Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ECG Circuit PDF
Hochgeladen von
arduino signaux cardiaquesOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ECG Circuit PDF
Hochgeladen von
arduino signaux cardiaquesCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
instructables
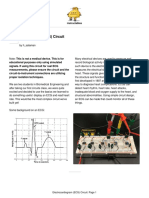
ECG Circuit
by JessicaB328
An ECG is a test that measures the electrical activity the power outlet in the wall. The low pass filter
of the heart by recording the heart's rhythm and ensures that high frequency noise is removed from
activity. It works by taking and reading signals from the circuit for better signal detection.
the heart using leads that are attached to an
electrocardiograph machine. This Instructable will Before starting this Instructable, it would be helpful to
show you how to build a circuit that records, filters, familiarize yourself with the uA741 General Purpose
and displays the bioelectric signal of the heart. This is Operational Amplifier. The different pins in the op-
not a medical device. This is for educational purposes amp have different purposes and the circuit will not
only using simulated signals. If using this circuit for work if they are connected incorrectly. Connecting the
real ECG measurements, please ensure the circuit pins to the breadboard incorrectly is also an easy way
and the circuit-to-instrument connections are utilizing to fry the op-amp and make it non-functional. The link
proper isolation techniques. below contains the schematic used for the op-amps in
this instructable.
This circuit contains three different stages wired http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/ua741.pdf
together in series with a LabView program. The
resistors in the instrumentation amplifier were Image Source:
calculated with a gain of 975 to ensure that the small http://ak0.picdn.net/shutterstock/videos/17671660/thu
signals from the heart can still be picked up the mb/1.jpg
circuit. The notch filter takes out the 60 Hz noise from
ECG Circuit: Page 1
Step 1: Collect Materials
Materials needed for all 3 stages of filter:
Oscilloscope
Function generator
Power supply (+15V, -15V)
Solderless breadboard
Various banana cables and alligator clips
ECG Electrode Stickers
Various jumper wires
Instrumentation amplifier:
3 Op-amps (uA741)
Resistors:
1k x3
12 k x 2
39 k x 2
Notch Filter:
1 Op-amp (uA741)
Resistors:
1.6 k x 2
417 k
Capacitors:
100 nF x 2
200 nF
Low Pass Filter:
1 Op-Amp (uA741)
Resistors:
23.8 k
43 k
Capacitors:
22 nF
47 nF
ECG Circuit: Page 2
Step 2: Build Instrumentation Amplifier
Biological signals often only output voltages between After your circuit is built, test to make sure that it is
0.2 and 2 mV [2]. These voltages are too small to be working correctly by measuring the voltage at Vout
analyzed on the oscilloscope so we needed to build (shown as node 2 in the image above). We used the
an amplifier. function generator to send a sine wave with an input
amplitude voltage of 20 mV to our instrumentation
amplifier. Anything too far above this will not give you k range.
the results you are looking for because the op amps
were only getting a certain amount of power of -15 [2]“High Performance Electrocardiogram (ECG)
and +15 V. Compare the output of the function Signal Conditioning | Education | Analog Devices.”
generator to the output of your instrumentation [Online]. Available:
amplifier and look for a gain of close to 1000 V. http://www.analog.com/en/education/education-
(Vout/Vin should be very close to 1000). library/articles/high-perf-electrocardiogram-signal-
conditioning.html. [Accessed: 10-Dec-2017].]
Tip for troubleshooting: Make sure all resistors are in
Step 3: Build Notch Filter
Our notch filter was designed to filter out a frequency signal at 60 Hz! Test frequencies around 60 Hz as
at 60 Hz. We want to filter out the 60 Hz from our well to make sure that no other frequencies are being
signal because that is the frequency of the alternating filtered out accidentally.
current found in electrical outlets.
Tip for troubleshooting: If you can’t get exactly -20dB
When testing the notch filter, measure the peak-to- at 60 Hz, pick one resistor and change it slightly until
peak ratio between the input and output graphs. At 60 you get the desired results. We had to play around
Hz, there should be a ratio of -20 dB or better. This is with the value of R2 until we got the results we
because at -20 dB, the output voltage is essentially wanted.
0V, meaning that you successfully filtered out the
ECG Circuit: Page 3
Step 4: Build Low Pass Filter
Our low pass filter was designed with a cutoff frequency is within a few Hz of 150 Hz your circuit
frequency of 150 Hz. We chose this cutoff because should still work. Our cutoff ended up being 153 Hz.
the widest diagnostic range for an ECG is 0.05 Hz - The range for biological signals will fluctuate a little in
150 Hz, assuming a motionless and low noise the body so as long as you are not off more than a
environment [3]. The low pass filter is able to get rid few Hz, your circuit should still work.
of high frequency noise coming from muscles or other
parts of the body[4]. [3] “ECG Filters | MEDTEQ.” [Online]. Available:
http://www.medteq.info/med/ECGFilters. [Accessed:
In order to test this circuit to ensure that it is working 10-Dec-2017].
correctly, measure Vout (shown as node 1 in the
circuit diagram). At 150 Hz, the amplitude of the [4] K. L. Venkatachalam, J. E. Herbrandson, and S. J.
output signal should be 0.7 times the amplitude of the Asirvatham, “Signals and Signal Processing for the
input signal. We used an input signal of 1V in order to Electrophysiologist: Part I: Electrogram Acquisition,”
be able to easy see that our output should be 0.7 at Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol., vol. 4, no. 6, pp.
150 Hz. 965–973, Dec. 2011.
Tips for troubleshooting: as long as your cutoff
ECG Circuit: Page 4
Step 5: Create LabView Program
[5] “BME 305 Design Lab Project “ (Fall 2017).
This labview block diagram is designed to analyze the signal going through the program, detect ECG peaks,
collect the time difference between the peaks, and mathematically calculate the BPM. It also outputs a graph of
the ECG waveform.
Step 6: Connect All Three Stages
Connect all three circuits in series by connecting the are all connected to the same ground terminal.
output of the instrumentation amplifier to the input of
the notch filter and the output of the notch filter to the In the instrumentation amplifier, the second op-amp
input of the low pass filter. Connect the output of the needs to be ungrounded so that two electrode leads
low pass filter to the DAQ assistant and connect the that are connected to the test subject can each
DAQ assistant to the computer. When wiring the connect to a different op amp in the first stage of that
circuits together, make sure that the power strips for filter.
each breadboard are connected and the ground strips
Step 7: Get Signals From a Human Test Subject
One electrode sticker should be placed on each wrist, and one should be placed on the ankle for ground. Use
alligator clips to connect the two wrist electrodes to the inputs of the instrumentation amplifier and the ankle to
ground. When ready, click “run” on the LabView program and see your heart rate and ECG on the screen!
ECG Circuit: Page 5
ECG Circuit: Page 6
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) Circuit: InstructablesDokument10 SeitenElectrocardiogram (ECG) Circuit: InstructablesDulanjalee KatulandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Proj4 - ECG EMG AmplifierDokument6 SeitenProj4 - ECG EMG AmplifierPerumal VigneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Make Your Own Electrocardiogram ECGDokument8 SeitenMake Your Own Electrocardiogram ECGDavid Altamirano del AngelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesVon EverandAudio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Instrumentationamplifier ECGDokument35 SeitenInstrumentationamplifier ECGRoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Lab Assignment: Read and Review Sections 2.4, 2.8.2, 9.9.3, 13.4, 13.5, and 13.9 inDokument11 SeitenPre-Lab Assignment: Read and Review Sections 2.4, 2.8.2, 9.9.3, 13.4, 13.5, and 13.9 inThe_Dude1138Noch keine Bewertungen
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Von EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Electronic Devices Lab - Exp - 7 - Student - Manual (Summer 18-19)Dokument4 SeitenElectronic Devices Lab - Exp - 7 - Student - Manual (Summer 18-19)MD MONIM ISLAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conference Proceeding NTAFM 2013Dokument3 SeitenConference Proceeding NTAFM 2013atifthestarNoch keine Bewertungen
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Von EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Low Pass Filter 1st OrderDokument7 SeitenLow Pass Filter 1st OrdervlsijpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsVon EverandAudio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG PosterDokument1 SeiteECG PosterJack MarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorVon Everand110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Wein Bridge Oscillator: f =1/2π√R1C1R2C2Dokument11 SeitenWein Bridge Oscillator: f =1/2π√R1C1R2C2krishna goggiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project 2 EE087732Dokument13 SeitenProject 2 EE087732Mei QiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit & Devices Lab ManualDokument107 SeitenCircuit & Devices Lab ManualKALAIMATHI100% (2)
- ECG Circuit Analysis and Design Engineers LabsDokument29 SeitenECG Circuit Analysis and Design Engineers LabsDebasish HalderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Circuits Lab ManualDokument34 SeitenElectric Circuits Lab ManualMohamad FariezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3Dokument5 SeitenLab 3Ricardo VelazquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Es2c0 Lab Assessment PDFDokument28 SeitenEs2c0 Lab Assessment PDFdinski desNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELEC3106 Lab 1 - Op-Amp MeasurementsDokument3 SeitenELEC3106 Lab 1 - Op-Amp MeasurementsRuben CollinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- That You Read All The Background Information of This Laboratory BEFORE Proceding With The ExperimentDokument14 SeitenThat You Read All The Background Information of This Laboratory BEFORE Proceding With The ExperimentRajith MohananNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Two Lead ECGDokument9 SeitenA Two Lead ECGbiplab260187Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiDokument28 SeitenLaboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiAtul SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure - AC Circuits and Signal Modulation - W20Dokument6 SeitenProcedure - AC Circuits and Signal Modulation - W20ChocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 332 Lab 3Dokument10 SeitenEE 332 Lab 3Nguyễn Văn ThiệnNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokument11 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSudha SivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELVIS AC Circuit ToolsDokument7 SeitenELVIS AC Circuit ToolsHermes PolancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 3 - Common Emitter AmplifierDokument6 SeitenExperiment 3 - Common Emitter AmplifierAsyraf Norahairuzan100% (1)
- Electric Circuits Lab ManualDokument33 SeitenElectric Circuits Lab Manualsheikmd80% (5)
- Biomedicak Instrumentation LabDokument56 SeitenBiomedicak Instrumentation LabMD. ASHIQUR RAHMAN 1602111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eee334 Lab#1 Ltspice and Lab Orientation - Instruments and MeasurementsDokument9 SeitenEee334 Lab#1 Ltspice and Lab Orientation - Instruments and Measurementsplaystation0% (1)
- American International University-Bangladesh: Electronic DevicesDokument5 SeitenAmerican International University-Bangladesh: Electronic DevicesAnamNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Machines Lab ManualDokument52 SeitenAC Machines Lab ManualmitulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrators, Differentiators, and Simple Filters: 6. PrelabDokument15 SeitenIntegrators, Differentiators, and Simple Filters: 6. PrelabMIn LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 02 IOBoard RED2Dokument19 SeitenExp 02 IOBoard RED2Daniel AdebayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecg CircuitDokument12 SeitenEcg CircuitAbdullah AfifiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrator Circuits: 7.0.1 ReadingDokument5 SeitenIntegrator Circuits: 7.0.1 Readingnaveenkv10_105528408Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECG AmplifierDokument8 SeitenECG AmplifierBosco LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIC Lab ManualDokument57 SeitenLIC Lab ManualsfundsNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC and ECAD LabDokument88 SeitenIC and ECAD LabVeerayya JavvajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1-Bjt AmplifierDokument8 SeitenLab 1-Bjt Amplifierhasnain3257100% (1)
- Thapar University Patiala: BE-EIC (VII Semester) Mid-Sem Sept. 2015Dokument1 SeiteThapar University Patiala: BE-EIC (VII Semester) Mid-Sem Sept. 2015Rishabh SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic ElectronicsDokument126 SeitenBasic ElectronicsFarazNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELEC4810 Notes-4 PDFDokument27 SeitenELEC4810 Notes-4 PDFKwan ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics Course Lab WorkbookDokument103 SeitenBasic Electronics Course Lab WorkbookApril ShowersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 9Dokument5 SeitenLab 9gratz_redobleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of The Real Time ECG Signal Processing and Monitoring System Using Lab VIEW With Data Acquisition SystemDokument4 SeitenDesign of The Real Time ECG Signal Processing and Monitoring System Using Lab VIEW With Data Acquisition SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt 6Dokument3 SeitenExpt 6sabitavabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kstatham Project Final ReportDokument17 SeitenKstatham Project Final ReportZulqarnain HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- AKNM - 3049 - AKNMGptcDokument53 SeitenAKNM - 3049 - AKNMGptchod eceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aic Modified 1Dokument80 SeitenAic Modified 1leevasusanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications QtyDokument0 SeitenCommon Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications Qtyagama1188Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Circuit Design (December 2016)Dokument65 SeitenElectronic Circuit Design (December 2016)Qasim LodhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trucks Fin Eu PCDokument117 SeitenTrucks Fin Eu PCjeanpienaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared by (Hospital Pharmacist) Primary & Secondary Healthcare DepartmentDokument11 SeitenPrepared by (Hospital Pharmacist) Primary & Secondary Healthcare DepartmentwaqasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be Project Presentation SuspensionDokument17 SeitenBe Project Presentation SuspensionGabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omnivision Man lp06xx Rev0 0611Dokument18 SeitenOmnivision Man lp06xx Rev0 0611ivan ramirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBRO News 2004Dokument8 SeitenIBRO News 2004International Brain Research Organization100% (1)
- 2017 Induction Programme V1Dokument3 Seiten2017 Induction Programme V1AL SolmiranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afm Udc A320-500Dokument600 SeitenAfm Udc A320-500melitiyaprorok100% (1)
- 2017 Hyundai Sonata L4-2.4L Engine Controls (Powertrain Management) - ALLDATA RepairDokument6 Seiten2017 Hyundai Sonata L4-2.4L Engine Controls (Powertrain Management) - ALLDATA RepairChino PlagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Make FireworksDokument14 SeitenHow To Make FireworksLeonardo BiancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Da13 DDR N1 14000305 254 0Dokument3 SeitenDa13 DDR N1 14000305 254 0Hamed NazariNoch keine Bewertungen
- GenesDokument33 SeitenGenesJerick RoxasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bosch Rexroth EFC3600 Manual PDFDokument238 SeitenBosch Rexroth EFC3600 Manual PDFHomero Rios PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beautiful Results: Simple Procedure 1. Etch 2. Bond 3. RestoreDokument4 SeitenBeautiful Results: Simple Procedure 1. Etch 2. Bond 3. RestoreEuclides Soza CalvoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deutz Fahr Rear Axle T 7100 Workshop ManualDokument22 SeitenDeutz Fahr Rear Axle T 7100 Workshop Manualcindybennettmd040595jbw100% (134)
- Paper 1Dokument4 SeitenPaper 1asa.henfield2Noch keine Bewertungen
- DE (Diatomaceous Earth) BenefitsDokument9 SeitenDE (Diatomaceous Earth) BenefitsIlqa116100% (1)
- Unusual and Marvelous MapsDokument33 SeitenUnusual and Marvelous MapsRajarajan100% (1)
- Ncs University System Department of Health Sciences: Discipline (MLT-04) (VIROLOGY &MYCOLOGY)Dokument5 SeitenNcs University System Department of Health Sciences: Discipline (MLT-04) (VIROLOGY &MYCOLOGY)Habib UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure - Citadines Flatiron Phnom Penh - EnglishDokument4 SeitenBrochure - Citadines Flatiron Phnom Penh - EnglishTix VirakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alginate Impression MaterialDokument92 SeitenAlginate Impression MaterialrusschallengerNoch keine Bewertungen
- r315 Quick Start PDFDokument80 Seitenr315 Quick Start PDFfdsfasdsfadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Euler StrutDokument16 SeitenSimple Euler StrutDaniel MabengoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rolling Fig Q A AnalysisDokument11 SeitenRolling Fig Q A AnalysisRavinder Antil100% (9)
- HK USP CompactDokument56 SeitenHK USP CompactJonathan CrenshawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helminths: NematodesDokument17 SeitenHelminths: NematodesNicolle PanchoNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFORMATION SHEET No. 1.1.1Dokument7 SeitenINFORMATION SHEET No. 1.1.1Sandre Walden-SCSCNoch keine Bewertungen
- P&S U V PracticeDokument4 SeitenP&S U V PracticeHari KrushnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portable Load Banks: CressallDokument1 SeitePortable Load Banks: CressallYashveer26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Think Before Buying: ReadingDokument1 SeiteThink Before Buying: ReadingadrianmaiarotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NL0520 NEPAL SagarmathaDokument12 SeitenNL0520 NEPAL SagarmathaPrashantpal RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionVon EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (331)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tVon EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (27)
- The Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceVon EverandThe Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionVon EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (543)
- Foundations of Western Civilization II: A History of the Modern Western World (Transcript)Von EverandFoundations of Western Civilization II: A History of the Modern Western World (Transcript)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (12)
- Beginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Fourth EditionVon EverandBeginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Fourth EditionBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (10)
- Arduino and Raspberry Pi Sensor Projects for the Evil GeniusVon EverandArduino and Raspberry Pi Sensor Projects for the Evil GeniusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsVon EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- The Homeowner's DIY Guide to Electrical WiringVon EverandThe Homeowner's DIY Guide to Electrical WiringBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersVon Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonVon EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- A Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeVon EverandA Mind at Play: How Claude Shannon Invented the Information AgeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (53)
- The Fast Track to Your Extra Class Ham Radio License: Covers All FCC Amateur Extra Class Exam Questions July 1, 2020 Through June 30, 2024Von EverandThe Fast Track to Your Extra Class Ham Radio License: Covers All FCC Amateur Extra Class Exam Questions July 1, 2020 Through June 30, 2024Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsVon EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...Von EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...Noch keine Bewertungen
- Retro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsVon EverandRetro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldVon EverandEmpires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (87)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeVon EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (10)
- IEC 61850-Based Smart Substations: Principles, Testing, Operation and MaintenanceVon EverandIEC 61850-Based Smart Substations: Principles, Testing, Operation and MaintenanceYubo YuanBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialVon EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Guide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)Von EverandGuide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Electric Powertrain: Energy Systems, Power Electronics and Drives for Hybrid, Electric and Fuel Cell VehiclesVon EverandElectric Powertrain: Energy Systems, Power Electronics and Drives for Hybrid, Electric and Fuel Cell VehiclesNoch keine Bewertungen