Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
KEM MAD Sample Exam (Chem 17, 3rd LE)
Hochgeladen von
Nyka C.Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
KEM MAD Sample Exam (Chem 17, 3rd LE)
Hochgeladen von
Nyka C.Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chemistry 17 (Third Long Exam)
I. Modified True or False: Read the following statements carefully, and then write TRUE if the statement is
true. Otherwise, change the underlined word to make the statement true.
1. Zn can be substituted by Mg as an oxidizing agent in Experiment # 14 (Selected Redox Reactions).
2. A certain voltage is applied in an electrolytic cell to make a non-spontaneous reaction spontaneous.
3. A yellow precipitate, Zn3[Fe(CN)2], is produced if K4Fe(CN)6 is added to a Zn2+ solution.
4. The charge of Co in the complex [CoCl(NO2)(NH3)4]+ is +4.
5. The cell reaction of a primary battery can be reversed by passing electricity through the battery.
6. Cr3+ interferes with the formation of the red lake in the prescence of NH4OAc and aluminon reagent.
7. The coordination number of Pt(en)2I2C2O4 is 4.
8. Electrons flow from anode to cathode in an electrolytic cell.
9. NH4+ is the only cation that did not form a precipitate with 3.0 M NaOH.
10. Only NO2-, NO3- and CrO42- give positive result in the test for strong reducing anions.
II. Multiple Choice: Choose the letter of the best answer.
1. What is the cell reaction for a charging lead battery?
A. PbO2(s) + Pb(s) + 2H+(aq) + 2HSO4-(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
B. PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2HSO4-(aq) + 4e- → PbSO4(s) + H2(g) + 2H2O(l) + SO42-(aq)
C. 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l) → PbO2(s) + Pb(s) + 2H+(aq) + 2HSO4-(aq)
D. PbSO4(s) + H2(g) + 2H2O(l) + SO42-(aq) → PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2HSO4-(aq) + 4e-
2. The following anions interfere with the formation of a brown ring in the confirmatory test of Nitrate:
A. Chloride, Thiocyanate, Nitrite C. Iodide, Thiocyanate, Oxalate
B. Thiocyanate, Nitrite, Bromide D. Bromide, Nitrite, Sulfate
3. Which of the following complexes are diamagnetic?
A. [CoF6]3- B. [Fe(CN)6]3- C. [Co(H2O)6]2+ D. [Co(NH3)6]3+
4. Calculate the equilibrium constant at 25 ˚C for the reaction:
Pb2+(aq) + Sn(s) → Pb(s) + Sn2+(aq) (E0Pb2+/Pb = -0.126 V, E0Sn2+/Sn = -0.14 V)
A. 0.34 B. 9.7 x 108 C.2.97 D. 1.0 x 10-9
5. Which of the following is not a characteristic of the complex [Fe(CN)6]3-?
A. Pairing energy is greater than splitting energy
B. Low spin complex
C. Produces large crystal field splitting.
D. Strong-field complex
III. Qualitative Analysis.
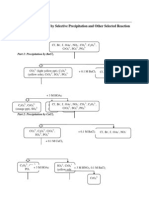
A. Determine Cations A to E and compounds F and G.
Cations A, B, C, D and E
6.0 M HCl
White ppt F from Cation A Cations B, C, D and E
6.0 M NH3
White ppt from NVR for
Cation B and C Cation D and E
X’s NH3 3.0 M NaOH
White ppt of White ppt of C White ppt due Pungent
B dissolves undissolved to Cation D colorless gas G
due to Cation E
Test
Yellow-green
Flame
B. Determine anions H-L and compounds M-R.
Cations H, I, J, K and L
FeCl3
K3Fe(CN)6
Blue ppt M due to Anion H and I Anions J, K and L
Acidified AgNO3 Acidified AgNO3
NVR due to H Yellow ppt N White ppt O NVR due to K and L
due to anion I due to anion J
6M H2SO4 AgNO3
1M FeSO4 X’s NH3
Brown solution Colorless solution White ppt NVR due to L
due to Fe(NO)2+ due to K
6M H2SO4
6M H2SO4
Acid R that has a
Effervescence Q vinegar smell
IV. Problem Solving
1. a. Determine the standard reduction potential of Cr3+(aq) + 3e- → Cr(s) given the E˚red of E˚Cr2+/Cr = -0.91V
and E˚Cr3+/Cr2+ = -0.41V.
b. Using Cr3+(aq) + 3e- → Cr(s) as the anode with [Cr3+] = 1M, determine whether the reaction is
spontaneous or not, and if Pb(s) can be plated out from the following cathodes:
i. PbSO4(s) + 2e- → Pb(s) + SO42-(aq) E˚red = -0.356
ii. Pb (aq) + 2e → Pb(s)
2+ - E˚red = -0.126
Note: The concentrations of all aqueous species are 1M.
c. Solve for the equilibrium constant for the reactions in (b) which is/are spontaneous.
2. Consider the frost diagram for Vanadium in acidic medium.
Frost Diagram, Vanadium, pH = 0
0 V
VO2+
-1
NE0red (V)
-2 V2+ VO2+
V3+
-3
0 1 2 3 4 5
Oxidation Number (N)
a. Which vanadium series is the most stable?
b. Which species is the strongest oxidizing agent?
c. Which species is the strongest reducing agent?
d. Will V3+ disproportionate to V2+ and VO2+?
e. Will VO2+ and V3+ comproportionate to VO2+?
3. a. Determine which complex is high-spin and which is low-spin between [Ni(H2O)6]2+ and [Ni(CN)4]2-.
b. What is the charge of Ni in the low-spin complex? Write its electronic configuration. Draw the orbital
diagram of the complex if it is diamagnetic.
c. Name the high spin complex in (a).
d. Write the water dissociation reaction of the high spin complex in (a).
e. From the reaction in (d), name the conjugate of the high-spin complex.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Long Quiz 2: Mipmalgapo (Chem 17 X2)Dokument3 SeitenLong Quiz 2: Mipmalgapo (Chem 17 X2)Paolo QuinteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 17 - 3rd Lab Long ExamDokument4 SeitenChem 17 - 3rd Lab Long ExamMarko Grant Albos OrozcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 17 (Second Long Sample Exam)Dokument2 SeitenChemistry 17 (Second Long Sample Exam)Nyka C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- KEM Tutorials Chem 17 Module (3rd Exam)Dokument10 SeitenKEM Tutorials Chem 17 Module (3rd Exam)Nyka C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 17 Lab 3rd LE ReviewerDokument3 SeitenChem 17 Lab 3rd LE ReviewerJamie Joice Noche100% (1)
- UP Academic League of Chemical Engineering Students (UP ALCHEMES)Dokument10 SeitenUP Academic League of Chemical Engineering Students (UP ALCHEMES)Jerremiah YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1: CalorimetryDokument4 SeitenExperiment 1: CalorimetryNeil Mark EnriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formal Report in Chem17Dokument6 SeitenFormal Report in Chem17ellets100% (1)
- H2 Equilibrium and Ideal GasDokument9 SeitenH2 Equilibrium and Ideal GaskitoniumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 17 LE 1 Answers1Dokument11 SeitenChem 17 LE 1 Answers1alyssa100% (1)
- UP ACME - Chem 28 - 2nd LE SamplexDokument4 SeitenUP ACME - Chem 28 - 2nd LE SamplexDoom RefugeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selected Reactions of Some AnionsDokument5 SeitenSelected Reactions of Some AnionsJay JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 26 1 Midterms ReviewDokument15 SeitenChem 26 1 Midterms ReviewAlyzza Victoria TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 17 Lab Manual 2Dokument28 SeitenChem 17 Lab Manual 2Chrizamae BarlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formal Report (Experiment 5 RDR)Dokument8 SeitenFormal Report (Experiment 5 RDR)Jay Jay0% (1)
- RedOx Reactions Lab ReportDokument3 SeitenRedOx Reactions Lab ReportRicky HulipasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 28 Problem Set 2Dokument1 SeiteChem 28 Problem Set 2Anonymous ee5dOjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atq E5Dokument2 SeitenAtq E5BuiHopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 26 3rd LE NotesDokument18 SeitenChem 26 3rd LE NotesYshaReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOURCE: General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications 10Dokument3 SeitenSOURCE: General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications 10Jerremiah YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 17 Expt 8 Fr2 FinalDokument12 SeitenChem 17 Expt 8 Fr2 FinalMarrod CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- FR1 Chem 28.1 Expt 1Dokument11 SeitenFR1 Chem 28.1 Expt 1Marrod CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Determination of Soda Ash Composition by Double Indicator TitrationDokument2 SeitenQuantitative Determination of Soda Ash Composition by Double Indicator TitrationAlexander Gordon InesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desalination by freezing advantages over evaporationDokument4 SeitenDesalination by freezing advantages over evaporationRalph John UgalinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Statistical Concepts in The Determination of Weight Variation in SamplesDokument2 SeitenApplication of Statistical Concepts in The Determination of Weight Variation in SamplesCharlette InaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- cHEM 26 LE 1 NOTESDokument3 SeitencHEM 26 LE 1 NOTESChrissa GuicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Final) Spectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A ReactionDokument8 Seiten(Final) Spectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A ReactionJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transference NumberDokument4 SeitenTransference NumberLin Xian Xing50% (2)
- Chemistry 16 Comprehensive Samplex (ANSWER KEY For Non-PSolv)Dokument5 SeitenChemistry 16 Comprehensive Samplex (ANSWER KEY For Non-PSolv)Laia Valencia100% (1)
- S D E C R / E 5: Pectrophotometric Etermination OF THE Quilibrium Onstant OF A Eaction XperimentDokument14 SeitenS D E C R / E 5: Pectrophotometric Etermination OF THE Quilibrium Onstant OF A Eaction XperimentKenneth Dionysus SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 28.1 Midterm PSDokument2 SeitenChem 28.1 Midterm PSAnonymous ee5dOjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample First Long Exam (Chem 17) : CHEM 17 (2 Sem, AY 15 - 16) UP ACME - Page 1 of 5Dokument5 SeitenSample First Long Exam (Chem 17) : CHEM 17 (2 Sem, AY 15 - 16) UP ACME - Page 1 of 5Jasper DumalaogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric Edta TitrationDokument12 SeitenQuantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric Edta TitrationmariemfranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Statistical Concepts in The Determination of Weight Variation in Coin SamplesDokument3 SeitenApplication of Statistical Concepts in The Determination of Weight Variation in Coin SamplesMicah PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 14Dokument13 SeitenLab 14Alfie16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA TitrationDokument14 SeitenQuantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA Titrationabcd efgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis of Cation and Anions Chem 16Dokument6 SeitenQualitative Analysis of Cation and Anions Chem 16Almira Kaye CuadraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem16 LE3 SamplexDokument3 SeitenChem16 LE3 SamplexmariemfranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 31 Prob Set Org Mech NucleophilicDokument3 SeitenChem 31 Prob Set Org Mech NucleophilicJolaine ValloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of The Solubility Product Constant of Calcium HydroxideDokument2 SeitenDetermination of The Solubility Product Constant of Calcium HydroxideJunko TsukudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atq 4Dokument4 SeitenAtq 4Martina BlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calorimetry Lab ReportDokument6 SeitenCalorimetry Lab ReportFrances Abegail QuezonNoch keine Bewertungen
- UP ALCHEMES Chem 17 LE 1 ReviewDokument6 SeitenUP ALCHEMES Chem 17 LE 1 Reviewkennethleo69100% (1)
- S E C H: Olubility Quilibrium of Alcium YdroxideDokument6 SeitenS E C H: Olubility Quilibrium of Alcium YdroxideDoom RefugeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Chemistry - Chemical Equilibrium LabDokument4 SeitenAP Chemistry - Chemical Equilibrium LabJonathan Chen100% (1)
- CHEM 31 PROBLEM SET 1 IDENTIFY HYBRIDIZATIONS, RESONANCE STRUCTURESDokument2 SeitenCHEM 31 PROBLEM SET 1 IDENTIFY HYBRIDIZATIONS, RESONANCE STRUCTURESNat DabuétNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clean Water Identification: Determining Dissolved Oxygen Utilizing Winkler's MethodDokument9 SeitenClean Water Identification: Determining Dissolved Oxygen Utilizing Winkler's MethodKyra CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 3 Transference NumberDokument3 SeitenExperiment 3 Transference NumberRicky JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solubility Equilibrium of Calcium HydroxideDokument5 SeitenSolubility Equilibrium of Calcium HydroxideZyrle Nikko Uchida100% (1)
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Equilibrium Constant (KeqDokument7 SeitenSpectrophotometric Determination of Equilibrium Constant (KeqFrances Abegail QuezonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 31.1 Postlab 9Dokument1 SeiteChem 31.1 Postlab 9Sellina SyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formal Report Experiment 3Dokument6 SeitenFormal Report Experiment 3Rafael Lee100% (2)
- KHP LabDokument5 SeitenKHP LabSantino MusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 40.1 Lab PoliciesandBufferReviewDokument12 SeitenChem 40.1 Lab PoliciesandBufferReviewYshaReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 28.1 Experiment 8 Formal ReportDokument6 SeitenChem 28.1 Experiment 8 Formal ReportMara Krista CooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase Diagram of Three-Component Liquid SystemDokument11 SeitenPhase Diagram of Three-Component Liquid SystemVanessa Denise Aguilar100% (2)
- Answer All Question in This SectionDokument8 SeitenAnswer All Question in This SectionMuhd FaiZNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM 2013 SEM 2Dokument5 SeitenSTPM 2013 SEM 2m-4306022Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plkno1whcc Chemistry 2122 p1qDokument22 SeitenPlkno1whcc Chemistry 2122 p1qChun Kit LauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growing shrimp and tilapia together in indoor aquacultureDokument13 SeitenGrowing shrimp and tilapia together in indoor aquaculturetushar patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- HF Scientific Online Chlorine Monitors and Reagents - CLXDokument3 SeitenHF Scientific Online Chlorine Monitors and Reagents - CLXMCE ProcessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science 20 - Lesson PlanDokument7 SeitenPhysical Science 20 - Lesson Planapi-349567441Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gibberellins: Regulators of Plant HeightDokument17 SeitenGibberellins: Regulators of Plant HeightPratiwi DwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - Synthesis of Nanomaterials - 2009 Ashby - Nanomaterials Nanotechnology An Introduction PDFDokument17 SeitenChapter 8 - Synthesis of Nanomaterials - 2009 Ashby - Nanomaterials Nanotechnology An Introduction PDFkaoru9010-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ms 01 140Dokument74 SeitenMs 01 140Prateek RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument76 SeitenPDFRavishankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP 360 CmanualDokument35 SeitenSP 360 CmanualencontreelrepuestoNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Vibration Control in BuildingsDokument45 SeitenAn Introduction To Vibration Control in Buildingsosama alabsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macromolecules: Question Paper 1Dokument8 SeitenMacromolecules: Question Paper 1Bridgette LombardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gear CalculationDokument58 SeitenGear CalculationSachin KubasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of O-Rings For SealingDokument87 SeitenDesign of O-Rings For Sealingsiva rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valvoline Lithium Ep2 GreaseDokument1 SeiteValvoline Lithium Ep2 GreaseDicky PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anodising Vs Powder CoatingDokument3 SeitenAnodising Vs Powder CoatingCgpscAspirantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Engineering SyllabusDokument49 SeitenEnergy Engineering SyllabusKarthiik88Noch keine Bewertungen
- YSI Model 55: Handheld Dissolved Oxygen and Temperature SystemDokument26 SeitenYSI Model 55: Handheld Dissolved Oxygen and Temperature Systemdwisdt9044Noch keine Bewertungen
- ApplicationNote PH Measurement JamJellies EN 30538204Dokument4 SeitenApplicationNote PH Measurement JamJellies EN 30538204MarcinNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP 5973 Quick ReferenceDokument28 SeitenHP 5973 Quick ReferenceDavid ruizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 (Semicon) FLOYDDokument2 SeitenChapter 1 (Semicon) FLOYDanon_337840562Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laprak Distilasi UapDokument11 SeitenLaprak Distilasi UapRetnani Arum PertiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qorpak 2018 CatalogDokument104 SeitenQorpak 2018 Catalog東栄大出Noch keine Bewertungen
- TDS - RheoFIT 764Dokument2 SeitenTDS - RheoFIT 764aahtagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Fuel InjectionDokument5 SeitenDiesel Fuel Injectiondamith21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Density PhET Lab SheetDokument5 SeitenDensity PhET Lab SheetJasper Johnston100% (1)
- Moldavite Ukazka PDFDokument15 SeitenMoldavite Ukazka PDFNeven Žižić100% (1)
- Material Data Sheet: Casting Material: Stainless Steel CF8MDokument9 SeitenMaterial Data Sheet: Casting Material: Stainless Steel CF8MakshayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biocide Selection Guide: Oil and GasDokument8 SeitenBiocide Selection Guide: Oil and GasJOSEANTONIO2001100% (1)
- Determination of Vinyl Chloride Monomer in Food Contact Materials by Solid Phase Microextraction Coupled With Gas Chromatography/Mass SpectrometryDokument6 SeitenDetermination of Vinyl Chloride Monomer in Food Contact Materials by Solid Phase Microextraction Coupled With Gas Chromatography/Mass SpectrometryPhuongthuy127Noch keine Bewertungen
- WRS 2008 CatalogDokument34 SeitenWRS 2008 CatalogYimmy Alexander Parra MarulandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Compounds Chemistry GuideDokument20 SeitenCarbon Compounds Chemistry Guideirisyyy27Noch keine Bewertungen