Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
DC Injection Motor Brake Instructions
Hochgeladen von
prasiva@04Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DC Injection Motor Brake Instructions
Hochgeladen von
prasiva@04Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Installation Manual for dc Injection Brake Units
HHI Drives Europe
INJ Series DC brake modules
PDS 11-30-100A 1 Issue 3
Installation Manual for dc Injection Brake Units
Contents, 1. Safety.
2. Installation.
3. Setting Up.
4. Diagrams.
5. Specifications.
6. Timing Diagram.
7. Outlines
8. Thermal Ratings.
HHI Drives Europe.
PO Box 2091.
Bolton
BL5 2ZS
U.K.
Tel. 08452 300 501
Email http://www.hhidrives.com/contact.htm
Web www.hhidrives.com
Date, May 2005
PDS 11-30-100A 2 Issue 3
Installation Manual for dc Injection Brake Units
1. Safety.
Modification of any machine may require a safety risk assessment. As a result of the risk
assessment additional safety systems or interlocks may be required. Safety relays are available if
required. Please contact us if you require help with a risk assessment or any other safety equipment.
Read this manual fully before installation. The assembly is an electrical system which must be
installed by a competent person. Ensure all authorised persons are aware of the dangers and safe
working practices.
1.1. Safety Electrical.
The voltage at some of the terminals is high enough to endanger life. The terminals have only
protection against accidental contact. The module must be installed in a panel to which unauthorised
access is denied.
Semiconductor fuses should be fitted to protect only the brake module. Upstream BS88 fuses
must be provided to protect the wiring. The wiring should conform with the latest IEE regulations, or
local regulations whichever are more stringent.
1.2. Safety Mechanical.
Rotating and moving machinery can cause injury or endanger life. Installation of any
additional control to a machine must be carried out by a competent person.
Consideration must be taken of any potential hazards. These may be couplings: threaded
couplings which may unscrew if the motor is stopped, couplings fixed by shear-pins would need to be
checked to see if these stand the stopping torque, friction couplings would need to be checked to see if
these stand the torque. The machine mountings must be checked to see if they can stand the forces
during stopping.
2. Installation.
The brake module is intended to be wired downstream of the machine isolator and any motor
overload relay. The module may require an auxiliary contactor of its own in some starter circuits.
Please refer to the typical installation diagrams at the back of this manual. A cursory view of the
diagrams will show that the brake significantly alters the starter circuit
2.1. Earth Connection.
The brake assembly must have an earth connection. The earth cable cross section should be as
big as the cable used for the power wiring.
PDS 11-30-100A 3 Issue 3
Installation Manual for dc Injection Brake Units
3. Setting Up.
3.1 General.
The minimum equipment required is a dc clip-on ammeter. Be sure to measure the current in
one of the motor windings which are to carry the dc injection current. One of the motor connections
does not carry any current during braking.
Ensure that the set up is carried out with the maximum moment of inertia (load) coupled to the
motor shaft. And that any friction is removed, e.g. no work piece in the machine.
A series of test start-stop cycles will be made during setting up. If the installation has been
done correctly, be aware that the brake unit should deny re-starting during braking.
Also be aware that the duty is limited by the braking current, and the ambient temperature.
Too many stop / start cycles in close succession may damage the unit. See the specifications for some
idea of permissible duty.
The procedure requires the machine to be run up to normal speed, and the brake (stop)
applied. During the braking period the current is monitored, and adjusted up to the maximum permitted
by the motor, and the maximum permitted by the duty of the application.
3.2. Current. B
The front panel of the module has a screw-driver adjustment for current.. Minimum current is
fully anticlockwise. The current must be measured with a dc meter. The rated current of the unit will be
achieved at somewhere below 100% depending on the motor.
The current is proportional to the braking torque. Consistent with duty and module rating the
DC current may be set up to 2 x the motor full load current (flc). Above 2 x flc the braking torque will
begin to fall. If the dc current is applied to one winding or to windings in series, the flc is the star
current. If the dc current is applied to the motor in delta configuration then the flc is the delta current.
3.2. Time. A
The front panel of the module has a screw-driver adjustment for time. The duration of the braking can
be adjusted between 1 and 10 seconds. The adjustment is logarithmic with 2s at 50%, and 3s at 75%.
Minimum time is fully clockwise. (Not the same as the current control.)
3.3. Procedure.
1. Initially set the time for about 4 seconds (50%). The time is long enough to allow the current
meter to get a good indication, and short enough to keep the duty low during repeated stop / starts.
2. Set the current adjustment to about 20% and start the machine. Stop the machine and observe
the current in a motor line which is carrying the DC injection. It is not necessary to attain full speed
before stop is applied.
3. Adjust the current setting and repeat the stop / start until the desired current is attained.
4. Start the machine, and allow it to get to operating speed. Stop the machine and observe the
residual speed when the braking has stopped. If the machine is still running, the brake time should be
increased. If the machine has stopped, it may be possible to reduce the brake time. It does no harm to
have the brake applied for half a second after the machine has reached standstill.
The brake is now set for use.
PDS 11-30-100A 4 Issue 3
Installation Manual for dc Injection Brake Units
3.4. Alternative Procedure.
The previous set-up was dominated by the current setting. In some applications you may wish
to stop a little less quickly. Set the brake time first, and then increase the current until standstill is
achieved within the desired time as follows
1. Initially set the current for about 30%. The current is high enough to allow the current meter to
get a good indication, and short enough to keep the duty low during repeated stop / starts.
2. Set the time adjustment to the desired amount and start the machine. Allow the machine to
reach full speed and stop the machine. Observe the current in a motor line which is carrying the DC
injection. Check that the brake action is sustained over the desired stopping time.
3. Adjust the current setting and repeat the stop / start until the machine stops within the desired
stopping time.
The brake is now set for use.
3.5. Monitoring Brake Activity.
Detecting brake activity can be done in several ways as follows
1 Observe the current meter. Braking only occurs when current is flowing. The current ceases
about 1 second before the brake cycle is ended.
2 Where fitted, listen for the brake contactor to drop out. Current ceases about 1 second earlier.
3 Listen to the sound of the motor. During braking the motor noise may be heard as a low
"growl". The harmonic currents in the motor during braking are predominantly 50Hz. The
characteristic hum of domestic equipment by comparison is an octave higher.
3.6. Temperature.
On initial setting add some extra time or current in excess the setting which just stops the
machine. Add 15% for example. After initial setting-up check the braking during a normal work period.
As the motor heats up during use, the resistance of the windings will rise a little. The machine may
come to rest a little later than it did during setting-up
PDS 11-30-100A 5 Issue 3
Installation Manual for dc Injection Brake Units
4. Diagrams.
PDS 11-30-100A 6 Issue 3
Installation Manual for dc Injection Brake Units
PDS 11-30-100A 7 Issue 3
Installation Manual for dc Injection Brake Units
PDS 11-30-100A 8 Issue 3
Installation Manual for dc Injection Brake Units
5. Specifications.
5.1. General Function.
U1.U2. Ac power and control
D,C. Dc output to motor.
3 Gate drive for 50A / 100A assemblies
4 Enable input, referenced to U2.
1,0,2. Isolated changeover contacts energised when braking.
A Brake time adjustment.
B Brake current adjustment.
An external contactor connects the unit to the motor. When an enable signal is given dc
current is generated from the ac supply. The unit allows for manual adjustment of the current. The time
for which the current is applied is also manually set on the unit. An internal contact set is energised
during braking so that the motor is disconnected from the external start circuit, and the start circuit is
defeated.
5.2. Ratings.
Models INJ-[ ]-[ ][ ][ ][ ]-[ ][ ][ ]
H-11A H-30A H-36A L-30A L-36A H-75A H-100A
-ASS -ASS
Motor kW 2.2 5.5 7.5 3 4 18.5 37
Voltage ac 400V 400 400 230 230 400 400 Vac 50-60Hz
Current dc 11 30 36 30 36 75 120 Adc output
Voltage dc max 150 150 150 85 85 150 150 Vdc output
Duty 40OC 10 3 15 3 15 50 50 % side by side
15 5 15 5 15 50 50 % 10mm clearance.
Terminals Accept wire 1.0mm2 -2.5mm2. 16 25 mm2
Protection IP20
Height mm 75 75 75 75 75 135 135
Width mm 45 45 60 45 60 130 215
Depth mm 120 120 120 120 120 125 125
Contacts 0,1,2. AC 250V, 2A, 250VA
Time control 1 to 10 seconds
Current control 0 to 100% output voltage rating. Current should not be allowed to exceed rating of
unit. Maximum attainable current depends on motor resistance.
Input Fuses 16 16 16 16 16 25 50 Amps aR
Semiconductor type
Contactor Motor current rating at AC3
PDS 11-30-100A 9 Issue 3
Installation Manual for dc Injection Brake Units
6. Timing Diagram
MOTOR RUN CONTACTORS ENERGISED
BRAKE CONTACTOR ENERGISED
MOTOR CURRENT
0.3 SECONDS 1.5 SECONDS
CONTROL CONTACTS 0,1,2. 0,1 CLOSED 1,2 CLOSED
DC INJECTION BRAKE TIMING
BRAKE UNITS UP TO 5kW
DRG. NO. CDKIM002 ISS.0 DATE 27JA05
7 Outlines
Mount units with heatsink fins running vertically.
PDS 11-30-100A 10 Issue 3
Installation Manual for dc Injection Brake Units
8 Thermal Ratings.
PDS 11-30-100A 11 Issue 3
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Thomson Electrac HD Linear Actuator Motion Control per CAN BusVon EverandThomson Electrac HD Linear Actuator Motion Control per CAN BusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat426a PDFDokument90 SeitenCat426a PDFJuan PenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seiwa Explorer3 User Manual EnglishDokument118 SeitenSeiwa Explorer3 User Manual EnglishNomofnamorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Manual: All-Around-Weeder Radius SL PlusDokument85 SeitenOperating Manual: All-Around-Weeder Radius SL PlusPaul DanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Denon Poa-6600 ServiceDokument33 SeitenDenon Poa-6600 ServiceOrlando RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- LISTER Gamma Workshop ManualDokument128 SeitenLISTER Gamma Workshop ManualTata MolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Holland T5000 Series Tractor Specifications: T5040 T5050 T5060 T5070Dokument2 SeitenNew Holland T5000 Series Tractor Specifications: T5040 T5050 T5060 T5070Victor Nunes0% (1)
- Barudan BEAT-804, - 806, - 808, - M804, - M806, - M808-YS PDFDokument78 SeitenBarudan BEAT-804, - 806, - 808, - M804, - M806, - M808-YS PDFanyelo sanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 175 DocDokument107 Seiten175 DocjoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Massey Ferguson MF 178 TRACTORS (FR) Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 957368)Dokument15 SeitenMassey Ferguson MF 178 TRACTORS (FR) Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 957368)bvk29800220% (1)
- 2954 4960 01 - Branded EU Lighting Tower - ENDokument50 Seiten2954 4960 01 - Branded EU Lighting Tower - ENIlarion Ciobanu100% (1)
- Manual HorschDokument74 SeitenManual HorschFabianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 65002-0001 Terex Ta33Dokument59 Seiten65002-0001 Terex Ta33reman partsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conventional Colchester Lathe Assembly ManualDokument5 SeitenConventional Colchester Lathe Assembly Manualmiguel angel reyes pinillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulics 1Dokument50 SeitenHydraulics 1Vivek VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opimod 8200Dokument84 SeitenOpimod 8200UTC_ITSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 RDDokument4 Seiten100 RDMahmoud EldabahNoch keine Bewertungen
- SM Tm3989 Knott A4Dokument1 SeiteSM Tm3989 Knott A4Marc GlebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Drive One 161110 PDFDokument174 SeitenCatalogo Drive One 161110 PDFIdiLab EmprendimientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GS2 GS 2668, 3268 DC: Model: Serial NumberDokument6 SeitenGS2 GS 2668, 3268 DC: Model: Serial Numbermiperrito08Noch keine Bewertungen
- DENAIR DVA Series Direct Driven Air Compressor User ManualDokument42 SeitenDENAIR DVA Series Direct Driven Air Compressor User ManualMichelPiconValverdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1sbc100122c0202 ch04Dokument47 Seiten1sbc100122c0202 ch04mathankumar1980Noch keine Bewertungen
- Welger D4006-4060-6006-6060 Owner Manual 1251-99-03-05 BADokument164 SeitenWelger D4006-4060-6006-6060 Owner Manual 1251-99-03-05 BARui SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karcher Operation ManualDokument60 SeitenKarcher Operation ManualDadi SucahyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Inversor 110-130Dokument146 SeitenHydraulic Inversor 110-130koaa85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deutz Fahr Serie 1000 6 Cylinders Euro 2 Engine Service Repair ManualDokument16 SeitenDeutz Fahr Serie 1000 6 Cylinders Euro 2 Engine Service Repair ManuallaopaodunNoch keine Bewertungen
- TM1588 John Deere 750C, 850C Crawler Dozer Diagnostic Operation and Test Technical ManualDokument11 SeitenTM1588 John Deere 750C, 850C Crawler Dozer Diagnostic Operation and Test Technical Manualtteelsars0% (1)
- cqm13392 7jDokument8 Seitencqm13392 7jsunilbholNoch keine Bewertungen
- DX68 Hose Crimping Machine User Manual (Introductions)Dokument4 SeitenDX68 Hose Crimping Machine User Manual (Introductions)Leanne GeermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altech User Manual AlRitmaDokument63 SeitenAltech User Manual AlRitmaAndrew AllanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 08 23 Case IH MagnumPartsDokument4 Seiten2011 08 23 Case IH MagnumPartsdanutspataruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orbital Motors: TMT, Tmtu, TMTW, TMT FL and TMTW FLDokument52 SeitenOrbital Motors: TMT, Tmtu, TMTW, TMT FL and TMTW FLMudduKrishna shettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acme A349 Service ManualDokument34 SeitenAcme A349 Service ManualCristian DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts Manual: Issue 13Dokument141 SeitenParts Manual: Issue 13Юра ПименовNoch keine Bewertungen
- ManualDokument1 SeiteManualFlorin SpataruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrive IOMDokument14 SeitenHydrive IOMCristopher PatricioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wet Disc Brake With Dowel Pins: Model W3H (360 MM) Maintenance Manual MM-20195Dokument52 SeitenWet Disc Brake With Dowel Pins: Model W3H (360 MM) Maintenance Manual MM-20195Antonio MejicanosNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC238USLC: Tier 4 Final EngineDokument20 SeitenPC238USLC: Tier 4 Final EngineAbhinandan PadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gradall G3R Service ManualDokument573 SeitenGradall G3R Service ManualSlater EbelingNoch keine Bewertungen
- GNF41810 GrundigDokument44 SeitenGNF41810 Grundigjocastells7390Noch keine Bewertungen
- Etectric Generating Ptants: Operator'S Manuat AND Parts CatalogDokument54 SeitenEtectric Generating Ptants: Operator'S Manuat AND Parts CatalogBruce EgglestonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motorola gr1225 User ManualDokument3 SeitenMotorola gr1225 User ManualBinnui Navarro NavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- E+l Elstretcher - En-04 - 12-2017 - 363850Dokument32 SeitenE+l Elstretcher - En-04 - 12-2017 - 363850steve jobsNoch keine Bewertungen
- John Deere 328 Skid Steer Service Repair Manual (TM2192)Dokument14 SeitenJohn Deere 328 Skid Steer Service Repair Manual (TM2192)laopaodunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide Cu2 CuvcDokument151 SeitenGuide Cu2 CuvcEngr Huzaifa QureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dacts704c Diesel Generator Auto ControllerDokument27 SeitenDacts704c Diesel Generator Auto ControllerRahmat Noor IlhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- JCB Vibromax ManualDokument222 SeitenJCB Vibromax Manualroyreid99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case CX ProspektDokument8 SeitenCase CX Prospektvejnik070% (1)
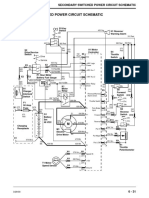
- Secondary Switched Power Circuit Schematic: Electrical SystemDokument1 SeiteSecondary Switched Power Circuit Schematic: Electrical Systempavli999100% (1)
- Taylor VertexDokument6 SeitenTaylor VertexdeutscheafrikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Inch Pipe Threader: Owner'S ManualDokument13 Seiten4 Inch Pipe Threader: Owner'S ManualzzapiecheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual: Diesel EnginesDokument64 SeitenService Manual: Diesel EnginesWilmanVillatoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syncrowave 250Dokument14 SeitenSyncrowave 250creatriosNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuadDokument14 SeitenQuadnprashanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRC2000 Operating ManualDokument121 SeitenPRC2000 Operating Manualmjam100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Launch TLT240SB 2 Post Lift ManualDokument49 SeitenLaunch TLT240SB 2 Post Lift ManualLuis PupialesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16efoz 20eozDokument92 Seiten16efoz 20eozJorge FierroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lcs Troubleshooting Manual - Rev 1Dokument38 SeitenLcs Troubleshooting Manual - Rev 1Andre VPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tecumseh H60-75505R Motor Parts ManualDokument8 SeitenTecumseh H60-75505R Motor Parts ManualTim MckennaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Machines - II: T.E./Insem. - 108Dokument2 SeitenTheory of Machines - II: T.E./Insem. - 108palashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forged Eye Bolts PDFDokument2 SeitenForged Eye Bolts PDFAmit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12V Cummins Torque Specs PDFDokument8 Seiten12V Cummins Torque Specs PDF180976Noch keine Bewertungen
- Autopilot Servo - Maintenance PracticesDokument16 SeitenAutopilot Servo - Maintenance PracticesEleazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piston Displacement - 104132Dokument36 SeitenPiston Displacement - 104132Usman GhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daewoo Matiz 03 SM f8c Sohc Engine 0 8lDokument20 SeitenDaewoo Matiz 03 SM f8c Sohc Engine 0 8ldorothy100% (54)
- UG-40 Dial and Lever Governors: Installation and Operation ManualDokument62 SeitenUG-40 Dial and Lever Governors: Installation and Operation Manualoscar monroyNoch keine Bewertungen
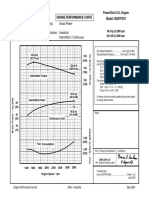
- 4008TAG1-2A - 844-924kWm Emission Compliant Epak PN1833 - 3Dokument2 Seiten4008TAG1-2A - 844-924kWm Emission Compliant Epak PN1833 - 3Ali Reza PishevarNoch keine Bewertungen
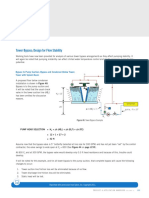
- Cooling Tower Bypass LineDokument1 SeiteCooling Tower Bypass LinekapsarcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chain Feed CF 145 H + RH 714 Maintenance Instruction: C 31360 - 4 en 0904 / JT 1Dokument22 SeitenChain Feed CF 145 H + RH 714 Maintenance Instruction: C 31360 - 4 en 0904 / JT 1cristianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sec6 8035Dokument355 SeitenSec6 8035Benmorsli AhceneNoch keine Bewertungen
- TTR90 2002Dokument288 SeitenTTR90 2002Tengu KazeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AFPX 513: Medium Capacity Solids-Ejecting Centrifuge For Animal and Fish Processing IndustriesDokument2 SeitenAFPX 513: Medium Capacity Solids-Ejecting Centrifuge For Animal and Fish Processing IndustriesMARCO VERAMENDINoch keine Bewertungen
- Atlas Copco Boomer L2D Operators InstructionsDokument120 SeitenAtlas Copco Boomer L2D Operators InstructionsHai Van100% (14)
- 4024TF270 66hp t2Dokument2 Seiten4024TF270 66hp t2Irwin JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEng 156 - Manufacturing and Industrial Processes Report SheetDokument8 SeitenMEng 156 - Manufacturing and Industrial Processes Report SheetKeanu EspinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.06 EC 10M QUAD BOP Man PDFDokument23 Seiten4.06 EC 10M QUAD BOP Man PDFAlexander tulcanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CompressorDokument13 SeitenCompressorjerick garlejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- klf300 c1c4 4wd Parts List PDFDokument108 Seitenklf300 c1c4 4wd Parts List PDFOliverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omm 1106eDokument84 SeitenOmm 1106eDedy setiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pittman GM9236S027Dokument0 SeitenPittman GM9236S027Nicola's SacNoch keine Bewertungen
- FME OP BrochureDokument2 SeitenFME OP BrochureMartin KratkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stepper MotorsDokument26 SeitenStepper MotorsRam Kumar GogadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Se O Nly: Part CatalogueDokument63 SeitenSe O Nly: Part CatalogueTrần Hải PhụngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autotransformer StarterDokument22 SeitenAutotransformer StarterSiswoyo SuwidjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sauer & SohnDokument50 SeitenSauer & SohnILLUMINATOR100% (1)
- 5 TC Update by S Koblenz PDFDokument25 Seiten5 TC Update by S Koblenz PDFg arvNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS19 Repair ManualDokument676 SeitenDS19 Repair Manualcka250100% (1)
- Pittman Full Product CatalogDokument67 SeitenPittman Full Product CatalogKhoa NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet: Mounting Kits According To DIN EN 15081Dokument2 SeitenData Sheet: Mounting Kits According To DIN EN 15081joseocsilvaNoch keine Bewertungen