Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of Inguinal Hernia
Hochgeladen von
Cleobebs Agustin100%(2)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (2 Abstimmungen)
2K Ansichten3 SeitenMy own pathophysiology of Inguinal hernia
Originaltitel
cleo.agustin_ Pathophysiology of Inguinal Hernia
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenMy own pathophysiology of Inguinal hernia
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(2)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (2 Abstimmungen)
2K Ansichten3 SeitenCleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of Inguinal Hernia
Hochgeladen von
Cleobebs AgustinMy own pathophysiology of Inguinal hernia
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
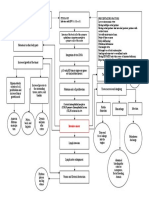
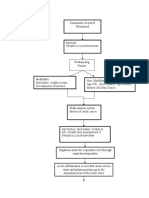
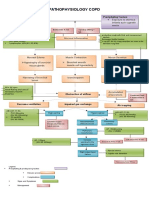
PATHOPHYSILOGY of INGUINAL HERNIA
Predisposing Factor: Precipitating Factor:
-Age (Older) -Prolonged Standing, lifting,
-Straining to have bowel
-Family History of Hernia movement
-Sex (90% Males) -Obesity, Heavy Lifting, Coughing
-Diseases (Ascites,
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt,
COPD)
-Cigarette Smoking
-Lack of Exercise
-Surgical Procedures
-Chronic Constipation
-Standing for long period of time
Increased pressure in abdominal compartment
Weakness of Intra-abdominal wall and which spermatic cord emerges
Weakness of Inguinal canal into scrotum
Direct Inguinal Hernia
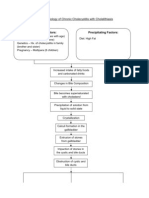
Affect function of posterior inguinal
Improper closure of inguinal area wall
Increased intra abdominal
Indirect Inguinal Hernia pressure
Stragulation Protruded Bowel
(Narrow Neck) muscle weakness
Rest in Inguinal Canal Inguinal ring remains open
Move down in Scrotum
Vague Discomfort Hernia contents slides in P
out of abdominal defect
Lumps Hesselback triangle
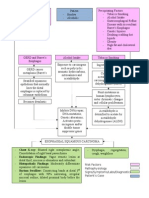
area
Bulge at one or both
Sides of groin Transversalis Facia
Inflammation weakened
Signs and Symptoms may increase in size
-Aching
-Burning Swollen or Enlarged Scrotum Degeneration and
-Gurgling Sensation and fatty changes
Of aponeurosis
Segments of intestine prolapsed
Through the defect of anterior Feeling of Pain and
Abdominal wall Weakness discomfort
Mass Below inguinal Ligament
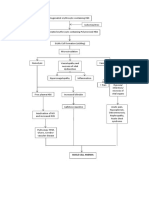
Sequestration of fluid in the lumen Palpable impulse Swollen or
enlarged
of the herniated bowel generated by the sac
Scrotum with its content
Impairs lymphatic and venous drainage
Inflammation impaired blood supply
Swelling
Increases intraluminal Pressure
Congestion of wall
Intravasations of blood into the hernia sac
Bowel wall loses pinkish and shining color
Dull congested bowel segment
Loss of tone within bowel wall
Bacterial proliferation
Subsequent infection of blood-stained fluid in the hernia sac
Gangrene
Not Treated: Perforation and Peritonitis
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Myoma PathoniixDokument1 SeiteMyoma PathoniixRendel FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cervical Cancer PathophysiologyDokument1 SeiteCervical Cancer PathophysiologyBea Dela Cena100% (2)
- Hirschsprung Disease: A Congenital Birth Defect of the IntestinesDokument3 SeitenHirschsprung Disease: A Congenital Birth Defect of the IntestinesJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Client Initials: Medical Diagnosis: Cephalopelvic Disproportion Eu DEFINITION: The RelationshipDokument2 SeitenClient Initials: Medical Diagnosis: Cephalopelvic Disproportion Eu DEFINITION: The RelationshipLyssa Monique67% (3)
- PathophysiologyDokument2 SeitenPathophysiologyapi-19762967100% (1)
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating FactorsDokument3 SeitenAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating FactorsKyla ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyDokument3 SeitenPost Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyRizalyn QuindipanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iii. Textbook Discussion A. Definition: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDokument3 SeitenIii. Textbook Discussion A. Definition: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsVianne ArcenioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Cancer Pathophysiology: Predisposing FactorDokument3 SeitenLiver Cancer Pathophysiology: Predisposing FactorTarantado100% (2)
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia OverviewDokument3 SeitenAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia OverviewKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Hirschsprung DiseaseDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Hirschsprung DiseaseAlinor Abubacar100% (1)
- Case of OsteosarcomaDokument25 SeitenCase of Osteosarcomadocs2009100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer: Predisposing Factors, Cell Changes, SymptomsDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Breast Cancer: Predisposing Factors, Cell Changes, SymptomsEggy Pascual100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationJhevilin RM100% (1)
- Case Report Buerger DiseaseDokument36 SeitenCase Report Buerger DiseaseKhaeruz Zahra67% (3)
- Hemorrhoidectomy Case StudyDokument19 SeitenHemorrhoidectomy Case StudyJoyJoy Tabada CalunsagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug-Study NCPDokument5 SeitenDrug-Study NCPMURILLO, FRANK JOMARI C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Patho Intussusception RevisedDokument8 SeitenPatho Intussusception RevisedPj Gabano60% (5)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDokument4 SeitenPathophysiology of PneumoniaDimpal ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology OsteosarcomaDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology OsteosarcomaVernadeth Dumagat50% (2)
- Doctors Order LoveDokument4 SeitenDoctors Order LoveAubrey Unique EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Lung Cancer Concept MapDokument3 SeitenFinal Lung Cancer Concept MapKaycee TolingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predisposing Factors Age Diet Dehydration Precipitating Factors Family or Personal History Digestive Diseases and SurgeryDokument2 SeitenPredisposing Factors Age Diet Dehydration Precipitating Factors Family or Personal History Digestive Diseases and SurgeryChloé Jane HilarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Dokument2 SeitenPathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Jamie HaravataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course in The Ward: DialysisDokument4 SeitenCourse in The Ward: DialysisRayjundie EstradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic or InstrumentsDokument21 SeitenBasic or InstrumentsMabes100% (1)
- Chronic Cholecystitis With Cholelithiasis PathoDokument2 SeitenChronic Cholecystitis With Cholelithiasis PathoBill Clinton Lamira BabanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Ovarian Cancer Meigs Pathophysio PDFDokument3 SeitenFinal Ovarian Cancer Meigs Pathophysio PDFCathy Santos100% (1)
- Esophageal Cancer Risk Factors, Pathophysiology, and Surgical ManagementDokument2 SeitenEsophageal Cancer Risk Factors, Pathophysiology, and Surgical Managementroshmae100% (4)
- Assessing Nursing Diagnoses and Expected OutcomesDokument20 SeitenAssessing Nursing Diagnoses and Expected OutcomesZamranosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gaviscon Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenGaviscon Drug StudyJOANNA MAE ABIA SALOMONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of PneumoniaMaria Cristina100% (1)
- Naprex Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenNaprex Drug StudyAngelica shane NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology Sickle Cell AnemiaDokument1 SeitePathophysiology Sickle Cell AnemiaTine GuibaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signifance of The Study (Version 2)Dokument2 SeitenSignifance of The Study (Version 2)Wajiha Esmula TiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management For OsteosarcomaDokument2 SeitenManagement For OsteosarcomakyawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pott's Disease NCPDokument7 SeitenPott's Disease NCPkristel_nicole18yahoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY - Placenta PreviaDokument5 SeitenPATHOPHYSIOLOGY - Placenta PreviaFretzgine Lou Manuel100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of PharyngitisDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of PharyngitisKRISTINE BULACAN100% (1)
- Osteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Dokument34 SeitenOsteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Angelic khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course in The WardDokument7 SeitenCourse in The WardDanicaEdonFelarcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Dokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Katherine Clarisse Carvajal Lavarias100% (1)
- Hemorrhoids Pathophysiology Book BasedDokument1 SeiteHemorrhoids Pathophysiology Book BasedFate ZephyrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Endometrial HyperplasiaDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Endometrial Hyperplasiatinatin989100% (2)
- Lung Cancer Guide: Causes, Tests, SymptomsDokument4 SeitenLung Cancer Guide: Causes, Tests, SymptomsJoanna Marie EsperanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care of Patient With Pregnancy Uterine Delivered by Primary Cs Secondary To Cephalopelvic DisproportionDokument38 SeitenCare of Patient With Pregnancy Uterine Delivered by Primary Cs Secondary To Cephalopelvic DisproportionLuayon Francis100% (1)
- Copd PathDokument2 SeitenCopd Pathnursing concept maps100% (2)
- TRIAGE Sorting Patients in EDDokument10 SeitenTRIAGE Sorting Patients in EDRocelyn CristobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addison's Disease Patho-PhysiologyDokument1 SeiteAddison's Disease Patho-PhysiologyAca Ramirez100% (3)
- Colon Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Stages & TreatmentDokument17 SeitenColon Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Stages & TreatmentYaska MusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ambag Q RinDokument1 SeiteAmbag Q RinErryl Justine AdvinculaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bedah II PDFDokument71 SeitenBedah II PDFAnggitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pa Tho Physiology of Hiatal HerniaDokument1 SeitePa Tho Physiology of Hiatal HerniaChiskie Faldas Genodia100% (1)
- Abdominal SymptomsDokument21 SeitenAbdominal SymptomsKiara GovenderNoch keine Bewertungen
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDokument2 SeitenPATHOPHYSIOLOGYVanessa SumalbagNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEC 15.1 - Abdominal HerniasDokument37 SeitenLEC 15.1 - Abdominal HerniasTudor CorneaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angel Problem 4a GITDokument48 SeitenAngel Problem 4a GITMaxend Arselino SilooyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inguinal and Femoral HerniaDokument50 SeitenInguinal and Femoral HerniaFafa NabihaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology - AppendicitisDokument5 SeitenPathophysiology - AppendicitisAzielle Joyce RosquetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Askep Hernia Sri HariyaniDokument40 SeitenAskep Hernia Sri Hariyaninanang nafi100% (1)
- Cleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of SarcoidosisDokument1 SeiteCleo - Agustin - Pathophysiology of SarcoidosisCleobebs AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dengue PoathoDokument6 SeitenDengue PoathoCleobebs Agustin100% (1)
- Khleeo - Anatomy and Physiology Female Rep. SystemDokument4 SeitenKhleeo - Anatomy and Physiology Female Rep. SystemCleobebs AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Spongy Degeneration of The Brain: Precipitating FactorsDokument4 SeitenPathophysiology of Spongy Degeneration of The Brain: Precipitating FactorsCleobebs AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Spongy Degeneration of The Brain: Precipitating FactorsDokument4 SeitenPathophysiology of Spongy Degeneration of The Brain: Precipitating FactorsCleobebs AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Spongy Degeneration of The Brain: Precipitating FactorsDokument4 SeitenPathophysiology of Spongy Degeneration of The Brain: Precipitating FactorsCleobebs AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASHRAE Std 62.1 Ventilation StandardDokument38 SeitenASHRAE Std 62.1 Ventilation Standardcoolth2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Building An ArgumentDokument9 SeitenBuilding An ArgumentunutulmazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corn SpecDokument4 SeitenCorn SpecJohanna MullerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ancient Indian Medicine Systems OverviewDokument11 SeitenAncient Indian Medicine Systems OverviewAmrutha AyinavoluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osteoporosis: What Is Osteoporosis? What Are Osteoporosis Symptoms?Dokument2 SeitenOsteoporosis: What Is Osteoporosis? What Are Osteoporosis Symptoms?Ayman FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chymoral Plus'Dokument3 SeitenChymoral Plus'Neha SureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- MHFL Functional FoodsDokument24 SeitenMHFL Functional FoodsZekel HealthcareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Narcolepsy: Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentsDokument2 SeitenUnderstanding Narcolepsy: Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentsAl Adip Indra MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HIV Prevention: HSCI 225 BY Mutua Moses MuluDokument23 SeitenHIV Prevention: HSCI 225 BY Mutua Moses MuluJibril MohamudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ekstrak Kulit Buah Naga Super Merah Sebagai Anti-Kanker PayudaraDokument5 SeitenEkstrak Kulit Buah Naga Super Merah Sebagai Anti-Kanker PayudaraWildatul Latifah IINoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Facebook BmiDokument29 Seiten9 Facebook BmiDin Flores MacawiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cognidox - A Complete Guide To Medical Device DevelopmentDokument38 SeitenCognidox - A Complete Guide To Medical Device DevelopmentcivicbladeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergent Care Clinic StudyDokument5 SeitenEmergent Care Clinic StudyAna Bienne0% (1)
- UntitledDokument221 SeitenUntitledlaljadeff12Noch keine Bewertungen
- F&F LetterDokument3 SeitenF&F LetterJaskeerat Singh50% (2)
- Sspc-Ab 2Dokument3 SeitenSspc-Ab 2HafidzManafNoch keine Bewertungen
- 80-Article Text-264-1-10-20200729Dokument6 Seiten80-Article Text-264-1-10-20200729ulfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Division Memorandum - s2020 - 241Dokument16 SeitenDivision Memorandum - s2020 - 241ARLENE MARASIGANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of Physical Fitness and Physical Activity. Fifty Years of Change 3PDokument12 SeitenMeasurement of Physical Fitness and Physical Activity. Fifty Years of Change 3PMuhd NashhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPJ LAS Q2 Week 1 To 5Dokument67 SeitenSPJ LAS Q2 Week 1 To 5Lovilyn EncarnacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Name: Proposed Icomc & BMC Building Complex Phe Design ReportDokument19 SeitenProject Name: Proposed Icomc & BMC Building Complex Phe Design ReportAmit Kumar MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progress Test 04Dokument6 SeitenProgress Test 04Lemmy the GamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beta Lactam Antibiotics Structure, Classification and MechanismDokument15 SeitenBeta Lactam Antibiotics Structure, Classification and MechanismNiharika ModiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Back Pain Dr. Hardhi PRanataDokument57 SeitenLow Back Pain Dr. Hardhi PRanataPerwita ArumingtyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comet Assay: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument11 SeitenComet Assay: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediasuryasivNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSN 3G GRP 4 Research TitlesDokument6 SeitenBSN 3G GRP 4 Research TitlesUjean Santos SagaralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latest Requirements on Safe Lifting OperationsDokument22 SeitenLatest Requirements on Safe Lifting OperationsThanThanscc100% (1)
- Diabetes and Hearing Loss (Pamela Parker MD)Dokument2 SeitenDiabetes and Hearing Loss (Pamela Parker MD)Sartika Rizky HapsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal LupusDokument19 SeitenNeonatal Lupusyogeshraval368Noch keine Bewertungen
- Addressing The Impact of Foster Care On Biological Children and Their FamiliesDokument21 SeitenAddressing The Impact of Foster Care On Biological Children and Their Familiesapi-274766448Noch keine Bewertungen