Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Benguet State University: I. Assessing Oxygenation
Hochgeladen von
PANGPANGDEO Shanne Delle B.Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Benguet State University: I. Assessing Oxygenation
Hochgeladen von
PANGPANGDEO Shanne Delle B.Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Vision: A PREMIER UNIVERSITY delivering
world-class education that promotes
Benguet State University “Excellent nursing education that
provides graduates with self-direction,
sustainable development amidst climate
change. COLLEGE OF NURSING competence and compassion.”
Mission: To provide quality education to La Trinidad, Benguet “The College of nursing is committed to
enhance food security, sustainable provide a strong academic and
communities, industry innovation, climate
www.bsu.edu.ph/ 422- 2127 professional foundation for the practice
resilience, gender equality, institutional of nursing.”
development and partnerships.
I. ASSESSING OXYGENATION
A. RESPIRATION
Throwback time! You’ve already learned about how to assess the respiration of your patient in your level
II competencies. If you can remember, we utilize the four techniques of assessment namely: Inspection, Palpation,
Percussion and Auscultation. For patients with oxygenation problems, we also utilize the pulse oximetry and ABG
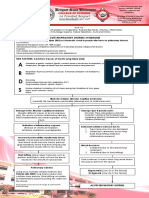
results as part of evaluating the oxygenation status. The photo below shows you a picture of a patient in
respiratory distress. It’s time to jog your memory! Imagine yourself assessing this patient. Take a moment. What
do you inspect? What do you palpate? How do you percuss? How do you auscultate? Close your eyes and give
yourself some time to visualize the ward setting and imagine performing these assessments. Follow the checklist
provided below as you assess this patient.
Inspection
Skin color
Nail beds
Capillary Refill Time
Coughing
Breathing pattern
Chest rise and fall
RR
Use of accessory muscles
Palpation
Tactile Fremitus
Chest excursion
Percussion
Resonant sounds
Hyper-resonant sounds
Dull sounds
Tympanic sounds
Auscultation
Breath Sounds
Other Assessments
SpO2
ABG
X-Ray
Have you successfully evaluated for all the assessments in the checklist? If not, don’t worry. We can review
them in the context of a patient in distress. Refer to the table below:
INSPECTION ❖ Skin color Pallor/ Cyanotic? Pinkish?
❖ Nail beds Pale? Cyanotic? Clubbing present?
❖ Capillary Refill Time More than 2 seconds? This might
indicate respiratory or circulatory
problem.
❖ Coughing Productive or non-productive? Mucus
consistency, thickness and amounts?
❖ Breathing pattern Difficulty of breathing? Labored?
Shallow or deep breaths?
❖ Chest rise and fall Abdominal breathing? Complete rise and
fall?
Vision: A PREMIER UNIVERSITY delivering
world-class education that promotes
Benguet State University “Excellent nursing education that
provides graduates with self-direction,
sustainable development amidst climate
change. COLLEGE OF NURSING competence and compassion.”
Mission: To provide quality education to La Trinidad, Benguet “The College of nursing is committed to
enhance food security, sustainable provide a strong academic and
communities, industry innovation, climate
www.bsu.edu.ph/ 422- 2127 professional foundation for the practice
resilience, gender equality, institutional of nursing.”
development and partnerships.
❖ RR 1 breath = one inspiration and one
expiration; how many breaths per min?
Normal is 12- 20 breaths/min
❖ Use of accessory Use of substernal, intercostal muscles
muscles and sternocleidomastoid muscles?
Nasal/alar flaring?
PALPATION ❖ Tactile Fremitus Elicited by telling your patient to say
“99” or “33” while palpating the chest to
feel for vibration. This will test if air is
reaching all areas of the lungs.
❖ Chest excursion/ Elicited by palpating the chest and telling
expansion your patient to inhale and exhale. This
will test if both lungs are expanding well
and equally.
PERCUSSION ❖ Resonant sounds This is the normal percussion sounds to
be expected in the lungs.
❖ Hyper-resonant This may indicate an excessive residual
sounds air volume in the lungs upon exhalation
giving a louder sound when percussed.
Common in restrictive lung diseases such
as COPDs.
❖ Dull sounds This may indicate firm tissue. Common
in patients who developed fibrosis on
the lung tissue.
❖ Flat sounds This indicates presence of soft tissue.
❖ Tympanic sounds Not normally heard in chest percussion.
AUSCULTATION ❖ Breath Sounds Normally clear. The presences of
rhonchi, crackles or rales indicate fluid in
the lungs and common during infection.
Stridor and wheezing are for upper
airway obstructions such as asthma.
❖ Bronchial sounds Heard over the anterior chest near the
second and third intercostal space.
Inspiration: Expiration ratio is 1:2
❖ Bronchovesicular Heard over the bronchial area and
posterior chest between the scapulae.
Inspiration: Expiration ratio is 1:1
❖ Vesicular Sounds Heard over most lung fields. Inspiration:
Expiration ratio is 2:1
OTHER ASSESSMENTS ❖ SpO2 Estimate of level of oxygen in the
periphery; Normally 95% to 100%.
Hypoxia might be determined if below
95% and consistent with other signs and
symptoms.
❖ Arterial Blood Gas We check the PaO2 or oxygen saturation
in the serum; normally 80 to 100 mmHg.
This is the most accurate measurement
of oxygen level.
❖ X-Ray This could be used to detect presence of
obstruction along the airway or the
presence of fluid, fibrosis and mass in
the lungs.
Vision: A PREMIER UNIVERSITY delivering
world-class education that promotes
Benguet State University “Excellent nursing education that
provides graduates with self-direction,
sustainable development amidst climate
change. COLLEGE OF NURSING competence and compassion.”
Mission: To provide quality education to La Trinidad, Benguet “The College of nursing is committed to
enhance food security, sustainable provide a strong academic and
communities, industry innovation, climate
www.bsu.edu.ph/ 422- 2127 professional foundation for the practice
resilience, gender equality, institutional of nursing.”
development and partnerships.
OTHERS
1. Assignments
2. Advance reading
3. Asynchronous video for better explanation of the procedure and computation
REFERENCES
Bates' Visual Guide to Physical Examination. (n.d.). Examination of Thorax and Lungs [Video].
YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NCIf7WJDWd8
Berman, A. T., Snyder, S., & Frandsen, G. (2015). Kozier & Erb's fundamentals of nursing:
Concepts, process, and practice (10th) edition. MACMILLAN HEINEMANN
Perry, A. G., & Potter, P. A. (2017). Mosby's pocket guide to nursing skills and procedures - E-
book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Pooler, C. (2009). Porth pathophysiology: Concepts of altered health states. Lippincott
Williams & Wilkins.
Prepared and submitted:
RLE CLINICAL FACILITATOR
Recommending approval:
JOCYLYN W. ANGELES, RN., MAN
Chairman, Dep’t of Clinical Instruction
Approved:
JUDE L. TAYABEN, PhDN
Dean
Vision: A PREMIER UNIVERSITY delivering
world-class education that promotes
Benguet State University “Excellent nursing education that
provides graduates with self-direction,
sustainable development amidst climate
change. COLLEGE OF NURSING competence and compassion.”
Mission: To provide quality education to La Trinidad, Benguet “The College of nursing is committed to
enhance food security, sustainable provide a strong academic and
communities, industry innovation, climate
www.bsu.edu.ph/ 422- 2127 professional foundation for the practice
resilience, gender equality, institutional of nursing.”
development and partnerships.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Monochrome Photo 2022 CalendarDokument12 SeitenMonochrome Photo 2022 CalendarPANGPANGDEO Shanne Delle B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- III. The Procedure (Oxygen Therapy)Dokument4 SeitenIII. The Procedure (Oxygen Therapy)PANGPANGDEO Shanne Delle B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- College of Nursing: Benguet State UniversityDokument4 SeitenCollege of Nursing: Benguet State UniversityPANGPANGDEO Shanne Delle B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- In Patient Face Sheet: Caesarean Section 082.1Dokument8 SeitenIn Patient Face Sheet: Caesarean Section 082.1PANGPANGDEO Shanne Delle B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pangpangdeo Shanne Delle B. - Worksheet 5 ArdsDokument7 SeitenPangpangdeo Shanne Delle B. - Worksheet 5 ArdsPANGPANGDEO Shanne Delle B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular WorksheetDokument9 SeitenCardiovascular WorksheetPANGPANGDEO Shanne Delle B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pangpangdeo Shanne Delle B. - Worksheet 4Dokument4 SeitenPangpangdeo Shanne Delle B. - Worksheet 4PANGPANGDEO Shanne Delle B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- B9 Barangay AmbuklaoDokument15 SeitenB9 Barangay AmbuklaoPANGPANGDEO Shanne Delle B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- DM Pulmonary MedicineDokument7 SeitenDM Pulmonary MedicineAJITH KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passable 350 Q&aDokument76 SeitenPassable 350 Q&aDavid Yousef100% (1)
- Cough and HomoeopathyDokument14 SeitenCough and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho PhysiologyDokument4 SeitenAcute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho Physiologyroseanne18100% (4)
- Airways. DR HUSNIDokument89 SeitenAirways. DR HUSNIFarah Fauziah RachmawatieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flutter and Other DeviceDokument39 SeitenFlutter and Other DeviceEira LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomedical InstrumentationDokument16 SeitenBiomedical InstrumentationGhanshyam DhruwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumothorax and Pneumomediastinum: Dr. Emad EfatDokument89 SeitenPneumothorax and Pneumomediastinum: Dr. Emad Efatinterna MANADONoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen TherapyDokument34 SeitenOxygen Therapysarahsheikh28100% (5)
- Mechanical VentilationDokument29 SeitenMechanical VentilationAbdul Hamid Alraiyes100% (8)
- 8 Shaped WalkDokument1 Seite8 Shaped WalkAmy MyzaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Byssinosis-Health Hazards From Cotton DustDokument32 SeitenByssinosis-Health Hazards From Cotton DustRajesh Dwivedi100% (1)
- ACM 603 Operation and Service ManualDokument26 SeitenACM 603 Operation and Service Manualhluevano100% (1)
- Case 4-2021: A 70-Year-Old Woman With Dyspnea On Exertion and Abnormal Findings On Chest ImagingDokument12 SeitenCase 4-2021: A 70-Year-Old Woman With Dyspnea On Exertion and Abnormal Findings On Chest ImagingBruno ConteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratorycasestudy 1Dokument2 SeitenRespiratorycasestudy 1api-265854240Noch keine Bewertungen
- Baby Gender Determination in Scuba DiversDokument9 SeitenBaby Gender Determination in Scuba DiversDaniel CaskNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Dyspnoea and Haemoptysis My Notes Add Jimmy's PDF Notes On & OrganiseDokument171 SeitenAcute Dyspnoea and Haemoptysis My Notes Add Jimmy's PDF Notes On & OrganisewwwrgrobinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto PeepDokument6 SeitenAuto PeepVadelain GaldamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes of Human Physiology Class 11Dokument9 SeitenNotes of Human Physiology Class 11ADWAITH LALU100% (1)
- Integrated Science NotesDokument115 SeitenIntegrated Science Notesserene munga100% (1)
- Learning Plan in Science 9Dokument6 SeitenLearning Plan in Science 9Pang ChixxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory AlkalosisDokument2 SeitenRespiratory AlkalosisDamilola AdamolekunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System - WikipediaDokument1 SeiteRespiratory System - WikipediaMatias Kristel AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- PneumothoraxDokument7 SeitenPneumothoraxjutah2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fleximag - 110xxxx-Ne-22-01 Instruction and Service ManualDokument135 SeitenFleximag - 110xxxx-Ne-22-01 Instruction and Service ManualWalter Perdomo50% (2)
- Blue Booklet 2009 Website VersionDokument45 SeitenBlue Booklet 2009 Website VersionguolguinNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Anesthesia 1 PDFDokument49 SeitenGeneral Anesthesia 1 PDFYokita JanarthananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map Finished 2Dokument6 SeitenConcept Map Finished 2api-352785497100% (1)
- Lung ExaminationDokument14 SeitenLung Examinationსალომე მუმლაძე “Slay” TMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Pemeriksaan Fisik Tanda VitalDokument39 SeitenPemeriksaan Fisik Tanda VitalOmHada'Noch keine Bewertungen