noch keine Bewertungen
- Australian Curriculum Links Specific Lesson Objective Assessment (What & How) Teaching & Learning Experiences ResourcesDokument5 SeitenAustralian Curriculum Links Specific Lesson Objective Assessment (What & How) Teaching & Learning Experiences Resourcesapi-312379725Noch keine Bewertungen
- Day and Night Unit PlansDokument4 SeitenDay and Night Unit Plansapi-372386525Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan ClilDokument7 SeitenLesson Plan ClilAlexandra ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ict LessonsDokument4 SeitenIct Lessonsapi-450705198Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guereque Thematic UnitDokument3 SeitenGuereque Thematic Unitapi-632150632Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map: (Option 1)Dokument6 SeitenConcept Map: (Option 1)api-359195305Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map Bronwyn LeunigDokument1 SeiteConcept Map Bronwyn Leunigapi-459465715Noch keine Bewertungen
- FPDDokument5 SeitenFPDapi-431984665Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concept MapDokument1 SeiteConcept Mapapi-459338702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unpacked Skill Unpacked Concept ContextDokument3 SeitenUnpacked Skill Unpacked Concept Contextapi-239563463Noch keine Bewertungen
- TERM/WEEKS: 4/3 Year Level: 5 Learning Area/Topic: ScienceDokument5 SeitenTERM/WEEKS: 4/3 Year Level: 5 Learning Area/Topic: Scienceapi-389638207Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map 1Dokument1 SeiteConcept Map 1api-451268851Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Sundial - Grade 6 Lesson PlansDokument11 SeitenThe Human Sundial - Grade 6 Lesson PlansGalanopoulosApostoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curiosity: The Story of A Mars Rover Teachers' GuideDokument2 SeitenCuriosity: The Story of A Mars Rover Teachers' GuideCandlewick PressNoch keine Bewertungen
- TERM/WEEKS: 1-1 Year Level: 5 LEARNING AREA/TOPIC: Science (ACSSU078)Dokument5 SeitenTERM/WEEKS: 1-1 Year Level: 5 LEARNING AREA/TOPIC: Science (ACSSU078)api-450699852Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geography-Unit-Plan 3Dokument16 SeitenGeography-Unit-Plan 3api-388943110Noch keine Bewertungen
- Web First Nation Tipi Symbols Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenWeb First Nation Tipi Symbols Lesson Planapi-699407674Noch keine Bewertungen
- Template ClilDokument5 SeitenTemplate ClilangelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ST Josephs Waroona Geography Planning Year One - ReviewedDokument9 SeitenST Josephs Waroona Geography Planning Year One - Reviewedapi-350667498Noch keine Bewertungen
- Moon and Shadows Day 2Dokument3 SeitenMoon and Shadows Day 2api-399894465Noch keine Bewertungen
- WHLP - May 15 - 19Dokument4 SeitenWHLP - May 15 - 19CRISTINE RAYNESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explore Our Solar System What Are Some Characteristics of Your Favorite Planet? 2nd GradeDokument4 SeitenExplore Our Solar System What Are Some Characteristics of Your Favorite Planet? 2nd Gradeapi-396599947Noch keine Bewertungen
- Walk 1Dokument2 SeitenWalk 1api-574802089Noch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT PLAN - Social Studies (Geography Content) NAME OF TEACHER: Sati S. Sahadeo-Bhola Class: Unit: The Physical Earth and Human InteractionDokument11 SeitenUNIT PLAN - Social Studies (Geography Content) NAME OF TEACHER: Sati S. Sahadeo-Bhola Class: Unit: The Physical Earth and Human Interactionapi-552889757Noch keine Bewertungen
- Block PlanDokument3 SeitenBlock Planapi-354529334Noch keine Bewertungen
- Breemiller FulllessonDokument9 SeitenBreemiller Fulllessonapi-349571958Noch keine Bewertungen
- Overview Concept Map FPDDokument13 SeitenOverview Concept Map FPDapi-409519942Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Assessment Reporting RecordingDokument19 SeitenLesson Plan Assessment Reporting Recordingapi-372230733Noch keine Bewertungen
- FPD Lesson 3Dokument2 SeitenFPD Lesson 3api-408800981Noch keine Bewertungen
- The OneDokument6 SeitenThe Oneapi-450908062Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Final Copy) Compiled Study Material Class VIII - EnglsihDokument165 Seiten(Final Copy) Compiled Study Material Class VIII - EnglsihKPOP IS LIFENoch keine Bewertungen
- English Assignment 3Dokument7 SeitenEnglish Assignment 3api-261245238Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solar System Choice BoardDokument2 SeitenSolar System Choice Boardapi-240468538Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concept MapDokument1 SeiteConcept Mapapi-451196897Noch keine Bewertungen
- FPD Lesson 1Dokument3 SeitenFPD Lesson 1api-408800981Noch keine Bewertungen
- CAORES REYMARK V.BEED2BLK.53 - FINAL REQUIREMENT IN TEGr102 REVISED LESSON PLAN 1Dokument4 SeitenCAORES REYMARK V.BEED2BLK.53 - FINAL REQUIREMENT IN TEGr102 REVISED LESSON PLAN 1Sherrymae MasanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powerful Social Studies Lesson Plan OutlineDokument14 SeitenPowerful Social Studies Lesson Plan Outlineapi-302197375Noch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Science 12Dokument2 SeitenEarth Science 12Lester EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept MapDokument1 SeiteConcept Mapapi-408787954Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 5 Science: Scsa LinksDokument2 SeitenYear 5 Science: Scsa Linksapi-444625626Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Grade World Geography Lesson Plans Week 4Dokument8 Seiten8th Grade World Geography Lesson Plans Week 4christopher salberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept MapDokument1 SeiteConcept Mapapi-566850795Noch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Science FPDDokument10 SeitenPrimary Science FPDapi-451107029Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yr5 Jan-Feb Overview 2023 3Dokument1 SeiteYr5 Jan-Feb Overview 2023 3ayaabouaufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interdisciplinary Learning WalkerDokument10 SeitenInterdisciplinary Learning Walkerapi-521335305Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acción Didáctica 5th Grade May - July 2022Dokument7 SeitenAcción Didáctica 5th Grade May - July 2022Haz Antonio Obando GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- FPD Sci 2Dokument4 SeitenFPD Sci 2api-389651191Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9th Curriculum Guide A - BDokument10 Seiten9th Curriculum Guide A - BmayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demo Comets Asteroids and MeteorsDokument2 SeitenDemo Comets Asteroids and Meteorsgrace roma khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 MYP Course of Study 1Dokument20 SeitenGrade 8 MYP Course of Study 1inaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forward Planning DocumentsDokument7 SeitenForward Planning Documentsapi-451064185Noch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Science FPD 5esDokument9 SeitenPrimary Science FPD 5esapi-483301246Noch keine Bewertungen
- Student Copy of Week of 9 7 2Dokument4 SeitenStudent Copy of Week of 9 7 2api-442784864Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integration Concept Map Science Year 5 Chemical SciencesDokument15 SeitenIntegration Concept Map Science Year 5 Chemical Sciencesapi-483174743Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map SubmissionDokument1 SeiteConcept Map Submissionapi-562307312Noch keine Bewertungen
- Broadening The CanonDokument7 SeitenBroadening The Canonapi-610747915Noch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Science FPD 5esDokument12 SeitenPrimary Science FPD 5esapi-335772646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment StratsDokument1 SeiteAssessment Stratsapi-335772646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Science FPDDokument9 SeitenPrimary Science FPDapi-335772646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sundials Design BriefDokument1 SeiteSundials Design Briefapi-335772646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 3 OverviewsDokument1 SeiteYear 3 Overviewsapi-335772646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Communicate Positively With Your PassengersDokument5 SeitenCommunicate Positively With Your PassengersAARAVNoch keine Bewertungen
- If Lightning Strikes Close To You Would You Go Blind - QuoraDokument1 SeiteIf Lightning Strikes Close To You Would You Go Blind - QuoraEm RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of ContentsDokument78 SeitenTable of ContentsTitli KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Grammar Lab A1-A2 (Trascinato) 5Dokument7 SeitenMy Grammar Lab A1-A2 (Trascinato) 5Andrea MarchettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 8 Performance Task 3Dokument1 SeiteScience 8 Performance Task 3Alvin Gultia67% (3)
- The Lord of The East Wind The Catholic Biblical QuDokument244 SeitenThe Lord of The East Wind The Catholic Biblical QuBelchior TobiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS 7 Exercise 1Dokument5 SeitenCS 7 Exercise 1Kish Lucky EstabilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- No Fear Shakespeare The Tempest PDFDokument69 SeitenNo Fear Shakespeare The Tempest PDFRagulNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 EMDAT ReportDokument8 Seiten2021 EMDAT ReportNirdeshKumarSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPL Meteorology SyllabusDokument15 SeitenCPL Meteorology SyllabusBhavesh GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movement Planets in Solar SystemDokument36 SeitenMovement Planets in Solar SystemAlva SevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical System CycloneDokument36 SeitenElectrical System CycloneNishant NagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modelling Climate and Societal ResiliencDokument17 SeitenModelling Climate and Societal ResilienccctNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journalistic WritingDokument3 SeitenJournalistic WritingMaddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist For Painting Work of Structural SteelDokument3 SeitenChecklist For Painting Work of Structural Steelajit karandikar78% (9)
- Source A: Insert To Paper 1Dokument4 SeitenSource A: Insert To Paper 1Eva AwuyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- RanchidistwxDokument4 SeitenRanchidistwxMC Ranchi ImdNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSG THPT Mock Exam 01Dokument18 SeitenHSG THPT Mock Exam 01eros061107Noch keine Bewertungen
- Malinche - Laura Esquivel: 21stlit ReviewerDokument3 SeitenMalinche - Laura Esquivel: 21stlit ReviewerAdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen: LOCK: Storm Warning ExcerptDokument27 SeitenGen: LOCK: Storm Warning ExcerptI Read YANoch keine Bewertungen
- Cement Based PaintsDokument16 SeitenCement Based PaintsMohd SalahuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Freshwater Fishing Secrets North American Fishing Annas ArchiveDokument168 SeitenFreshwater Fishing Secrets North American Fishing Annas ArchiveCaian MoreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advancing Research On Compound Weather and ClimateDokument17 SeitenAdvancing Research On Compound Weather and Climatewaqar.ulhassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTSB ReportDokument9 SeitenNTSB ReportNewsTeam20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curing Cement PlasterDokument3 SeitenCuring Cement PlasterChristian LlagasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Easy Steps To Better Detailing: The Complete GuideDokument49 Seiten5 Easy Steps To Better Detailing: The Complete GuideShaina aprilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final2 RoundDokument14 SeitenFinal2 RoundJeth J LungayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Riga ATCC1Dokument43 SeitenRiga ATCC1Vakaris DobrovolskasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Research HWDokument6 SeitenLegal Research HWGale Calaycay LaenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Aggregates: Standard Specification ForDokument11 SeitenConcrete Aggregates: Standard Specification ForEdgardo Humberto GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen