Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Anatomy and Physiology Guide
Hochgeladen von
Ianne RanchezOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Anatomy and Physiology Guide
Hochgeladen von
Ianne RanchezCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Anatomy and Physiology
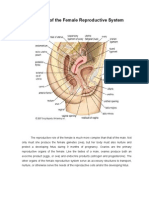
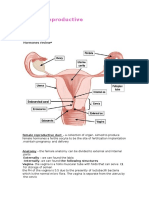
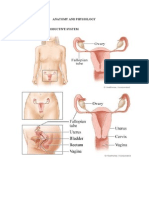
• Vagina: A muscular passageway that leads from the vulva (external
genitalia) to the cervix.
• Cervix: A small hole at the end of the vagina through which sperm
passes into the uterus. Also serves as a protective barrier for the uterus.
During childbirth, the cervix dilates (widens) to permit the baby to descend
from the uterus into the vagina for birth.
• Uterus: A hollow organ that houses the baby during pregnancy. During
childbirth, the uterine muscles contract to push out the baby. Each month,
unless a fetus has been conceived, the uterine wall sheds its lining (see The
Menstrual Cycle and Ovulation below).
• Ovaries: Two organs that produce hormones and store eggs. Each
ovary releases one egg per month.
• Fallopian tubes: Muscular tubes that eggs released from the ovaries
must traverse to reach the uterus.
The Menstrual Cycle and Ovulation
Each month a woman’s body goes through a menstrual cycle. A woman can
become pregnant only during ovulation, a several-day phase in the middle of the
menstrual cycle when one of the ovaries releases an egg.
If the ovulated egg is fertilized by a man’s sperm following sexual intercourse, it
will implant in the endometrium, the lining of the uterus that becomes the placenta
during pregnancy. The placenta nurtures the fertilized egg as it develops and grows
into a baby.
Female Anatomy
Events Weeks of
Pregnancy
1st Trimester
The woman's last period before 0
fertilization occurs.
Fertilization occurs. 2
The fertilized egg (zygote)
begins to develop into a hollow
ball of cells called the blastocyst.
The blastocyst implants in the 3
wall of uterus.The amniotic sac
begins to form.
The area that will become the 5
brain and spinal cord (neural
tube) begins to develop.
The heart and major blood 6
vessels are developing. The
beating heart can be seen during
ultrasonography.
The beginnings of arms and legs 7
appear.
Bones and muscles form. The 9
face and neck develop.
Brain waves can be detected.
The skeleton is formed. Fingers
and toes are fully defined.
The kidneys begin to function. 10
Almost all organs are completely
formed.
The fetus can move and respond
to touch (when prodded through
the woman's abdomen).
The woman has gained some
weight, and her abdomen may
be slightly enlarged.
2nd Trimester
The fetus's sex can be identified. 14
The fetus can hear.
The fetus's fingers can grasp. 16
The fetus moves more
vigorously, so that the mother
can feel it.
The fetus's body begins to fill out
as fat is deposited beneath the
skin. Hair appears on the head
and skin. Eyebrows and
eyelashes are present.
The placenta is fully formed. 20
The fetus has a chance of 24
survival outside the uterus.
The woman begins to gain
weight more rapidly.
3rd Trimester
The fetus is active, changing 25
positions often.
The lungs continue to mature.
The fetus's head moves into
position for delivery.
On average, the fetus is about
20 inches long and weighs about
7 pounds. The woman's
enlarged abdomen causes the
navel to bulge.
Delivery 37-42
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Anatomy Kenneth MaternalDokument22 SeitenAnatomy Kenneth Maternalkennedy14344Noch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive SystemDokument7 SeitenFemale Reproductive SystemyannieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDokument5 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemNURSETOPNOTCHER80% (5)
- Female Reproductive Anatomy GuideDokument9 SeitenFemale Reproductive Anatomy GuidePinkeyinthecityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive AnatomyDokument35 SeitenFemale Reproductive AnatomySasikala MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument14 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyIvee BustaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney Anatomy: NephronDokument3 SeitenKidney Anatomy: NephronNeil AlviarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nasal Cavity. The Nasal Cavity, Also Known As TheDokument11 SeitenNasal Cavity. The Nasal Cavity, Also Known As TheWilly Chandra HermawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic SystemDokument25 SeitenLymphatic Systemumar khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1753 5923 1 PB PDFDokument4 Seiten1753 5923 1 PB PDFlisa chadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Dr. Aguirre Pancreas: ND RDDokument3 SeitenAnatomy Dr. Aguirre Pancreas: ND RDAlbert CorderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive SystemDokument6 SeitenFemale Reproductive SystemממתצמתצמצתNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gavino and Aguilera (Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Organ)Dokument4 SeitenGavino and Aguilera (Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Organ)Allyne GavinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Female Reproductive Anatomy GuideDokument10 SeitenThe Female Reproductive Anatomy GuideBurni GuevaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive SystemDokument6 SeitenReproductive SystemDara BMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Maternal AnatomyDokument6 SeitenChapter 2 Maternal AnatomyRaja Ahmad Rusdan MusyawirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive System ExplainedDokument17 SeitenFemale Reproductive System ExplainedJasmaine RivoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alteration in Reproductive HealthDokument139 SeitenAlteration in Reproductive HealthNylia Ollirb AdenipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ection I. The Female Reproductive System 1-1. GENERALDokument9 SeitenEction I. The Female Reproductive System 1-1. GENERALNheil_Christop_4211Noch keine Bewertungen
- Autonomic Nervous System PharmacologyDokument13 SeitenAutonomic Nervous System PharmacologySam BotNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSIOLOGY OF THYROID GLANDDokument9 SeitenPHYSIOLOGY OF THYROID GLANDAbby EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female External GenitaliaDokument9 SeitenFemale External Genitaliabuhari rabiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDokument52 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemAjay DNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPP Anatomy of Endocrine SystemDokument23 SeitenPPP Anatomy of Endocrine SystemMarisol AcostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health AssessmentDokument2 SeitenHealth AssessmentrojeanrubinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joints Anatomy PresentationDokument41 SeitenJoints Anatomy Presentationahmadnaveed99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Renal SystemDokument18 SeitenRenal SystemS GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Planning Methods - LatestDokument59 SeitenFamily Planning Methods - LatestGenevieve VillaflorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument6 SeitenAnatomy and Physiologybadgurl08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Submitted By: Diana M. Resultay A301/Group-3B Submitted To: Ms. ReyesDokument9 SeitenSubmitted By: Diana M. Resultay A301/Group-3B Submitted To: Ms. ReyesDiannetotz MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument5 SeitenKidney Anatomy and PhysiologyDianne MacaraigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goitre: Dr. Sandhya Gupta Assistant Professor General SurgeryDokument59 SeitenGoitre: Dr. Sandhya Gupta Assistant Professor General SurgerySandhya guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDokument5 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartSimona Daniela VilcuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body TissuesDokument29 SeitenBody TissuesPurplesmilezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LECTURE Nervous SystemDokument4 SeitenLECTURE Nervous SystemanonymousNoch keine Bewertungen
- TolitsDokument42 SeitenTolitsAzela TuzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Back CareDokument20 SeitenBack Caresafina khstoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The BreastDokument6 SeitenAnatomy of The BreastJuliana Andres100% (1)
- Immunization Programme: National Health MissionDokument11 SeitenImmunization Programme: National Health MissionAnimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mantoux Test: Pirquet Test, or PPD Test For Purified Protein Derivative) Is A Diagnostic Tool ForDokument5 SeitenMantoux Test: Pirquet Test, or PPD Test For Purified Protein Derivative) Is A Diagnostic Tool ForGurmeet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 9 Episiotomy and Nursing Management: 9.0 ObjectivesDokument8 SeitenUnit 9 Episiotomy and Nursing Management: 9.0 ObjectivesSudip Kumar DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Female Pelvis: Namasinga JoyceDokument79 SeitenThe Female Pelvis: Namasinga JoyceNamaganda NajjatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LUMBERPUNCTURDokument14 SeitenLUMBERPUNCTURRahul VasavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EndocrinologyDokument7 SeitenEndocrinologyVijith.V.kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fertilization MICRO TEACHING - PDF NeewDokument8 SeitenFertilization MICRO TEACHING - PDF NeewPooja DeoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Anatomy 101 EmbryologyDokument4 SeitenHuman Anatomy 101 EmbryologyKonstantinos TheodosiadisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of BVDokument16 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of BVMarivic DianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impulses Which Are Rapid and Specific and CauseDokument9 SeitenImpulses Which Are Rapid and Specific and CauseCellina De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDokument42 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemLiangkiuwiliuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postpartum Care: PuerperiumDokument4 SeitenPostpartum Care: PuerperiumBenedict Paul RaguntonNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Renal SystemDokument15 SeitenThe Human Renal SystemChuche SustentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DefibrillationDokument13 SeitenDefibrillationKristine VedadNoch keine Bewertungen
- LabouranalgesiaDokument45 SeitenLabouranalgesiaA.H.ANoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.5.3.1 - Perkembangan Janin Intrauterin Dan Gangguan Yang Mungkin TimbulDokument54 Seiten1.5.3.1 - Perkembangan Janin Intrauterin Dan Gangguan Yang Mungkin TimbulMuhammad Fatkhi100% (1)
- Pap TestDokument24 SeitenPap TestAmirah MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of PancreasDokument6 SeitenAnatomy of PancreasNariska CooperNoch keine Bewertungen
- BreastDokument2 SeitenBreastPretty UNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Female PelvisDokument6 SeitenThe Female PelvisDrParth JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 - Lower Limb-Fascial Compartments of Thigh - Student VersionDokument28 Seiten2013 - Lower Limb-Fascial Compartments of Thigh - Student Versionmarina_shawkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive System 1Dokument3 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive System 1gilbertgarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intervention AutismDokument2 SeitenIntervention AutismIanne RanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pa Tho Physiology of AnemiaDokument1 SeitePa Tho Physiology of AnemiaRasper PascualNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumonia - Home Treatment: Call911or Other Emergency Services Immediately If YouDokument3 SeitenPneumonia - Home Treatment: Call911or Other Emergency Services Immediately If YouIanne RanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnatomyDokument2 SeitenAnatomyIanne RanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument6 SeitenHeart Anatomy and PhysiologyIanne RanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADHD Psycho PathologyDokument2 SeitenADHD Psycho PathologyIanne RanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Music and Art TherapyDokument6 SeitenMusic and Art TherapyIanne Ranchez100% (1)
- Heart Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument6 SeitenHeart Anatomy and PhysiologyIanne RanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of Breech PresentationDokument2 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of Breech Presentationeskempertus0% (2)
- Breast Feeding and PostDokument4 SeitenBreast Feeding and PostMichaela BernadasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal Child Nursing ModuleDokument7 SeitenMaternal Child Nursing ModuleWizzardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partograph: DR Ban Hadi F.I.C.O.G. 2018Dokument35 SeitenPartograph: DR Ban Hadi F.I.C.O.G. 2018Ammar AlnajjarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breat Feeding BasicConcept PDFDokument1 SeiteBreat Feeding BasicConcept PDFmp1757Noch keine Bewertungen
- Midwives' Role in Empowering WomenDokument6 SeitenMidwives' Role in Empowering WomennurvalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Methods of Family PlanningDokument23 SeitenMechanical Methods of Family PlanningJaspere Nicole Aldea100% (1)
- Nur 194 Mod 2Dokument5 SeitenNur 194 Mod 2Mendoza Winchelle Kyla R.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teenage PregnancyDokument7 SeitenTeenage PregnancyDAYAP, DESEREE Z.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ovarian New GrowthDokument1 SeiteOvarian New GrowthLouie Cedrick Camposano Tria50% (2)
- Lingayen's MNCHN OrdinanceDokument15 SeitenLingayen's MNCHN OrdinanceAbraham AstoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breastfeeding InfoDokument2 SeitenBreastfeeding InfoThe Vancouver SunNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPARISON OF BACK MASSAGE AND POSTPARTUM GYMNASTICS ON UTERINE INVOLUTIONDokument7 SeitenCOMPARISON OF BACK MASSAGE AND POSTPARTUM GYMNASTICS ON UTERINE INVOLUTIONDina AryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Planning Methods: Presented byDokument56 SeitenFamily Planning Methods: Presented byNise Mon KuriakoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controversies in Family Planning: How To Manage A Fractured IUDDokument5 SeitenControversies in Family Planning: How To Manage A Fractured IUDPridina SyadirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 SMDokument10 Seiten1 SMVina GraciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Premature Rupture of MembranDokument21 SeitenPremature Rupture of MembranMarfu'ah HariyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Pre Gestation and Gestational ConditionsDokument88 Seiten2 Pre Gestation and Gestational Conditionslermacornel61Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bacterial VaginosisDokument2 SeitenBacterial VaginosisArgelia CamachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- VBAC or Repeat CDokument26 SeitenVBAC or Repeat CoanamemoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menstrual Disorders 2Dokument39 SeitenMenstrual Disorders 2Nanang HidayatullohNoch keine Bewertungen
- OBGYN Department Duty ReportDokument29 SeitenOBGYN Department Duty ReportRizkilbs LbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- SuganyaDokument102 SeitenSuganyaAlok BhartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenatal CareDokument39 SeitenAntenatal CareGAURAV100% (1)
- 3.1.5.3 Patologi Anatomi Sistem Urogenital Dan PayudaraDokument70 Seiten3.1.5.3 Patologi Anatomi Sistem Urogenital Dan PayudaraaiysahmirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labor Stages, Dystocia Causes and ManagementDokument3 SeitenLabor Stages, Dystocia Causes and ManagementAllan NacinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polycystic Ovary SyndromeDokument13 SeitenPolycystic Ovary SyndromeLIZARDO CRUZADO DIAZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For PMTCT of HIVAIDS in Kenya-1Dokument82 SeitenGuidelines For PMTCT of HIVAIDS in Kenya-1Simon Wanjiru100% (1)
- Gas Paper of Obs &obs Nursing PDFDokument18 SeitenGas Paper of Obs &obs Nursing PDFyasodha maharajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lat XiDokument3 SeitenLat XiEsa NadhirNoch keine Bewertungen