Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
From Genes To Proteins
Hochgeladen von
Ederlyn ZateOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
From Genes To Proteins
Hochgeladen von
Ederlyn ZateCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
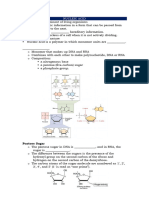
FROM GENES TO PROTEINS
Name _____________________
Directions:
Complete the table by checking the correct column for each statement.
Statement DNA RNA
1. Contains ribose ✓
2. Composed of a double chain of nucleotides ✓
3. Contains Deoxyribose ✓
4. Contains Uracil ✓
5. Contains Thymine ✓
6. Composed of a single chain of nucleotides ✓
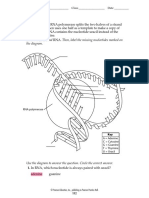
1. Label the diagram by completing the sequence of nitrogen bases in the
mRNA. Use these letters: A, U, C, G, T.
DNA Chain
UC G A A U C G C G U A U U G
mRNA Chain
2. What is it that acts as a template for making RNA? RNA polymerase uses
one of the DNA strands as a template to make a new complementary RNA_____
molecule._________________________________________________________
3. What is meant by transcription? The process of copying a sequence of DNA
to produce a complementary strand of RNA______________________________
4. What are two types of RNA? messenger RNA (mRNA) and transfer RNA__
(tRNA).__________________________________________________________
5. Which type of RNA is transcribed from DNA and contains the code for
polypeptide formation? pre-mRNA is transcribed from DNA and encoded by___
original gene to build polypeptide._____________________________________
6. What is the difference between an intron and an exon? An intron is the__
part of the mRNA that gets cut out and does NOT code for proteins while the___
exons are the part that get linked together and go on to be translated into______
proteins._________________________________________________________
7. What happens to mRNA after processing is complete? mRNA leaves the
nucleus and attaches to a ribosome in the cytoplasm for translation.__________
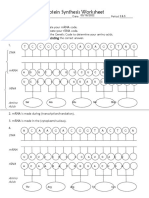
II. Directions:
Use this sheet to practice using the table below which will be used to decipher
the genetic code.
DNA Coding Strand mRNA tRNA Amino acid
A U A Cysteine (Cys)
C G C
A U A
A U A Tyrosine (Tyr)
T A U
G C G
T A U Isoleucine (Ile)
A U A
G C G
G C G Glutamine (Gln)
T A U
T A U
T A U Asparagine (Asn)
T A U
A U A
T A U Serine (Ser)
C G C
G C G
C G C Glycine (Gly)
C G C
C G C
G C G Leucine (Leu)
A U A
A U A
C G C Glycine (Gly)
C G C
T A U
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- DNA Protein Synthesis WorksheetDokument4 SeitenDNA Protein Synthesis WorksheetKate Nicole AndraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic AcidDokument6 SeitenNucleic AcidCherold RoldanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human β-globin Gene Sequence Reveals Sickle-Cell MutationDokument5 SeitenHuman β-globin Gene Sequence Reveals Sickle-Cell MutationB Riaz AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- FILE 20230308 111109 Tutor-Genetics-solutionDokument25 SeitenFILE 20230308 111109 Tutor-Genetics-solutionthuytrang21032004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDokument36 SeitenDeoxyribonucleic AcidAlex LlanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Codon AlphabetDokument2 SeitenDNA Codon AlphabetOmar ElhosaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 Genetic Code KESDokument19 SeitenLesson 2 Genetic Code KESMaliha RiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- B Globin Student HandoutDokument2 SeitenB Globin Student HandoutDr-Qussai ZuriegatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Label The The Diagram.: TranscriptionDokument4 SeitenLabel The The Diagram.: TranscriptionLeonard PolancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Translation and ModificationDokument49 SeitenTranslation and ModificationYasmin BalochNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and Translation Exercise VER2 SolutionDokument3 SeitenTranscription and Translation Exercise VER2 SolutionShanny McshannsNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCHS317 SU2.5 - Translation - FMDokument55 SeitenBCHS317 SU2.5 - Translation - FMKAGISO BRIAN MOTSHUPHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Kami Export - Protein Synthesis Worksheet-GOODDokument2 SeitenKami Export - Protein Synthesis Worksheet-GOODGlory RajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription-Translation Wksht1Dokument4 SeitenTranscription-Translation Wksht1Jap (Dham) JiracharnchaisiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- POGIL - Gene - Expression Translation SDokument8 SeitenPOGIL - Gene - Expression Translation Sandrew fortneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decode DNA clues to lab passwordsDokument2 SeitenDecode DNA clues to lab passwordsGela ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Gene Expression Translation SDokument6 Seiten15 Gene Expression Translation SHelp Me Study TutoringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic Acid SequenceDokument8 SeitenNucleic Acid SequenceMujahidul HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology VCE Unit 3, Chapter 3 TestDokument9 SeitenBiology VCE Unit 3, Chapter 3 Testnidhi patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Biology 1Dokument12 Seiten(Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Biology 1Melis ATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic Acid SequenceDokument8 SeitenNucleic Acid Sequencewatson191Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises Genetics USTH2022Dokument15 SeitenExercises Genetics USTH2022yungiang157Noch keine Bewertungen
- Genes UnfoldDokument7 SeitenGenes UnfoldJezTian ExplorerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDokument5 SeitenProtein Synthesis WorksheetCody AllenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharma Lec 2ADokument22 SeitenPharma Lec 2AQusay Al MaghayerhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signature Assignment 4 Central Dogma 1Dokument5 SeitenSignature Assignment 4 Central Dogma 1api-709276885Noch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Synthesis Codons & Amino AcidsDokument3 SeitenProtein Synthesis Codons & Amino AcidsDANICE LUNANoch keine Bewertungen
- Is Located On The Transfer RNA (tRNA) Shape at One End and Carries The Three Letter Code of The On The Other End Codon AnticodonDokument42 SeitenIs Located On The Transfer RNA (tRNA) Shape at One End and Carries The Three Letter Code of The On The Other End Codon AnticodonbkgirlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kami Export - Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Dokument6 SeitenKami Export - Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Camila Corvalan100% (5)
- Celll Reproduction and RegulationDokument17 SeitenCelll Reproduction and RegulationsachyjobNoch keine Bewertungen
- LECT-10: mRNA Processing, Genetic Code, and Protein SynthesisDokument30 SeitenLECT-10: mRNA Processing, Genetic Code, and Protein SynthesisNita SofianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and Translation PracticeDokument2 SeitenTranscription and Translation PracticeKajal VaghasiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The RNA Codons: Arlegui, Ronnel A. MTW-11:30AM-12:30PM Bsn-Ii-F Biochemistry LectureDokument4 SeitenThe RNA Codons: Arlegui, Ronnel A. MTW-11:30AM-12:30PM Bsn-Ii-F Biochemistry LecturePaul Orly FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Codon Chart: U C A G UDokument3 SeitenCodon Chart: U C A G UyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- signature assignment 4 central dogmaDokument6 Seitensignature assignment 4 central dogmaapi-631586093Noch keine Bewertungen
- mRNAcodonchart PDFDokument2 SeitenmRNAcodonchart PDFFerdinand Fremista JrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Dokument6 SeitenGene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Camila CorvalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription & Translation PracticeDokument2 SeitenTranscription & Translation PracticenkirsammerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central Dogma Review KEYDokument8 SeitenCentral Dogma Review KEYeula faith miracle andam0% (1)
- Central Dogma: DNA RNADokument42 SeitenCentral Dogma: DNA RNAGayu KjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet ExplainedDokument2 SeitenProtein Synthesis Worksheet ExplainedJuan Esteban Escandon AgudeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is The Science of Heredity. Heredity Is The Transmission of Genetic or Physical Traits From Parent To OffspringDokument81 SeitenIs The Science of Heredity. Heredity Is The Transmission of Genetic or Physical Traits From Parent To OffspringRanin, Manilac Melissa SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signature Assignment 4 Central DogmaDokument6 SeitenSignature Assignment 4 Central Dogmaapi-724481252Noch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix I: IA IUPAC Nucleotide Ambiguity CodesDokument2 SeitenAppendix I: IA IUPAC Nucleotide Ambiguity Codespeeps007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practicals in GeneticsDokument112 SeitenPracticals in GeneticscarlosaeserranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To GeneticsDokument43 SeitenAn Introduction To Geneticsrifatalib4u3504Noch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Synthesis Practice (Sidney Berjamin)Dokument3 SeitenProtein Synthesis Practice (Sidney Berjamin)sidney berjaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review TestDokument5 SeitenReview TestPoppy SmokeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Codon Bingo Game PDFDokument3 SeitenCodon Bingo Game PDFCody DarrenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 2 BioDokument2 SeitenActivity 2 BioTrafelgar DNoch keine Bewertungen
- BioCentralDogmaWorksheet 1Dokument3 SeitenBioCentralDogmaWorksheet 1jaelajeanine326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mutations ActivityDokument4 SeitenMutations ActivityJoe ByntineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konsep Dasar Biologi MolekulerDokument78 SeitenKonsep Dasar Biologi MolekulerpipitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konsep Dasar Biologi MolekulerDokument78 SeitenKonsep Dasar Biologi Molekulerpipit100% (1)
- Amino Acids & ProteinsDokument42 SeitenAmino Acids & ProteinsElla Mae MagbatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SASTA Topic 3 Test mk2 WriteDokument9 SeitenSASTA Topic 3 Test mk2 WriteAmber YipNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Molecular BiologyDokument7 SeitenAn Introduction To Molecular BiologyMaricon TubonNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Worksheet AnswersDokument2 SeitenDNA Worksheet AnswersJohnric Delacruz50% (2)
- Critical Survey of Stability Constants of EDTA Complexes: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Stability Constants of Metal ComplexesVon EverandCritical Survey of Stability Constants of EDTA Complexes: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Stability Constants of Metal ComplexesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci Fi Sep30Dokument1 SeiteSci Fi Sep30Ederlyn ZateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research ReviewerDokument4 SeitenResearch ReviewerEderlyn ZateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Distribution CurveDokument2 SeitenNormal Distribution CurveEderlyn ZateNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTD Pheno Study Student LeadershipDokument16 SeitenRTD Pheno Study Student LeadershipEderlyn ZateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module5 Act1-2Dokument2 SeitenModule5 Act1-2Ederlyn ZateNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Replication - Labeling: DNA Primase DNA LigaseDokument2 SeitenDNA Replication - Labeling: DNA Primase DNA LigaseEderlyn ZateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 16: Mass-to-Mass Stoichiometry ProblemsDokument4 SeitenModule 16: Mass-to-Mass Stoichiometry ProblemsEderlyn ZateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDokument2 SeitenProtein Synthesis WorksheetEderlyn Zate100% (1)
- Agricultural Biotechnology SyllabusDokument2 SeitenAgricultural Biotechnology SyllabusKamlesh SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Does Copper Not React With Nitrogen?: ChemistryDokument2 SeitenWhy Does Copper Not React With Nitrogen?: ChemistryDoaa NassarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis and Strain Differentiation of Avian Influenza Viruses by Restriction Fragment Mass AnalysisDokument7 SeitenDiagnosis and Strain Differentiation of Avian Influenza Viruses by Restriction Fragment Mass AnalysisLe Phuong NamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomolecules Crash Course NotesDokument22 SeitenBiomolecules Crash Course NotesAayush sainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Institute: Uips Department: PharmacyDokument19 SeitenInstitute: Uips Department: Pharmacydeepika bhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acids and Proteins - Lecture NotesDokument17 SeitenAmino Acids and Proteins - Lecture NotesAyukafangha EtandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actin Structure and FunctionDokument20 SeitenActin Structure and FunctionMonoj BaruahNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHP 1 - Basic Elements in LifeDokument14 SeitenCHP 1 - Basic Elements in LifeShaaru TharshiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology ch9-02 PPT LectureDokument33 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology ch9-02 PPT LectureFaith PhelpsNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSC (P) 18 Sem.I III V PDFDokument9 SeitenBSC (P) 18 Sem.I III V PDFHarshit KaluchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2&3 - Action Potential and Resting MembraneDokument28 Seiten2&3 - Action Potential and Resting MembraneTejesswinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Autophagy in CancerDokument7 SeitenThe Role of Autophagy in CancerAlexander VigenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell FoldableDokument2 SeitenCell Foldableapi-310503032Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Revision Tutorial Core Topic 2 and 4 AnsDokument35 Seiten2015 Revision Tutorial Core Topic 2 and 4 AnsliveaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAFTAR PERSEDIAAN OPD RSUD Prof. DR. H.M Chatib QuzwainDokument171 SeitenDAFTAR PERSEDIAAN OPD RSUD Prof. DR. H.M Chatib QuzwainTrisia Mayang SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 PlasmidsDokument17 Seiten10 Plasmidsparduman kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimation & Extraction of DNADokument5 SeitenEstimation & Extraction of DNAR .K.BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module in TicsDokument20 SeitenModule in TicsEmyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pymol Commands GatesDokument8 SeitenPymol Commands GatesSandeep KaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles NotesDokument17 SeitenCell Organelles Notesava zNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioradiations: High-Resolution Melt AnalysisDokument36 SeitenBioradiations: High-Resolution Melt AnalysisDr-Dalya ShakirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Enzymology 1Dokument29 SeitenClinical Enzymology 1reuben kwotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biological Revolution: Periodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences Vol. 3 No. 1 (2015) Available Online atDokument2 SeitenThe Biological Revolution: Periodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences Vol. 3 No. 1 (2015) Available Online atAngel TaylorNoch keine Bewertungen
- DMD 106 010793 PDFDokument6 SeitenDMD 106 010793 PDFTetteh JudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macromolecules Extension ActivityDokument4 SeitenMacromolecules Extension Activityapi-375285021Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mitochondrial DysfunctionDokument3 SeitenMitochondrial Dysfunctiontilaran1100% (1)
- Nucleic Acid Metabolism PDFDokument29 SeitenNucleic Acid Metabolism PDFtrinitysugumar100% (1)
- 2012 JuneDokument198 Seiten2012 JunealiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatty Acid MetabolismDokument28 SeitenFatty Acid MetabolismMitchelle SaurambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fmicb 12 751571Dokument13 SeitenFmicb 12 751571Tron TronNoch keine Bewertungen