Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
(S) Chapter 2&3
Hochgeladen von
Vilma TayumOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
(S) Chapter 2&3
Hochgeladen von
Vilma TayumCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
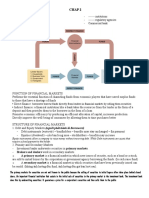
Chapter 2- Overview of the Financial System
Function: channel funds from lender-savers to borrower-spenders
Principal lender-savers are households
Most important borrower-spenders- business and government
Flow of funds:
Direct finance- borrowers borrow directly from lenders in financial market by selling them
**securities- financial instruments, claim on borrower’s future income or assets
Bond- debt security, promises to make payments for specified time
Stock- security entitles owner a share of company’s profits and assets
Role of financial markets
Structure
Debt and Equity Markets
*Bond or Mortgage
*Stock
Primary and Secondary Market
Primary Market- important assistant, investment bank- underwriting securities
Secondary Market
Examples: New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated
Quotation System),
Brokers- agents of investors who match buyers with sellers of securities
Dealers- link buyers and sellers by buying and selling securities
Important functions:
1. Easy to sell financial instruments to raise cash, more liquid
2. Determine price of security that issuing firm sells in primary market
Secondary markets organized in two ways: Exchanges and Over-the-counter Markets
Exchanges- buyers and sellers meet at central location to conduct trades
Over-the-counter- where dealers are ready to buy and sell securities to anyone willing to accept their
prices
Money Market – short-term debt instruments are traded
-least price fluctuations, least risky investments
FRUNC
*US treasury bills- most liquid, most actively traded
-safest, no possibility of default
*Negotiable Bank Certificates of Deposit-
*Commercial Paper
*Repurchase Agreements-
*Federal funds-
Capital Markets – longer-term debts and equity instruments are traded
*Stocks- equity claims on net income and assets
*Mortgages and mortgage-backed securities- SMCCS
*Corporate Bonds-
*State and Local Government Bonds-
*Consumer and Bank Commercial Loans
Internationalization of Financial Markets
Foreign bonds
Eurobond
Eurocurrencies
Function of Financial intermediaries:
Indirect Finance- process called financial intermediation
*reduce Transaction cost- the time and money spent in carrying out financial transactions
Economies of scale
*promote risk sharing- asset transformation; reduce exposure of investor to risk
Asymmetric information:
Before the transaction results to adverse selection
After. Moral hazard
As we have seen, financial intermediaries play an important role in the economy because they provide
liquidity services, promote risk sharing, and solve information problems, thereby allowing small savers
and borrowers to benefit from the existence of financial markets.
Types of Intermediaries
1. Depository institutions
-commercial banks CT
-thrift institutions: savings and loan associations, mutual savings bank and credit unions
*lia: deposits
2. Contractual savings institutions
-Life insurance companies
-Fire and casualty insurance company
LFP
- Pension funds and government retirement funds
*source of funds: premiums from policies
*assets: municipal bonds, corporate stock and bonds
3. Investment intermediaries
-finance companies, *assets: consumer and business loans
-mutual funds MMF
- Money market mutual funds.
*primary assets: money market instruments
-investment banks
Regulation of Financial system
- increase the information available to investors
- to ensure the soundness of the financial system.
To avoid financial panics, there are 6 types of regulations:
1. Restrictions on entry
2. Disclosure
3. Restrictions on assets and activities
4. Deposit insurance
5. Limits on competition
6. Restrictions on interest rates
Chapter 3: Money
Functions:
1. as a medium of exchange
Criteria to function as money:
1. Easily standardized
2. Widely accepted
3. Divisible
4. Easy to carry
5. Not deteriorate quickly
-avoids double coincidence of wants on a barter economy, reduce cost
- encourage specialization and division of labor
2. as a unit of account
= N(N-1)/2
-reduces prices needed in the economy, reduce transaction cost
3. as a store of value
- store of value depends on the price level
- inflation
Evolution of Payments system- method of conducting transactions in the economy
Commodity money- made up of metals or valuable commodity
Disadv. Heavy, hard to transport
Fiat money- paper currency, legal tender accepted as payments but not convertible
Adv.lighter than coins and metals
Disadv. Easily stolen and expensive to transport in large amounts, issues of counterfeiting
Checks- instruction from you to banks to transfer money
- no need to carry large amounts
- improve efficiency of payments system
- reduces transportation cost
- written for any amount
- loss from theft is reduced
- convenient receipts for purchases
disadv. Takes time
Electronic payment-
E-money- money in electronic form
1. debit card
2. more advanced, stored-value card, more sophisticated, smart card
3. e-cash
. The Federal Reserve System has defined two different measures of the money supply—M1 and
M2. These measures are not equivalent and do not always move together, so they cannot be used
interchangeably by policymakers. Obtaining the precise, correct measure of money does seem to
matter and has implications for the conduct of monetary policy
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 2 Changes in MaterialsDokument35 SeitenScience: Quarter 1 - Module 2 Changes in MaterialsVilma Tayum71% (7)
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 2 Changes in MaterialsDokument35 SeitenScience: Quarter 1 - Module 2 Changes in MaterialsVilma Tayum71% (7)
- Financial System, Markets and ServicesDokument65 SeitenFinancial System, Markets and Servicessatya123b8101100% (1)
- © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaDokument56 Seiten© The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaTejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUMMARY 1 (Chapter 2&3)Dokument7 SeitenSUMMARY 1 (Chapter 2&3)Kadek Indah Dwi CahyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-CHMSC FinMgt2-FinMar. Module 1Dokument4 Seiten2-CHMSC FinMgt2-FinMar. Module 1Christopher ApaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- USLS. FinMgt2-FinMar. Module 1Dokument5 SeitenUSLS. FinMgt2-FinMar. Module 1Marian Augelio PolancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 2-3 - 4 - 5 LTTCDokument24 SeitenChap 2-3 - 4 - 5 LTTCQuyên NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Economics of Money and Financial MarketsDokument16 SeitenThe Economics of Money and Financial MarketsThanh Thủy KhuấtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial System ResumeDokument4 SeitenFinancial System ResumeRim ChtiouiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cifa Financial Institutions and Markets PDFDokument104 SeitenCifa Financial Institutions and Markets PDFMswakubaffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument4 SeitenChapter 2Phương Anh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resumo MarketsDokument18 SeitenResumo Marketsjose silvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gitman - Principle of Managerial Finance Chapter 2 SummaryDokument6 SeitenGitman - Principle of Managerial Finance Chapter 2 SummaryNisha hernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Finance ReportDokument4 SeitenGlobal Finance ReportLORIDELLE ABONALESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2: Overview of The Financial SystemDokument43 SeitenChapter 2: Overview of The Financial Systememre kutayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1. Economies of Financial SystemDokument31 SeitenChapter 1. Economies of Financial Systembr bhandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- IFS NotesDokument4 SeitenIFS NoteskirsurkulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Instruments, Financial Markets, and Financial InstitutionsDokument32 SeitenFinancial Instruments, Financial Markets, and Financial InstitutionsJunaid JamshaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Institution Institutions and MarketsDokument13 SeitenFinancial Institution Institutions and Marketstarekegn gezahegnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fins1612 Notes: Topic 1: Introduction (Chapter 1: A Modern Financial System: An Overview)Dokument6 SeitenFins1612 Notes: Topic 1: Introduction (Chapter 1: A Modern Financial System: An Overview)mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument40 SeitenChapter 2Farapple24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Institutions and MarketsDokument20 SeitenFinancial Institutions and MarketsCome-all NathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Money Payment System-2Dokument42 SeitenIntroduction To Money Payment System-2lawwrrance chanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introducing Money and Interest RatesDokument3 SeitenIntroducing Money and Interest RatesJrlyn DaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter #1: Essence of Banking: 3) Financial System: ElementsDokument7 SeitenChapter #1: Essence of Banking: 3) Financial System: ElementsPedro ArteagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 18Dokument11 SeitenCH 18Huten VasellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Institutions NotesDokument12 SeitenFinancial Institutions NotesSherif ElSheemyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Money, Banking, and Financial MarketsDokument11 SeitenChapter 1: Money, Banking, and Financial MarketsKerby Gail RulonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 5 Money The Central Bank and Interest RateDokument5 SeitenUNIT 5 Money The Central Bank and Interest RateNguyễn Phương LinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 Introduction SDokument39 SeitenChapter1 Introduction STuong Vi Nguyen PhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Markets and Institutions: Fundamenta Ls of Corporate FinanceDokument18 SeitenFinancial Markets and Institutions: Fundamenta Ls of Corporate Financehamza_ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDokument19 SeitenFinancial Markets and InstitutionsHashir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BFI Reviewer (Midterm) 1Dokument4 SeitenBFI Reviewer (Midterm) 1tiniee0510Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4: Lending and Borrowing in The Financial System (Part I)Dokument6 SeitenLesson 4: Lending and Borrowing in The Financial System (Part I)Jamille Rose PagulayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fin 2 Prelim NotesDokument8 SeitenFin 2 Prelim NotesChaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FUNDAMENTALS (Introduction) Financial MarketsDokument18 SeitenFUNDAMENTALS (Introduction) Financial MarketslykaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1-3 - FMDokument4 SeitenModule 1-3 - FMryokie dumpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ifss Mod-1Dokument24 SeitenIfss Mod-1ŚŰBHÁM řájNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Financial SystemDokument33 SeitenOverview of Financial SystemmengistuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bac821 Financial SystemsDokument13 SeitenBac821 Financial SystemsLinet OrigiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monetary and Financial Economic: 2 Année de La Grande Ecole de L'institut de RabatDokument23 SeitenMonetary and Financial Economic: 2 Année de La Grande Ecole de L'institut de RabatIsmaîl TemsamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 1 1.1 Financial Intermediation: Market FailuresDokument3 SeitenChap 1 1.1 Financial Intermediation: Market FailurestrangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Three: Financial Instruments, Financial Markets, and Financial InstitutionsDokument62 SeitenChapter Three: Financial Instruments, Financial Markets, and Financial InstitutionsE-man HuckymNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of The Financial SystemDokument18 SeitenOverview of The Financial Systemcamilleescote562Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECN 506-Chapter 1Dokument6 SeitenECN 506-Chapter 1Emme ChuteNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECN 506-Chapter 1Dokument6 SeitenECN 506-Chapter 1Emme ChuteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Money MarketDokument4 SeitenMoney MarketivandimaunahannnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 1Dokument13 SeitenSession 1Mohamed BadawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Financial MarketsDokument12 SeitenSummary Financial MarketsNgoc AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. What Is The Money MarketDokument18 SeitenI. What Is The Money MarketThanh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- GK FM&I Q&ADokument8 SeitenGK FM&I Q&Acương trươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Financial System ContDokument9 SeitenOverview of Financial System ContBienvenido JmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument5 SeitenChapter 1trangvnngn0308Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 2Dokument54 SeitenChap 2Yeshiwork GirmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 STOCKS 101Dokument4 SeitenChapter 1 STOCKS 101Annadelle Dimatulac LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One An Overview of The Financial System Definition of The Financial SystemDokument10 SeitenChapter One An Overview of The Financial System Definition of The Financial SystemSeid KassawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Markets (Chapter 5)Dokument3 SeitenFinancial Markets (Chapter 5)Kyla DayawonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABIYDokument9 SeitenABIYEyob HaylemariamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 248 Chapter 2 SummaryDokument13 Seiten248 Chapter 2 SummaryAhmed KHALILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To FinanceDokument25 SeitenChapter 1 - Introduction To Financedoanthunguyet.pisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Unorthodoxy: Practicable Views on Money, Banking and InvestingVon EverandFinancial Unorthodoxy: Practicable Views on Money, Banking and InvestingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proper Etiquette and Safety in The Use of Facilities and Equipment 11Dokument2 SeitenProper Etiquette and Safety in The Use of Facilities and Equipment 11Vilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekly Home Learning Plan Week 1 Q1 - VILMA - PupilsDokument1 SeiteWeekly Home Learning Plan Week 1 Q1 - VILMA - PupilsVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indicator 4 Level 1Dokument2 SeitenIndicator 4 Level 1Vilma Tayum100% (1)
- WW3 English3 Q4Dokument1 SeiteWW3 English3 Q4Vilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acr SmeaDokument1 SeiteAcr SmeaVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAILY PAYMENT OF DELIVERIES of Bread DOMADokument2 SeitenDAILY PAYMENT OF DELIVERIES of Bread DOMAVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekly Mail and Fitness Plan 2.ODokument3 SeitenWeekly Mail and Fitness Plan 2.OVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Region: Division: Date of Submission: - Contact Number: Supply OfficerDokument37 SeitenRegion: Division: Date of Submission: - Contact Number: Supply OfficerVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Four Spheres in Stage PresenceDokument1 SeiteThe Four Spheres in Stage PresenceVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACR During The Conduct of SmeaDokument1 SeiteACR During The Conduct of SmeaVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accountability FrameworkDokument1 SeiteAccountability FrameworkVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Lesson Plan in Science IiiDokument3 SeitenA Lesson Plan in Science IiiVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Lesson Plan in English IiiDokument3 SeitenA Lesson Plan in English IiiVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Completion ReportDokument1 SeiteActivity Completion ReportVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biweekly 3.1 - QDokument3 SeitenBiweekly 3.1 - QVilma Tayum100% (1)
- 7:00 - 7:20 Teacher's Preparation 7:20 - 7:40 Flag Ceremony 7:40-8:00 Tooth Brushing 8:00 - 9:50 English 3Dokument5 Seiten7:00 - 7:20 Teacher's Preparation 7:20 - 7:40 Flag Ceremony 7:40-8:00 Tooth Brushing 8:00 - 9:50 English 3Vilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Asset Registry Template Manual Version 07.19.2018 (For Department of Education)Dokument6 SeitenNational Asset Registry Template Manual Version 07.19.2018 (For Department of Education)Vilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pagtitiwalasasarili: I. LayuninDokument6 SeitenPagtitiwalasasarili: I. LayuninVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8:10 - 9:00 English 3 I. Objectives II. Subject MatterDokument4 Seiten8:10 - 9:00 English 3 I. Objectives II. Subject MatterVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7:00 - 7:20 Teacher's Preparation 7:20 - 7:40 Flag Ceremony 7:40-8:00 Tooth Brushing 8:00 - 9:00 English 3Dokument4 Seiten7:00 - 7:20 Teacher's Preparation 7:20 - 7:40 Flag Ceremony 7:40-8:00 Tooth Brushing 8:00 - 9:00 English 3Vilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edukasyon Sa Pagpapakatao: Pagiging PilipinoDokument2 SeitenEdukasyon Sa Pagpapakatao: Pagiging PilipinoVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP Qi, WK2, D1Dokument5 SeitenLP Qi, WK2, D1Vilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date: June 13, 2018 Wednesday: Value Focus: AccuracyDokument4 SeitenDate: June 13, 2018 Wednesday: Value Focus: AccuracyVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date: June 14, 2018 Thursday: Value Focus: AccuracyDokument3 SeitenDate: June 14, 2018 Thursday: Value Focus: AccuracyVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honesty Honesty : Edukasyon Sa Pagpapakatao MathematicsDokument1 SeiteHonesty Honesty : Edukasyon Sa Pagpapakatao MathematicsVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teacher'S Portfolio Grade - Iii: Learning Delivery Modalities CourseDokument65 SeitenTeacher'S Portfolio Grade - Iii: Learning Delivery Modalities CourseVilma TayumNoch keine Bewertungen
- ViniDokument34 SeitenViniNishantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research PaperDokument5 SeitenResearch PaperPradnya ShejwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- InvestmentsDokument60 SeitenInvestmentsKristy SullivanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-1: Submitted By: Bipin SahooDokument48 SeitenChapter-1: Submitted By: Bipin SahooAshis Sahoo100% (1)
- Fin 460 REPORTDokument26 SeitenFin 460 REPORTMd. Iftekhar RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security Analysis AND Portfolio Management: Mba Iii Semester PristDokument15 SeitenSecurity Analysis AND Portfolio Management: Mba Iii Semester PristSingh CharuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 PakistanDokument62 Seiten6 PakistanKhalil Ur Rehman YousafzaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effect of Round Number Bias in U.S. and Chinese Stock MarketsDokument38 SeitenThe Effect of Round Number Bias in U.S. and Chinese Stock MarketsEric GuoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ra 8424 - NircDokument123 SeitenRa 8424 - NircJOHAYNIENoch keine Bewertungen
- BloombergBrief HF Newsletter 201459Dokument9 SeitenBloombergBrief HF Newsletter 201459AbhishekSinghGaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Corporation Code AmendmentsDokument39 SeitenRevised Corporation Code AmendmentsJui ProvidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Challenges Faced in RE FinanceDokument2 SeitenChallenges Faced in RE FinanceSmriti MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partnerships: Formation, Operation and Ownership ChangesDokument17 SeitenPartnerships: Formation, Operation and Ownership ChangesSyifa MuthmainnahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stock StrategiesDokument29 SeitenStock StrategiesHans CNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAC3684 SIPM March 2011Dokument7 SeitenBAC3684 SIPM March 2011chunlun87Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Project Report On Commodity Market With Special Reference To Gold at Karvy Stock ExchangeDokument85 SeitenA Project Report On Commodity Market With Special Reference To Gold at Karvy Stock ExchangeBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)100% (5)
- December 2013Dokument4 SeitenDecember 2013Heather PageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inefficient Markets and The New FinanceDokument18 SeitenInefficient Markets and The New FinanceMariam TayyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demat Account BobDokument28 SeitenDemat Account BobRavi AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Reporting and GovernanceDokument210 SeitenCorporate Reporting and Governanceisabella ayikuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profile of Sonali BankDokument24 SeitenProfile of Sonali BankRahi RebaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5. Equity MarketsDokument150 SeitenChapter 5. Equity MarketsHiếu Nhi TrịnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- DBRealty AnandRathi 061010Dokument135 SeitenDBRealty AnandRathi 061010Adishree AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ias - 28 PDFDokument16 SeitenIas - 28 PDFANoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine Capital Letter To PDLI BoardDokument7 SeitenEngine Capital Letter To PDLI BoardfilipandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditing Practice (AP) : #128 Maginhawa ST., Brgy. Teacher's Village East, Quezon City Pinnaclecpareview - PHDokument27 SeitenAuditing Practice (AP) : #128 Maginhawa ST., Brgy. Teacher's Village East, Quezon City Pinnaclecpareview - PHWinnie ToribioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Argentina StandaloneDokument3 SeitenArgentina StandaloneBAE NegociosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Cash Flow To Equity Discount ModelsDokument2 SeitenFree Cash Flow To Equity Discount ModelsDavid Ignacio Berastain HurtadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - The Value of Common Stocks (Compatibility Mode)Dokument18 SeitenChapter 4 - The Value of Common Stocks (Compatibility Mode)Hanh TranNoch keine Bewertungen