Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Meniere's Disease Guide
Hochgeladen von
John Harvey PerezOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Meniere's Disease Guide
Hochgeladen von
John Harvey PerezCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MENIERE'S DISEASE
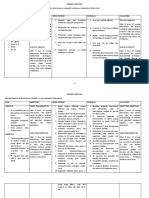
1.)What are the signs and symptoms according to subjective and objective assesment
•vertigo
•Fluctuating, progressive, unilateral (in one ear) or bilateral (in both ears) hearing loss.
•A sensation of fullness or pressure in one or both ears.
•Unilateral or bilatera ltinnitus
•abnormal side-to-side eye movements, known as nystagmus
•ataxia, or an abnormal, unsteady walking gait
2.) Give atleast 3 Nursing Diagnosis of this specific client then prioritize
• Anxiety r/t the sudden episodes of complete disorientation that cause the person to fall
secondary to vertigo
• Altered comfort r/t the sensation of spinning motion, fluctuating hearing loss, and tinnitus
• Risk for injury r/t the disorder of the inner ear
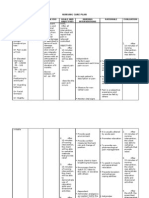
PRIORITIZATION
NURSING PROBLEM RANK JUSTIFICATION
Anxiety r/t the sudden 1 The nature of the problem high.
episodes of complete It is considered as an actual
disorientation that cause the factor. It belongs to the basic
person to physiologic need in Maslow’s
fall secondary to vertigo Hierarchy of Needs. In terms of
the resources, both the client and
the nurse have sufficient
resources.
Altered comfort r/t the 2 The nature of the problem is
sensation of spinning motion, medium. It is considered as an
fluctuating hearing loss, and actual factor. It belongs to the
tinnitus physiologic needs in Maslow’s
Hierarchy of Needs.
In terms of the resources, both
the client and the nurse have the
resources.
Risk for injury r/t the disorder 3 The nature of the problem is low
of the inner ear because it only requires minimal
nursing support. It is considered
as an potential factor. In terms of
the resources, both the client and
the nurse have the resources.
3.) What are the Nursing Interventions including the Health Teaching Plan
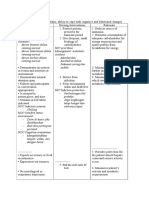
A.) Anxiety r/t the sudden episodes of complete disorientation that cause the person
to fall secondary to vertigo
Interventions
•Provide accurate, consistent information regarding prognosis of the disease.
Avoid arguing about patient’s perceptions of the situation
•Provide open environment in which the patient feels safe to discuss feelings or to
refrain from talking
•Explain procedures, providing opportunity for questions and honest answer
•Maintain a calm manner while interacting with patient.
•Encourage patient to talk about anxious feelings and examine anxiety-provoking
situations if able to identify them. Assist patient in assessing the situation realistically and
recognizing factors leading to the anxious feelings. Avoid false
reassurances
B.) Altered comfort r/t the sensation of spinning motion, fluctuating hearing loss, and
tinnitus
Interventions
•Provide a quiet and peaceful environment
•Provide time to rest and promote general comfort measures
•Stay with the patient who appeared anxious
•Assess the patient’s power needs or needs for control.
•Enhance the patient’s sense of autonomy. Do this by involving the patient in
decision making, by giving information, and by enabling the patient to control the
environment as appropriate. Encourage patient to identify strength
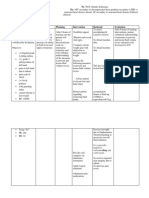
C.) Risk for injury r/t the disorder of the inner ear
Interventions
•Maintain a safe environment
•Assist with ambulation and self care activities as needed
•Keep side rails raised and bed in low position
•Encourage patient to drink prescribed fluid amounts. If oral fluids are tolerated,
provide oral fluids patient prefers. Place at bedside within easy reach. Provide
fresh water and a straw. Be creative in selecting fluid sources (e.g., flavored
gelatin, frozen juice bars, sports drink).
•Assist patient if unable to feed self and encourage caregiver to assist with
feedings as appropriate
4.) After the intervention what are the intended outcome/s
5.) Pathophysiology
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NCP Sensory PerceptionDokument2 SeitenNCP Sensory PerceptionGina TangneneiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community health nursing role in caring for clientsDokument3 SeitenCommunity health nursing role in caring for clientsEthan Marcos GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetic Patient with DehydrationDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Diabetic Patient with DehydrationRodolfo Bong SemaneroNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDokument9 SeitenNCP For Disturbed Sensory PerceptionRYAN SAPLADNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP GCP FinalDokument15 SeitenNCP GCP FinalssilvozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breast Cancer Risk For InfectionDokument6 SeitenBreast Cancer Risk For Infectionam peNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Bronchial Asthma PatientDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Bronchial Asthma PatientissaiahnicolleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Impaired SwallowingDokument3 SeitenRisk For Impaired SwallowingCalimlim Kim100% (1)
- NCP Impaired SkinDokument2 SeitenNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for PneumoniaDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan for PneumoniaFARAH MAE MEDINANoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy MalaiseDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy Malaise06eltianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Fall and Risk For Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Pantoprazole, Ketorolac, Cefoxitin Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenRisk For Fall and Risk For Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Pantoprazole, Ketorolac, Cefoxitin Drug StudyKevin John ReaLubit SaLisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pain Control AssessmentDokument3 SeitenAcute Pain Control Assessmentjordan aguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 'Urdaneta City University College of Health Sciences: Bachelor of Science in NursingDokument4 Seiten'Urdaneta City University College of Health Sciences: Bachelor of Science in NursingDan Dan ManaoisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Improving HygieneDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Improving HygieneMartin Lєtmaku EspinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deficient KnowledgeDokument3 SeitenDeficient KnowledgeCamilleAnneRoseRabinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Silliman UniveristyDokument17 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Silliman UniveristyKassandra LabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)Dokument2 SeitenNCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)R Hornilla ArcegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For Ulnar SurgeryDokument5 SeitenNCP For Ulnar SurgeryjiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Pain ManagementDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Acute Pain ManagementSheene Lysethea Sioteco AguilosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk for Infection Nursing Care PlanDokument2 SeitenRisk for Infection Nursing Care PlanKarl-Ren LacanilaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Cushing's SyndromeDokument2 SeitenNCP Cushing's SyndromeChristine LebicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP CSDokument4 SeitenSP CSKhan HansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For InfectionDokument3 SeitenRisk For Infectionprickybiik100% (1)
- Or NCP (Impaired Elimination)Dokument1 SeiteOr NCP (Impaired Elimination)Nikki M. ArapolNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Alzheimers DiseaseDokument2 SeitenNCP Alzheimers DiseaseShawn TejanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Intolerance R/T Generalized WeaknessDokument3 SeitenActivity Intolerance R/T Generalized Weaknesschanmin limNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENERAL SANTOS DOCTORS’ MEDICAL SCHOOL FOUNDATION NURSING CARE PLANDokument4 SeitenGENERAL SANTOS DOCTORS’ MEDICAL SCHOOL FOUNDATION NURSING CARE PLANFran LanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing and Managing Risk of AspirationDokument6 SeitenAssessing and Managing Risk of AspirationaianrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDokument3 SeitenImpaired Skin IntegrityAubrey SungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doxofylline: D 400 MG TabletsDokument33 SeitenDoxofylline: D 400 MG TabletsBibek Singh Mahat100% (2)
- "Nagtatae Siya 4 Days Na" As Verbalized by The Mother. Inatake of Causative Agents Irritation of The Stomach Inflammation of The Stomach Increase GI Motility DiarrrheaDokument4 Seiten"Nagtatae Siya 4 Days Na" As Verbalized by The Mother. Inatake of Causative Agents Irritation of The Stomach Inflammation of The Stomach Increase GI Motility DiarrrheaMelissa MhelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Peritonsillar AbscessDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Peritonsillar AbscessKevin Leo Lucero AragonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 NCP - Acute Pain FinalDokument3 Seiten4 NCP - Acute Pain FinalElisha Gine AndalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing care plan for hypovolemiaDokument8 SeitenNursing care plan for hypovolemiaGusmila SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case PresentationDokument5 SeitenCase PresentationJARIETTA OCHOANoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP FeuDokument2 SeitenNCP FeuFejlean Angelica AntineoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pain Assessment and Nursing InterventionsDokument1 SeiteAcute Pain Assessment and Nursing InterventionsAi RouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Volume DeficitDokument2 SeitenFluid Volume DeficitRuby AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- IVs & DVs of Nursing Research StudiesDokument3 SeitenIVs & DVs of Nursing Research StudiesReynard Kevin FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Acute Confusion 1-4Dokument2 SeitenRisk For Acute Confusion 1-4DewiRestiNazullyQiran100% (1)
- NCP Readiness RevisionDokument3 SeitenNCP Readiness RevisionimnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism Case StudiesDokument3 SeitenMetabolism Case StudiesEpoy Bantawig0% (1)
- Subjective:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenSubjective:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationAyra PunzalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Nursing Diagnosis Found in Nursing Care Plans For HypertensionDokument2 SeitenCommon Nursing Diagnosis Found in Nursing Care Plans For HypertensionRaveen mayiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument10 SeitenNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care ManagementDokument7 SeitenNursing Care ManagementDinarkram Rabreca EculNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDokument6 SeitenImpaired Verbal CommunicationLaura Sansonetti100% (1)
- Hypertension, Anxiety, Airway NCPDokument6 SeitenHypertension, Anxiety, Airway NCPHana Sanchez AlobaidanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired kidney function nursing careDokument21 SeitenImpaired kidney function nursing careKate ManalastasNoch keine Bewertungen
- GonorrheaDokument2 SeitenGonorrheaLeizel ApolonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDokument2 SeitenScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDokument4 SeitenNCP Impaired Skin IntegrityElgie SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTP of AsthmaDokument1 SeiteHTP of AsthmaMarland Faith Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument7 SeitenNursing Care PlanRhitzle Ann100% (1)
- Vertigo Nursing PrioritizationDokument1 SeiteVertigo Nursing PrioritizationAnnaMae Paula Fababier NaguitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24 January 2020 / Prof. Dennis Cuadra: Fundamentals of NusringDokument12 Seiten24 January 2020 / Prof. Dennis Cuadra: Fundamentals of NusringLeilah DelilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Phobic Anxiety DisorderDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Phobic Anxiety DisorderLadybelle GototosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Theory (1)Dokument12 SeitenNursing Theory (1)bldewnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- With RationaleDokument4 SeitenWith RationaleKaren mae alvarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nsg. Research Chap. 1 - 3Dokument38 SeitenNsg. Research Chap. 1 - 3John Harvey PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Lecture 6Dokument3 SeitenPharmacology Lecture 6John Harvey PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- EBN Febrile Seizure PediaDokument6 SeitenEBN Febrile Seizure PediaJohn Harvey PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knee Orthosis: Ocampo, Marjorie Ann PDokument14 SeitenKnee Orthosis: Ocampo, Marjorie Ann PJohn Harvey PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blakemore & Robbins (2012)Dokument8 SeitenBlakemore & Robbins (2012)Renzo LanfrancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otmc CH02Dokument16 SeitenOtmc CH02Gabriel ParksNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGNOU MBA MS-01 Solved Assignments 2010 #Dokument27 SeitenIGNOU MBA MS-01 Solved Assignments 2010 #shikhabhalla1984Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Absenteeism in AcademicsDokument5 SeitenEffects of Absenteeism in AcademicsShain Sahagun100% (1)
- Session 1 - Cont - EthonographyDokument10 SeitenSession 1 - Cont - EthonographyhopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teori Personaliti PsikodinamikDokument11 SeitenTeori Personaliti Psikodinamikabdul raimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Dreams PDFDokument2 SeitenOn Dreams PDFSpencer0% (5)
- Placebo EffectDokument3 SeitenPlacebo EffectMarnee BrowerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooley Looking Glass SelfDokument13 SeitenCooley Looking Glass SelfFlorina Nadorra Ramos100% (1)
- Their Story of Love and LossDokument6 SeitenTheir Story of Love and Lossmamello mashanyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portfolio: Results-Based Performance Management SystemDokument84 SeitenPortfolio: Results-Based Performance Management SystemRichard Manuel CabigtingNoch keine Bewertungen
- L5 U5 - Lessons 1-2 - 2022Dokument33 SeitenL5 U5 - Lessons 1-2 - 2022Adriana SalgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 17Dokument12 SeitenChap 17Sonal KaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signs & Symptoms of An Eating DisorderDokument2 SeitenSigns & Symptoms of An Eating DisorderWrendell BrecioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diss Week 1Dokument22 SeitenDiss Week 1airaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forms of EducationDokument6 SeitenForms of Educationआयुष शुक्ल100% (2)
- Listado 13Dokument436 SeitenListado 13Abel Hernandez SoteloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug EducationDokument2 SeitenDrug EducationDiana De Leon Cas100% (2)
- Development of Indigenous Personality Measures in the PhilippinesDokument19 SeitenDevelopment of Indigenous Personality Measures in the Philippinessimply_tin67% (3)
- St. Vincent de Ferrer College of Camarin, IncDokument2 SeitenSt. Vincent de Ferrer College of Camarin, IncMichelle Gutierrez SibayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Great Place To Work SurveyDokument14 SeitenGreat Place To Work SurveyfahadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 Chapter-Ii PDFDokument60 Seiten08 Chapter-Ii PDFAnupNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Research Proposal On Awareness of College Students in Cebu Institute of Technology-University Towards Contemporary Diaspora and Globalization and Its FacetsDokument12 SeitenA Research Proposal On Awareness of College Students in Cebu Institute of Technology-University Towards Contemporary Diaspora and Globalization and Its FacetsKaren Joy ReasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom Observation Report Robin Pegg 11Dokument4 SeitenClassroom Observation Report Robin Pegg 11api-337384040Noch keine Bewertungen
- Judge, Heller, & Klinger (2008) PDFDokument12 SeitenJudge, Heller, & Klinger (2008) PDFJuan OkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pe Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenPe Lesson Planapi-238051278Noch keine Bewertungen
- Initiative WorksheetDokument1 SeiteInitiative Worksheetapi-611550432Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Concept and Nature of SelfDokument10 SeitenModule 1 Concept and Nature of SelfKrizha SisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Restoring Normality for Displaced ChildrenDokument5 SeitenRestoring Normality for Displaced ChildrenEugen TerseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal Ambivalence and Ideal MotheringDokument6 SeitenMaternal Ambivalence and Ideal MotheringAna Laura NascimentoNoch keine Bewertungen