Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Micro-Teach 1
Hochgeladen von
api-427904098Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Micro-Teach 1
Hochgeladen von
api-427904098Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
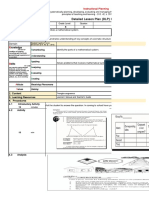
Tarleton State University’s Expected Lesson Cycle
Clinical Teacher’s Name: Sophia Mack Subject/Grade: 5th Grade Math
TEKS Addressed:
(3) Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop and
use strategies and methods for positive rational number computations in order to solve problems
with efficiency and accuracy. The student is expected to:
(G) solve for quotients of decimals to the hundredths, up to four-digit dividends and
two-digit whole number divisors, using strategies and algorithms, including the standard
algorithm;
LESSON OBJECTIVE Addressed:
Students will demonstrate knowledge of division steps and how to apply them when working
with decimals by actively participating in a relay race activity and answering practice problems
with 80% mastery.
CCRS Addressed:
I. Numeric Reasoning
B. Number operations
1. Perform computations with real and complex numbers.
a. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide real numbers accurately, including
irrational numbers, numbers with exponents, and absolute value.
VIII. Problem Solving and Reasoning
C. Real world problem solving
1. Formulate a solution to a real-world situation based on the solution to a
mathematical problem.
a. Formulate a solution to a real-world situation based on the solution to a
mathematical problem.
b. Convert given information into an appropriate mathematical model.
c. Interpret results of the mathematical problem in terms of the original
real-world situation.
ELPS Addressed:
(1) Cross-curricular second language acquisition/learning strategies. The student is expected to:
(A) use prior knowledge and experiences to understand meanings in English;
Tarleton State University’s Expected Lesson Cycle
(B) monitor oral and written language production and employ self-corrective techniques
or other resources;
(C) use strategic learning techniques such as concept mapping, drawing, memorizing,
comparing, contrasting, and reviewing to acquire basic and grade-level vocabulary;
(D) speak using learning strategies such as requesting assistance, employing non-verbal
cues, and using synonyms and circumlocution (conveying ideas by defining or describing
when exact English words are not known);
(E) internalize new basic and academic language by using and reusing it in meaningful
ways in speaking and writing activities that build concept and language attainment;
(F) use accessible language and learn new and essential language in the process
Technology Application (taken from the TEKS):
(2) Communication and collaboration. The student collaborates and communicates both locally
and globally using digital tools and resources to reinforce and promote learning. The student is
expected to:
(C) collaborate effectively through personal learning communities and social
environments;
(D) select and use appropriate collaboration tools;
Materials and Resources Needed
Smartboard
Problem Sheet
Pencil
Whiteboard
Dry-Erase Markers
Chart Paper
Lesson Cycle Component Estimated Checks for understanding,
Time questioning, monitoring,
adjusting, Assessing
Focus:
(What is the content? What is the learner doing, What is the 5 minutes Explain to students that for this
teacher doing?) lesson they will be learning how to
divide decimals by whole numbers.
Ask students to give several
examples of when they might need
to divide decimals. Take several
Tarleton State University’s Expected Lesson Cycle
examples. Remind them that money
is represented as a decimal.
Give students an example to think
about. Example: You and your two
friends ran a lemonade stand. You
made $63.12. How much money
would each person get?
Write the problem out on the board
and explain the steps for solving it.
Key Words: Dividend, Divisor
Explanation and Check for Understanding:
(What is the content? What is the learner doing, What is the 15 minutes Go back to the problem written on
teacher doing?) the board.
Explain that the first step is to write
a decimal point where the quotient,
or the answer to a division problem,
will be, directly above the decimal
point in the dividend.
Tell students that the rest of the
problem is just like a long division
problem with whole numbers.
Acronym: Dad, Mom, Brother,
Sister (Divide, Multiply, Bring
Down, Subtract)
Work out the problem on the
Smartboard, being sure to model
your thinking process.
Give two more examples and have
students walk you through the
division steps.
Lesson Cycle Component Estimated Checks for understanding,
Time questioning, monitoring,
adjusting, Assessing
Guided Practice and Check for Mastery:
(What is the content? What is the learner doing, What is the 15 minutes Students will do a relay race to
teacher doing?) solve decimal division problems.
They will get into groups of four
and each person will have a
different task: divide, multiply,
bring down, and subtract.
Tarleton State University’s Expected Lesson Cycle
The "divide" person will begin by
writing the problem on the
whiteboard or chart paper. The rest
of the group will line up behind
them in order of their tasks.
When you say "go," the person
dividing will complete the first step
of the problem. They will then hand
the marker to the next person, who
will complete her task. This will
continue until the problem is
solved. The entire group will sit
down when the problem is
complete to show the teacher they
are finished.
Teammates are allowed to help the
person completing the task,
however, they are not allowed to
leave their line or yell.
In order to win the game a team
must not only be the first to solve
their problem, but they must also
have the correct answer.
Lesson Cycle Component Estimated Checks for understanding,
Time questioning, monitoring,
adjusting, Assessing
Independent Practice and Monitor
(What is the content? What is the learner doing, What is the 15 minutes Students will complete a problem
teacher doing?) sheet in order to show
comprehension of the steps
involved with dividing decimals.
They will work out decimal
division problems and explain their
thinking process using sentence
frames.
"First, I ____. The number I got
was ____."
"Then, I ____. The number I got
was ____."
"Next, I____. The number I got was
____."
"The last thing I did was ____."
Tarleton State University’s Expected Lesson Cycle
Possible words for the word bank
may include the vocabulary terms
and the words "divide," "multiply,"
"bring down," and "subtract."
Extension (as needed) Aligned with Objective:
(What is the content? What is the learner doing, What is the 10 minutes Challenge students to write their
teacher doing?) own word problems that require
dividing decimals by whole
numbers. Students can trade their
problems with a classmate and
solve them.
Intervention (as needed) Based on Mastery:
(What is the content? What is the learner doing, What is the 15 minutes Students who struggle with factors
teacher doing?) and multiplication facts can use a
multiplication chart to help them
work through the problems. These
students could also have an
example problem worked out for
them to refer to as they complete
problems.
Closure:
(What is the content? What is the learner doing, What is the 5 minutes After the relay race, ask students
teacher doing?) what the most difficult part of it
was for them. Have students
explain how the activity helped
them and what they learned.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Write About Math, Grade 8: The Test ConnectionVon EverandWrite About Math, Grade 8: The Test ConnectionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Technology Integration Lesson PlanDokument6 SeitenTechnology Integration Lesson Planapi-703885341Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Detailed 1-Day Lesson PlanDokument4 Seiten1 Detailed 1-Day Lesson Planapi-533847098Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math 6 Q1 Week 4 PDFDokument6 SeitenMath 6 Q1 Week 4 PDFantonetteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Official Maed Lesson PlanDokument3 SeitenOfficial Maed Lesson Planapi-402314432Noch keine Bewertungen
- Technology: Integration Lesson Plan TemplateDokument5 SeitenTechnology: Integration Lesson Plan Templateapi-384826843Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Maths Teacher's Resource for DecimalsDokument11 SeitenNCERT Maths Teacher's Resource for DecimalsKriti ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bowles Sabrina-Lessonplanfinal DraftDokument4 SeitenBowles Sabrina-Lessonplanfinal Draftapi-489671443Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math g1 m1 Topic I Lesson 36Dokument11 SeitenMath g1 m1 Topic I Lesson 36ioaaysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 Week 1 PlansDokument11 SeitenUnit 5 Week 1 Plansapi-320210178Noch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Notebook LessonDokument9 SeitenSmart Notebook Lessonapi-344649238Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 Lesson Plan FormatDokument5 Seiten2020 Lesson Plan Formatapi-504433706Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 6 - Drawing The Graph of A Pattern Part 2Dokument2 SeitenLesson 6 - Drawing The Graph of A Pattern Part 2api-412107487Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math Review Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenMath Review Lesson Planapi-439333272Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adding and Subtracting FractionsDokument4 SeitenAdding and Subtracting Fractionsapi-508898016Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ed 201 Real Video Lesson Plan W NetsDokument3 SeitenEd 201 Real Video Lesson Plan W Netsapi-242176930Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blog Lesson Plan KFDokument5 SeitenBlog Lesson Plan KFapi-643705176Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 4 5 Multiplication Division Unit PlanDokument18 SeitenGrade 4 5 Multiplication Division Unit Planapi-607924870Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edtpa Math Lesson One-1Dokument3 SeitenEdtpa Math Lesson One-1api-405532979100% (1)
- Decimals Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenDecimals Lesson Planapi-439333272Noch keine Bewertungen
- EMTAP guide for dividing decimals & whole numbersDokument6 SeitenEMTAP guide for dividing decimals & whole numbersBernadine Jacob TrinidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math6week 7-Day 2Dokument6 SeitenMath6week 7-Day 2Ana BonifacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rational Number ActivityDokument15 SeitenRational Number Activityneomatrix70Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Mnlete C09L04 PDFDokument8 Seiten4 Mnlete C09L04 PDFAhmed SalemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fractions - Adding and Subtracting Fractions With Unlike Denominators Brooke Kofflin Melanie Dever Baker College of JacksonDokument12 SeitenFractions - Adding and Subtracting Fractions With Unlike Denominators Brooke Kofflin Melanie Dever Baker College of Jacksonapi-291807067Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dec 6th Decimals GR 7Dokument2 SeitenDec 6th Decimals GR 7api-443854323Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tree Diagram TechniqueDokument5 SeitenTree Diagram TechniqueTherence UbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan: Step 1: Curriculum ConnectionsDokument5 SeitenLesson Plan: Step 1: Curriculum Connectionsapi-396694469Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instructional Planning GuideDokument8 SeitenInstructional Planning GuidePablo JimeneaNoch keine Bewertungen
- G7 Mathematics-DLL-Q1-W6Dokument3 SeitenG7 Mathematics-DLL-Q1-W6Gim SadolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Converting Fractions 10x10 Lesson 2Dokument3 SeitenConverting Fractions 10x10 Lesson 2api-497020000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan With FeedbackDokument8 SeitenLesson Plan With Feedbackapi-549198873Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math Lesson Plan Template: Specific Learning Objectives For This LessonDokument6 SeitenMath Lesson Plan Template: Specific Learning Objectives For This Lessonapi-383270255Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week - 5Dokument3 SeitenWeek - 5Pablo JimeneaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching & Learning Plans: Decimals and Place ValueDokument35 SeitenTeaching & Learning Plans: Decimals and Place ValueSmartBugamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hedden FractionsUbD LessonDokument10 SeitenHedden FractionsUbD Lessonallison_hedden8930Noch keine Bewertungen
- Labang DLP 1Dokument8 SeitenLabang DLP 1Weldon LabangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math5 Jul8Dokument14 SeitenMath5 Jul8RoderickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of Teacher Candidate Lesson Overview: Solving Two-Digit Multiplication Problems Using Area ModelsDokument8 SeitenName of Teacher Candidate Lesson Overview: Solving Two-Digit Multiplication Problems Using Area Modelsapi-437233462Noch keine Bewertungen
- DLP 6Dokument4 SeitenDLP 6Richel Mae ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Domino Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenDomino Lesson Planapi-372539116Noch keine Bewertungen
- Three Lesson Plans For PortfolioDokument7 SeitenThree Lesson Plans For Portfolioapi-507182013Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 3 Maths Unit 4 5Dokument5 Seiten2 3 Maths Unit 4 5api-357196503Noch keine Bewertungen
- GR 5 LP SimplificationDokument3 SeitenGR 5 LP SimplificationRaja MvNoch keine Bewertungen
- CW Math Lesson PlanDokument3 SeitenCW Math Lesson Planapi-397855178Noch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Lesson Plan Subject:: Form Class Date Week Time Venue Attendance ThemeDokument3 SeitenDaily Lesson Plan Subject:: Form Class Date Week Time Venue Attendance ThemeHafizah PakahNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH UN RL GR7 DecimalsandFractionsDokument3 SeitenMATH UN RL GR7 DecimalsandFractionsMatemáticas Sergio CuautleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Idea 4 TemplateDokument2 SeitenLesson Idea 4 Templateapi-630696785Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jboyds Pop 1 SpringDokument5 SeitenJboyds Pop 1 Springapi-543265604Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan: Step 1: Curriculum ConnectionsDokument7 SeitenLesson Plan: Step 1: Curriculum Connectionsapi-390378000Noch keine Bewertungen
- UH COE Lesson Plan Template (Direct Instruction)Dokument3 SeitenUH COE Lesson Plan Template (Direct Instruction)api-505207950Noch keine Bewertungen
- Liz Math NarrativeDokument4 SeitenLiz Math Narrativeapi-366960283Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5e Lesson PlanDokument4 Seiten5e Lesson Planapi-644664041Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math Thematic Unit Lesson PlanDokument8 SeitenMath Thematic Unit Lesson Planapi-556755635Noch keine Bewertungen
- BM I-5Dokument5 SeitenBM I-5Maricel Perea BeranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pop Cycle 3Dokument5 SeitenPop Cycle 3api-506408572Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 Subtracting 3-Digit Numbers - Addition and Subtraction 3 - and 4-DigitDokument6 SeitenLesson 3 Subtracting 3-Digit Numbers - Addition and Subtraction 3 - and 4-Digitapi-597075380Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 16Dokument4 SeitenLesson 16api-447406874Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Quadratic EquationsDokument3 SeitenTeaching Quadratic EquationsJenny Domincel PrudenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mystery Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenMystery Lesson Planapi-348627392Noch keine Bewertungen
- Brownwood Community Resource FileDokument4 SeitenBrownwood Community Resource Fileapi-427904098Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sophia Mack Resume 2Dokument2 SeitenSophia Mack Resume 2api-427904098Noch keine Bewertungen
- MackDokument2 SeitenMackapi-427904098Noch keine Bewertungen
- MackDokument23 SeitenMackapi-427904098Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Study and Centers Project Part 2Dokument11 SeitenUnit Study and Centers Project Part 2api-427904098Noch keine Bewertungen
- MackDokument7 SeitenMackapi-427904098Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kindergarten Lesson Plan Week 38Dokument16 SeitenKindergarten Lesson Plan Week 38Kimmy Dora LptNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sets and Venn Diagrams maths questionsDokument4 SeitenSets and Venn Diagrams maths questionsAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annexure-74. (B.sc. (Hons) Maths (REVISED)Dokument86 SeitenAnnexure-74. (B.sc. (Hons) Maths (REVISED)hmingthansangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dummit and Foote Abstract Algebra SolutionsDokument157 SeitenDummit and Foote Abstract Algebra SolutionsVale VanegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prefatory Remarks To A General Introduction To The Study of Nature by Charles de Koninck. Manual, Prentice Hall. Corrected by T. de Koninck and C. de KoninckDokument9 SeitenPrefatory Remarks To A General Introduction To The Study of Nature by Charles de Koninck. Manual, Prentice Hall. Corrected by T. de Koninck and C. de KoninckBart MazzettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Division of ScienceDokument26 SeitenLesson 1 Division of ScienceSalve CatarrojaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Errorunacademyfinal2Dokument80 Seiten14 Errorunacademyfinal2QXnocMF5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Division of Science: MathematicsDokument26 SeitenDivision of Science: Mathematics1 Vallanta, Jonathan Jr. P.Noch keine Bewertungen
- MATH 7 ADM Module 3 FinalDokument34 SeitenMATH 7 ADM Module 3 FinalSenrin Tutorials100% (1)
- Algebra For College Students 7ed (2013) Chapter 2Dokument88 SeitenAlgebra For College Students 7ed (2013) Chapter 2Reign ManeseNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPAT Overview & Test Prep GuideDokument91 SeitenGPAT Overview & Test Prep GuideJV Si62% (13)
- Math1034sg2019sem1 PDFDokument84 SeitenMath1034sg2019sem1 PDFThanyani NeswiswiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARITHMETIC SEQUENCE - (Module 1)Dokument45 SeitenARITHMETIC SEQUENCE - (Module 1)Sophia Denise Agbuya0% (1)
- MWB Grade 6Dokument24 SeitenMWB Grade 6Joanne Casanova50% (2)
- CLMD4A MathG7Dokument40 SeitenCLMD4A MathG7Keith Lustañas Abesamis70% (10)
- Complex Numbers GuideDokument17 SeitenComplex Numbers GuideGus EdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- WS PolynomialsDokument4 SeitenWS PolynomialsAaratrika DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using The Place Mat To Tell How ManyDokument4 SeitenUsing The Place Mat To Tell How ManyDigi-BlockNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1 AnsDokument4 SeitenCH 1 AnsNap DoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan (OperationOfIntegers) - ZozobradoBSEDMath4ADokument6 SeitenSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan (OperationOfIntegers) - ZozobradoBSEDMath4AArman ZozobradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Classification of NumbersDokument41 SeitenUnderstanding Classification of NumbersAjeet Sony100% (1)
- Information Technology Grade 10Dokument2 SeitenInformation Technology Grade 10Candice ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Florante D. Cenas, LPT, MAMT Abigail V. Santisteban, LPT Baby Jean Baligasa, LPTDokument62 SeitenFlorante D. Cenas, LPT, MAMT Abigail V. Santisteban, LPT Baby Jean Baligasa, LPTChantra Marie Forgosa Amodia100% (1)
- WS2 Real Number System PDFDokument3 SeitenWS2 Real Number System PDFazetinasjcNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRE Practice Test 1 Quant 18 PointDokument76 SeitenGRE Practice Test 1 Quant 18 PointWalaa AbojnahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Number Systemss From BCA-121 Computer Fundamental PDFDokument14 SeitenNumber Systemss From BCA-121 Computer Fundamental PDFUdeshika Wanninayake100% (1)
- The Easiest Way To Understand AlgebraDokument67 SeitenThe Easiest Way To Understand Algebraepito3Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2017-18 Grade 6 Term I Mathematics PDFDokument5 Seiten2017-18 Grade 6 Term I Mathematics PDFHarsha Bharat DamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DBOW Math G5Dokument24 SeitenDBOW Math G5Mary Rose ArengaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tinywow - Ann Montague-Smith, Tony Cotton, Alice Hansen, Alison J. Price - Mathematics in Early Years Education-Routle - 35153768Dokument14 SeitenTinywow - Ann Montague-Smith, Tony Cotton, Alice Hansen, Alison J. Price - Mathematics in Early Years Education-Routle - 35153768Linh Phạm KhánhNoch keine Bewertungen