Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bpi209 Sap Business Workflow Case Studies at Nestle Usa
Hochgeladen von
fj_pastorOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bpi209 Sap Business Workflow Case Studies at Nestle Usa
Hochgeladen von
fj_pastorCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
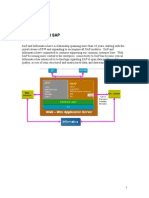
Session ID: BPI209
SAP Business Workflow
Case Studies at Nestle
USA
Ram Chintamaneni, Module Configurer -
SAP Workflow
Introduction
Background/History
Material Master Workflow
COPA/ZMAT and Automatic Batch creation
workflows
Customer Master Workflow
Purchase Order Approval workflow
Q&A
What Workshop Encompasses
History of why workflows at Nestle USA
Understanding Material creation and change process
Material creation
Material extensions (Plants, Dist. Channels and Storage locations)
Material activation
Material change requests and approvals
Seeing how COPA/ZMAT and Batch Creation process are
incorporated into Material workflow
Automatic updates to the ZMAT tables through workflow
Automatic population of Material Master (Accounting view)
Automatic Batch creation through workflow at the time of material
activation
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 4
What Workshop Encompasses continued
Understand Customer workflow process
Customer creation and Blocking
Customer extension
Customer unblocking (activation)
Customer change workflow
The PO Approval workflow process
PO Creation/ PO Change
PO Approval (Acknowledgement or Release)
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 5
Material Master Workflow – Before workflow solution
In the beginning -- if a material number was needed – a PIN form (excel
spread sheet) was initiated and passed to four different groups for data
collection, then sent to Central Master Data (MD) for data entry.
Hard copy passed by hand to each person – bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and
time consuming
The MD Team would then manually create the record in Opera
Multiple keying of the same data, many errors, bottleneck
If a change was needed, the user simply sent an email to MD Team and
the change would be entered.
Accountability and traceability were poor due the system recorded the ID of
the Master Data user making the change, not that of the user requesting the
change.
Change requests were made via e-mails to the Master Data Group, who
then manually entered the change requested.
Storage of PIN forms / Change requests – much paper and storage space
Supporting documentation was difficult to maintain and access.
Held on Share point – access limited to one person at a time
In 1998, Nestle (USA) began implementation of SAP with the Finance and
Master Data modules.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 6
Material Master Workflow – Before workflow solution
continued
Mid 1999 implemented SAP Master Data and Finance complete.
The SAP implementation, added more requirements and attributes to the
material master and needed to be populated
From 30-40 to Over 150
4 groups climbed to 14 groups that needed to supplied information.
Scaling-up the existing PIN Form process would be much too
complicated and complex.
Maintaining the integrity of the spreadsheets
Routing spreadsheet to so many users -- almost impossible.
Processing times – new SAP requirements
Central Master Data the single data entry point -- Traceability non-existing
Ownership still a problem -- if data owners were entering data themselves,
accuracy and accountability would soon follow
Data accuracy -- downstream impact further costs in operations with errors
Costs – more people would have been needed to perform the as task
An effective and efficient process would be critical
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 7
Material Master Workflow – Approach
Interviews conducted with many users of the existing processes;
including customers, material, vendors master data and purchase order
processing.
The broad scope, of the SAP implementation
14 different groups had some responsibility for master data, of these
8 or 9 (i.e. Finance, Marketing, Packaging) were within the six Divisions
the others (i.e. Supply Chain) were corporate level.
Ownership of the data continues to be the biggest problem.
Everyone wants it to be correct but no one want to own it.
Some attribute ownership is straightforward
Quality -- owner of shelf-life – and they wanted to own it.
Finance -- the obvious owner for Standard Price.
The Business did not understand the how the SAP attributes were used
nor what was “workflow”.
New requirements emerged – understand the data, exactly how the
attributes worked and the downstream impacts – ownership changed.
One attribute, the apparently simple ‘Net weight’, changed ownership four times! The
current owner is Regulatory Affairs, although Marketing, Finance and Packaging are all
effected by it.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 8
Material Master Workflow – Approach continued
SAP had many more new attributes then before -- Advanced
Planner and Optimizer APO, was driving (new) MRP functions;
planning time
Procurement
purchasing value key
2001 - The current workflow was designed and implemented
Further refinement and enhancements developed and
implemented
2005 automatic batch creation and full material activation across
required locations
2004 automatic creation of Accounting views with COPA/ZMAT
update
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 9
Material Master Workflow – Results
The PIN FORM processes was not a fit with SAP, the results -- Workflow.
Precise comparison between the new and old process is difficult, as along
with the new workflow process many new groups and attributes were
added, which significantly increasing the workload and number of groups
involved.
What can be noted though is;
Efficiency overall increased by decentralizing Master data
Workload is assigned to the appropriate users – single data entry
Decreased headcount (central vs. decentralized) 12 to 4
Single point contact 'master data lead' within each division
z 4 leads for 6 division.
Accountability and traceability strengthened
ErrorRates using the PIN form was so high that it required additional data
checking procedures -- taking as much as 2 weeks.
Error Rate using workflows have dropped considerably
z from 98% first time error to less the 2%.
Firsttime quality by eliminated double entry by a non data owner
Auditing and tracking of workflows reducing bottlenecks
Ownership of data
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 10
Material Master Workflow – Results continued
Cycle time improved from 4-6 weeks to 2-4 weeks
This may not seem an improvement, but remember there are more
attributes and groups now -- However using the old Excel process
with the current complexity of SAP the material master would
have resulted in significantly increased the cycle time.
It is important to note -- lack of understanding and knowledge of the
attributes will increase the cycle time
The process is still very dependent on the availability and
accessibility of users processing the workflow.
Overall the workflow process is about 30% faster and more accurate
Supporting documentation for a material is now all in one place.
SAP reports can be run to monitor and track workflows.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 11
Material Master Workflow – Learning’s
Before Workflows material creation and activation took 3-4 weeks.
Using workflow this can now take as little as 3 days .
Ensure data being managed is actually necessary -- At first the Nestle
SAP implementation team identified about 250 fields but two thirds of
these were not needed.
Clear business definitions of each attribute is crucial -- Define each field
carefully.
Ensure that you understand what the tool will be able to do for you.
Involve Security in workflow definition.
Define the flows to minimize delays and manual handling of the data.
Define data ownership before creating workflows -- As ownership
changes based on requirements.
Train people in functional, not divisional, groups.
Bottom Line:
Establishing business definition and ownership of the material attributes
required for SAP was the key in implementing an effective data
management processes and minimizing error rates
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 12
Material Master Workflow
Material Creation process after workflow solution:
2-step -- semi-automated process.
MCR (Material Creation Request)
MCR is an add-on form to SAP
Initiating
the MCR and preliminary data collection is done by the data owners
onto MCR form -- strengthens data ownership and accountability
MCR tracking and visibility all within SAP
Progress reports can be run to monitor/identify
z Process improvements -- Cycle times -- Bottlenecks
Materialnumber assignment, logic check and triggering main workflow is
done by division leads
Main Workflow
Pre-activematerials are routed electronically to the appropriate user at the
appropriate time for data input.
Data owner enters the relevant data directly into SAP through workflow items
z Duplicate Data entry eliminated -- Keying error are reduced
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 13
Material Master Workflow continued
Master Data Divisional Lead assist with expediting a material
through the MCR and in workflow processes.
Visibility of the MCR and Main workflow while routing
Identify bottlenecks
Control when a material is activated
Create reports
Outlook reminders for the past due workflow items
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 14
Material Creation Request (MCR) Workflow
MCR routing Process
MARKETING Rejected
MCR
Notification of
Code
Master Data Assignment
Division Lead
DIVISIONAL FINANCE reviews MCR
Approved MCR
Lead creates pre-
DEMAND PLANNER
active material record
in SAP
SUPPLY PLANNER System automatically
extends material to all
locations listed on MCR
SUPPLY CHAIN
FORECAST SUPPORT
NO
View Create to be
SUPPLY CHAIN triggered?
DECISION SUPPORT
YES
View Creation
PACKAGING Workflow
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 15
Material Creation Request (MCR) Form – Initiation
Finished Goods (FERT) MCR Consumer unit (ZCSU) MCR
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 16
Material Creation Request (MCR) Form - Routing
Marketing role initiates the MCR, completes assigned information
and starts the routing process.
Data owner validation is check at each step in the MCR before
routing is allowed.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 17
Material Creation Request (MCR) Form - Routing
Once data is validated the MCR is allowed to route to the next step
(Finance role)
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 18
Material Creation Request (MCR) Form - Submitting
All steps are validated before the MCR workflow can be routed.
Routing continues through all the assignments on the the workflow
diagram.The packaging role submits the MCR, which then routes to
the Master Data lead to review and approval.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 19
Master Data Lead - MCR Validation and Approval
Master Data Lead does a validity check, assigns the material
number, approves the MCR and Triggers the main workflow.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 20
Triggering Main Workflow
After the MCR approval, Basic data and Classification views will be
automatically populated with MCR data and from the default tables.
Master Data lead completes these two views in the dialog mode by
completing the workflow item.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 21
Workflow Dashboard
After the material is created the status is Pre-active and ready for view
routing. At this time, most of the material views like Sales, MRP,
Purchasing, Work scheduling, Forecasting, Quality management and
Storage views will be completed in the background with the values from the
MCR and from the default tables.
The main workflow is triggered
Storage view
Accounting view
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 22
Material Master Main Workflow
Material View routing process
Basic Data &
SUPPLY
Extras Views MARKETING eBusiness Dashboard
Lead PLANNER Master Data
Divisional Lead
reviews
completed
Sales Views SUPPLY QUALITY DIVISIONAL
SALES material
Background PLANNER MGT. FINANCE
Forecasting, Quality Mgt., Work
System
Scheduling, MRP and Purchasing Views
automatically
Background
extends the
material to the
appropriate
Storage &
QUALITY PRODUCT distribution
Extras Views PACKAGING channels and
Background MGT. DEVELOPMENT
storage locations
Classification
DIVISIONAL MD Lead
View
Lead FINANCE prompts system
to activate the
Accounting Views material at all
Divisional Finance
ZMAT/COPA Form Accounting Views - Background levels (material,
•Standard price breakdown plant, distribution
• Standard price • Valuation Class
channel)
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 23
Main Workflow View Routing
When the views are routed to the data owner the populated values
entered came from the the MCR, the data owner validate this
information or corrects it.
e.g. Storage view shelf life – Data Owner Quality - values will be
validated or corrected.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 24
Accounting view -- COPA/ZMAT Workflow
Accounting view – Data Owner Manufacturing Finance (FM) –
The work item is sent to the FM role to enter the standard cost components
on the form and to update the ZMAT* tables.
When creating this view the COPA/ZMAT form is presented for population.
Note: Accounting view
has not been created
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 25
Accounting view -- COPA/ZMAT Workflow
After updating the COPA/ZMAT form, the total standard cost will be
updated in the accounting view for all the plants on the MCR .
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 26
Master Data Lead – Material Extension
Master Data lead receives the 2nd Dash board step after all the
views were maintained during Material view routing workflow. After
completion of the dash board step, distribution channel and storage
location extensions will be done automatically for all the locations
on the MCR.
Other Dist. Channel
extensions
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 27
Master Data Lead – Material Extension
Other Storage Location extensions
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 28
Master Data Lead – Material Activation
After activating the material by the Master data lead, all the statuses(X-Plant status,
X-Dist. Chain status, Dchain-spec status and Plant spec material status) on the
material will be automatically updated along with the valid from date being changed
to the date on which the material got activated.
After the material activation, MCR initiator receives the SAP Office message with
the MCR and Material number information.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 29
Batch Creation
After the material activation, automatic batch creation will be done
in the background for batches ‘UNKNOWNRES’ and
‘UNKNOWNNR’.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 30
Material Master Change Workflow
Requestor creates a
change request by
entering transaction
code CC01 into SAP
The “Valid on” date should be
specified, or set at one year from
current date for immediate changes
Requestor executes
change request from
their SAP Inbox and
enters changes on
SAP view.
Master Data Divisional
Lead reviews request
for dependencies and
releases change
request
Check date =
current date + Is the Is the
System waits for
1 year “Valid on” date no “Valid on” date no the actual date to
equal to the equal to the
match current date
check date? current date?
yes
yes
System activates
changes
System notifies Steps in the shaded area are
requestor that the automatically performed by
change has been SAP in the background
activated
End
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 31
Creating a Change Request using CC01
Valid from date
Enter the material number
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 32
Change Request Workflow – MM12
e.g. user would like to change the material group
Workflow inbox Planned change (MM12)
View selection
Change requester
Workflow inbox
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 33
Change Request Workflow – MM12
Changing the Material group
Using MM12, changing the
material group from 0027 to
0020
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 34
Change Request Workflow – Lead Approval
The change request flows to the Master Data leads to review the
material change and approve the request
Approve the request
Master Data lead reviews
the requested changes
Material group changed
Verify the material changes from 0027 to 0020
after workflow completion
using MM03
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 35
Customer Master Create Workflow
Customer Master Create Workflow Creating a Bill-
Bill-to (B.1)
CREDIT creates or AOC transfers information from the
Broker/Sales Rep form and creates a request by
completing Customer Master Request (CMR)
• Sales org. • City • Postal c ode • APC number
• Dist. Channel
Notif ication
• P.O. box city • Region (US Only) • CSC number
• Division • Telephone #s • Countr y • Planning Act number
sent to AOC
• Title • Telebox (Team #) • Int’net adrs • Attribut e 5
• Name1 • Search Term • Fax number
• Name 2,3,4 • PO box • PO box Pc ode
• District • Language • Customer Group 4
Address Data
Reject INITIATOR approves • Title Credit
CMR Billing • Name 1 • Search ter m • Telebox • City • Countr y
(1st level approval) Credit • Name 2 • Language • Fax number • Postal c ode • PO Box
• Name 3 • Telephone 1 • Internet address • District • PO Box City
• Payment ter ms • Pay m guar pr oc • Name 4 • Telephone 2 • Street • Region (US Only) • PO Box Pcode
Approv e
Account Management
Reject Credit
• Sort key • Last i nt. c alc. • Previous a/c no.
• Recon. Account • Last k ey date • Int. c alc. Freq
Reject • Interes t indicator
Completely
Credit enters data on
CMR and approves if not Contact Person
a duplicate customer Credit
(2nd level approval) • Function • Telephone # • Fax • Region • District • Title
• Recon account • First Name • Department • Street • Postal C ode • City • Comm. ty pe
• Credit Entit y (in • Last N ame • PO Box • Language k eys • PO Box Pcode • Country k ey • Name (1,2,3)
Alt Payer field) • For m of address • Time Zone • Sort fiel d • PO Box City
• Acctg clerk
Notif ication Control Data
sent to AOC Credit
• Vendor • Industry
Reject Approv e
Correspondence System reviews all
Credit dependencies and
• Accounting cler k • Leg Dunn Pr ocess • Groupi ng k ey • Dunn block activates the General
• Last dunned • Dunni ng cl erk • Clerk’s internet • Dunni ng procedur e
• Customer us er • Dunn l evel addr ess • Account st atement Bill-To record
• Dunni ng reci pient • Clerk’s fax • Account at cus tomer
Corp Sales MD enters
data on CMR and
creates the general Bill-to record
(3rd level approval)
Payment Transactions Billing
Credit
• Payment ter ms • Next payee • House bank • Selecti on rul e
• Toleranc e group • Rsn code c onv • Credit memo t er ms • Indiv. Pay ment
• Loc kbox • Pay ment method • Pay ment bl ock • Groupi ng k ey
Approv e • Rec. Pmnt History suppl ement • Pay ment methods • EDI Pmnt advic e
CorpSales
Corp SalesMDMDextends
extendsrecord
record Credit Maintenance SubRecord
totoother
Corp otherSales
Sales Sales Areas(as
MD Areas
extends (as many
record
many Credit (NOTE: This is a separ ate wor k item, not a view)
Corp Sales
to other MDnecessary)
as
Sales creates
Areas (asand
many
as necessary)
extends record to other Sales • Customer acc ount number
as necessary)
Areas (as many as necessary)
Corp Sales MD routes
view s for input *
Italicized attributes are optional
* Please see Diag. B.2
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 36
Customer Master Extension Workflow
Extending a Sold-
Sold-To to Sales Areas (S.2)
Customer Master
Extension
AOC approves CMR Notif ication per
(1st level approval) Sales Area
sent to AOC
• Customer group • Customer Group 2
Approv e Sales Areas
Reject 02, 03 & 05
Inventory Control enters
data on CMR All Other Sales Areas
(3rd lev el approv al) & EDI button is YES
• Customer Group 2
Notif ication
sent to AOC Reject Sales Areas 02
Approv e 03, & 05 & EDI
Reject button is Y ES
All Other Sales Areas
EDI approves Data on CMR & EDI button is NO
(3rd lev el approv al)
Sales Areas 02, 03
& 05 & EDI button
is NO
Approv e
Reject
Reject
Completely
Corp Sales MD
approves/rejects based
on Bill-to status or if it is
a duplicate
(4th lev el approv al)
• District Sales System reviews all
Sales Support System reviews
Sales Operations Sales Support dependencies andallall
System reviews
Sales Operations dependencies
activates and
the General
Sales
• Price groupOperations Support dependencies
activates the and
General
Approv e • Price group Sold-To record
• Price group activates
Sold-Toeach Sold-To
record
Sales Area record
Corp Sales MD creates
general record and extends
record to other Sales Areas
(as many as necessary)
Corp Sales MD routes
views for input
Note: System cannot activate, by Sales Area, Sold-to until
its Bill-to and Ship-to are complete.
Italicized attributes are optional
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 37
Customer Master Changing a Bill-to Workflow
C h a n g in g a B i ll - t o
C R E D IT o r A O C in it ia t e s t h e B ill- to c h a n g e r e q u e s t. N o t if ic a t io n
b y c o m p le tin g C u s t o m e r M a s te r R e q u e s t ( C M R ) s e n t t o AO C
R e je c t
I N IT I A T O R a p p r o v es
Ch a n g e Re q u e s t
( 1 s t lev e l a p p r ov a l)
A p p ro v e
R e je c t
C re d
C it
R EaDpI prT oa vp esp r ocvheasn g e
C h a nr eg qe uRe es qt u e s t
(2 n d lev
leveel laapppprroovvaal)l)
R e je c t
A p p ro v e
A O C a p p r ov e s
Ch a n g e Re q u e s t
R e je c t ( 3 rd le v e l a p p r ov a l)
C o m p le t e ly
A p p ro v e
C o r p S a le s M D a p p r ov e s C M R
( 4 t h le v e l a p pr o v a l)
A p p ro v e
S y s te m u p d ate s th e
s t a tu s o f c u s t o m e r r e co r d
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 38
AOC initiates CMR process
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 39
5
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 40
AOC submits and approves the CMR
7 8
Workflow items displayed in
1 Credit’s Inbox
Credit’s
2
Inbox
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 41
Credit selects CMR to process
3
Workflow items displayed in Corp Sales
MD’s Inbox
1
Corp Sales MD selects CMR to
2 process
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 42
3
Corp Sales MD runs BDC
4 session to create Customer
record
1
Corp Sales MD selects
specific Dist Channel to
extend the customer
record to
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 43
Corp Sales MD runs BDC
3 session to extend Customer
record to dist. Channel “01”
2 Corp Sales MD approved CMR for extension
process
Views routed to Functional
Grps
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 44
Credit view
Credit maintenance View
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 45
Billing and Payment view maintenance
Payment view
Billing view
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 46
Workflow History for the CMR
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 47
Workflow log before Customer activation
Workflow will in the wait mode after completing all the views.
Customer gets activated after running the activation program after
all the account group dependencies were met.
Following flow shows wait step before the activation program
execution
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 48
Workflow log after Customer activation
After the execution of the activation program , the blocks on the
customer got removed and the customer is ready for use.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 49
Customer activated
Customer activation status reflects on the CMR
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 50
Purchase Order Approval Workflow
No
PO Created, Forward
Subject to PO Need Higher
Changed, Yes Workitem to Release? Yes No PO Released
Release? Release?
Un-released Approver
Yes
No
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 51
Purchase Order Approval Workflow
After creating the PO, the PO creator gets a workflow item to specify
an approver to release the PO.
Specify the user who should approve the PO.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 52
Purchase Order Approval Workflow
Approver receives the work item to release the PO. Based on the
release authorization, the approver can acknowledge/approve the
PO.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 53
Purchase Order Approval Workflow
This PO requires additional approval(s).
Specify the user who should approve the PO.
This user will not be able to approve this PO.
Send for acknowledgement anyways?
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 54
Summary
Workflows has improved
Efficiencies
Accountability/Traceability
Cycle time
Documentation storage and retrieval
The workflows have been designed for flexibility and modifiable
to meet the business needs.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 55
Questions?
Q&A
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 56
Further Information
Î Public Web:
www.sap.com
www.sdn.sap.com
SAP NetWeaver Developer‘s Guide:
www.sdn.sap.com/sdn/developersguide.sdn
Î Americas’ SAP Users’ Group (ASUG)
www.asug.com
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 57
Copyright 2005 SAP AG. All Rights Reserved
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or for any purpose without the express permission of SAP AG. The information
contained herein may be changed without prior notice.
Some software products marketed by SAP AG and its distributors contain proprietary software components of other software vendors.
Microsoft, Windows, Outlook, and PowerPoint are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
IBM, DB2, DB2 Universal Database, OS/2, Parallel Sysplex, MVS/ESA, AIX, S/390, AS/400, OS/390, OS/400, iSeries, pSeries, xSeries, zSeries, z/OS, AFP,
Intelligent Miner, WebSphere, Netfinity, Tivoli, and Informix are trademarks or registered trademarks of IBM Corporation in the United States and/or other
countries.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation.
UNIX, X/Open, OSF/1, and Motif are registered trademarks of the Open Group.
Citrix, ICA, Program Neighborhood, MetaFrame, WinFrame, VideoFrame, and MultiWin are trademarks or registered trademarks of Citrix Systems, Inc.
HTML, XML, XHTML and W3C are trademarks or registered trademarks of W3C®, World Wide Web Consortium, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Java is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
JavaScript is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc., used under license for technology invented and implemented by Netscape.
MaxDB is a trademark of MySQL AB, Sweden.
SAP, R/3, mySAP, mySAP.com, xApps, xApp, SAP NetWeaver and other SAP products and services mentioned herein as well as their respective logos are
trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP AG in Germany and in several other countries all over the world. All other product and service names mentioned
are the trademarks of their respective companies. Data contained in this document serves informational purposes only. National product specifications
may vary.
The information in this document is proprietary to SAP. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, or transmitted in any form or for any purpose
without the express prior written permission of SAP AG.
This document is a preliminary version and not subject to your license agreement or any other agreement with SAP. This document contains only intended
strategies, developments, and functionalities of the SAP® product and is not intended to be binding upon SAP to any particular course of business, product
strategy, and/or development. Please note that this document is subject to change and may be changed by SAP at any time without notice.
SAP assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions in this document. SAP does not warrant the accuracy or completeness of the information, text, graphics,
links, or other items contained within this material. This document is provided without a warranty of any kind, either express or implied, including but not limited
to the implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, or non-infringement.
SAP shall have no liability for damages of any kind including without limitation direct, special, indirect, or consequential damages that may result from the use
of these materials. This limitation shall not apply in cases of intent or gross negligence.
The statutory liability for personal injury and defective products is not affected. SAP has no control over the information that you may access through the use
of hot links contained in these materials and does not endorse your use of third-party Web pages nor provide any warranty whatsoever relating to third-party
Web pages.
© SAP TechEd ’05 / BPI209 / 58
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- German Language CourseDokument210 SeitenGerman Language Course42099% (71)
- Data Migration Strategy and SAPDokument8 SeitenData Migration Strategy and SAPJohn100% (3)
- Visual Management ScoreboardsDokument10 SeitenVisual Management Scoreboardsfj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Migration About One of Best PractisesDokument15 SeitenData Migration About One of Best Practisesraju100% (2)
- Material Master Data GovernanceDokument5 SeitenMaterial Master Data GovernanceManuel BarbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ice-Cream ProductionDokument65 SeitenIce-Cream ProductionMujtaba HaseebNoch keine Bewertungen
- mf8240 160824142620 PDFDokument698 Seitenmf8240 160824142620 PDFArgopartsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gear Metrology ReportDokument59 SeitenGear Metrology Reportsanjay261289Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperion PlanningDokument53 SeitenHyperion PlanningRamesh Krishnamoorthy100% (1)
- Clarinet Scales PracticeDokument3 SeitenClarinet Scales Practicefj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clarinet Scales PracticeDokument3 SeitenClarinet Scales Practicefj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Onboaring 1.1Dokument123 SeitenOnboaring 1.1Sun HiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP Master Data Governance: Implementation Project (Supplier)Dokument39 SeitenSAP Master Data Governance: Implementation Project (Supplier)ANDRESFELIPEALVIZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Improvement & Performance Management Made Simple: The Fasttrack Approach to Getting Results QuicklyVon EverandProcess Improvement & Performance Management Made Simple: The Fasttrack Approach to Getting Results QuicklyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro S4HANA Using Global Bike Slides MM en v3.3Dokument53 SeitenIntro S4HANA Using Global Bike Slides MM en v3.3Nalin KNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP Basis Configuration Frequently Asked QuestionsVon EverandSAP Basis Configuration Frequently Asked QuestionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (4)
- Schneider Electric - GovernanceDokument9 SeitenSchneider Electric - GovernanceJames ENoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP S/4HANA Asset Management GuideDokument14 SeitenSAP S/4HANA Asset Management GuideSumitra Balan100% (1)
- Data Migration-Conversion To SAP From Legacy Systems - Our Strategy (A 101ERPTEAM White Paper)Dokument8 SeitenData Migration-Conversion To SAP From Legacy Systems - Our Strategy (A 101ERPTEAM White Paper)Shahid_ONNoch keine Bewertungen
- The MSP’s Guide to the Ultimate Client Experience: Optimizing service efficiency, account management productivity, and client engagement with a modern digital-first approach.Von EverandThe MSP’s Guide to the Ultimate Client Experience: Optimizing service efficiency, account management productivity, and client engagement with a modern digital-first approach.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Simulations of Piano StringsDokument7 SeitenNumerical Simulations of Piano StringsMihai DincaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bashar Discusses Monatomics, White Powder Gold and Ormus MineralsDokument32 SeitenBashar Discusses Monatomics, White Powder Gold and Ormus MineralsFlorin V. Iagaru100% (6)
- Driving Business Value With MDMDokument38 SeitenDriving Business Value With MDMglobal4321Noch keine Bewertungen
- LTMC For Master Data Step by Step Process - SAP BlogsDokument24 SeitenLTMC For Master Data Step by Step Process - SAP BlogsshamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1: Business Consolidation With SAP Group Reporting OverviewDokument3 SeitenUnit 1: Business Consolidation With SAP Group Reporting Overviews4hanasd 1809Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cantece Si Colinde de Craciun Partituri PianDokument44 SeitenCantece Si Colinde de Craciun Partituri PianAlexandra PavloviciNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP ECC FI Transaction Codes: Unofficial Certification and Review GuideVon EverandSAP ECC FI Transaction Codes: Unofficial Certification and Review GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Data Migration Material MasterDokument19 SeitenData Migration Material Mastervenkay1123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resume - SAP Plan To Produce Lead - SurreshkumarDokument3 SeitenResume - SAP Plan To Produce Lead - SurreshkumarJaime DudleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual tone frequencies have hidden qualitiesDokument7 SeitenIndividual tone frequencies have hidden qualitiesArnauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mysap Fi Fieldbook: Fi Fieldbuch Auf Der Systeme Anwendungen Und Produkte in Der DatenverarbeitungVon EverandMysap Fi Fieldbook: Fi Fieldbuch Auf Der Systeme Anwendungen Und Produkte in Der DatenverarbeitungBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- SAP SD MM Functional Consultant Resume PDFDokument3 SeitenSAP SD MM Functional Consultant Resume PDFrajkumaraei83% (6)
- ASAP Methodology - Phase 1: Project PreparationDokument3 SeitenASAP Methodology - Phase 1: Project PreparationMaheshKarnatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide to Cross-Subject Area ReportsDokument19 SeitenGuide to Cross-Subject Area Reportssatyanarayana NVSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Migration Sap MM PDFDokument32 SeitenData Migration Sap MM PDFBCHERIFNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1032 The New User Experience For SAP ERP Human Capital Management HR RenewalDokument39 Seiten1032 The New User Experience For SAP ERP Human Capital Management HR Renewalbilal_k_ranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP ASAP MethodologyDokument7 SeitenSAP ASAP Methodologyhardik kachhadiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP FI Training MaterialDokument67 SeitenSAP FI Training Materialamarnathreddyl50% (4)
- SAP ASAP Methodology PhasesDokument2 SeitenSAP ASAP Methodology PhasesAnjali RathoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- ERP Case Study-Hero HondaDokument19 SeitenERP Case Study-Hero HondaKranthi Kumar Raju100% (2)
- It and RetailDokument49 SeitenIt and RetailchetnachhabraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Governance in Practice at Commscope: Lessons Learned From A Technical PerspectiveDokument35 SeitenData Governance in Practice at Commscope: Lessons Learned From A Technical Perspectivevenkat2122Noch keine Bewertungen
- MM04Dokument7 SeitenMM04changingmomentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Dat Am GNT RoleDokument15 SeitenMaster Dat Am GNT RolearthryxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing - Delivery ProcessDokument4 SeitenData Warehousing - Delivery ProcessPhine TanayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadrate: A Simple Solution For Uploading Data Into SAPDokument2 SeitenQuadrate: A Simple Solution For Uploading Data Into SAPRamesh GanapathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mohd Farhan Usmani - SapDokument4 SeitenMohd Farhan Usmani - Sapfarhanusm9712Noch keine Bewertungen
- 611 SAPMassChangeDokument9 Seiten611 SAPMassChangemailstosjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manjunath MDokument3 SeitenManjunath MAshok PrasathNoch keine Bewertungen
- DMBI Unit-2Dokument36 SeitenDMBI Unit-2Paras SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of Quality Management: Pn. Norkisme Zainal Abidin 019 620 8585 Norkisme@ukm - Edu.myDokument32 SeitenEssentials of Quality Management: Pn. Norkisme Zainal Abidin 019 620 8585 Norkisme@ukm - Edu.mygeena1980Noch keine Bewertungen
- THARINDU THARAKA BANDURATHNA-TemplateDokument4 SeitenTHARINDU THARAKA BANDURATHNA-TemplatekanimozhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Andrew Haywood CV 2010Dokument6 SeitenAndrew Haywood CV 2010Dobber0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project RPRT JituDokument5 SeitenProject RPRT JitujitssssNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyndi CodyDokument7 SeitenCyndi Codys4 hanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP Resume Sample 1: Don K. DennisDokument3 SeitenSAP Resume Sample 1: Don K. DennisMehedi KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To SAP HanaDokument30 SeitenIntroduction To SAP Hanaanupamrc100% (2)
- 2 AccDokument3 Seiten2 AccEliz QilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erp Final Working ReportDokument12 SeitenErp Final Working ReportUme RubabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction SAP - HANADokument31 SeitenIntroduction SAP - HANAhari1221Noch keine Bewertungen
- IT Management in Supply Chains - Omkar Khairmode - HPGDJL213544Dokument15 SeitenIT Management in Supply Chains - Omkar Khairmode - HPGDJL213544Venkatesh KamathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Note - PMISDokument7 SeitenConcept Note - PMISAjitabh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systems ReportDokument10 SeitenSystems ReportCalvin PooleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaya Prakash SAP MM ResumeDokument4 SeitenJaya Prakash SAP MM Resumesandeepsankar777Noch keine Bewertungen
- PowerExchange - SAP Functionality OverviewDokument13 SeitenPowerExchange - SAP Functionality OverviewMahesh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) : Presented byDokument20 SeitenEnterprise Resource Planning (ERP) : Presented byAvadhesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume 11Dokument3 SeitenResume 11allan237Noch keine Bewertungen
- SAP Certifications and Trainings SummaryDokument96 SeitenSAP Certifications and Trainings SummaryBasavaraj WantamutteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yogesh KumarDokument2 SeitenYogesh KumarSneha More Pandey100% (1)
- Dayal: SAP Sap S/4 Hana Soft SkillsDokument2 SeitenDayal: SAP Sap S/4 Hana Soft SkillsDebraj RayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Idoc - Pub - Sap MM Module ResumeDokument3 SeitenIdoc - Pub - Sap MM Module ResumeVijaybhaskar ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EB 10 Secrets To Win With Analytics enDokument17 SeitenEB 10 Secrets To Win With Analytics enfj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Create Visual Workplace 5S-Plus GuideDokument40 SeitenCreate Visual Workplace 5S-Plus Guidefj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project PresentationDokument53 SeitenProject PresentationMauro63Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grey Cast IronDokument97 SeitenGrey Cast IronSiddharth GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clarinet fingering chart guideDokument2 SeitenClarinet fingering chart guidefj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture1a PDFDokument38 SeitenLecture1a PDFAnand1832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study SMEDDokument18 SeitenCase Study SMEDMathijs91100% (2)
- Guia para Facilitador 5 SDokument16 SeitenGuia para Facilitador 5 SEve LynNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 Costa Et Al SMEDDokument8 Seiten2013 Costa Et Al SMEDfj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Value - Stream - Mapping - VSM - Jarkko ErikshammarDokument34 SeitenValue - Stream - Mapping - VSM - Jarkko Erikshammarfj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Territories: Management Techniques To Define Organized, Productive, Safe and Work AreasDokument5 SeitenVisual Territories: Management Techniques To Define Organized, Productive, Safe and Work Areasfj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection and Measurement of Tooth ThicknessDokument14 SeitenInspection and Measurement of Tooth Thicknessfj_pastor100% (1)
- LeadershipDokument10 SeitenLeadershipfj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering Box Adjustment PageDokument3 SeitenSteering Box Adjustment Pagefj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 66 Abba SOSDokument4 Seiten66 Abba SOSMiguel Muñoz VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abba - Knowing Me Knowing YouDokument4 SeitenAbba - Knowing Me Knowing Youfj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abba - One - of - UsDokument3 SeitenAbba - One - of - Usfj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goodheart Willcox Ch13Dokument11 SeitenGoodheart Willcox Ch13fj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artistic Large Scale CastingDokument4 SeitenArtistic Large Scale Castingfj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charts For Short Run SPCDokument7 SeitenCharts For Short Run SPCfj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Example in Steel Casting The One Person Hitch Housing For The 2 and 5 Ton TrucksDokument26 SeitenAn Example in Steel Casting The One Person Hitch Housing For The 2 and 5 Ton Trucksram3106Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diseno de Mazarotas PDFDokument45 SeitenDiseno de Mazarotas PDFAriel GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NASA TrackShoeDokument31 SeitenNASA TrackShoefj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- SFSA Casteel ReporterDokument3 SeitenSFSA Casteel Reporterfj_pastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 10 Performance Task 1Dokument2 SeitenMathematics 10 Performance Task 1SnowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Guide VLSI Aspirants FAQ Physical DesignDokument3 SeitenEssential Guide VLSI Aspirants FAQ Physical DesignRohith RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anthony Robbins With Harvard Business SchoolDokument3 SeitenAnthony Robbins With Harvard Business SchoolluffylovemangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JBF Winter2010-CPFR IssueDokument52 SeitenJBF Winter2010-CPFR IssueakashkrsnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 9000 Audit Checklist for Quality Management SystemsDokument28 SeitenISO 9000 Audit Checklist for Quality Management SystemsphilipalexjonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulation and Evaluation of Lansoprazole Delayed Release PelletsDokument20 SeitenFormulation and Evaluation of Lansoprazole Delayed Release PelletsUmair MazharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causal Inference For The Brave and True - Causal Inference For The Brave and TrueDokument2 SeitenCausal Inference For The Brave and True - Causal Inference For The Brave and TrueVkook ForeverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rexroth HABDokument20 SeitenRexroth HABeleceng1979Noch keine Bewertungen
- Materi HAZOP Dan Relevansi Terhadap ASME Dan APIDokument9 SeitenMateri HAZOP Dan Relevansi Terhadap ASME Dan APIAhmad KharisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tuomo Summanen Michael Pollitt: Case Study: British Telecom: Searching For A Winning StrategyDokument34 SeitenTuomo Summanen Michael Pollitt: Case Study: British Telecom: Searching For A Winning StrategyRanganath ChowdaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry 2 - LAS 2 LEARNING CAPSULEDokument5 SeitenGeneral Chemistry 2 - LAS 2 LEARNING CAPSULEMark RazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kamran Afzal ResumeDokument2 SeitenKamran Afzal ResumeChelsea ElizabethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Large Generator Protection enDokument14 SeitenLarge Generator Protection enNguyen Xuan TungNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDokument3 SeitenGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridaySheilaMarB.Esteban100% (1)
- FMVSS 139 2022-10-01Dokument7 SeitenFMVSS 139 2022-10-01skr_757Noch keine Bewertungen
- Middle Range TheoriesDokument134 SeitenMiddle Range TheoriesMary Joyce MejiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Molecular Engineering Hierarchical Pore-Interface Based On TD-Kinetic Synergy Strategy For Efficient CO2 Capture and SeparationDokument10 SeitenFunctional Molecular Engineering Hierarchical Pore-Interface Based On TD-Kinetic Synergy Strategy For Efficient CO2 Capture and SeparationAnanthakishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operator Interface SERIES 300 Device Platform EAGLE OS ET-316-TXDokument6 SeitenOperator Interface SERIES 300 Device Platform EAGLE OS ET-316-TXDecoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths ReportDokument3 SeitenMaths ReportShishir BogatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tos Template Arpan 1Dokument25 SeitenTos Template Arpan 1florence s. fernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DHP UM 015 IHP24 HART User ManualDokument70 SeitenDHP UM 015 IHP24 HART User Manualkumar ambujNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix 1c Bridge Profiles Allan TrussesDokument43 SeitenAppendix 1c Bridge Profiles Allan TrussesJosue LewandowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 TestDokument7 SeitenChapter 10 Testapi-348969276Noch keine Bewertungen
- WHLP in Reading and Writing Week 8Dokument4 SeitenWHLP in Reading and Writing Week 8Manuel Despabiladeras0% (2)