Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics: Crust Mantle Plate Boundaries Thrust Faults Oceanic Spreading Ridges Transform Faults
Hochgeladen von
Faye Andrea FranciscoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics: Crust Mantle Plate Boundaries Thrust Faults Oceanic Spreading Ridges Transform Faults
Hochgeladen von
Faye Andrea FranciscoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Plate Tectonics
plate tectonics
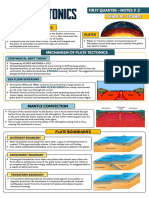
Plate Tectonics is the theory supported by a wide range of evidence that considers
the earth's crust and upper mantle to be composed of several large, thin, relatively rigid
plates that move relative to one another. Slip on faults that define the plate
boundaries commonly results in earthquakes. Several styles of faults bound the plates,
including thrust faults along which plate material is subducted or consumed in the
mantle, oceanic spreading ridges along which new crustal material is produced,
and transform faults that accommodate horizontal slip (strike slip) between adjoining
plates.
Mantle convection currents, ridge push and slab pull are three of the forces that have
been proposed as the main drivers of plate movement
There are a number of competing theories that attempt to explain what drives the
movement of tectonic plates. Three of the forces that have been proposed as the main
drivers of tectonic plate movement are:
-mantle convection currents— warm mantle currents drive and carry plates of
lithosphere along a like a conveyor belt;
-ridge push (buoyant upwelling mantle at mid-ocean ridges) — newly-formed
plates at oceanic ridges are warm, and so have a higher elevation at the oceanic
ridge than the colder, more dense plate material further away; gravity causes the
higher plate at the ridge to push away the lithosphere that lies further from the
ridge;
-slab pull — older, colder plates sink at subduction zones, because as they cool,
they become more dense than the underlying mantle. The cooler sinking plate
pulls the rest of the warmer plate along behind it.
Recent research has shown that the major driving force for most plate movement is
slab pull, because the plates with more of their edges being subducted are the faster-
moving ones. However ridge push is also presented in recent research to be a force
that drives the movement of plates.
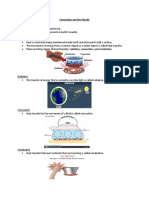
What is Convection Current
A convection current is a process which involves the movement of energy from
one place to another. Convection currents tend to move a fluid or gas particles from
one place to another. These are created as a result of the differences occurring within
the densities and temperature of a specific gas or a fluid
mportance of Convection Current
What are convection currents in the earth?
Convection currents are the movement of fluid as a result of differential heating
or convection. In the case of the Earth, convection currents refer to the motion of
molten rock in the mantle as radioactive decay heats up magma, causing it to rise and
driving the global-scale flow of magma
What effect does convection have on Earth's interior?
Convection in the mantle is the same as convection in a pot of water on a
stove. Convection currents within Earth's mantle form as material near the core heats
up. As the core heats the bottom layer of mantle material, particles move more rapidly,
decreasing its density and causing it to rise.
How do we use convection in everyday life?
Everyday Examples of Convection
1. Boiling water - The heat passes from the burner into the pot, heating the water at
the bottom. ...
2. Radiator - Puts warm air out at the top and draws in cooler air at the bottom.
3. Steaming cup of hot tea - The steam is showing heat being transfered into the
air.
What do convection currents cause?
Convection currents are the result of differential heating. Lighter (less dense), warm
material rises while heavier (more dense) cool material sinks. It is this movement that
creates circulation patterns known as convection currents in the atmosphere, in water,
and in the mantle of Earth.
How does convection affect us?
Convection currents are part of what drives global circulation of the Earth's
atmosphere. ... Convection currents in the air and sea lead to weather. Magma in the
Earth's mantle moves in convection currents. The hot core heats the material above it,
causing it to rise toward the crust, where it cools
Why do convection currents cause plates to move?
Plates at our planet's surface move because of the intense heat in the Earth's core
that causes molten rock in the mantle layer to move. It moves in a pattern called
a convection cell that forms when warm material rises, cools, and eventually sink
down. As the cooled material sinks down, it is warmed and rises again
What happens when tectonic plates move?
When the plates move they collide or spread apart allowing the very hot molten
material called lava to escape from the mantle. When collisions occur they produce
mountains, deep underwater valleys called trenches, and volcanoes.
What will happen if the Earth has no tectonic plates?
Without tectonic forces, our lives will be greatly changed. Let's look at the social
implications first. Without plate tectonics, there will be far less human deaths from
natural disasters such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and even tsunamis.
There would be much less destruction to the Earth.
What happens if plate tectonics stopped?
If all volcanism stops, so does sea floor spreading—and thus plate tectonics as well.
And if plate tectonics stops, Earth eventually (through erosion) loses most or all of the
continents where most terrestrial life exists. In addition, CO2 is removed from the
atmosphere via weathering, causing our planet to freeze
Will plate tectonics ever stop?
The computer model showed that in Earth's youth, its interior was too hot and runny to
push around the giant chunks of crust. After the planet's interior cooled for some 400
million years, tectonic plates began shifting and sinking. This process was stop-and-
go for about 2 billion years
What would happen if the convection currents stopped?
Answer 1: If all convection currents on Earth stopped that would be a natural
disaster. The amount of heat which the sun radiates at us sets the temperature of the
Earth's surface. ... So if convection completely stopped the high and low
temperatures would force people and animals to move away from the poles and
equator
Driving Forces of Plate Motion
Lithospheric plates are part of a planetary scale thermal convection system. The
energy source for plate tectonics is Earth’s internal heat while the forces moving the
plates are the “ridge push” and “slab pull” gravity forces.
It was once thought that mantle convection could drive plate motions. Early textbooks
showed mantle convection cells, like in a beaker of hot liquid on a Bunson burner,
pushing plates along from below. Convection in the mantle, certainly plays a role, but
doesn’t explain how some plates move faster than the convective currents beneath
them. What would cause that? Current dynamic models have plates moving as part of
a gravity-driven convection system that pushes young hot plates away from spreading
ridges and pulls old cold plates down into subduction zones.
The Earth and Tectonic Plates
Tectonic shift is the movement of the plates that make up Earth's crust. ... The
heat from radioactive processes within the planet's interior causes the plates to move,
sometimes toward and sometimes away from each other.
This movement is called plate motion, or tectonic shift.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksVon EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- EARTHS-MECHANISM PPTDokument15 SeitenEARTHS-MECHANISM PPTLourdes Largado100% (1)
- This Is Your Presentation TitleDokument10 SeitenThis Is Your Presentation Titleken arellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 Quarter 1 Lesson 8Dokument2 SeitenScience 10 Quarter 1 Lesson 8ViaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module in Science 10-Week 6Dokument8 SeitenModule in Science 10-Week 6daisy sorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convection Currents: What Is A Current?Dokument8 SeitenConvection Currents: What Is A Current?Ravi MothoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plate Tectonics GR 10Dokument2 SeitenPlate Tectonics GR 10musaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qim 7Dokument7 SeitenQim 7Mae JeminaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10Dokument1 SeiteScience 10Glaidylle Jade PagasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portfolio in Earth Sci - OrigDokument12 SeitenPortfolio in Earth Sci - OrigKATHYREN GERASMIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Teoría de Tectónica de PlacasDokument4 SeitenTeoría de Tectónica de PlacasANDRES CAMILO LASSO PAEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 Week 7 For PrintingDokument5 SeitenScience 10 Week 7 For PrintingDennis PacursaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plate Tectonics: Second GradeDokument12 SeitenPlate Tectonics: Second GradeSilvara Rifu RinamuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lebs ScienceDokument9 SeitenLebs ScienceVince Casison Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 01Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 01Sahir Aly BadarpuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEO-151 Assignment 1Dokument4 SeitenGEO-151 Assignment 1Valo GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AAAAADokument5 SeitenAAAAAlorence caneteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 - Science WW2: Dominican College of Tarlac, IncDokument3 SeitenGrade 10 - Science WW2: Dominican College of Tarlac, IncKerol Arkie TarrielaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReflectionDokument2 SeitenReflectionJoy MalibiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akka 1Dokument4 SeitenAkka 1Priyanka PatheparapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pangea As A Result of Plate Tectonic MDokument8 SeitenPangea As A Result of Plate Tectonic MAlya Zahira Aziz 06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanisms of Plate MotionsDokument5 SeitenMechanisms of Plate MotionsJeric OliverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Lecture 05Dokument7 SeitenEarth Lecture 05cheryl tayasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plate Tectonics 1Dokument1 SeitePlate Tectonics 1api-297681510Noch keine Bewertungen
- Earthquake Engineering ReportDokument21 SeitenEarthquake Engineering ReportEsrael Corporal BalusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson in Seafloor Spreading Magnetic Reversal and Theoryr of Plate TectonicDokument3 SeitenLesson in Seafloor Spreading Magnetic Reversal and Theoryr of Plate TectonicChristine Mae Francisco BartoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describe The Possible Causes of Plate MovementDokument16 SeitenDescribe The Possible Causes of Plate MovementmtchqnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Find The EpicenterDokument14 SeitenFind The EpicenterSam V.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering SeismologyDokument60 SeitenEngineering SeismologyprashmceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemically, The Layers of Earth Are As Follow: Crust, Upper Mantle, LowerDokument8 SeitenChemically, The Layers of Earth Are As Follow: Crust, Upper Mantle, LowerMarg EraesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Written Report in Science Group 4Dokument11 SeitenWritten Report in Science Group 4Stephen Tracy TabamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PlateDrivers 220110 noTimeCodesDokument2 SeitenPlateDrivers 220110 noTimeCodesOlugbemiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Anatomy of A Tectonic PlateDokument2 SeitenThe Anatomy of A Tectonic PlateIan Vincent CadisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science g10Dokument4 SeitenScience g10Julia Amor DestuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal ConvectionDokument3 SeitenThermal ConvectionOktavian SatriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tectonic PlatesDokument30 SeitenTectonic Platesarmelinda carranzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inbound 4455879487521745204Dokument1 SeiteInbound 4455879487521745204Jezell Ann Marie YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convection and The Mantle - Gr. 6 Lesson NotesDokument2 SeitenConvection and The Mantle - Gr. 6 Lesson NotesJung Ahn HongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plate Tectonics 1 WorksheetDokument2 SeitenPlate Tectonics 1 Worksheetapi-28268810533% (3)
- 4.earth's Internal HeatDokument3 Seiten4.earth's Internal HeatShekaina Faith Cuizon Lozada100% (1)
- Earth's MechanismDokument26 SeitenEarth's MechanismMARITES DURANGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes 2 - Plate TectonicsDokument1 SeiteNotes 2 - Plate TectonicsSabrina May LabradorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 - Convection & Reynolds NumberDokument19 Seiten11 - Convection & Reynolds NumberMahir MahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10Dokument27 SeitenScience 10Matet HidalgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convection Current PamphletDokument3 SeitenConvection Current PamphletMaycee ʚĭɞNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Environmental Sciences: Submitted To: Ma'am Rabia Shezadi Submitted By: Maryam AsgharDokument6 SeitenDepartment of Environmental Sciences: Submitted To: Ma'am Rabia Shezadi Submitted By: Maryam AsgharKOKKOOKNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Turbulent Earth I. Questions To Pose: An Uneasy PlanetDokument32 SeitenThe Turbulent Earth I. Questions To Pose: An Uneasy PlanetsshoeburrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade10 Lesson 4Dokument21 SeitenGrade10 Lesson 4Ka KlasmeytNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plate Tectonics and Seismography Class 7.5Dokument27 SeitenPlate Tectonics and Seismography Class 7.5Monica SreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convection and The MantleDokument49 SeitenConvection and The MantlesalmeohenzgabryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Quarter 1 - Week 2 Earth and Spaces Geological PhenomenaDokument57 SeitenLearning Quarter 1 - Week 2 Earth and Spaces Geological PhenomenaCely Marie VillarazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seafloor Spreading: Geomagnetic ReversalsDokument6 SeitenSeafloor Spreading: Geomagnetic Reversalsprincess laraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Engineering GeologyDokument84 SeitenIntroduction To Engineering GeologyTan U-ShangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer 8 ScienceDokument16 SeitenReviewer 8 ScienceJhanna Gil BuctolanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON 1-Location of Plate TectonicsDokument16 SeitenLESSON 1-Location of Plate TectonicsAndreaNicoleBanzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geologia Trabajo 2Dokument14 SeitenGeologia Trabajo 2MARIA CAMILA PAZ SOLARTENoch keine Bewertungen
- Geologic Processes Inside EarthDokument1 SeiteGeologic Processes Inside EarthLA LacuarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Support Material For Cambridge Checkpoint Registered StudentsDokument7 SeitenScience Support Material For Cambridge Checkpoint Registered StudentsmariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genesis IntroDokument19 SeitenGenesis IntroNeil Villa MepranumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Francisco, Faye Andrea Go BSN 3-BDokument2 SeitenFrancisco, Faye Andrea Go BSN 3-BFaye Andrea FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The New World of Coke: Things Go Better With CokeDokument1 SeiteThe New World of Coke: Things Go Better With CokeFaye Andrea FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Cebu Normal UniversityDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Cebu Normal UniversityFaye Andrea FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDokument4 SeitenCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityFaye Andrea FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Povidone Iodine Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenPovidone Iodine Drug StudyFaye Andrea Francisco100% (1)
- Tramadol + ParacetamolDokument4 SeitenTramadol + ParacetamolFaye Andrea Francisco100% (2)
- Acetylcysteine Drug Study - FranciscoDokument4 SeitenAcetylcysteine Drug Study - FranciscoFaye Andrea Francisco100% (1)
- Captopril Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenCaptopril Drug StudyFaye Andrea Francisco100% (1)
- Revision SPM 2018 Paper 2Dokument70 SeitenRevision SPM 2018 Paper 2Azie Nurul Akhtar75% (4)
- Lesson 1: Basic Terminology and ConceptsDokument160 SeitenLesson 1: Basic Terminology and Conceptsdiala alazraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulae and Oxidation NumbersDokument14 SeitenFormulae and Oxidation NumbersDoc_CrocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Drag ForcesDokument5 SeitenNon Drag ForcesRelining MineralsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyanide Generation, Corrosion, Treatment, and Discharge at A Petroleum RefineryDokument19 SeitenCyanide Generation, Corrosion, Treatment, and Discharge at A Petroleum Refinery陳冠宏Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reniso Triton - FispqDokument10 SeitenReniso Triton - FispqJp PracianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4.11: Life Science - Photosynthesis & RespirationDokument4 SeitenLesson 4.11: Life Science - Photosynthesis & RespirationGaby SalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 02Dokument27 SeitenCH 02Aaron GuralskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interphase Mass TransferDokument55 SeitenInterphase Mass TransferRishab SrivatsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP Unit 2Dokument61 SeitenMP Unit 2Abhishek KhatavkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single-Event Effects in Silicon Carbide High Voltage Power DevicesDokument17 SeitenSingle-Event Effects in Silicon Carbide High Voltage Power DevicesTeststeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risks and Safety Measures Intig Welding ProcessDokument5 SeitenRisks and Safety Measures Intig Welding ProcessSeminarski radoviNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO-5554-1978 - Determinação de AmidoDokument8 SeitenISO-5554-1978 - Determinação de AmidoIsaac AlvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Unit 2 For Cape ExaminationsDokument275 SeitenBiology Unit 2 For Cape ExaminationsArmaggedon85% (13)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 5 (Series Circuit)Dokument12 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 5 (Series Circuit)Shiella Mae Olermo Cardona100% (2)
- Say My Name (Organichem) Phase 1.0Dokument115 SeitenSay My Name (Organichem) Phase 1.0Dinesh RamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.SC - Agricuture 4 Year Code A PCBDokument16 SeitenB.SC - Agricuture 4 Year Code A PCBsachin sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/42Dokument20 SeitenCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/42septinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acoustics 4Dokument24 SeitenAcoustics 4That GuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of Crushing Strength of Coal AgglomeraDokument5 SeitenMeasurement of Crushing Strength of Coal AgglomeraAnonymous 4PuFzARNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 262 Specimen Blanking Machines For Specimen Preparation of Metals PI enDokument5 Seiten17 262 Specimen Blanking Machines For Specimen Preparation of Metals PI enDanan GentleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auststab Technical Note: Lime Stabilisation PracticeDokument8 SeitenAuststab Technical Note: Lime Stabilisation PracticeazmanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vasco 6000 EsiteDokument2 SeitenVasco 6000 EsiteBruno GomesNoch keine Bewertungen
- KSSM Science Form 4 Chapter 9 9.1Dokument47 SeitenKSSM Science Form 4 Chapter 9 9.1TSE100% (1)
- Shuttlecock DynamicsDokument6 SeitenShuttlecock Dynamicshokl88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3heatengine PhysicDokument3 SeitenLab 3heatengine Physicapi-263500375Noch keine Bewertungen
- GEN PHY Module 3Dokument6 SeitenGEN PHY Module 3Joshua James Sanguenza RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQA Chemistry: 4.3 Measuring Enthalpy Changes Follow Up SheetDokument2 SeitenAQA Chemistry: 4.3 Measuring Enthalpy Changes Follow Up SheetDaniel's RevisionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paul DiracDokument6 SeitenPaul DiracLeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum Field Theory A Modern Introduction (Michio Kaku)Dokument8 SeitenQuantum Field Theory A Modern Introduction (Michio Kaku)Daniel Parra0% (1)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincVon EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (137)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessVon EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseVon EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (69)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (33)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionVon EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (811)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesVon EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (21)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersVon EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldVon EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (18)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterVon EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsVon EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (65)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutVon EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (142)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeVon EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (19)
- The Best American Science And Nature Writing 2021Von EverandThe Best American Science And Nature Writing 2021Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (8)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsVon EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (13)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsVon EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (223)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogVon EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (10)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeVon EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)