Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Was Were PDF
Hochgeladen von
Francisco José Valero FernándezOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Was Were PDF
Hochgeladen von
Francisco José Valero FernándezCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
English Department’s Blog – IES CARLOS CANO
Grammar
Section
Was & Were
SER / ESTAR (Past Tense)
Was/were is used to talk about yourself and other people, animals or things, in the PAST TIME. The Spanish
translation is SER or ESTAR, and you have to choose one of the meanings depending on the context. For
example:
- She was Spanish (Ella era española)
- She was in Spain. (Ella estaba en España)
- She was from Spain. (Ella era de España)
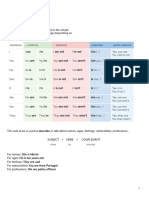
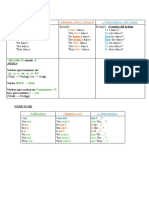
AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE
FULL FORM CONTRACTED FORM FULL FORM SHORT ANSWERS
I was I was not I wasn’t Was I? Yes, I was / No, I wasn’t
You were You were not You weren’t Were you? Yes, you were / No, you weren’t
He was He was not He wasn’t Was he? Yes, he was / No, he wasn’t
She was She was not She wasn’t Was she? Yes, she was / No, she wasn’t
It was It was not It wasn’t Was it? Yes, it was / No, it wasn’t
We were We were not We weren’t Were we? Yes, we were / No, we weren’t
You were You were not You weren’t Were you? Yes, you were / No, you weren’t
They were They were not They weren’t Were they? Yes, they were / No, they weren’t
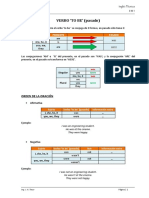
HABER (Past Tense)
We can also use WAS/WERE with There to talk about things you could see or things you know exist IN THE
PAST. The Spanish translation is HABÍA. For example:
- There was a chair in the classroom. (Había una silla en la clase)
- There were two chairs in the classroom. (Había dos sillas en la clase)
AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE
FULL FORM FULL FORM CONTRACTED FORM FULL FORM SHORT ANSWERS
Yes, there was
There was There was not There wasn’t Was there?
No, there wasn’t
Yes, there were
There were There were not There weren’t Were there?
No, there weren’t
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- HowtoStudyKorean Unit 1 PDFDokument292 SeitenHowtoStudyKorean Unit 1 PDFHilma NianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Word Families: No. Verbs Nouns Adjectives AdverbsDokument5 SeitenCommon Word Families: No. Verbs Nouns Adjectives AdverbsChuu ChuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- English VerbsDokument4 SeitenEnglish VerbsLeidy RochaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabla Repaso Contenidos Gramaticales PDFDokument12 SeitenTabla Repaso Contenidos Gramaticales PDFOhana Centro de Estudios100% (1)
- I2ci Grammar 8 Verbs Ing or InfinitiveDokument15 SeitenI2ci Grammar 8 Verbs Ing or InfinitiveDanielSánchezMartínezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Todo de InglesDokument12 SeitenTodo de InglesJose MarquinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflexive Verbs - Spanish EjerciciosDokument8 SeitenReflexive Verbs - Spanish EjercicioskarbolikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar-Like + V.ing-WorksheetDokument2 SeitenGrammar-Like + V.ing-WorksheetNannyNoch keine Bewertungen
- English For BeginnersDokument7 SeitenEnglish For Beginnerssoty999100% (8)
- Verb Charts: Be, Have Got, Present Simple and Present ContinuousDokument2 SeitenVerb Charts: Be, Have Got, Present Simple and Present ContinuousPau100% (1)
- To Be and There To Be Simple PastDokument2 SeitenTo Be and There To Be Simple PastORANCELI MORENONoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula B2 Exam File (Pearson Education)Dokument47 SeitenFormula B2 Exam File (Pearson Education)Alexánder Becerra50% (4)
- List of Irregular Verbs: #Infinitive Past Past Participle Progressive Form MeaningDokument6 SeitenList of Irregular Verbs: #Infinitive Past Past Participle Progressive Form MeaningPauli Nita0% (1)
- English 9: Quarter 3 - Week - 6 Competency: Use Verbals: InfinitivesDokument8 SeitenEnglish 9: Quarter 3 - Week - 6 Competency: Use Verbals: InfinitivesIrish SidlacanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grama Tica GeneralDokument5 SeitenGrama Tica GeneralIngrid Garcia MoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 - To Be Verb in PastDokument1 SeiteLesson 2 - To Be Verb in PastJoao AlfandegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb To Be Past TenseDokument1 SeiteVerb To Be Past TenseDavid RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Was WereDokument1 SeiteWas WereMuhd SyahmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2A.Past Simple SheetsDokument2 Seiten2A.Past Simple SheetsNooee JNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Past Simple Do Verbo TO BE) (Era, Eram) : Was / WereDokument1 Seite(Past Simple Do Verbo TO BE) (Era, Eram) : Was / WerePaula BronzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Be y To Have GotDokument1 SeiteTo Be y To Have GotFátima CortinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pasadosimpletobe PDFDokument1 SeitePasadosimpletobe PDFzuneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tema2 PASTSIMPLE TeoríaDokument3 SeitenTema2 PASTSIMPLE TeoríapaubobeNoch keine Bewertungen
- I He / She / It You We You They: Was / Were + Sujeto + Objeto/complementoDokument1 SeiteI He / She / It You We You They: Was / Were + Sujeto + Objeto/complementoAna FrancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- s1 Wordboard File 1a 1b Verb To Be NumbersDokument7 Seitens1 Wordboard File 1a 1b Verb To Be NumbersMateus SousaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 2 Past of Be (Was / Were)Dokument7 SeitenGroup 2 Past of Be (Was / Were)Stalin ToaquizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repaso 5º Unit 3Dokument1 SeiteRepaso 5º Unit 3Nuria SuárezNoch keine Bewertungen
- There Is... A, An... Some Any...Dokument30 SeitenThere Is... A, An... Some Any...EMMANUEL raymundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Documento Sin Título (2) 1Dokument1 SeiteDocumento Sin Título (2) 1Maria RubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aa Ee Ii Oo Uu Yy: BB CC DD FF GG HH JJ KK LL MM NN PP QQ RR Ss TT VV WW XX ZZDokument2 SeitenAa Ee Ii Oo Uu Yy: BB CC DD FF GG HH JJ KK LL MM NN PP QQ RR Ss TT VV WW XX ZZaygulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apuntes Inglés BasicoDokument8 SeitenApuntes Inglés BasicoAriadna PinheiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past SimpleDokument1 SeitePast SimpleAlexander Lace TelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Is EasyDokument2 SeitenEnglish Is EasyNafirKeyh100% (1)
- To Be (Recuperado Automáticamente)Dokument5 SeitenTo Be (Recuperado Automáticamente)Vanesa Garcia SevillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TO BE - СУМ (present) : Affirmative Negative Short answersDokument8 SeitenTO BE - СУМ (present) : Affirmative Negative Short answersDragana JakovlevskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7: All About People: Henry VIII Oscar Wilde William ShakespeareDokument22 SeitenUnit 7: All About People: Henry VIII Oscar Wilde William ShakespeareAmericanbritish EnglishschoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material de Soporte Curso de Ingles Basico 2012Dokument44 SeitenMaterial de Soporte Curso de Ingles Basico 2012Yennire SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past TenseDokument1 SeitePast TenseNICOL LAURA GARCIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Inglés Técnico (2021) - Actividad 12Dokument5 SeitenInglés Técnico (2021) - Actividad 12One Beat- Nathan GarrixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Subject Pronouns: (Present Tense) To (Marca El Infinitivo de Los Verbos) Be (Ser/estar)Dokument3 SeitenPersonal Subject Pronouns: (Present Tense) To (Marca El Infinitivo de Los Verbos) Be (Ser/estar)José VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Was Were Explanation AdaptadaDokument1 SeiteWas Were Explanation AdaptadaSofiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic English GrammarDokument11 SeitenBasic English Grammarloely mikrotik100% (1)
- Basic 03 The Past: Grammar ReferenceDokument1 SeiteBasic 03 The Past: Grammar ReferenceAnonymous oT5cglJGQxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb Be-Verb To BeDokument4 SeitenVerb Be-Verb To BeKamil HenriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- English - Review Verbo To Be - PresentDokument1 SeiteEnglish - Review Verbo To Be - PresentPollyanna MeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past To BeDokument6 SeitenPast To BefabiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Continuous: Form Affirmative Negative Interrogative Short AnswersDokument1 SeitePast Continuous: Form Affirmative Negative Interrogative Short Answersclaudia centremultiprofessionalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 LessonDokument9 Seiten01 LessonTrifu NicoletaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Practice - Verb To Be: Subject PronounsDokument2 SeitenGrammar Practice - Verb To Be: Subject PronounsAndrea CarvalhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb To Be 08.09Dokument4 SeitenVerb To Be 08.09Lucas Jeremias JaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Have Got: Affirmative Negative Interrogative Answers Long Form Short Form Long Form Short Form +Dokument1 SeiteHave Got: Affirmative Negative Interrogative Answers Long Form Short Form Long Form Short Form +Zaharia Anca-LiviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be + Going To É Usado para Falar Sobre PlanosDokument1 SeiteBe + Going To É Usado para Falar Sobre PlanosPedro Rodrigues CameloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colegio Carlos Julio Garcia: There Was/There Were (Hay Singular/Hay Plural)Dokument6 SeitenColegio Carlos Julio Garcia: There Was/There Were (Hay Singular/Hay Plural)Kaleth BecerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asking Questions Bingo FREE English PROPSDokument4 SeitenAsking Questions Bingo FREE English PROPSAmirkhan PRONoch keine Bewertungen
- Past ContinuousDokument6 SeitenPast ContinuousValNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Pronouns and Verb To BeDokument6 SeitenPersonal Pronouns and Verb To BeMaría Jesús Valerio BeltránNoch keine Bewertungen
- Le Verbe BE 6Ã Me CoursDokument2 SeitenLe Verbe BE 6Ã Me Cours8wrf6nj8qgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combinados 1-CopiarDokument45 SeitenCombinados 1-CopiarEliezer Peña del AguilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comb InglDokument27 SeitenComb InglEliezer Peña del AguilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doesn't Doesn't: + AfirmativaDokument3 SeitenDoesn't Doesn't: + AfirmativaRaneirosNoch keine Bewertungen
- We Form The Past Continuous WithDokument3 SeitenWe Form The Past Continuous WithJuan Esteban Ayala100% (1)
- We Form The Past Continuous WithDokument3 SeitenWe Form The Past Continuous WithFernando OyuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 - Unit 1Dokument1 Seite03 - Unit 1MaykaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect ProgressiveDokument1 SeitePerfect ProgressiveEcaterina IsacescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Week 10 I.CDokument14 SeitenLesson Plan Week 10 I.CAROON NOEL FABIAN LEANDRONoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb BE BritishCouncilDokument4 SeitenVerb BE BritishCouncilFAVargasANoch keine Bewertungen
- My Portfolio IIIDokument19 SeitenMy Portfolio IIIPercy Huanca Ch100% (1)
- Verb To Be PresentationDokument10 SeitenVerb To Be PresentationSiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation: Like/love + - Ing FormDokument2 SeitenPresentation: Like/love + - Ing FormRonald MamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 18. Modal Verbs and Modal WordsDokument21 SeitenLecture 18. Modal Verbs and Modal WordsМария АрнаутNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examen Extraordinario Interchange IntroADokument4 SeitenExamen Extraordinario Interchange IntroAIssa RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gerund and Infinitive With Changes of Meaning Grammar Drills Information Gap Activities 83902Dokument2 SeitenGerund and Infinitive With Changes of Meaning Grammar Drills Information Gap Activities 83902Dany Cuevas Velazquez100% (1)
- Lesson 4 Linguistic CompetenceDokument15 SeitenLesson 4 Linguistic CompetenceShinji100% (1)
- Dwi Puji S 053 & Lucky P 058 LESSON PLANDokument5 SeitenDwi Puji S 053 & Lucky P 058 LESSON PLANAan 007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Garfield 2 Reported SpeechDokument5 SeitenGarfield 2 Reported SpeechNifty0% (1)
- 5th Class Exercise On Kinds of Adjectives - English GrammarDokument3 Seiten5th Class Exercise On Kinds of Adjectives - English GrammarSuvashreePradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of Speech: Nouns vs. Verbs: Super Teacher WorksheetsDokument2 SeitenParts of Speech: Nouns vs. Verbs: Super Teacher WorksheetsWilliam GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses: Active FormDokument26 SeitenTenses: Active FormAldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 Nouns Articles S V AgreementDokument17 SeitenUnit 5 Nouns Articles S V Agreement2257010141Noch keine Bewertungen
- English ErrorsDokument3 SeitenEnglish ErrorsBog VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tablica - Vremena - Angliyskogo - Glagola 1Dokument1 SeiteTablica - Vremena - Angliyskogo - Glagola 1OlesiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laser A1plus Word ListDokument10 SeitenLaser A1plus Word ListPeggy ThomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anam Hijab Word Formation ProcessDokument6 SeitenAnam Hijab Word Formation ProcessAnam HijabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Focus in Year 6 KSSRDokument5 SeitenGrammar Focus in Year 6 KSSRPretty Elka K GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of NounsDokument3 SeitenTypes of NounsAngel Bengan100% (1)
- The Faint Fresh Flame of The Young Year Flushes From Leaf To Flower and From Flower To Fruit and Fruit and Leaf Are As Gold and Fire (Swineburn)Dokument4 SeitenThe Faint Fresh Flame of The Young Year Flushes From Leaf To Flower and From Flower To Fruit and Fruit and Leaf Are As Gold and Fire (Swineburn)Irina ParkhomenkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment For June 17Dokument8 SeitenAssignment For June 17Jessona RajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Vs Passive VoiceDokument39 SeitenActive Vs Passive VoiceSofia MansoorNoch keine Bewertungen