Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Appendix Eb - Steel Reinforced Elastic Bearings: Dimensions
Hochgeladen von
Sudip ShresthaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Appendix Eb - Steel Reinforced Elastic Bearings: Dimensions
Hochgeladen von
Sudip ShresthaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
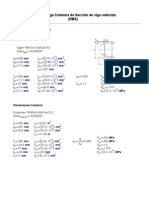
Appendix EB
Bridge Design Manual - 2002 Steel Reinforced Elastic Bearings Design
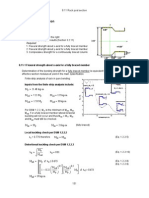
APPENDIX EB - STEEL REINFORCED ELASTIC BEARINGS
Dimensions:
L := 350 ⋅mm length of a rectangular elastomeric bearing (parallel to longitudinal bridge axis)
W := 500 ⋅mm width of the bearing in the transverse direction
hr := 11 ⋅mm thickness of thickest elastomeric layer in elastoneric bearing
hs := 4 ⋅mm thickness of the steel reinforcement
hrt := 99 ⋅mm total elastomeric thickness
n := 6 number of interior layers of elastomer
shape factor for the thickest elastomeric layer: (for rectangular bearings without holes)
L ⋅W
S :=
2 ⋅hr ⋅( L + W) S = 9.36 /1/ 6.2.5.1-1 /4/ 14.7.5.1-1
(8.5)
Material Properties:
G := 1.2 ⋅MPa shear modulus of the elastomer
Fy := 500 ⋅MPa yield strength of steel reinforcement
f´c := 20 ⋅MPa concrete compressiv strength
Loads and rotations:
VS := 1900 ⋅kN maximum total vertical load at the service limit state
VL := 1000 ⋅kN maximum live vertical load at the service limit state
HS := 160 ⋅kN maximum total horisontal load at the service limit state
VS.min := 900 ⋅kN minimum total vertical load at the service limit state
∆ s := 45 ⋅mm maximum shear deformation of the elastomer at the service limit state
θ s := 0.005 ⋅rad rotation about any axis of the pad
Γ := L length of pad if rotation is about its transverse axis, or width of
pad if rotation is about its longitudinal axis
The calculations are based on:
BRIDGE DESIGN MANUAL, VOL I /1/
BRIDGE DESIGN MANUAL, VOL II /2/
BRIDGE DESIGN MANUAL, VOL III /3/
AASHTTO /4/
Ethiopian Roads Authority Page EB-1
Appendix EB
Steel Reinforced Elastic Bearings Design Bridge Design Manual - 2002
Design requirements
Compressive Stress
average compressive stress due to the total load:
σ S := 1.66 ⋅G ⋅S σ S = 18.6 MPa /1/ 6.2.5.3-1 /4/ 14.7.5.3.2-1
(8.7)
σ S := σ S if σ S < 11 ⋅MPa
σ S = 11 MPa
11 ⋅MPa otherwise
VS
σ Sd := σ Sd = 10.9 MPa
L⋅W
condition:= "OK!" if σ Sd ≤ σ S
"No!" otherwise
condition = "OK!"
average compressive stress due to live load:
σ L := 0.66 ⋅G ⋅S σ L = 7.4 MPa /1/ 6.2.5.3-2 /4/ 14.7.5.3.2-2
(8.8)
VL
σ Ld := σ Ld = 5.71 MPa
L⋅W
condition:= "OK!" if σ Ld ≤ σ L
"No!" otherwise
condition = "OK!"
Compressive deflection
VS − VL
σ := σ = 5.143 MPa
L⋅W
ε := 4.3 ⋅% /1/ Fig C 6.2.5.4-1
Figure 8-4
δ := ε ⋅hr ⋅n δ = 2.8 mm (8.11)
/1/ 6.2.5.4-1 /4/ 14.7.5.3.3-1
condition:= "OK!" if δ ≤ 3 ⋅mm
"No!" otherwise condition = "OK!"
Shear Deformation
the bearing shold satisfy: 2 ⋅∆ s ≤ hrt /1/ 6.2.5.5-1 /4/ 14.7.5.3.4-1
(8.12)
hrt = 99 mm
2 ⋅∆ s = 90 mm
condition:= "OK!" if 2 ⋅∆ s ≤ hrt
Page EB-2 Ethiopian Roads Authority
Appendix EB
Steel Reinforced Elastic Bearings Design Bridge Design Manual - 2002
Combined Compression and Rotation
Rectangular bearings may be taken to satisfy uplift requirements if they satisfy:
§ θs · § Γ · 2
σ S := 1.0 ⋅G ⋅S ⋅¨ ¸ ⋅¨ ¸ σ S = 9.5 MPa /4/ 14.7.5.3.5-1 (8.13)
© n ¹ © hr ¹
VS
σ Sd :=
L⋅W σ Sd = 10.9 MPa
condition:= "OK!" if σ Sd > σ S
"No!" otherwise condition = "OK!"
Rectangular bearings subjected to shear should also satisfy:
ª § θ s · § Γ · 2º
σ S := 1.875 ⋅G ⋅S ⋅« 1 − 0.20 ⋅¨ ¸ ⋅¨ ¸ » σ S = 17.5 MPa /1/ 6.2.5.6-1 /4/ 14.7.5.3.5-2
(8.14)
¬ © n ¹ © hr ¹ ¼
VS
σ Sd :=
L⋅W σ Sd = 10.9 MPa
condition:= "OK!" if σ Sd < σ S
"No!" otherwise condition = "OK!"
Stability of Elastomeric Bearings
Define:
hrt
1.92 ⋅
L
A := A = 0.037 /1/ 6.2.5.7-2 /4/ 14.7.5.3.6-3
(8.16)
2.0 ⋅L
S⋅ 1 +
W
2.67
B := B = 0.0214 /1/ 6.2.5.7-3 /4/ 14.7.5.3.6-4
(8.17)
§
S ⋅( S + 2.0) ⋅¨ 1 +
L ·
¸
© 4.0 ⋅W ¹
If the bridge deck is free to translate horisontally:
G
σ S := σ S = 22.4 MPa /1/ 6.2.5.7-2 /4/ 14.7.5.3.6-1
(8.18)
2A − B
VS
σ Sd := σ Sd = 10.9 MPa
L⋅W
condition:= "OK!" if σ Sd ≤ σ S
"No!" otherwise condition = "OK!"
Page EB-3 Ethiopian Roads Authority
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Appendix Eb - Steel Reinforced Elastic Bearings: DimensionsDokument3 SeitenAppendix Eb - Steel Reinforced Elastic Bearings: Dimensionstonying86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix Eb - Steel Reinforced Elastic Bearings: DimensionsDokument3 SeitenAppendix Eb - Steel Reinforced Elastic Bearings: DimensionsHundeejireenyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Equations For FRP - Strengthening of Columns: by G. Monti and S. AlessandriDokument18 SeitenDesign Equations For FRP - Strengthening of Columns: by G. Monti and S. Alessandrivlad lupasteanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 06-Chapter 6 Slope StabilityDokument114 SeitenLesson 06-Chapter 6 Slope StabilityHussam EzzatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing DesignDokument16 SeitenBearing DesignOmar NajmNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Buckling of Columns - 04-08-23Dokument5 Seiten1 - Buckling of Columns - 04-08-23greenlava2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anchorage Length CalculationDokument6 SeitenAnchorage Length Calculationranjit.bhambotarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary CH 7Dokument6 SeitenSummary CH 7lode89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Piles Capacity Ref Man 140726Dokument16 SeitenPiles Capacity Ref Man 140726Dedy KristiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stairway 1Dokument10 SeitenStairway 1Anissah ManialaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic2 FatigueDokument36 SeitenTopic2 Fatigue777894292Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8 11 Rack StrengthDokument5 Seiten8 11 Rack StrengthDiego PovedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- R55 09 02 R55 Annex6 Drawbars 20141114-2Dokument4 SeitenR55 09 02 R55 Annex6 Drawbars 20141114-2Carlos AmorimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Characteristics NotesDokument14 SeitenMaterial Characteristics NotesIlyas H. AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSA A23.3 DeflectionsDokument11 SeitenCSA A23.3 Deflections700spymaster007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Fluctuating LoadDokument30 SeitenUnit 2 Fluctuating Loadaditya.1540011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes04 Static Load JBs 10Dokument21 SeitenNotes04 Static Load JBs 10MuhammadAbdulRasoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample - Roof Purlin, Continuous SpanDokument3 SeitenSample - Roof Purlin, Continuous SpanVance KangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 23 Shaft and Its Design Based On StrengthDokument9 Seiten23 Shaft and Its Design Based On StrengthPRASAD326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tubular Truss ExampleDokument12 SeitenTubular Truss ExampleMock Khang Hi100% (1)
- Deflection1 Bhatt BookDokument10 SeitenDeflection1 Bhatt BookthirumalaichettiarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 286 8 Deflection of Hull StructuresDokument11 Seiten286 8 Deflection of Hull StructuresJuan SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course C-2020 Steel Beam Design by ASD/LRFD Steel Construction ManualDokument20 SeitenCourse C-2020 Steel Beam Design by ASD/LRFD Steel Construction ManualChitra DeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 PDFDokument5 SeitenChapter 5 PDFWendimu TolessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gear StressDokument12 SeitenGear StressPrithviraj Daga100% (1)
- FootingsDokument9 SeitenFootingsRiza May SalutanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.-Planilla Rbs w24x76 - w14x211 A250espDokument14 Seiten1.-Planilla Rbs w24x76 - w14x211 A250espGabriel Contreras AlfaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-1 Low Cycle Fatigue - High Cycle Fatigue - BDokument9 Seiten4-1 Low Cycle Fatigue - High Cycle Fatigue - BkandeabigaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Method For Lateral and Lateral Torsional Buckling of Structural Components in Eurocode 3Dokument12 SeitenGeneral Method For Lateral and Lateral Torsional Buckling of Structural Components in Eurocode 3VivaCharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Component DesignDokument32 SeitenComponent Designdaniel hambissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Beam DesignDokument26 SeitenSteel Beam DesignWazini D. Izani100% (1)
- Two-Phase Flow Pressure DropDokument4 SeitenTwo-Phase Flow Pressure DropStevenMvuyana100% (1)
- Abutment Design ExampleDokument56 SeitenAbutment Design Examplezrilek1Noch keine Bewertungen
- SHEARCONNECTION7Dokument21 SeitenSHEARCONNECTION7Pyae PyaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 5. Beam Analysis and Design PDFDokument61 SeitenChap 5. Beam Analysis and Design PDFRafael Joshua LedesmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter J Design of ConnectionsDokument16 SeitenChapter J Design of Connectionsghosh73Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2.1 Loads Evaluation: Thermal Coefficient C 1Dokument19 Seiten3.2.1 Loads Evaluation: Thermal Coefficient C 1DragosPatrascuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ps1 SolutionsDokument4 Seitenps1 Solutionshakdogera123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Moment of ResistanceDokument10 SeitenMoment of ResistanceBabaYakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Design Method ADokument4 SeitenBearing Design Method ADhurai KesavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Balanced Cantilever BridgeDokument32 SeitenDesign of Balanced Cantilever BridgeMorsed Al MamunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Fluid Mechanics 10th Edition Elger Solutions ManualDokument79 SeitenEngineering Fluid Mechanics 10th Edition Elger Solutions ManualDanielThomasxjfoq100% (21)
- Tutorial Questions and Answers - 2011Dokument10 SeitenTutorial Questions and Answers - 2011Jan ScarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serviceability Ex.1 (9-21-2020)Dokument4 SeitenServiceability Ex.1 (9-21-2020)Michelle DangcalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.1 Introduction To Column Buckling: No Failure Implied!!!Dokument14 Seiten12.1 Introduction To Column Buckling: No Failure Implied!!!delu19980809809809Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal StressDokument25 SeitenThermal StressFaiZul IshAkNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABC If Ogf - RCCD - BUILDING - ELEMENTSDokument53 SeitenABC If Ogf - RCCD - BUILDING - ELEMENTSVikash AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 FoundationsDokument30 SeitenLecture 5 FoundationsCarel De JagerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fracture: KL Murty MSE 450Dokument9 SeitenFracture: KL Murty MSE 450azizieh5701Noch keine Bewertungen
- Box Girder Design CraneDokument8 SeitenBox Girder Design CraneSomi Khan100% (2)
- 4a - CRITICAL STATE OF SOIL MECHANICS Light BKGRD Black Fonts-27092020Dokument59 Seiten4a - CRITICAL STATE OF SOIL MECHANICS Light BKGRD Black Fonts-27092020rihongkeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesVon Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue of Textile and Short Fiber Reinforced CompositesVon EverandFatigue of Textile and Short Fiber Reinforced CompositesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials: Theory and ExamplesVon EverandStrength of Materials: Theory and ExamplesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (14)
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsVon EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex-1: Foundation Design: Footing D E S I G N Rea C Ti o N SDokument21 SeitenAnnex-1: Foundation Design: Footing D E S I G N Rea C Ti o N SSudip ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Mode Period UX UY UZ Sum UX Sum UY Sum UZ SecDokument4 SeitenCase Mode Period UX UY UZ Sum UX Sum UY Sum UZ SecSudip ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tamang: SAFE Analysis & Design ReportDokument52 SeitenTamang: SAFE Analysis & Design ReportSudip ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRIDGE Resource Guide: American Wood Council Lusas StructurepointDokument1 SeiteBRIDGE Resource Guide: American Wood Council Lusas StructurepointSudip ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometrical Properties Material Properties: Design of Saw Tooth/Slabless StairDokument4 SeitenGeometrical Properties Material Properties: Design of Saw Tooth/Slabless StairSudip ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix MBDokument37 SeitenAppendix MBSudip ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix GB - 16.6m C/C SPAN & 7.32m CLEAR BRIDGE WIDTH R.C.D.Girder Superstructure Design by LRFD MethodDokument28 SeitenAppendix GB - 16.6m C/C SPAN & 7.32m CLEAR BRIDGE WIDTH R.C.D.Girder Superstructure Design by LRFD MethodSudip ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AKJ-LSD 2000-20mDokument14 SeitenAKJ-LSD 2000-20mSudip ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AASHTO BEAMS Standard DimentionsDokument16 SeitenAASHTO BEAMS Standard Dimentionsjedidestroyer100% (1)
- Pci Bridge Design ManualDokument9 SeitenPci Bridge Design ManualSudip ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kathmandu University Design of Column Section Designed By:: Er. Sudip ShresthaDokument9 SeitenKathmandu University Design of Column Section Designed By:: Er. Sudip ShresthaSudip ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 6Dokument133 SeitenSection 6ILAYAPERUMAL K100% (2)
- Casting DefectsDokument2 SeitenCasting DefectskoushikraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSC Materials Science Nanotechnology Syllabus MSU BarodaDokument12 SeitenMSC Materials Science Nanotechnology Syllabus MSU BarodaSoumalyaBhowmikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aisc Bracing Connections 01 PDFDokument69 SeitenAisc Bracing Connections 01 PDFPatrick PolujanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S0079670013001196 Main PDFDokument77 Seiten1 s2.0 S0079670013001196 Main PDFDivyaratanKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Fracture MechanicsDokument63 SeitenIntroduction To Fracture MechanicsSaAhRaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modelling of Bolted Connections by The Finite Element Method: September 2017Dokument16 SeitenModelling of Bolted Connections by The Finite Element Method: September 2017jhonatan romero castilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Designing Elastomeric Vibration IsolatorsDokument26 SeitenIntroduction To Designing Elastomeric Vibration IsolatorsDurukan Burak DilekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexural MembersDokument20 SeitenFlexural MembersLimelrac Santos100% (1)
- Extrusion Die Swell Simulation of Tire Tread Compound Using Viscoelastic Equation of Phan Thien & Tanner (PTT Model)Dokument7 SeitenExtrusion Die Swell Simulation of Tire Tread Compound Using Viscoelastic Equation of Phan Thien & Tanner (PTT Model)Ashutosh Kudale100% (1)
- DCS - Design of Beams - Lect2Dokument15 SeitenDCS - Design of Beams - Lect2Saket ThakkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jawaban Soal No 2. MacromekanikDokument7 SeitenJawaban Soal No 2. MacromekanikHASAN FUADI1006808166100% (1)
- Behaviour of Aluminium Structures in Fire - A ReviDokument7 SeitenBehaviour of Aluminium Structures in Fire - A RevitamaranmNoch keine Bewertungen
- In The Name of Allah The Most Gracious The Most MercifulDokument26 SeitenIn The Name of Allah The Most Gracious The Most MercifulSalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogels and Its Applications: Damanhour University Faculty of PharmacyDokument7 SeitenHydrogels and Its Applications: Damanhour University Faculty of Pharmacyزياد محمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hilti Corrosion-Handbook EN PDFDokument48 SeitenHilti Corrosion-Handbook EN PDFElenildo BarrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThermoplasticsDokument3 SeitenThermoplasticsMadhuShakthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plate INDIA CODEDokument4 SeitenBase Plate INDIA CODEbama sankari100% (1)
- Closed-Form SolutionsDokument13 SeitenClosed-Form SolutionsBza ZaBugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction and Building Materials: Tomasz ZdebDokument9 SeitenConstruction and Building Materials: Tomasz ZdebYosua DitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enderby 1990Dokument96 SeitenEnderby 1990Fadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bernt - EC3 1 5Dokument44 SeitenBernt - EC3 1 5Rosario BlancaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Japanese Codes - Steel Design Per 2005 AIJ: 12B.2 Member CapacitiesDokument4 SeitenJapanese Codes - Steel Design Per 2005 AIJ: 12B.2 Member Capacitiesmarkyboy23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Table 5.1. Nominal Strength Per Unit Area of BoltsDokument1 SeiteTable 5.1. Nominal Strength Per Unit Area of BoltsNwe OoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temper Embittlement CalculationDokument3 SeitenTemper Embittlement CalculationVasu RajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Structure Factor The Structure Factor: Suggested ReadingDokument28 SeitenThe Structure Factor The Structure Factor: Suggested ReadingShubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS 7910Dokument12 SeitenBS 7910ggsachary0% (1)
- Definition of The Quasi Fermi EnergyDokument3 SeitenDefinition of The Quasi Fermi EnergyFlor EsperanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm c1161 13Dokument19 SeitenAstm c1161 13Taiana BonadioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Statement: Fluid CepDokument6 SeitenProblem Statement: Fluid CepMuneer AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen