Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Genre (Definition, Kinds, and Pairs of Text)
Hochgeladen von
Rio Septa ArOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Genre (Definition, Kinds, and Pairs of Text)
Hochgeladen von
Rio Septa ArCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Name : Rio Septa Ardhana
NPM : 19420082
Class : Writing 3B
Topic of Discussion : Genre (definition, kinds, and pairs of text).
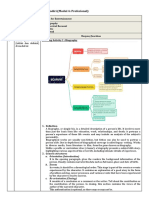
A. DEFINITION
1. Genre is used to refer to particular text-types, not to traditional varieties of literature. It is a type
or kind of text, defined in terms of its social purposes; also the level of context dealing with
social purpose. Genre is a category of cultural. It can be thought of as staged, goal-oriented
social process which is followed by all writers or speakers in their production of any text.
2. Genre are how things get done, when language is used to accomplish them. They range from
literary to far form literary forms: poems, narratives, expositions, lectures, seminar, recipes,
manuals, appointment making, service encounters, news broadcast and so on. The term genre
is used here to embrace each of the linguistically realized activity types which comprise so
much of our culture
3. Use genre to read and write—to interpret, manage, construct, and negotiate various types of
text—and that our use of genre is mediated by our understanding of form, our affiliations with
communities, and our involvement in contexts doesn’t explain the specific ways that genres
“operationalize” typified activities, to use Russell’s (1997) term, particularly when the activities
under consideration are reading and writing.
4. A literary genre is a category of literary composition. Genres may be be determined by
technique, tone, content, or even lenght. The distintctions between genres and categories are
flexible and loosely defined, often with subgroups. Many books contain elements from different
genres.
5. Genre, as referring to generally unchanging regularities in conventions of form and content,
usually with reference to literary works, allowing readers to identify, for example classes of
work such as poetry, fiction, and drama….Such classification of text has extended as well to
prescriptive classification in school writing and thus the familiar categories of exposition,
description, argumentation, and narration
B. KINDS
1. Story genre, consists of six genres; they are narrative, news story, exemplum, anecdote, and
recount, spoof.
2. Factual genre, is divided into procedure, explanation, report, exposition, and discussion,
description, review.
C. PAIRS OF TEXT
A. SOCIAL FUNCTION
1. STORY GENRE
STORY GENRE SOCIAL FUNCTION
Narrative To amuse, entertain and to deal with actual or various experience in
different ways.
News Story Factual text which informs readers events of the day which are
considered newsworthy or important.
Exemplum To dealt with incidents that are in some respects out of the usual, point
to some general value in the cultural context.
Anecdote To share with others an account of an unusual or amusing incident.
Recount To retell events for the purpose of informing or entertaining.
Spoof To retell an event with a humorous twist.
2. FACTUAL GENRE
FACTUAL GENRE SOCIAL FUNCTION
Prosedure To describe how something is accomplished through a sequence of
actions or steps.
Explanation To explain the processes involved in the formation or workings of natural
or socio-cultural phenomena.
Report To describe the way things are, with reference to arrange or natural,
manmade and social phenomena in our environment.
Exposition To persuade the reader or listener that something is the case.
Discussion To present (at least) two points of view about an issue.
Description To describe a particular person, place or thing.
Review To critique an art work or event for a public audience.
B. SCHEMATIC STRUCTURE
1. STORY GENRE
STORY GENRE SCHEMATIC STRUCTURE
Narrative Orientation, evaluation, complication, resolution, reorientation.
News Story Newsworthly event (s), background event (s), sources.
Exemplum Abstract or synopsis, orientation, incidents (s), judgement (s),
reorientation
Anecdote Abstract, orientation, crisis, reaction, coda.
Recount Orientation, events, reorientation.
Spoof Orientation, event (s), twist.
2. FACTUAL GENRE
FACTUAL GENRE SCHEMATIC STRUCTURE
Prosedure Goal, materials, step 1-n.
Explanation A general statement to position the reader, a sequenced explanation of
why or how something occurs.
Report General classification, description (parts, qualities, habits or behavior (if
living); uses (if non-natural).
Exposition Thesis, arguments, reiteration/summing up.
Discussion Issue, arguments for and against or statements of differing points of
view, conclusion or recommendations.
Description Identification, description.
Review Orientation, interpretative recount, evaluation, evaluative summation.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Genre-Based Writing DR PDFDokument9 SeitenGenre-Based Writing DR PDFMala FakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructional Genre (School Genres) : Dr. Rudi Hartono, S.S., M.PDDokument50 SeitenInstructional Genre (School Genres) : Dr. Rudi Hartono, S.S., M.PDRizky RamaDhan PerDanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peta Materi Bahasa InggrisDokument51 SeitenPeta Materi Bahasa Inggrislio100% (1)
- Creative Writing - Quarter 1 - LAS - ContinuationDokument24 SeitenCreative Writing - Quarter 1 - LAS - ContinuationRonald MayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FileContent-1 231107 213056Dokument2 SeitenFileContent-1 231107 213056Tako MenabdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preliminary: 1.1 BackgroundDokument15 SeitenPreliminary: 1.1 BackgroundIntan Dung GieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Literature SyllabusDokument44 SeitenPhilippine Literature SyllabusFroscheNoch keine Bewertungen
- LK 1 - Modul 4 ProfesionalDokument5 SeitenLK 1 - Modul 4 ProfesionalAnang SusantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molo - Task 5 Types of FeaturesDokument11 SeitenMolo - Task 5 Types of FeaturesRaulene MoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning NotesDokument6 SeitenLearning NotesRatih RinandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SENIOR-HS Creative-Nonfiction Q1 LP9Dokument16 SeitenSENIOR-HS Creative-Nonfiction Q1 LP9joan DoblonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Activity Sheet Identifying Literary Elements, Literary Techniques and Literary Devices in Various Modes of FictionDokument16 SeitenLearning Activity Sheet Identifying Literary Elements, Literary Techniques and Literary Devices in Various Modes of Fictionmaria lovella batara70% (10)
- Genre (Kinds of Texts)Dokument11 SeitenGenre (Kinds of Texts)DesnitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng RevieerDokument5 SeitenEng RevieerSTEPHEN LACHICANoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE LESSON 1 LitDokument9 SeitenMODULE LESSON 1 LitSheian MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDokument23 Seiten21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldHarold Ambuyoc100% (1)
- Power Point Bahan Ajar Bahasa InggrisDokument39 SeitenPower Point Bahan Ajar Bahasa InggrisLIAN NASUTION100% (1)
- Unit 33 Versión ResumidaDokument10 SeitenUnit 33 Versión ResumidaalexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument4 SeitenChapter 4Arnie John P. MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Brief History of Genre Pedagogy in Australian Curriculum and PracticeDokument16 SeitenA Brief History of Genre Pedagogy in Australian Curriculum and PracticeMartina Fernandez-FascioloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.narrative ParagraphDokument8 Seiten1.narrative ParagraphAmalia Aftah100% (1)
- Creative Writing Week4 8Dokument31 SeitenCreative Writing Week4 8Brielle ManuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macam-Macam Text Genre & ContohnyaDokument9 SeitenMacam-Macam Text Genre & ContohnyaFadhlanminnaallah Wani'mah WamaghfiratawarahmahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 3Dokument5 SeitenWorksheet 3Laila OlfindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FictionDokument17 SeitenFictionMaKenJi100% (1)
- Eng6 PPT - Informational TextsDokument33 SeitenEng6 PPT - Informational TextsErnita Corpuz RaymundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- St. Anthony College Calapan City, Inc.: World LiteratureDokument11 SeitenSt. Anthony College Calapan City, Inc.: World LiteraturexxxxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2Dokument2 SeitenLesson 2Lerramie Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE IN CREATIVE NONFICTION Week 3 and Week 4Dokument5 SeitenMODULE IN CREATIVE NONFICTION Week 3 and Week 4Jaja Cabatic100% (2)
- Chapter 1 Recount TextDokument10 SeitenChapter 1 Recount Textpentol gorengNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Inggris (Report Text)Dokument10 SeitenB. Inggris (Report Text)Lianurcahyono BagasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 35 Explanatory Texts. Structure and CharacteristicsDokument9 SeitenUnit 35 Explanatory Texts. Structure and CharacteristicsMiriam Reinoso SánchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENG 5 Q4 W1 DAY 3 Distinguish Text-Types According To Features (Structural and Language) - Enumeration BY Sir Ray L. MarasiganDokument30 SeitenENG 5 Q4 W1 DAY 3 Distinguish Text-Types According To Features (Structural and Language) - Enumeration BY Sir Ray L. MarasiganMary Ann Esguerra100% (1)
- Reviewer in RWDokument8 SeitenReviewer in RWSOFIA MARIE BATRINANoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 Lecture World Lit Part 1Dokument52 Seiten2020 Lecture World Lit Part 1Bruce Bryan BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature of The World 2Dokument51 SeitenLiterature of The World 2Charlene SuliganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5-8Dokument8 SeitenModule 5-8PhielDaphine Nacionales100% (2)
- Scrwrit Lesson 1Dokument7 SeitenScrwrit Lesson 1Aihsirk ALedosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discourse Analysis and NarrativeDokument11 SeitenDiscourse Analysis and NarrativeJoehenson Nino Babao AlejadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- M5 Making Judgments About A Range of TextsDokument38 SeitenM5 Making Judgments About A Range of TextsVreia Zeiynt DeveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- LITERATUREDokument25 SeitenLITERATUREMa Elaine TrinidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literary VS Non LiteraryDokument9 SeitenLiterary VS Non Literaryikramjust38Noch keine Bewertungen
- Creative Nonfiction: Lesson TitleDokument21 SeitenCreative Nonfiction: Lesson TitleWinjoy GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compare and Contrast Patterns of Written Texts Across DisciplinesDokument4 SeitenCompare and Contrast Patterns of Written Texts Across Disciplineskaren bulauan67% (18)
- LK Modul 4 English For EntertainmentDokument7 SeitenLK Modul 4 English For EntertainmenttyaoktrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Dictionary 2Dokument13 SeitenMini Dictionary 2Ex PertzNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Co1Dokument5 SeitenDLL Co1Karina PiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON EXEMPLAR Grade 7-English Quarter 1 Lesson 1: Appreciating MyselfDokument9 SeitenLESSON EXEMPLAR Grade 7-English Quarter 1 Lesson 1: Appreciating MyselfFGacadSabadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Er03twais - ELT 202 Module 5Dokument7 SeitenEr03twais - ELT 202 Module 5Vincent BaliwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text TypesDokument5 SeitenText TypesMr.AngelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narration CompositionDokument5 SeitenNarration Compositionriverastudy01Noch keine Bewertungen
- CNF Las 3Dokument9 SeitenCNF Las 3Marianne D. PeritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 33 Descriptive TextsDokument12 SeitenUnit 33 Descriptive TextsMiriam Reinoso SánchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 32Dokument8 SeitenUnit 32Ardnas AtsocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membaca Pemahaman Teks Deskriptif (Praktek)Dokument38 SeitenMembaca Pemahaman Teks Deskriptif (Praktek)TaufikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forms of WritingDokument46 SeitenForms of WritingEmsi G. AcobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading and Writing (Forms of Writing)Dokument46 SeitenReading and Writing (Forms of Writing)Emsi G. AcobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Very Own Adventure: Towards a Poetics of the Short StoryVon EverandOur Very Own Adventure: Towards a Poetics of the Short StoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- March to Opulence: A Special Assortment of Classics, Biographies, Histories, Speeches, and More, for the Makers of a Bright TomorrowVon EverandMarch to Opulence: A Special Assortment of Classics, Biographies, Histories, Speeches, and More, for the Makers of a Bright TomorrowNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Years: Creating Community & OpportunityDokument20 Seiten10 Years: Creating Community & OpportunityAnonymous rdRt7wmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Models and Frameworks of Social Responsibility of BusinessDokument8 SeitenModels and Frameworks of Social Responsibility of Businesshoxhii100% (2)
- Crime Scene Sketches and MeasurementsDokument11 SeitenCrime Scene Sketches and MeasurementsBacolod PS SevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument6 SeitenCase StudyTrangia Plaza Michelle50% (2)
- MIS 320 Module Four Case Study Analysis Guidelines and Rubric Organizational E-Commerce Case Study Analysis: AmazonDokument2 SeitenMIS 320 Module Four Case Study Analysis Guidelines and Rubric Organizational E-Commerce Case Study Analysis: AmazonghanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brockton Police Log March 28, 2019Dokument17 SeitenBrockton Police Log March 28, 2019BBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Interview Frameworks - The Ultimate Guide (2022)Dokument32 SeitenCase Interview Frameworks - The Ultimate Guide (2022)Tomer Reuveni100% (1)
- Development of Human Resources in Bangladesh An Analysis of Institutional SupportsDokument8 SeitenDevelopment of Human Resources in Bangladesh An Analysis of Institutional SupportsDr. Mohammad Shamsuddoha100% (3)
- Usbeck-Ceremonial Storytelling (2019)Dokument333 SeitenUsbeck-Ceremonial Storytelling (2019)jbpicadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tourist Guide Website ProposalDokument4 SeitenTourist Guide Website ProposalEldon Rey Melgar0% (1)
- KR-G12 GSM Alarm System Instruction User GuideDokument21 SeitenKR-G12 GSM Alarm System Instruction User GuideFernando SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee133 Electronic Devices and Circuits AssignmentDokument2 SeitenEee133 Electronic Devices and Circuits Assignmentshobanraj1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management by Objectives PDFDokument25 SeitenManagement by Objectives PDFARslan AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUDITING II GROUP ASSIGNMENT Case 3.1 A Day in The Life of Brent DorseyDokument2 SeitenAUDITING II GROUP ASSIGNMENT Case 3.1 A Day in The Life of Brent DorseyCherry Blasoom100% (1)
- Qualifications Explained Factsheet PDFDokument2 SeitenQualifications Explained Factsheet PDFEzebunwo NwoforNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liberation Theology PaperDokument15 SeitenLiberation Theology PaperJose Gabriel HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pete The Cat Buttons LessonDokument6 SeitenPete The Cat Buttons Lessonapi-285851205Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Test Manajemen (DR. Victor P.K. Lengkong, SE, M.si)Dokument9 SeitenFinal Test Manajemen (DR. Victor P.K. Lengkong, SE, M.si)danielNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Central Park Apartment Owners Association - Bye LawsDokument25 SeitenThe Central Park Apartment Owners Association - Bye Lawskjacobgeorge1242100% (6)
- Draft Policies and Guidelines For The Deployment of Pre Service Teachers Sept. 7 2020Dokument14 SeitenDraft Policies and Guidelines For The Deployment of Pre Service Teachers Sept. 7 2020Sitty Salma Hadji AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidance and CounselingDokument6 SeitenGuidance and CounselingArmitha MukhromahNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOAL USBN Bahasa Inggris Paket BDokument10 SeitenSOAL USBN Bahasa Inggris Paket BArif Raya HarahapNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Prisoner's Dilemma?Dokument4 SeitenWhat Is The Prisoner's Dilemma?Mihaela VădeanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial/Residential Building Only) : "Tennessee Contractor's License Application"Dokument4 SeitenCommercial/Residential Building Only) : "Tennessee Contractor's License Application"Royal Maku ChiefNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 10 - Quiz 1Dokument2 SeitenECE 10 - Quiz 1Gian Paul BolanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- I GLC Hans Thomas HolmDokument31 SeitenI GLC Hans Thomas HolmRuddy Morales MejiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metropolitan Housing Project Company Case StudyDokument5 SeitenMetropolitan Housing Project Company Case StudyRafael Bunyi0% (1)
- Teaching With A Passion: James Angberg WangbergDokument2 SeitenTeaching With A Passion: James Angberg WangbergSydney PachecoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suara TEEAM 82nd Issue E-NewsletterDokument92 SeitenSuara TEEAM 82nd Issue E-NewsletterTan Bak PingNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Legacy of League of NationsDokument7 SeitenThe Legacy of League of NationsIoana LaviniaNoch keine Bewertungen