Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Glomerulonephritis Spreadsheet
Hochgeladen von
gurneeOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Glomerulonephritis Spreadsheet
Hochgeladen von
gurneeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
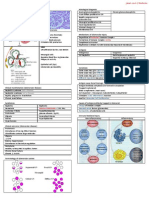
The Hallmark of glomerulonephritis is glomerular hematuria (acanthocytes and RBC casts or cellular casts), decline in renal function
and if it occurs rapidly even oliguria, hypertension and edema may be present. On light microscopy, glomerulonephritis may be
notable for “proliferative” changes (an influx of PMN’s). If the damage to the glomerulus is severe, there can be regions of necrosis
(call this necrotizing GN). If the glomerular damage leads to fibrin in the urinary space, a crescent may develop. These terms,
crescentic GN, necrotizing GN, proliferative GN, are descriptive and they don't indicate the cause of the nephritis. The terms acute
nephritis or rapidly progressive GN describe the acuity but also do not indicate the cause. Instead, we typically use clinical
information and the biopsy to characterize the disorder.
For glomerulonephritis cases for H2, we will characterize by the immune mechanism:
Mechanism and
Presentation Light Microscopy EM Immunofluorescence Treatment
Pathologic name
LINEAR Ribbon-like deposits of
STAINING of IgG If there is also IgG Immunosuppressive
pulmonary therapy
Anti-GBM disease involvement, Crescentic GN Diffuse
An autoimmune disease called and/or necrotizing subendothelial Plasmapheresis to
vs. α5 chain of type IV Goodpasture’s GN deposits remove the antibody
collagen, in situ
immune complex
formation
PAUCI-IMMUNE Depends on Immunosuppressive
In most cases, we whether it is part therapy
believe ANCA of systemic Since IF is
activates PMN which illness or renal negative, no
Crescentic GN
damage glomerular limited. May be deposits on EM
and/or necrotizing Negative
endothelium (and cANCA (assoc (IF tells us WHAT
GN
potentially other small with it is, EM tells us
vessels) sinus/respiratory where)
sx) or pANCA
(assoc with GI sx)
GRANULAR STAINING of Presentation Light Microscopy EM and IF Treatment
Immune complexes
(Examples explored in H2)
Post infectious (or post strep) Subepithelial humps AND Typically, benign
1. Antigen from infection subendothelial deposits course and
deposits subendothelial space and 10 days to 2 supportive care
form immune complex in situ or weeks AFTER IF with granular and
circulating immune complexes infection irregular IgG (more earlier
deposit in subendothelial space.
(infection has in course, less-perhaps
These immune complexes are
cleaned up by influx of PMN
resolved, this is a just in those occasional
2. Small amount of antigen is
renal limited humps-once the PMN
Proliferative changes
filtered and lands in subepithelial disorder) have done their work
(influx of PMN’s and
space, small amount of antibody is closed loops)
filtered and binds antigen in situ and
forms a hump. Not a lot of these, but
they persist
Varied Usually “mesangial Electron dense deposits If severe rapid
IgA nephropathy presentations and pattern” (IgA are primarily in the course,
Evolving understanding! IgA is the severity. Ex: - glycosylated and mesangium (which is immunosuppression.
antibody of mucosal immunity, Visible hematuria prominent on PAS contiguous with the If indolent course
patients with this disorder may have within 1-2 days of
stain) subendothelial space and characterized by
abnormal IgA response or type of URI
can invite) an influx of proteinuria, RAAS
IgA with “underglycosylation” -systemic illness
Henoch-Schönlein inflammatory cells blockade
which may make it sticky and
Purpura
SLE nephritis
Autoimmune disorder with circulating immune complexes (mainly IgG but can be all) that deposit in the glomerulus, activate complement
damage the glomeruli. We used this as an example to explain nephritis and nephrosis but students not responsible for more specifics
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pathology GlomerulonephritisDokument4 SeitenPathology GlomerulonephritisGerardLum100% (2)
- Differential Diagnosis of Glomerular DiseasesDokument2 SeitenDifferential Diagnosis of Glomerular DiseasesMaryam Fadah100% (1)
- Motor and Sensory Examination: Dr. Bandar Al Jafen, MD Consultant NeurologistDokument36 SeitenMotor and Sensory Examination: Dr. Bandar Al Jafen, MD Consultant NeurologistJim Jose Antony100% (1)
- DONOR SELECTION (Deferral) - BBDokument5 SeitenDONOR SELECTION (Deferral) - BBMaikka IlaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Urology Devices MarketDokument14 SeitenGlobal Urology Devices MarketNamrataNoch keine Bewertungen
- SGD Lupus Nephritis NotesDokument6 SeitenSGD Lupus Nephritis NotesfrnksusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myasthenia Gravis and Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome - Continuum December 2016Dokument28 SeitenMyasthenia Gravis and Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome - Continuum December 2016Habib G. Moutran BarrosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstructive JaundiceDokument13 SeitenObstructive JaundiceJeevan VijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guillain Barre Syndrome A ReviewDokument7 SeitenGuillain Barre Syndrome A ReviewEditor IJTSRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal PathDokument71 SeitenRenal PathSuha AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumonia Case StudyDokument8 SeitenPneumonia Case StudyChristopher John AgueloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infectioue Bursal Disease in PoultryDokument27 SeitenInfectioue Bursal Disease in PoultryGrowel Agrovet Private Limited.67% (3)
- Askep Kritis Sistem EndokrinDokument37 SeitenAskep Kritis Sistem EndokrinDerfina Bahagia iduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Renal Disorders - 9.11.19Dokument4 SeitenSummary of Renal Disorders - 9.11.19Nicole Juliette CCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disease PDFDokument6 SeitenDisease PDFJohn Christopher LucesNoch keine Bewertungen
- DISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneDokument5 SeitenDISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneHOPENoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Pathology I. Clinical Manifestations of Renal DiseasesDokument18 SeitenRenal Pathology I. Clinical Manifestations of Renal DiseasesKrisha Marie BadilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- @acute Nephritic SyndromeDokument3 Seiten@acute Nephritic SyndromeMazlia FarzanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Table RenalDokument2 SeitenGenetics Table RenalDavid KramerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases For The BoardsDokument2 SeitenDiseases For The BoardsBrendan MillinerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mediated Disorders: (Type Icrgn) Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane Antibody Ular Basement Membrane AntibodyDokument1 SeiteMediated Disorders: (Type Icrgn) Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane Antibody Ular Basement Membrane AntibodyDian Putri NingsihNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Page PDFDokument1 SeiteFirst Page PDFrayalarasatitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small Vessel Vasculitides: Key PointsDokument9 SeitenSmall Vessel Vasculitides: Key Pointscharoline gracetiani nataliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUGSTUDY2Dokument1 SeiteDRUGSTUDY2Erin Trisha Kristel GaspanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - 1st DraftDokument12 SeitenDrug Study - 1st DraftCarelle Faith Serrano AsuncionNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALSANGEDY BULLETS FOR PACES HypogammaglobulinemiaDokument2 SeitenALSANGEDY BULLETS FOR PACES HypogammaglobulinemiaushapadminivadivelswamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CANOMAD Responding To Weekly IV ImmunoglobulinDokument4 SeitenCANOMAD Responding To Weekly IV ImmunoglobulindoctorebrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical KidneyDokument13 SeitenMedical KidneyJose SirittNoch keine Bewertungen
- SN 1Dokument9 SeitenSN 1lilisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine GBS: Guillain Barre SyndromeDokument4 SeitenMedicine GBS: Guillain Barre SyndromedinakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: PathogenesisDokument5 SeitenSystemic Lupus Erythematosus: PathogenesisMiguel Cuevas DolotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument2 SeitenChapter 7Mychelle MenesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iga Nephropathy and Glucocorticoids - A Limbo Dance?: ControversiesinnephrologyDokument1 SeiteIga Nephropathy and Glucocorticoids - A Limbo Dance?: ControversiesinnephrologyNujhat TabassumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasma Exchange in Neurological Disease.Dokument10 SeitenPlasma Exchange in Neurological Disease.zaquvubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorder Etiology: Acute GlomerulonephritisDokument1 SeiteDisorder Etiology: Acute GlomerulonephritisChynna Izzabelle Alcantara AbellanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Approach To: Rapid Progressive GlomerulonephritisDokument38 SeitenClinical Approach To: Rapid Progressive GlomerulonephritisMiri PravdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- sfs087 2 PDFDokument4 Seitensfs087 2 PDFEl KeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myasthenia Gravis: Murali Thavasothy DCH MRCP FRCA Nicholas Hirsch FRCADokument3 SeitenMyasthenia Gravis: Murali Thavasothy DCH MRCP FRCA Nicholas Hirsch FRCAMirela CiobanescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Club Presentation RPGN-1Dokument53 SeitenJournal Club Presentation RPGN-1sagor9364Noch keine Bewertungen
- PATH - Nephritic SyndromeDokument14 SeitenPATH - Nephritic SyndromeMuhamad Zul ImanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membranous Nephropathy: From Models To Man: Review SeriesDokument8 SeitenMembranous Nephropathy: From Models To Man: Review SeriesmmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glomerular Diseases My NotesDokument5 SeitenGlomerular Diseases My Notesmalar_km43Noch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 151 Congenital AspleniaDokument3 SeitenBIO 151 Congenital AspleniaLance CarandangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudyUzziah Dharambai GurbuxaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocarditis 2016 PDFDokument2 SeitenEndocarditis 2016 PDFNiken DoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antoine 2017Dokument8 SeitenAntoine 2017Eliana NataliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Glomerular Basement Membrane Disease.18Dokument11 SeitenAnti Glomerular Basement Membrane Disease.18Lucas SilveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogenesis of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody-Mediated DiseaseDokument11 SeitenPathogenesis of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody-Mediated DiseasewilpmfmhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glomerular Disease - Dr. LuDokument8 SeitenGlomerular Disease - Dr. LuMACATANGAY, GAELLE LISETTENoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal DiseaseDokument5 SeitenRenal DiseasefeajhanineladagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type Alternative Names Often Mentioned Disorders Mediators DescriptionDokument2 SeitenType Alternative Names Often Mentioned Disorders Mediators DescriptionLokesh BakshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in An Immunocompetent IndivDokument7 SeitenCerebral Toxoplasmosis in An Immunocompetent IndivSultan GanieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Nephritic SyndromeDokument15 SeitenAcute Nephritic SyndromeTharen OfficialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bibliography: Life Span - Philadelphia, PA 19103: F.A. Davis CompanyDokument5 SeitenBibliography: Life Span - Philadelphia, PA 19103: F.A. Davis CompanyCarlos LleverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephritic SyndromeDokument15 SeitenNephritic Syndrome76q88b4yrxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome Pediatrico 2018Dokument4 SeitenGuillain-Barré Syndrome Pediatrico 2018Mariam Plata100% (1)
- IgA NephropathyDokument5 SeitenIgA NephropathyLara Patricia TamsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISLAB P2 - Anti-Streptolysin ODokument4 SeitenISLAB P2 - Anti-Streptolysin ODanielle Anne LambanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patologi GinjalDokument94 SeitenPatologi GinjalDenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 - Neuromuscular Disorders in The Intensive Care UnitDokument21 Seiten2021 - Neuromuscular Disorders in The Intensive Care UnitOlga Manco GuzmánNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pain in The Neck, Shoulder, Back, or Diffusely Over The Spine Is Also Common in The Early Stages, Occurring in 50% of PatientsDokument8 SeitenPain in The Neck, Shoulder, Back, or Diffusely Over The Spine Is Also Common in The Early Stages, Occurring in 50% of Patientsnathan asfahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3934 1 5718 1 10 20121128 PDFDokument7 Seiten3934 1 5718 1 10 20121128 PDFPosterilmiah Majestynas2019Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bagian Patologi Anatomi Fk-Uisu 2011Dokument22 SeitenBagian Patologi Anatomi Fk-Uisu 2011rizapuspairyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- MICRO 028 Atypical PneumoniaDokument5 SeitenMICRO 028 Atypical PneumoniaFamela Anne GOmez MadambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MeningitisDokument3 SeitenMeningitisDiana Fadhilah SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of The Drug Mechanism of Action Dosage Indicatio NS Contraindi Cations Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibiliti ESDokument5 SeitenName of The Drug Mechanism of Action Dosage Indicatio NS Contraindi Cations Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibiliti EShey aadarshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Toward Cervical Cancer and Cervical Cancer Screening and Its Associated Factors Among Women in The City of Bamenda, CameroonDokument17 SeitenKnowledge, Attitude and Practice Toward Cervical Cancer and Cervical Cancer Screening and Its Associated Factors Among Women in The City of Bamenda, CameroonEditor IJTSRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eward SKDRDokument87 SeitenEward SKDRBasroni FaizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Lifestyle Interventions On Type 2 Diabetes Management, A Comprehensive AnalysisDokument2 SeitenThe Impact of Lifestyle Interventions On Type 2 Diabetes Management, A Comprehensive AnalysisJohn nyoikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rubifen 10 MG Immediate Release TabletsDokument8 SeitenRubifen 10 MG Immediate Release TabletsMuse LoverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Removing Gallstones From Your Body: Recommended PracticeDokument1 SeiteRemoving Gallstones From Your Body: Recommended PracticeRyok DaysNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Stuart Crisp DR Per Grinsted: Written byDokument8 SeitenDR Stuart Crisp DR Per Grinsted: Written byRizky MarethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doon Institute of Medical Science2 (Exam Paper)Dokument3 SeitenDoon Institute of Medical Science2 (Exam Paper)Shaila PanchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sanford GuideDokument7 SeitenSanford GuideViniciusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled PresentationDokument228 SeitenUntitled PresentationSafira WasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrocardiografia BasicaDokument49 SeitenElectrocardiografia BasicaENRIQUEVERSAGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buy Augmentin 1000 - AllDayGenericDokument7 SeitenBuy Augmentin 1000 - AllDayGenericBonitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Washing Lesson PlanDokument9 SeitenHand Washing Lesson PlanLisa GurreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParkinsonDokument24 SeitenParkinsonSandy AgustianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5: PhysiotherapyDokument9 SeitenUnit 5: PhysiotherapyBial MediaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KSC WSSforKSCCQIDokument34 SeitenKSC WSSforKSCCQILệnhHồXungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral PathologyDokument31 SeitenOral PathologyAnonymous GyqTkXMwMNoch keine Bewertungen
- FTT and PEMDokument38 SeitenFTT and PEMdonaha87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment of Hyponatremia - Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH) and Reset OsmostatDokument15 SeitenTreatment of Hyponatremia - Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH) and Reset Osmostathoneyworks100% (1)
- Diagnosis: ChildrenDokument2 SeitenDiagnosis: ChildrencsomimagesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohol Word SearchDokument2 SeitenAlcohol Word SearchAndy Brooke0% (1)
- Symptoms and Signs: Compartment SyndromeDokument4 SeitenSymptoms and Signs: Compartment SyndromeajeikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifikasi Risiko Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDS) Pada Pekerja Pandai BesiDokument10 SeitenIdentifikasi Risiko Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDS) Pada Pekerja Pandai BesiTito MuharamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caso 2Dokument78 SeitenCaso 2Khairul ScNoch keine Bewertungen