Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Source of Unavailable Carbohydrate
Hochgeladen von
Ashma KhulalOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Source of Unavailable Carbohydrate
Hochgeladen von
Ashma KhulalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Source of Unavailable carbohydrate
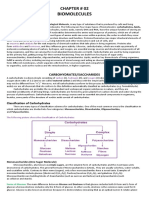
Carbohydrates, along with lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and other compounds are known as
biomolecules because they are closely associated with living organisms. Carbohydrates are
organic compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio 1:2:1. The word
“carbohydrate” includes polymers and other compounds synthesized from polyhydroxylated
aldehydes and ketones. Carbohydrates are commonly divided into monosaccharides,
oligosaccharides and polysaccharides
Carbohydrate biosynthesis in plants starting from carbon dioxide and water with the help of light
energy, i. e., photosynthesis, is the basis for the existence of all other organisms which depend on
the intake of organic substances with food. Carbohydrates represent one of the basic nutrients
and are quantitatively the most important source of energy. Their nutritional energy value
amounts to 17 kJ/g or kcal/g.
Available and Unavailable Carbohydrates
Available carbohydrates: It is defined as those, carbohydrate which are digested and
absorbed by the human small intestine and which are glucogenic. It can provide about 4 Calories
per gram of energy. Available carbohydrates include:
Sugars: glucose, fructose, galactose, mannose, sucrose, lactose, maltose, isomaltose,
isomaltulose and trehalose
Starch, dextrin and maltodextrin
Glycogen
Glycerol (glycerin)
Partially available carbohydrates: such as tagatose and sugar alcohols or polyols (sorbitol,
xylitol, etc.), are partially absorbed in the small intestine and partially fermented by colonic
bacteria into short-chain fatty acids and other nutrients that can be absorbed and can provide 1.5-
3.5 kilocalories per gram.
Unavailable carbohydrates: The unavailable carbohydrates were defined as those that are
not digested by the endogenous secretions of the human digestive tract. They include:
Soluble fiber: This type of fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like material. It can help
lower blood cholesterol and glucose levels. Soluble fiber is found in oats, peas, beans, apples,
citrus fruits, carrots, barley and psyllium. Soluble fiber (such as fructooligosaccharides (FOS),
galactosaccharides (GOS), galactomannans, glucomannans and resistant starches) can be broken
down (fermented) by the large intestinal bacteria into short-chain fatty acids, which can be
absorbed and can provide about 2 Calories per gram.
Insoluble fiber: Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water but it get insert into digestive
enzymes in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Examples are wheat bran, cellulose, and lignin.
Coarsely ground insoluble fiber triggers the secretion of mucus in the large intestine, providing
bulking. Finely ground insoluble fiber does not have this effect and can actually have a
constipating effect. Some forms of insoluble fiber, such as resistant starches, can be fermented in
the colon.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- BCH 317 CarbohydrateDokument3 SeitenBCH 317 CarbohydrateMARYJANE NZUBECHUKWU NJOKUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology ReportDokument64 SeitenBiology ReportChelo IlagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mishyree ReportDokument50 SeitenMishyree ReportMishyree AndatuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CarbohydratesDokument33 SeitenCarbohydratesCris PorlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify and Describe Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins As Food Substances State The Chemical and Physical Properties of Different Food SubstancesDokument18 SeitenIdentify and Describe Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins As Food Substances State The Chemical and Physical Properties of Different Food SubstancesLunactic ThanosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources and Applications of Carbohydrates.Dokument10 SeitenSources and Applications of Carbohydrates.Narges Malik100% (1)
- Lecture Two: Carbohydrate Lecture Two: CarbohydrateDokument24 SeitenLecture Two: Carbohydrate Lecture Two: Carbohydratesaacid bashir100% (1)
- Lesson 3 Biomolecules ReviewerDokument15 SeitenLesson 3 Biomolecules Reviewerjohnromar VilasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN Unit-IiDokument25 SeitenCN Unit-IiJohn Benedict Suiza VillaruelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates: Prepared By, Aparna M AjayDokument46 SeitenCarbohydrates: Prepared By, Aparna M AjayAparna KinginiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrients and Their Importance: M.ANAB 11-TDokument28 SeitenNutrients and Their Importance: M.ANAB 11-TAnab ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 4th Quarter Week 3Dokument12 SeitenGrade 10 4th Quarter Week 3KarenNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSM 212 Lecture NoteDokument20 SeitenHSM 212 Lecture NoteHaruna Muhammad AbdullahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asia Pacific College of Advanced STUDIES StudiesDokument14 SeitenAsia Pacific College of Advanced STUDIES StudiesJake LaylaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 - 1A2-3 Carbohydrates I & IIDokument30 SeitenLesson 3 - 1A2-3 Carbohydrates I & IIAlex SmirnovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asynchronous Review For Science 10 4TH PERIODICALDokument19 SeitenAsynchronous Review For Science 10 4TH PERIODICALchristian Jay HorseradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition in OrthodonticsDokument51 SeitenNutrition in OrthodonticsShweta DU80% (5)
- BiochemistryDokument19 SeitenBiochemistryUsman AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 CarbohydratesDokument9 SeitenModule 1 CarbohydratesBig BrotherNoch keine Bewertungen
- bIOLOGICAL CHO, CHONDokument82 SeitenbIOLOGICAL CHO, CHONgalauraaprilrose96Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates NotesDokument11 SeitenCarbohydrates Notesaliasger786inNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates and LipidsDokument11 SeitenCarbohydrates and LipidsCarlene OretaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Importance of Carbohydrates and LipidsDokument17 SeitenBiological Importance of Carbohydrates and LipidsAnaitum SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture No 5 & 6. Function of CarbohydratesDokument25 SeitenLecture No 5 & 6. Function of Carbohydratesmaryam khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition in OrthodonticsDokument56 SeitenNutrition in OrthodonticsNand Kishore DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 3 - Energy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)Dokument6 SeitenCHAPTER 3 - Energy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)Ira Lilian DumadaugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Human NutritionDokument16 SeitenAssignment Human NutritionSandya SandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CARBOHYDRATES ChemDokument8 SeitenCARBOHYDRATES ChemPriyesh MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are BiomoleculesDokument18 SeitenWhat Are Biomoleculessusan pajarilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)Dokument6 SeitenEnergy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)camille εϊзNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agronomy Assignment 2Dokument3 SeitenAgronomy Assignment 2Nguyễn Minh ThànhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition Carbs and FatsDokument24 SeitenNutrition Carbs and FatsSritama GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project On BiomoleculesDokument28 SeitenChemistry Project On BiomoleculesGAMING WITH TGK YTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument112 SeitenChapter 2Oltagon Nicole DupingayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant ConstituentsDokument10 SeitenPlant ConstituentstrixchialoveskimchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composition of CarbohydratesDokument6 SeitenComposition of Carbohydratesgeorgejhon1949Noch keine Bewertungen
- CARBOHYDRATESDokument23 SeitenCARBOHYDRATESClassen Mudenda KundaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohidraţii Sunt Clasificaţi Astfel 1. Simple CarbohydratesDokument3 SeitenCarbohidraţii Sunt Clasificaţi Astfel 1. Simple CarbohydratesMonica CreangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FatsDokument8 SeitenFatsHazel CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1Dokument12 SeitenWeek 1Prima LebananNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinDokument64 SeitenThe Biochemistry of Digestion, Absorption and Detoxification by Prof. Dr. Hedef D. El-YassinSayhidoen CepexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological MacromoleculesDokument6 SeitenBiological MacromoleculesTinay escaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Biology Notes - NutritionDokument4 SeitenSPM Biology Notes - NutritionSPM50% (2)
- NutritionDokument29 SeitenNutritioncutkarshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition and HormonesDokument59 SeitenNutrition and HormonesnivethaseshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CarbohydratesDokument93 SeitenCarbohydratesVenkateswarlu Yadavalli100% (2)
- 0 BooksDokument16 Seiten0 Bookskingsolo0789Noch keine Bewertungen
- BiomoleculesDokument11 SeitenBiomoleculesAdul basit mughalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CarbohydratesDokument22 SeitenCarbohydratesSHIFA ALTAFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To MacronutrientsDokument9 SeitenIntroduction To MacronutrientsBenard NyaumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOOD AND NUTRITION I Students NoteDokument41 SeitenFOOD AND NUTRITION I Students Noteakintundeprecious1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abdul Rahman AlwiDokument46 SeitenAbdul Rahman Alwiaimi BatrisyiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CarbsDokument20 SeitenCarbsKwebblekop JordiNoch keine Bewertungen
- M2 Lesson 1Dokument10 SeitenM2 Lesson 1Catherine Sinen ObinqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Science (Biological Sciences) : Dr. Sanawar IqbalDokument22 SeitenGeneral Science (Biological Sciences) : Dr. Sanawar IqbalAbdullah khalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomolecules and Its UsesDokument20 SeitenBiomolecules and Its UsesRajendra Swarnakar25% (4)
- Biomolecules and Its Various TypesDokument8 SeitenBiomolecules and Its Various TypesJALAL JAMINoch keine Bewertungen
- MBC 341 Lecture 1 2023Dokument16 SeitenMBC 341 Lecture 1 2023Jacina AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Book Written by Curtis Miles and Jane Rauton EntitledDokument6 SeitenA Book Written by Curtis Miles and Jane Rauton EntitledAshma KhulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Lactace Production During Muscle ConcentrationDokument3 SeitenRole of Lactace Production During Muscle ConcentrationAshma KhulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- In The Context of Nepal, Most of The Studies Have Identi Ed Iron de Ciency Anemia Only Based On Hemoglobin Level in The Context of Nepal, Most of The Studies Have Identi EdDokument10 SeitenIn The Context of Nepal, Most of The Studies Have Identi Ed Iron de Ciency Anemia Only Based On Hemoglobin Level in The Context of Nepal, Most of The Studies Have Identi EdAshma KhulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water ActivityDokument3 SeitenWater ActivityAshma KhulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Gultamine in Amino Acid MetabolismDokument2 SeitenRole of Gultamine in Amino Acid MetabolismAshma KhulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future Trend of Protein Utilization: A SeminarDokument20 SeitenFuture Trend of Protein Utilization: A SeminarAshma KhulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food AvaiabilityDokument7 SeitenFood AvaiabilityAshma KhulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antioxident BiscuitDokument1 SeiteAntioxident BiscuitAshma KhulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Can An Alternative Food System Feed Everyone?Dokument1 SeiteCan An Alternative Food System Feed Everyone?Ashma KhulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food AvaiabilityDokument7 SeitenFood AvaiabilityAshma KhulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antioxident BiscuitDokument1 SeiteAntioxident BiscuitAshma KhulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid 19 and NutritionDokument1 SeiteCovid 19 and NutritionAshma KhulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agrricultural Wastes As Protein SourceDokument1 SeiteAgrricultural Wastes As Protein SourceAshma KhulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversity Conservation: Thecla M. MutiaDokument9 SeitenBiodiversity Conservation: Thecla M. Mutiahsdf,asghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bisucuit Factory PDFDokument29 SeitenBisucuit Factory PDFLakshmi Krishnakumar100% (2)
- CH 26 PDFDokument32 SeitenCH 26 PDFkrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CARBOHYDRATESDokument19 SeitenCARBOHYDRATESLILY LINGGONNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Experience of (04) Massecuite Boiling System at Sanghar Sugar Mills LTDDokument11 SeitenAn Experience of (04) Massecuite Boiling System at Sanghar Sugar Mills LTDHayat Ur Rahim KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Assignment 2Dokument2 SeitenScience Assignment 2christian sanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmylaseDokument4 SeitenAmylaseRipunz RipunzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate Post Lab DiscussionDokument28 SeitenCarbohydrate Post Lab Discussionanon nymouseNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEC NOTES 4 - Carbohydrates (5) Colored PrintDokument5 SeitenLEC NOTES 4 - Carbohydrates (5) Colored PrintBetina De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates NotesDokument38 SeitenCarbohydrates NotesAtirahSakinahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gibson 2017 History of The Low Fodmap DietDokument3 SeitenGibson 2017 History of The Low Fodmap Dietdr.martynchukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrolisis of CarbohydratesDokument3 SeitenHydrolisis of CarbohydratesESTELLE RHINE HINDAP FRANCISCONoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabla Produccion de Azucar Por Centrales 1911-2002Dokument14 SeitenTabla Produccion de Azucar Por Centrales 1911-2002canadeazucar100% (1)
- Molecular Modeling Activity For Carbohydrates: NameDokument4 SeitenMolecular Modeling Activity For Carbohydrates: NamePhuc DangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1 Bio270 Odl 2020Dokument5 SeitenExperiment 1 Bio270 Odl 2020Nurmalisa HerwanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates II NEW JaiDokument10 SeitenCarbohydrates II NEW JaiNur SanaaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 25Dokument34 SeitenCH 25John Nicholson LanderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate NomenclatureDokument8 SeitenCarbohydrate NomenclatureAwais Naseer100% (3)
- Section3 Polysaccharides PDFDokument17 SeitenSection3 Polysaccharides PDFSHNoch keine Bewertungen
- About IcumsaDokument2 SeitenAbout IcumsabvsundarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Agr 232Dokument1 SeiteCase Study Agr 232Najwan AfiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 - 1Dokument35 SeitenUnit 2 - 1Sunita SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cifra Club - The Archies - Sugar SugarDokument4 SeitenCifra Club - The Archies - Sugar SugarFrancisco Javier Valenzuela BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry of Nutrients Unit 3 by Sir Mehmood Part 1Dokument30 SeitenChemistry of Nutrients Unit 3 by Sir Mehmood Part 1Khurram PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates: Occurrence, Structures and Chemistry: Rieder IchtenthalerDokument30 SeitenCarbohydrates: Occurrence, Structures and Chemistry: Rieder IchtenthalerAdriano Schindler Freire100% (1)
- 09july19 F.O.licht International Sugar Sweetener ReportDokument48 Seiten09july19 F.O.licht International Sugar Sweetener ReportAhmad Bilal100% (2)
- Chem113Lec-Activity 2-Carbohydrates ActivityDokument3 SeitenChem113Lec-Activity 2-Carbohydrates ActivityAlliana Denice VicencioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Carbohydrates: Ι H -C-Oh Ι Ι ΙDokument4 SeitenTypes of Carbohydrates: Ι H -C-Oh Ι Ι ΙTinder KamdevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Tests For CarbohydratesDokument6 SeitenQualitative Tests For CarbohydratesJennifer Heredia0% (1)
- Issct Processing Workshop 2014: Protea Hotel Hluhluwe, South AfricaDokument2 SeitenIssct Processing Workshop 2014: Protea Hotel Hluhluwe, South AfricaAnkit Katiyar IshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metode Pencucian Dan Penyaringan Pada Ekstraksi Pektin Dari Kulit DurianDokument6 SeitenMetode Pencucian Dan Penyaringan Pada Ekstraksi Pektin Dari Kulit Durianarif ihwandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Worksheet 3 Lesson 3: Polysaccharides: The Polymer Chain Desired Learning CompetenciesDokument3 SeitenUnit 2 Worksheet 3 Lesson 3: Polysaccharides: The Polymer Chain Desired Learning CompetenciesValenzuela Allene GraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellVon EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietVon EverandSummary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincVon EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (137)
- The Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonVon EverandThe Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (33)
- The Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyVon EverandThe Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Love Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)Von EverandLove Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (40)
- Eat & Run: My Unlikely Journey to Ultramarathon GreatnessVon EverandEat & Run: My Unlikely Journey to Ultramarathon GreatnessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthVon EverandSugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookVon EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Metabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeVon EverandMetabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyVon EverandThe Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingVon EverandThe Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Eat Complete: The 21 Nutrients That Fuel Brainpower, Boost Weight Loss, and Transform Your HealthVon EverandEat Complete: The 21 Nutrients That Fuel Brainpower, Boost Weight Loss, and Transform Your HealthBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Von EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (378)
- The Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsVon EverandThe Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (49)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellVon EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (81)
- Grit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeVon EverandGrit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Glucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarVon EverandGlucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (351)
- How Not to Die by Michael Greger MD, Gene Stone - Book Summary: Discover the Foods Scientifically Proven to Prevent and Reverse DiseaseVon EverandHow Not to Die by Michael Greger MD, Gene Stone - Book Summary: Discover the Foods Scientifically Proven to Prevent and Reverse DiseaseBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (84)
- Secrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainVon EverandSecrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (38)
- Eat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouVon EverandEat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeVon EverandHow to Be Well: The 6 Keys to a Happy and Healthy LifeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Find Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeVon EverandFind Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Molecules of Emotion: Why You Feel the Way You FeelVon EverandMolecules of Emotion: Why You Feel the Way You FeelBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (128)
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomVon EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- The Volumetrics Eating Plan: Techniques and Recipes for Feeling Full on Fewer CaloriesVon EverandThe Volumetrics Eating Plan: Techniques and Recipes for Feeling Full on Fewer CaloriesNoch keine Bewertungen