Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
MTA OD 366 External
Hochgeladen von
Slime ManOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MTA OD 366 External
Hochgeladen von
Slime ManCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
98-‐366
Networking
Fundamentals
Target
Audience
Candidates
for
this
exam
are
seeking
to
prove
fundamental
networking
knowledge
and
skills.
Before
taking
this
exam,
candidates
should
have
a
solid
foundational
knowledge
of
the
topics
outlined
in
this
preparation
guide.
It
is
recommended
that
candidates
become
familiar
with
the
concepts
and
the
technologies
described
here
by
taking
relevant
training
courses.
Candidates
are
expected
to
have
some
hands-‐on
experience
with
Windows
Server,
Windows
based
networking,
network
management
tools,
DNS,
TCP/IP,
names
resolution
process,
and
network
protocols
and
topologies.
Objective
Domain
1. Understanding
Network
Infrastructures
1.1. Understand
the
concepts
of
the
Internet,
intranet,
and
extranet.
This
objective
may
include
but
is
not
limited
to:
VPN,
security
zones,
firewalls
1.2. Understand
local
area
networks
(LANs).
This
objective
may
include
but
is
not
limited
to:
perimeter
networks;
addressing;
reserved
address
ranges
for
local
use
(including
local
loopback
ip),
VLANs;
wired
LAN
and
wireless
LAN
1.3. Understand
wide
area
networks
(WANs).
This
objective
may
include
but
is
not
limited
to:
leased
lines,
dial-‐up,
ISDN,
VPN,
T1,
T3,
E1,
E3,
DSL,
and
cable
and
their
characteristics
(speed,
availability)
1.4. Understand
wireless
networking.
This
objective
may
include
but
is
not
limited
to:
types
of
wireless
networking
standards
and
their
characteristics
(802.11A,
B,
G,
N
including
different
Ghz
ranges),
types
of
network
security
(for
example,
WPA/WEP/802.1X
),
point-‐to-‐point
(P2P)
wireless,
wireless
bridging
1.5. Understand
network
topologies
and
access
methods.
This
objective
may
include
but
is
not
limited
to:
star,
mesh,
ring
2. Understanding Network Hardware
2.1. Understand switches.
This objective may include but is not limited to: transmission speed; number and type of
ports; number of uplinks; speed of uplinks; managed or unmanaged switches; VLAN
capabilities; Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches, security options; hardware redundancy; support;
backplane speed; switching types, MAC table; understanding capabilities of hubs vs. switches
2.2. Understand routers.
This objective may include but is not limited to: transmission speed considerations, directly
connected routes, static routing, dynamic routing (routing protocols), default routes; routing
table and how it selects best routes; routing table memory, NAT, software routing in
Windows Server
2.3. Understand media types.
This objective may include but is not limited to: cable types and their characteristics,
including media segment length and speed; fibre optic; twisted pair shielded or non-‐shielded;
cabling, wireless; susceptibility to external interference (for example, machinery, power
cables); susceptibility to electricity (for example, lightning), susceptibility to interception
3. Understanding Protocols and Services
3.1. Understand the OSI model.
This objective may include but is not limited to: OSI model; TCP model; examples of devices,
protocols, and applications and which OSI/TCP layer they belong to; TCP and UDP; well-‐
known ports for most-‐used purposes (not necessarily Internet); packets and frames
3.2. Understand IPv4.
This objective may include but is not limited to: addressing, subnetting; NAT, static IP,
gateway; APIPA; network classes, classful/classless IP addressing;; reserved address ranges
for local use (including local loopback ip)
3.3. Understand IPv6.
This objective may include but is not limited to: subnetting; IPconfig; why use IPv6;
addressing; ipv4toipv6 tunneling protocols to ensure backwards compatibility; dual ip stack;
subnetmask; gateway; ports; packets; reserved address ranges for local use (including local
loopback ip)
3.4. Understand names resolution.
This objective may include but is not limited to: DNS, WINS, steps in the name resolution
process
3.5. Understand networking services.
This objective may include but is not limited to: DHCP, IPsec, remote access
3.6. Understand TCP/IP.
This objective may include but is not limited to: tools such as ping; tracert; pathping; Telnet;
IPconfig; netstat, reserved address ranges for local use (including local loopback ip); protocols
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Computer Networking Bootcamp: Routing, Switching And TroubleshootingVon EverandComputer Networking Bootcamp: Routing, Switching And TroubleshootingNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTA OD 366 ExternalDokument2 SeitenMTA OD 366 ExternalSlime ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTA OD 366 ExternalDokument2 SeitenMTA OD 366 ExternalSlime ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- 98-366 Networking Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDokument2 Seiten98-366 Networking Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredAlex PascuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTA: Networking Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDokument3 SeitenMTA: Networking Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredLuis Jesús Onsihuay AlbertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audience Description: 98-366: Networking FundamentalsDokument3 SeitenAudience Description: 98-366: Networking Fundamentalsraj kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCST+Networking+Objective+Domain Cisco Final wCiscoLogoDokument3 SeitenCCST+Networking+Objective+Domain Cisco Final wCiscoLogoYomeroGteitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CompTIA Network Plus Training Kit Exam N10-005Dokument704 SeitenCompTIA Network Plus Training Kit Exam N10-005bibivee50% (2)
- n10 005 PDFDokument704 Seitenn10 005 PDFPazNoch keine Bewertungen
- LabSIM Network+ Guide To Networks 5th - 6thDokument2 SeitenLabSIM Network+ Guide To Networks 5th - 6thCynthia Indah FebriyantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITS OD 101 NetworkingDokument2 SeitenITS OD 101 NetworkingMarsha SuperioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cse303 Computer-Networks TH 1.10 Sc04Dokument1 SeiteCse303 Computer-Networks TH 1.10 Sc04netgalaxy2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Document Cse 312Dokument74 SeitenLab Document Cse 312RAKIB UDDIN CHOWDHURY 1804107Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network and Data Communication Web BasisDokument9 SeitenNetwork and Data Communication Web BasisJearvi EvidorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring The Network: Principles of NetworkingDokument70 SeitenExploring The Network: Principles of NetworkingMutmainnah ZailanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDU CC 70405 ch04 - TakeawayDokument15 SeitenEDU CC 70405 ch04 - TakeawayMES BetiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sol10 Net CX 310 302Dokument2 SeitenSol10 Net CX 310 302manas199Noch keine Bewertungen
- Networking 1 TutorialDokument12 SeitenNetworking 1 TutorialSocaciu VioricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Plan (CSC305 - CN Theory)Dokument2 SeitenLecture Plan (CSC305 - CN Theory)cokope9857Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network SecurityDokument15 SeitenNetwork Securityegalakshman124Noch keine Bewertungen
- TDC 562:computer Network Design & Analysis (Internet Engineering)Dokument10 SeitenTDC 562:computer Network Design & Analysis (Internet Engineering)serenus_hawkNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Crash Course in NetworkingDokument12 SeitenA Crash Course in NetworkingVikram Raj SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Technologies: Nitin BirariDokument55 SeitenMobile Technologies: Nitin BirarinsbirariNoch keine Bewertungen
- DataComms Group 7 Assignment2020Dokument7 SeitenDataComms Group 7 Assignment2020Prince MavhuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Name: Huawei LTE Network Design and Dimensioning PlanningDokument2 SeitenCourse Name: Huawei LTE Network Design and Dimensioning PlanningGauravSwamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE Network DesignDokument2 SeitenLTE Network DesignGauravSwamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comp 327035225Dokument4 SeitenComp 327035225amritpalmrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking Fundamentals: Course DescriptionDokument4 SeitenNetworking Fundamentals: Course DescriptionWahyu OhNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHRMLDokument17 SeitenCHRMLjeffaidanterante346Noch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT Code: BIT 2116 UNIT NAME: Network Design and ManagementDokument13 SeitenUNIT Code: BIT 2116 UNIT NAME: Network Design and ManagementJohn KihiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telecommunications & Network Security Domain - : Cissp Common Body of Knowledge ReviewDokument100 SeitenTelecommunications & Network Security Domain - : Cissp Common Body of Knowledge ReviewmodoundNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Network Fundamentals - EngineeringDokument98 SeitenComputer Network Fundamentals - Engineeringc pardha krishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
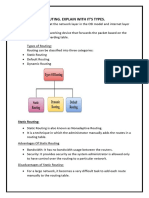
- What Is Routing. Explain With It'S TypesDokument9 SeitenWhat Is Routing. Explain With It'S TypesChaitra kharviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Security: CIS 739, Computer Security Prof. S. Dexter José R. Cordones 12/11/2006Dokument31 SeitenNetwork Security: CIS 739, Computer Security Prof. S. Dexter José R. Cordones 12/11/2006Abhishek VaishNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Introduction To Networks: The Open Systems Interconnection SpecificationsDokument12 Seiten1-Introduction To Networks: The Open Systems Interconnection Specificationsfatemeh sameniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Awsn Question Bank - 2017 RegulationDokument27 SeitenAwsn Question Bank - 2017 Regulation19021Dhanush raj.NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Must Have IP NextGen Network ReferenceDokument57 SeitenMust Have IP NextGen Network ReferenceTower_Doc0% (1)
- Computer-Network-Cheetsheet 2Dokument18 SeitenComputer-Network-Cheetsheet 2Nguyễn Ngọc PhụngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument16 SeitenAssignment 1goosam9992Noch keine Bewertungen
- SW 3/22/2010 CCNA3 Chap 7 Study Answers 1Dokument6 SeitenSW 3/22/2010 CCNA3 Chap 7 Study Answers 1Hien TauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2: Networking: Unit Code H/615/1619 Unit Type Core Unit Level 4 Credit Value 15Dokument6 SeitenUnit 2: Networking: Unit Code H/615/1619 Unit Type Core Unit Level 4 Credit Value 15Thandar LwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bitszc 481Dokument3 SeitenBitszc 481rvtymcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC Domain4Dokument67 SeitenCC Domain4sasijo9863Noch keine Bewertungen
- Networking Basic TopicsDokument5 SeitenNetworking Basic TopicsJSON AMARGANoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit2 NetworkingDokument8 SeitenUnit2 Networkingr.elmasri2Noch keine Bewertungen
- CN Module 3 Network Layer 2024Dokument148 SeitenCN Module 3 Network Layer 2024skjskjskj333Noch keine Bewertungen
- DPtech FW1000 Firewall Technical White PaperDokument16 SeitenDPtech FW1000 Firewall Technical White PaperNiran MaharjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- InterviewDokument27 SeitenInterviewJomelyne MangarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- VacancyDokument52 SeitenVacancySantosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Hoang Van HiepDokument22 SeitenAssignment Hoang Van Hiephai hoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- WN Question - AnswerDokument15 SeitenWN Question - AnswerManimegalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSC3002 Computer-Networks ETH 1 AC37Dokument3 SeitenCSC3002 Computer-Networks ETH 1 AC37;(Noch keine Bewertungen
- Networking AssignmentDokument80 SeitenNetworking AssignmentSimon NdongaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viva Questions Ec8563Dokument6 SeitenViva Questions Ec8563iyyanarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1-Modified-Introduction For Wireless NetworksDokument48 SeitenLec 1-Modified-Introduction For Wireless NetworksnawafNoch keine Bewertungen
- 201980090184+computer Network Final AssignmentDokument10 Seiten201980090184+computer Network Final AssignmentMd. Ziaul Haque ShiponNoch keine Bewertungen
- PART (1) : Assignment Brief and Guidance: (Scenario)Dokument15 SeitenPART (1) : Assignment Brief and Guidance: (Scenario)Minh Tuấn NgôNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 - Wireless and Mobile Computing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDokument10 SeitenUnit 4 - Wireless and Mobile Computing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inSana SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9066Dokument5 Seiten9066Aryan JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOKIA CounterDokument5 SeitenNOKIA Counterroni0% (2)
- JARVISDokument5 SeitenJARVISMuhammad AmmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- QlikView 11 Security - Authentication and AuthorizationDokument30 SeitenQlikView 11 Security - Authentication and AuthorizationDivya RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- WP DGAs in The Hands of Cyber CriminalsDokument6 SeitenWP DGAs in The Hands of Cyber CriminalsPatrick Edward PenetranteNoch keine Bewertungen
- SmartStruxure Solution - Devices and Communication BLDPRDE0234004Dokument12 SeitenSmartStruxure Solution - Devices and Communication BLDPRDE0234004FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FGT1 06 IPSec VPN PDFDokument12 SeitenFGT1 06 IPSec VPN PDFScott RushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexi WCDMA BTS - IntroductionDokument28 SeitenFlexi WCDMA BTS - Introductionhvalvassori100% (1)
- MSC Alcatel 7270 MSCDokument4 SeitenMSC Alcatel 7270 MSCzoquetacosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide For Beginners and IntermediatesDokument98 SeitenCisco CCNA Command Guide For Beginners and IntermediatesDenisNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Create A Ubuntu 12.04 x64 LTSP Server With 32bit Thin Clients - How To - The Fan Club - Dynamic Design SolutionsDokument14 SeitenHow To Create A Ubuntu 12.04 x64 LTSP Server With 32bit Thin Clients - How To - The Fan Club - Dynamic Design SolutionsKostas TrikalisNoch keine Bewertungen
- VoLTE One Pager Accessibility CounterBased V3 PDFDokument1 SeiteVoLTE One Pager Accessibility CounterBased V3 PDFshashi40410Noch keine Bewertungen
- Door Access & Time Attendance SystemDokument2 SeitenDoor Access & Time Attendance SystemPolycarp Danson SigaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DninebDokument2 SeitenDninebMouad TribakNoch keine Bewertungen
- HuaweiDokument4 SeitenHuaweiAdrian LugueNoch keine Bewertungen
- GarrettCom Product Selection Guide PDFDokument164 SeitenGarrettCom Product Selection Guide PDFJyotsna K. PantulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Recreate Clubusy NSFDokument2 SeitenHow To Recreate Clubusy NSFbkiran633Noch keine Bewertungen
- LeanIX - Poster - Best Practices To Define Technology StacksDokument1 SeiteLeanIX - Poster - Best Practices To Define Technology StacksPaul Vintimilla CarrascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 005 Business Continuity DR EDMDokument35 Seiten005 Business Continuity DR EDMsakthimurugan_sezhiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voip 2 GSMDokument46 SeitenVoip 2 GSMmotaz_omar9651Noch keine Bewertungen
- SVC and V7000 Command Line Interface Users Guide PDFDokument648 SeitenSVC and V7000 Command Line Interface Users Guide PDFPanzo Vézua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 IC3 Computing FundamentalsDokument4 Seiten3 IC3 Computing FundamentalsMuhammad KazimNoch keine Bewertungen
- CISA Mobile APP QuestionsDokument3 SeitenCISA Mobile APP QuestionsrushicNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Energy InfrastructureDokument32 Seiten6 Energy InfrastructuremeraatNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTP Audio and Video For The InternetDokument208 SeitenRTP Audio and Video For The InternetpvsairamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ict 403 ExamDokument3 SeitenIct 403 Examapi-313517608Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1769-AENTR FAQsDokument5 Seiten1769-AENTR FAQsCris JavichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge ICT Year 8 Topic 1 SlidesDokument19 SeitenCambridge ICT Year 8 Topic 1 SlidesIce SyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- F5 Good Better Best Licensing OverviewDokument2 SeitenF5 Good Better Best Licensing OverviewAhmad ShaugiNoch keine Bewertungen
- WI FI VikramDokument13 SeitenWI FI VikramSyed NaseerNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Make Successful Wifi 6 PocDokument24 SeitenHow To Make Successful Wifi 6 PocYasmine BoudhinaNoch keine Bewertungen