Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Unidad 9 E3
Hochgeladen von
Jaime Gonzalez0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
14 Ansichten4 SeitenThe purpose of a high CS signal is to a. Enable a memory or I / O device to communicate with The CPU. A low CS control signal and a high R / W control signal cause the outputs of the WRITE and READ gates to be low. One or both of the tri-state buffers are always in a high impedance state.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
UNIDAD 9 E3
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
TXT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe purpose of a high CS signal is to a. Enable a memory or I / O device to communicate with The CPU. A low CS control signal and a high R / W control signal cause the outputs of the WRITE and READ gates to be low. One or both of the tri-state buffers are always in a high impedance state.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als TXT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
14 Ansichten4 SeitenUnidad 9 E3
Hochgeladen von
Jaime GonzalezThe purpose of a high CS signal is to a. Enable a memory or I / O device to communicate with The CPU. A low CS control signal and a high R / W control signal cause the outputs of the WRITE and READ gates to be low. One or both of the tri-state buffers are always in a high impedance state.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als TXT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
UNIT 9 DATA BUS CONTROL
The CPU is in the read operating mode. The R/W signal is
b. high and data is transferred to the CPU.
The purpose of a high CS signal is to
a. enable a memory or I/O device to communicate with the CPU.
The logic states of inputs A and B are shown. The output of AND
gate 1 (W) is
b. low.
When the outputs of the WRITE and READ gates are low, the
b. CS control signal is low.
Can the outputs of the WRITE and READ gates be high at the same time?
b. no
The truth table for the READ and WRITE circuit is shown. A low CS control signal
and a high
R/W control signal cause the outputs of the WRITE gate to be
c. low and the READ gate to be low.
To transfer data from the CPU to an I/O device, which tri-state buffer has to be
enabled?
b. WRITE tri-state buffer.
When the READ tri-state buffer is enabled with a high READ signal, the output of
the WRITE
tri-state buffer is
c. in a high impedance state.
What prevents a CPU from writing and reading data to an I/O device at the same t
ime?
b. One or both of the tri-state buffers are always in a high impedance state.
3. b
4. b
5. b
6. b
7. a
8. a
9. b
10. a
11. a
12. b
Does the WRITE tri-state buffer output LED indicate that the CPU is writing the
data bit to the
I/O device?
b. no
Does the READ tri-state buffer LED indicate that the CPU is reading the data bit
from the I/O
device?
b. no
16. a
18. a
19. b
21. b
22. a
1. b
2. d
3. c
4. d
5. a
Exercise 2 Dynamic Control of a Data Bus
When the CPU wants to communicate with a device, the CPU causes
a. a high CS signal to the device.
The logic state of what signal determines if the CPU reads or writes to a device
?
b. R/W signal
When the CPU is reading from a device via the data bus, the outputs of all other
devices
connected to the data bus are in a
c. high-Z logic state.
4. b
5. c
6. c
7. b
9. b
10. a
11. a
13. a
14. b
15. b
1. a
2. d
3. a
4. b
5. c
UNIT TEST
The direction of data flow during computer read and write operations is in refer
ence to the
c. CPU.
Data transfer between the CPU and a memory chip or an I/O device is controlled b
y the
c. CS and R/W signals.
When the CPU wants to transfer data with an I/O device, the CPU enables the
a. device with a CS signal.
The purpose of the R/W signal is to
b. control the direction of data flow between the CPU and a memory chip or I/O d
evice.
The data bus of a computer is
a. a bidirectional bus: data flows in either direction on the bus.
This timing diagram shows the relationship of the signal and data
a. during a write operation.
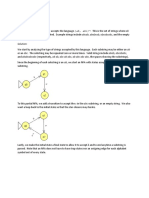
In this circuit, the inverter
d. ensures that both AND gates have complementary outputs when input A is logic
1.
In this circuit, AND gate output D is high when input A is
d. high and input B is low.
In this circuit, data is transferred from the DATA BUS to an I/O PORT when enabl
e signal C is
b. high and enable signal D is low.
In this circuit, data is transferred from the I/O PORT to the DATA BUS when enab
le signal C is
a. low and enable signal D is high.
4. a
7. a
9. a
4. a
7. a
9. c
4. a
7. a
9. d
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Is The Traditional IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) Fitting Into 5G World?Dokument2 SeitenIs The Traditional IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) Fitting Into 5G World?Moazzam TiwanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- 1.1-3 Computer System DesignDokument23 Seiten1.1-3 Computer System DesignGerald E BaculnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Excel VBADokument39 SeitenExcel VBAGreg MaslenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CommandsDokument264 SeitenCommandsseventhhemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- AP Computer Science - Types and VariablesDokument3 SeitenAP Computer Science - Types and Variablesjeongcho96Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Hycom Data ServiceDokument24 SeitenHycom Data ServiceitembolehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- HP ATP Server Solutions V2 - PD29287Dokument312 SeitenHP ATP Server Solutions V2 - PD29287DeepakNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- SRT DivDokument8 SeitenSRT Divdeepika0821843Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- AN2548Dokument24 SeitenAN2548KrocodileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- CVI SCAP Migration GuideDokument42 SeitenCVI SCAP Migration Guidescribd1408Noch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Nondeterministic Finite Automata Exercise2Dokument3 SeitenNondeterministic Finite Automata Exercise2Zain ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- 7 Hive NotesDokument36 Seiten7 Hive NotesSandeep BoyinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Final Exam - Object Oriented ProgrammingDokument7 SeitenFinal Exam - Object Oriented Programmingdj_eqc7227100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Unit 3Dokument46 SeitenUnit 3Vinod Srinivasan100% (1)
- Ut163 Usb ControllerDokument32 SeitenUt163 Usb Controllerelcomandante100% (8)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Result CodesDokument3 SeitenResult Codesl1braaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.854 Lecture Notes - Blocking FlowsDokument4 Seiten6.854 Lecture Notes - Blocking FlowskraxisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jira GuideDokument104 SeitenJira Guideioana_nekNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Scripting For Eda ToolsDokument7 SeitenScripting For Eda ToolsravindarsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Point Insertion For Test Coverage Improvement in DFT - Design For Testability (DFT) .HTMLDokument75 SeitenTest Point Insertion For Test Coverage Improvement in DFT - Design For Testability (DFT) .HTMLIlaiyaveni IyanduraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Golzarpoor BehroozDokument107 SeitenGolzarpoor BehroozDarko TešićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Buffer Size in Single and Multi Row Flexible Manufacturing Systems Through SimulationDokument11 SeitenDetermination of Buffer Size in Single and Multi Row Flexible Manufacturing Systems Through SimulationAmrik SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARM Cortex Portfolio - Public Version - V7Dokument4 SeitenARM Cortex Portfolio - Public Version - V7Aaron FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Limit ProblemsDokument3 SeitenSolutions To Limit ProblemsVince Cinco ParconNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- BC0034 Computer Concepts & C Programming Paper 2Dokument14 SeitenBC0034 Computer Concepts & C Programming Paper 2SeekEducation100% (1)
- LR Labs Overview DatasheetDokument3 SeitenLR Labs Overview DatasheetStrygwyr SeekerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blow Fish GuideDokument5 SeitenBlow Fish Guidemerlin664Noch keine Bewertungen
- CRUD Operations Using Jquery Dialog, Entity Framework and ASP PDFDokument20 SeitenCRUD Operations Using Jquery Dialog, Entity Framework and ASP PDFVjNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- MIS Vs TpsDokument13 SeitenMIS Vs TpsTushar Prasad88% (25)
- Kakasa Ka Ba Sa FilipinoDokument8 SeitenKakasa Ka Ba Sa FilipinoRizel M. BuhayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)