Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
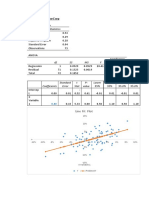
Recession Below Average Average Above Average Boom Expected Rate of Return
Hochgeladen von
Angel Kaye Nacionales JimenezOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Recession Below Average Average Above Average Boom Expected Rate of Return
Hochgeladen von
Angel Kaye Nacionales JimenezCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Jimenez, Angel Kaye BSA-2 ACC216 9:45-11:45 September 22, 2020
Requirement #1: Calculate the expected rate of return for both Stock X and Y.
Economy Probability x y
Recession 0.1 -10% -1 -35% -3.5
Below Average 0.2 2% 0.4 0 0
Average 0.4 12% 4.8 20% 8
Above average 0.2 20% 4 25% 5
Boom 0.1 38% 3.8 45% 4.5
Expected Rate of Return r̂ 0.12% 0.14%
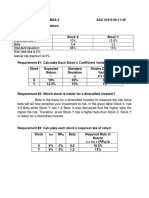
Requirement #2: Calculate the standard deviation of expected returns for both stocks.
Economy Probability x 𝛔𝟐 = [(𝒓 − 𝒓̂)𝟐 (𝑷𝒊 )] y
𝛔𝟐 = [(𝒓 − 𝒓̂)𝟐 (𝑷𝒊 )]
- 240.1
Recession 0.1 -10% -1 48.4 -3.5
35%
Below 39.2
0.2 2% 0.4 20.0 0 0
Average
Average 0.4 12% 4.8 0.0 20% 8 14.4
Above 24.2
0.2 20% 4 12.8 25% 5
average
Boom 0.1 38% 3.8 67.6 45% 4.5 96.1
Σ𝛔 𝟐
148.8 Σ𝛔 𝟐 414
20.35%
√Σ𝛔𝟐 12.20% √Σ𝛔𝟐
Requirement #3: Calculate the coefficient of variation for both stocks.
Economy X Y
r̂ CV=
𝑺𝒕𝒂𝒏𝒅𝒂𝒓𝒅 𝑫𝒆𝒗𝒊𝒂𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏 r̂ CV=
𝑺𝒕𝒂𝒏𝒅𝒂𝒓𝒅 𝑫𝒆𝒗𝒊𝒂𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏
𝑬𝒙𝒑𝒆𝒄𝒕𝒆𝒅 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝒓𝒆𝒕𝒖𝒓𝒏 𝑬𝒙𝒑𝒆𝒄𝒕𝒆𝒅 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝒓𝒆𝒕𝒖𝒓𝒏
Recession -1 48.4 -3.5 240.1
Below 39.2
0.4 20.0 0
Average
Average 4.8 0.0 8 14.4
Above 24.2
4 12.8 5
average
Boom 3.8 67.6 4.5 96.1
148.8 𝟏𝟐. 𝟐𝟎 414 𝟐𝟎. 𝟑𝟓
12% 𝑪𝑽 = = 𝟏. 𝟎𝟐 14%
20.35% 𝑪𝑽 = = 𝟏. 𝟒𝟓
√Σ𝛔 = 12.20%
𝟐
𝟏𝟐 𝟏𝟒
Requirement #4 : Question: Is it possible that most investors will regard Stock Y as being less risky
than Stock X? Explain.
As a risk investor, comparing the two stock. Stock Y may be a good investment
compared to Stock X because it has a greater expected return rate than Stock X. Stock Y
has 14.05% expected rate of return to investors compared to Stock X which has 12%
expected rate of return. Comparing the two stock on the standard deviation, Stock Y has
a bigger risk than stock X on about 8.15 percent more. There is no probability that investor
will regard that Stock Y has a lesser risk than Stock X.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- LYXORDokument5 SeitenLYXORRamalu Dinesh Reddy50% (2)
- Offer LetterDokument8 SeitenOffer LetterMadhavi Latha100% (3)
- Company Financial ManagementDokument8 SeitenCompany Financial ManagementMiconNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIN604 - HW1 - 18164052 - Farhan ZubairDokument8 SeitenFIN604 - HW1 - 18164052 - Farhan ZubairZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investment ManagementDokument17 SeitenInvestment ManagementRakshitha ChikkannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- China Dev Industrial Bank - MM JKT REGULER 43 - Raha, Febri Hartini, Irma WulandDokument31 SeitenChina Dev Industrial Bank - MM JKT REGULER 43 - Raha, Febri Hartini, Irma WulandRini Ramdhiani MuchtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial ManagementDokument8 SeitenFinancial ManagementMiconNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE AF Week Six LectureDokument23 SeitenCE AF Week Six LectureKhosi GrootboomNoch keine Bewertungen
- M5 - Risk and ReturnDokument76 SeitenM5 - Risk and ReturnZergaia WPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises w3Dokument6 SeitenExercises w3hqfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bai Many AssetsDokument3 SeitenBai Many AssetsGia Linh Nguyen HoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 5-1Dokument6 SeitenAssignment 5-1irineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activo A +B Pri (1) Valor PonderadoDokument11 SeitenActivo A +B Pri (1) Valor PonderadoRonny Baltazar H P - COD. ASOC. ADPR NoA2852016Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name of The Teacher: Gayathri Ravikumar Department: Commerce PG. Subject/Paper Class Year Date Class Time Unit TopicDokument7 SeitenName of The Teacher: Gayathri Ravikumar Department: Commerce PG. Subject/Paper Class Year Date Class Time Unit TopicGayu RkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lamp IranDokument8 SeitenLamp Iranjheck dhanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk and Return: Part IDokument48 SeitenRisk and Return: Part IaleknaumoskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk and Return: Centre For Financial Management, BangaloreDokument29 SeitenRisk and Return: Centre For Financial Management, BangalorekirishnakanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Download Essentials of Business Analytics 2nd Edition Camm Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDokument36 SeitenFull Download Essentials of Business Analytics 2nd Edition Camm Solutions Manual PDF Full Chaptertophet.layl0h8q100% (16)
- Introducción A Las Finanzas Corporativas: Méndez Briones Gustavo IsaacDokument10 SeitenIntroducción A Las Finanzas Corporativas: Méndez Briones Gustavo IsaacJavier VidalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non LinearDokument14 SeitenNon Linearuzumakideva26Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 8 Integrated Case - Merryl LynchDokument12 SeitenCH 8 Integrated Case - Merryl LynchNicolaus BagaskaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composite: Vanguard Mid-Cap Index Fund & Vanguard Long-Term Treasury Fund (5YR Performance Analysis)Dokument21 SeitenComposite: Vanguard Mid-Cap Index Fund & Vanguard Long-Term Treasury Fund (5YR Performance Analysis)Amnuay PraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Accounting Finance 4 - Kelompok 3Dokument5 SeitenTugas Accounting Finance 4 - Kelompok 3safira larasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 5 Risk and Return FULL VERSIONDokument4 SeitenClass 5 Risk and Return FULL VERSIONdbokishevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zero BetaDokument4 SeitenZero Betaoverhear sbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM11 - CH - 04 - Risk and Return The BasicsDokument48 SeitenFM11 - CH - 04 - Risk and Return The BasicsAneesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk and ReturnDokument4 SeitenRisk and ReturnMohammad UsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PI Industries Limited BSE 523642 Financials RatiosDokument5 SeitenPI Industries Limited BSE 523642 Financials RatiosRehan TyagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capital Budgeting With Risk MGMTDokument15 SeitenCapital Budgeting With Risk MGMTAmit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM11 CH 04 ShowDokument48 SeitenFM11 CH 04 ShowUyen LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capital Structure and Leverage (D. Bañas)Dokument6 SeitenCapital Structure and Leverage (D. Bañas)DAISYBELLE S. BAÑASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative AnalysisDokument6 SeitenQuantitative AnalysisUSD 654Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year Stock A Stock B Stock CDokument1 SeiteYear Stock A Stock B Stock Csushant ahujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Ratio:: Current Assets Current LiabilitiesDokument5 SeitenCurrent Ratio:: Current Assets Current LiabilitiesshamarjitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benitez, Jewel Ann Q. Analysis #3Dokument7 SeitenBenitez, Jewel Ann Q. Analysis #3MIKASANoch keine Bewertungen
- Written Activity 3.1: Solution: Compute The Expected Value of OutcomeDokument2 SeitenWritten Activity 3.1: Solution: Compute The Expected Value of OutcomeMary angel ZurbanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tarea 7 Finanzas CorpDokument12 SeitenTarea 7 Finanzas Corpvuzo123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Regression Statistics: Assignment-1: Hero Motorcorp 1) Calculation of BetaDokument2 SeitenRegression Statistics: Assignment-1: Hero Motorcorp 1) Calculation of BetaDivyansh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Managerial Finance: Risk and ReturnDokument57 SeitenPrinciples of Managerial Finance: Risk and ReturnJoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE A Cre8tiveDokument3 SeitenCASE A Cre8tivepanadol_o2Noch keine Bewertungen
- I II III: in Millions of USD (Year 2013)Dokument6 SeitenI II III: in Millions of USD (Year 2013)Karen May AlonsagayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example Martin USDokument12 SeitenExample Martin USsadia anmolNoch keine Bewertungen
- KHAICHEM StockReport 20230829 2208Dokument12 SeitenKHAICHEM StockReport 20230829 2208rajbus lessNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch06 Tool KitDokument36 Seitench06 Tool KitBrandon FrancomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wk14 - Decision, Uncertainty and RiskDokument29 SeitenWk14 - Decision, Uncertainty and Riskce.adedotun.ojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Storytelling With Data (Presentation Ver.)Dokument209 SeitenStorytelling With Data (Presentation Ver.)erickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opportunities Weight Rate Weighted Score: Poor (1), Below Average (2), Above Average (3), SuperiorDokument15 SeitenOpportunities Weight Rate Weighted Score: Poor (1), Below Average (2), Above Average (3), SuperiorKim AndalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- S&P Default Rates and Recovery Jan07Dokument9 SeitenS&P Default Rates and Recovery Jan07gimy2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sessions 5 & 6Dokument33 SeitenSessions 5 & 6Bhavya JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Net Revenue Cost of Sales Gross Profit Ebit - Operating Result Ebitda Net IncomeDokument15 SeitenNet Revenue Cost of Sales Gross Profit Ebit - Operating Result Ebitda Net IncomevhibeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Corporate Finance 10th Edition Brealey Solutions ManualDokument14 SeitenPrinciples of Corporate Finance 10th Edition Brealey Solutions Manualbrainykabassoullw100% (23)
- Mini Case Chapter 6 - Week 3Dokument6 SeitenMini Case Chapter 6 - Week 3georgejane100% (3)
- E) Investors Demand Higher Expected Rates of Return From Stocks With Returns That Are VeryDokument4 SeitenE) Investors Demand Higher Expected Rates of Return From Stocks With Returns That Are Veryssunday giftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2-Asset Allocation-Questions AwniW26jEKDokument21 SeitenModule 2-Asset Allocation-Questions AwniW26jEKKp PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk and Rates of Return Problem SolvingDokument7 SeitenRisk and Rates of Return Problem SolvingBlueBladeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NIFTY ACCELERATOR-100%: PAYOFF (Market Linked Debentures Idea)Dokument2 SeitenNIFTY ACCELERATOR-100%: PAYOFF (Market Linked Debentures Idea)Ashish ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FFM15, CH 08 (Risk), Chapter Model, 2-08-18Dokument17 SeitenFFM15, CH 08 (Risk), Chapter Model, 2-08-18Mỹ XuânNoch keine Bewertungen
- MacrodurDokument41 SeitenMacrodurnoel_manroeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proses Tabel Silang Mengategorikan Data Variabel X1 X2 X3 Y Menjadi 3 Kelas Tinggi Sedang Rendah, Atau Sesuai Kebutuhan, Misal: Baik, Cukup, KurangDokument3 SeitenProses Tabel Silang Mengategorikan Data Variabel X1 X2 X3 Y Menjadi 3 Kelas Tinggi Sedang Rendah, Atau Sesuai Kebutuhan, Misal: Baik, Cukup, KurangFirman AditamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk LogDokument13 SeitenRisk LogSathi shNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gmail - Returning ApplicantDokument1 SeiteGmail - Returning ApplicantAngel Kaye Nacionales JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jimenez - Act 3 FinalsDokument4 SeitenJimenez - Act 3 FinalsAngel Kaye Nacionales JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jimenez - Act 2 FinalsDokument3 SeitenJimenez - Act 2 FinalsAngel Kaye Nacionales JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jimenez, Angel Kaye October 8, 2020 Bsa 2 Year ACC 216 9:45-11:45 Assignment-Depreciation MethodsDokument4 SeitenJimenez, Angel Kaye October 8, 2020 Bsa 2 Year ACC 216 9:45-11:45 Assignment-Depreciation MethodsAngel Kaye Nacionales JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jimenez - Act 3 FinalsDokument4 SeitenJimenez - Act 3 FinalsAngel Kaye Nacionales JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- September 3, 2020, 730AM Group # 4 Members: Cagape, Patrice Cercado, Geran Jimenez, Angel Quiñanola, Alana Resabal, Mariel Sarmillo, WenzelDokument3 SeitenSeptember 3, 2020, 730AM Group # 4 Members: Cagape, Patrice Cercado, Geran Jimenez, Angel Quiñanola, Alana Resabal, Mariel Sarmillo, WenzelAngel Kaye Nacionales JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2 Caselette - Correction of ErrorsDokument37 SeitenCHAPTER 2 Caselette - Correction of Errorsmjc24100% (4)
- Catalogo de Partes Hero KarizmaDokument98 SeitenCatalogo de Partes Hero Karizmakamil motorsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Calculation of Braking System (Landcruiser) : AbstractDokument4 SeitenDesign Calculation of Braking System (Landcruiser) : AbstractDr. Aung Ko LattNoch keine Bewertungen
- GR No. 188213 - January 11, 2016 FACTS: Herein Petitioner, Natividad Cruz, Was The Punong Barangay or Chairperson of BarangayDokument6 SeitenGR No. 188213 - January 11, 2016 FACTS: Herein Petitioner, Natividad Cruz, Was The Punong Barangay or Chairperson of BarangayAilyn GaluraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nagpur Company List 2Dokument10 SeitenNagpur Company List 2Kaushik BachanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 010 Informed Search 2 - A StarDokument20 Seiten010 Informed Search 2 - A StarRashdeep SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guia de Desinstalación de ODOO EN UBUNTUDokument3 SeitenGuia de Desinstalación de ODOO EN UBUNTUjesusgom100% (1)
- Efqm Success-Story-Book LRDokument34 SeitenEfqm Success-Story-Book LRabdelmutalabNoch keine Bewertungen
- NF en 1317-5 In2Dokument23 SeitenNF en 1317-5 In2ArunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 7Dokument18 SeitenTopic 7Anonymous 0fCNL9T0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1: Unit 3 - Week 1Dokument80 SeitenAssignment 1: Unit 3 - Week 1sathiyan gsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business PlanDokument20 SeitenBusiness PlanRona BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bizagi Podcast TranscriptDokument6 SeitenBizagi Podcast TranscriptHortencia RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alabama GOP ResolutionDokument2 SeitenAlabama GOP ResolutionFox News67% (6)
- 14.symmetrix Toolings LLPDokument1 Seite14.symmetrix Toolings LLPAditiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Calculation Sheet: Project No: Date: Sheet No.:1 1 Computed By: SubjectDokument1 SeiteDesign Calculation Sheet: Project No: Date: Sheet No.:1 1 Computed By: SubjectAbdelfatah NewishyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mangla Refurbishment Project Salient FeaturesDokument8 SeitenMangla Refurbishment Project Salient FeaturesJAZPAKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ticket - Abibus PDFDokument1 SeiteTicket - Abibus PDFJosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualifications and Disqualifications of CandidatesDokument3 SeitenQualifications and Disqualifications of CandidatesCARLO JOSE BACTOLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Device Protocol - v2.2.4Dokument81 SeitenDevice Protocol - v2.2.4Aston MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuaverEd Lesson Plan 6-7Dokument10 SeitenQuaverEd Lesson Plan 6-7zgyleopardNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuickTransit SSLI Release Notes 1.1Dokument12 SeitenQuickTransit SSLI Release Notes 1.1subhrajitm47Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yosys+Nextpnr: An Open Source Framework From Verilog To Bitstream For Commercial FpgasDokument4 SeitenYosys+Nextpnr: An Open Source Framework From Verilog To Bitstream For Commercial FpgasFutsal AlcoletgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gcm02-Mt-Ing4 New1 PDFDokument57 SeitenGcm02-Mt-Ing4 New1 PDFabdel jabbar67% (3)
- Universal Declaration of Human RightsDokument36 SeitenUniversal Declaration of Human RightsJanine Regalado100% (4)
- Ruling The CountrysideDokument9 SeitenRuling The Countrysiderajesh duaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Needs Assessment Form Company Name: HRMO Address: Sta. Barbara Agoo, La UnionDokument2 SeitenNeeds Assessment Form Company Name: HRMO Address: Sta. Barbara Agoo, La UnionAlvin LaroyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A.R. Meenakshi v. State of Tamil Nadu, (Madras)Dokument9 SeitenA.R. Meenakshi v. State of Tamil Nadu, (Madras)J VenkatramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing NuocRut Ver02Dokument118 SeitenWriting NuocRut Ver02thuy linhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 93 .SG, CBR, MDD, PI, SP - GRDokument11 Seiten93 .SG, CBR, MDD, PI, SP - GRChandra Prakash KarkiNoch keine Bewertungen