Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sec Chap02
Hochgeladen von
Ahmed KhouriOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sec Chap02
Hochgeladen von
Ahmed KhouriCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CCNA Security Chapter 2
Securing Network Devices
2.1.1.1 Describe an edge router:
A term used in asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) networks, an edge
router is a device that routes data packets between one or more
local area networks (LANs) and an ATM backbone network, whether a
campus network or a wide area network (WAN).
2.1.1.3 • Physical Security
Place router in a secured, locked room
Install an uninterruptible power supply
• Operating System Security
Describe three critical areas of Use the latest stable version that meets network
router security: requirements
Keep a copy of the O/S and configuration file as a backup
• Router Hardening
Secure administrative control
Disable unused ports and interfaces
Disable unnecessary services
2.1.1.5
• Logs can easily be viewed through the SDM, or for easier use,
through a syslog viewer on any remote system.
• There are numerous Free remote syslog viewers, Kiwi is
When accessing the network relatively basic and free.
remotely, what precautions should • Configure the router/switch/etc to send logs to the PC’s ip
be taken? address that has kiwi installed.
• Kiwi automatically listens for syslog messages and displays
them.
2.1.2.1
1. Cain and Abel
2. John the Ripper
3. THC Hydra
4. Aircrack
Visit: 5. L0phtcrack
http://sectools.org/crackers.html to 6. Airsnort
see a list of password attack tools.
7. SolarWinds
8. Pwdump
9. RainbowCrack :
10. Brutus
Fatma Ali – H00084658 05-March-11 1
CCNA Security Chapter 2
Securing Network Devices
2.1.2.1
• Use at least eight characters, the more characters the
better really, but most people will find anything more than
about 15 characters difficult to remember.
• Use a random mixture of characters, upper and lower case,
numbers, punctuation, spaces and symbols.
• Don't use a word found in a dictionary, English or foreign.
Describe some common guidelines • Never use the same password twice.
for choosing strong passwords: • Choose a password that you can remember so that you don't
need to keep looking it up, this reduces the chance of
somebody discovering where you have written it down.
• Choose a password that you can type quickly, this reduces the
chance of somebody discovering your password by looking
over your shoulder.
2.1.2.2
Router>enable
Router#config
Describe the enable secret
password global configuration Router#configure terminal
command: Router(config)#enable secret cisco
Router(config)#
2.1.2.2
Router#config t
How can you protect Console Port
Router(config)#line console 0
access?
Router(config-line)#password cisco
Router(config-line)#login
2.1.2.2
Router#config t
How can you protect Virtual
Router(config)#line vty 0 4
Terminal Line (vty) access?
Router(config-line)#password class
Router(config-line)#login
2.1.2.2
It is equally important to configure a password on it. Router# config
How can you protect Auxiliary Port
t
(aux) access?
Router(config)# line aux 0
Router(config-line)#password SecR3t!pass
Router(config-line)# login
Fatma Ali – H00084658 05-March-11 2
CCNA Security Chapter 2
Securing Network Devices
2.1.2.3
• changing your password regularly can definitely
What can be done toincrease • Be sure to use a complex password for user log in purposes
the security of passwords?
2.1.2.4
R1# conf t
R1(config)# ip domain-name span.com
R1(config)# crypto key generate rsa general-keys modulus 1024
The name for the keys will be: R1.span.com
What command creates a secure % The key modulus size is 1024 bits
list of usernames and passwords in % Generating 1024 bit RSA keys, keys will be non-exportable...[OK]
a database on the router for local
login authentication? R1(config)#
*Dec 13 16:19:12.079: %SSH-5-ENABLED: SSH 1.99 has been
enabled
R1(config)# username Bob secret cisco
R1(config)# line vty 0 4
R1(config-line)# login local
R1(config-line)# transport input ssh
R1(config-line)# exit
2.1.3.1 What should be done to better To better configure security for virtual login connections, the login
configure security for virtual login process should be configured with specific parameters:
connections?
• Delays between successive login attempts
• Login shutdown if DoS attacks are suspected
• Generation of system logging messages for login detection
2.1.3.2 What commands are available to
configure a Cisco IOS device to Router# configure terminal
support enhanced login features?
Router(config)# login block-for seconds attempts tries within
seconds
Router(config)# login quiet-mode access-class {acl-name | acl-
number}
Router(config)# login delay seconds
Router(config)# login on-failure log [every login]
Router(config)# login on-success log [every login]
2.1.3.4 What commands can be used to login on-failure log [every login] generates logs for failed login
keep track of the number of requests.
successful and failed login
attempts.?
login on-success log [every login] generates log messages for
successful login requests.
Fatma Ali – H00084658 05-March-11 3
CCNA Security Chapter 2
Securing Network Devices
2.1.3.4 What command generates a log
message when the login failure rate Router# configure terminal
is exceeded?
Router(config)#security authentication failure rate
2.1.3.4
How can you verify that the login Router# show login
block-for command is configured
and which mode the router is
currently in?
2.1.3.4 What command displays more
information regarding failed login Router# show login failures
attempts?
2.1.3.5
Banners can be grateful they can provide user with warnings like do
not enter if you are not authorized
Why are banners important and
how can they be configured?
Router# config t
Router (config)#banner motd %Authorized Access Only!%
2.1.4.1 Describe the four steps to configure
routers for the SSH protocol: 1. Ensure that the target routers are running a Cisco IOS
Release 12.1(1)T image or later to support SSH.
2. Ensure that each of the target routers has a unique
hostname.
3. Ensure that each of the target routers is using the correct
domain name of the network.
4. Ensure that the target routers are configured for local
authentication, or for authentication, authorization, and
accounting (AAA) services for username or password
authentication, or both. This is mandatory for a router-to-router
SSH connection.
2.1.4.3 Describe how to configure and • R1# show ip ssh
confirm:
SSH version
SSH timeout period • SSH version
Number of authentication retries R1# config t
R1(config)# ip ssh version 2
Fatma Ali – H00084658 05-March-11 4
CCNA Security Chapter 2
Securing Network Devices
• SSH timeout period
R1(config)# ip ssh time-out 60
• Number of authentication retries
R1(config)# ip ssh authentication-retries 2
2.1.4.5 How can Cisco SDM be used to
configure an SSH daemon on a 1. Choose Configure > Additional Tasks > Router Access > SSH
router?
2. Possible status options:
• RSA key is not set on this router
• RSA key is set on this router
3. Enter a modulus size and
• generate a key, if there is
• no key configured
4. To configure SSH on the vty lines,
choose Configure > Additional Tasks > Router Access > VTY
2.1.4.5
To configure SSH on the vty lines,
Using Cisco SDM how are the vty
choose Configure > Additional
lines configured to support SSH?
Tasks > Router Access > VTY
2.2.1.1 What two levels of access to
commands does Cisco IOS • Privilege Levels
software CLI have?
• Role-Based CLI Access
2.2.1.2 Describe the privilege levels
available in the Cisco IOS CLI. • Sixteen privilege levels available
2.2.1.2 What is the command to set
privilege levels? R1# conf t
R1(config)# username USER privilege 1 secret cisco
R1(config)#
R1(config)# privilege exec level 5 ping
R1(config)# enable secret level 5 cisco5
R1(config)# username SUPPORT privilege 5 secret cisco5
R1(config)#
R1(config)# privilege exec level 10 reload
R1(config)# enable secret level 10 cisco10
R1(config)# username JR-ADMIN privilege 10 secret cisco10
R1(config)#
R1(config)# username ADMIN privilege 15 secret cisco123
R1(config)#
2.2.1.3 What are the two methods for • auth: Authenticates a packet by using either the Hashed
Fatma Ali – H00084658 05-March-11 5
CCNA Security Chapter 2
Securing Network Devices
assigning passwords to different Message Authentication Code (HMAC) with Message Digest 5
levels for authentication? (MD5) method or Secure Hash Algorithms (SHA) method.
• Priv: Authenticates a packet by using either the HMAC MD5 or
HMAC SHA algorithms and encrypts the packet using the Data
Encryption Standard (DES), Triple DES (3DES), or Advanced
Encryption Standard (AES) algorithms.
2.2.2.1 How can the limitations of • There is no access control to specific interfaces, ports, logical
assigning privilege levels be interfaces, and slots on a router
overcome?
• Commands available at lower privilege levels are always
executable at higher levels.
• Commands specifically set on a higher privilege level are not
available for lower-privileged users.
• Assigning a command with multiple keywords to a specific
privilege level also assigns any commands associated with the
first keywords to the same privilege level.
2.2.2.2 Role-based CLI provides which
three types of views? • Root View
• CLI View
• Superview
2.2.2.2 Describe the characteristics of Allow a network administrator to assign users and groups of users
Superviews: multiple CLI views at once instead of having to assign a single CLI
view per user with all commands associated to that one CLI view.
2.2.2.3 Describe the steps to create and
manage a specific view: 1. Enable aaa with the global configuration command aaa new-
model. Exit, and enter the root view with the command enable
view command.
2. Create a view using the parser view view-name command.
3. Assign a secret password to the view using the secret
encrypted-password command.
4. Assign commands to the selected view using the parser-mode
{include | include-exclusive | exclude} [all] [interface
interface-name | command] command in view configuration
mode.
5. Exit the view configuration mode by typing the command exit.
2.2.2.4 Describe the steps to create and
manage a superview: 1. Create a view using the parser view view-name superview
command and enter superview configuration mode.
2. Assign a secret password to the view using the secret
Fatma Ali – H00084658 05-March-11 6
CCNA Security Chapter 2
Securing Network Devices
encrypted-password command.
3. Assign an existing view using the view view-name command in
view configuration mode.
4. Exit the superview configuration mode by typing the command
exit.
2.3.1.2 1. What command enables Cisco
IOS image resilience? 1. router(config)# secure boot-image
2. What command takes a
snapshot of the router running 2. router(config)# secure boot-config
configuration and securely archives
it in persistent storage?
2.3.1.3 What command is used to verify
the existence of the secured files in R1# conf t
the archive?
R1(config)# secure boot-config restore filename.
2.3.1.3 Describe the steps to restore a
primary bootset from a secure 1. Reload the router using the reload command.
archive after the router has been
2. From ROMMON mode, enter the dir command to list the
tampered with:
contents of the device that contains the secure bootset file. The
device name can be found in the output of the show secure
bootset command.
3. Boot up the router using the secure bootset image using the boot
command with the filename found in step 2. Once the
compromised router boots, proceed to privileged EXEC mode and
restore the configuration.
4. Enter global configuration mode using conf t.
5. Restore the secure configuration to the supplied filename using
the secure boot-config restore filename.
2.3.1.4 Describe the steps necessary to
recover a lost router password: 1. Connect to the console port.
2. Use the show version command to view and record the
configuration register
3. Use the power switch to turn off the router, and then turn the
router back on.
4. Press Break on the terminal keyboard within 60 seconds of power
up to put the router into ROMmon.
5. At the rommon 1> prompt Type config 0x2142.
6. Type reset at the rommon 2> prompt. The router reboots, but
ignores the saved configuration.
7. Type no after each setup question, or press Ctrl-C to skip the
initial setup procedure.
8. Type enable at the Router> prompt.
Fatma Ali – H00084658 05-March-11 7
CCNA Security Chapter 2
Securing Network Devices
9. Type copy startup-config running-config to copy the NVRAM into
memory.
10. Type show running-config.
11. Enter global configuration and type the enable secret command
to change the enable secret password.
12. Issue the no shutdown command on every interface to be used.
Once enabled, issue a show ip interface brief command. Every
interface to be used should display ‘up up’.
13. Type config-register configuration_register_setting. The
configuration_register_setting is either the value recorded in
Step 2 or 0x2102 .
14. Save configuration changes using the copy running-config
startup-config command.
2.3.1.5 What command secures the router
from the normal password recovery R1(config)# no service password-recovery
process?
• Out-of-band (OOB): Information flows on a dedicated
2.3.2.2 Describe the two paths that the flow
management network on which no production traffic resides.
can take when logging and
managing information flow between
management hosts and the • In-band: Information flows across an enterprise production
managed devices: network, the Internet, or both using regular data channels.
2.3.3.1 Describe 5 different facilities to
which Cisco routers can send log • Console: Console logging is used when modifying or testing the
messages: router while it is connected to the console. Messages sent to the
console are not stored by the router and, therefore, are not very
valuable as security events.
• Terminal lines: Configure enabled EXEC sessions to receive
log messages on any terminal lines. Similar to console logging, this
type of logging is not stored by the router and, therefore, is only
valuable to the user on that line.
• Buffered logging: Store log messages in router memory. Log
messages are stored for a time, but events are cleared whenever
the router is rebooted.
• SNMP traps: Certain thresholds can be preconfigured. Events
can be processed by the router and forwarded as SNMP traps to
an external SNMP server. Requires the configuration and
maintenance of an SNMP system.
Fatma Ali – H00084658 05-March-11 8
CCNA Security Chapter 2
Securing Network Devices
• Syslog: Configure routers to forward log messages to an
external syslog service. This service can reside on any number of
servers, including Microsoft Windows and UNIX-based systems,
or the Cisco Security MARS appliance.
2.3.3.1 Describe the eight levels that Cisco • Commands available at lower privilege levels are always
router log messages fall into in executable at higher levels.
order of severity from highest to
• Commands specifically set on a higher privilege level are not
lowest:
available for lower-privileged users.
2.3.3.2 Describe the two types of systems
contained in Syslog • Syslog servers: Known as log hosts, these systems accept and
implementations:
process log messages from syslog clients.
• Syslog clients: Routers or other types of equipment that
generate and forward log messages to syslog servers.
2.3.3.2 Describe Cisco Security MARS and
explain how it uses logging Cisco Security MARS : is an appliance-based, all-inclusive solution
information:
that provides unmatched insight and control of your existing security
deployment. Part of Cisco's security management lifecycle
2.3.3.3 Describe the steps to activate and
configure system logging: 1. Set the destination logging host
2. Set the log severity (trap) level
3. Set the source interface
4. Enable logging
2.3.3.4 Describe the steps to enable syslog
logging using Cisco Security 1. Choose Configure > Additional Tasks > Router Properties > Logging
Device Manager:
2. Click Edit
3. Check Enable Logging Level and choose the desired logging level
4. Click Add, and enter an IP address of a logging host
5. Click OK
2.3.4.1 Describe SNMP: • Developed to manage nodes, such as servers, workstations,
routers, switches, hubs, and security appliances on an IP network
• All versions are Application Layer protocols that facilitate the
exchange of management information between network devices
• Part of the TCP/IP protocol suite
• Enables network administrators to manage network performance,
find and solve network problems, and plan for network growth
• Three separate versions of SNMP
2.3.4.1 Describe the components of
SNMP: a TCP/IP network management system and the terminology used to
describe them
Fatma Ali – H00084658 05-March-11 9
CCNA Security Chapter 2
Securing Network Devices
2.3.4.1 What are the three actions that a
manager node can use to view or servers, workstations, routers, switches, hubs, and security
alter information in a managed
appliances on an IP network
device?
2.3.4.2 Describe the two types of
community strings as they relate to • Provides read-only access to all objects in the MIB except
SNMP versions 1 and 2:
the community strings.
• Provides read-write access to all objects in the MIB except
the community strings.
2.3.4.4 Describe the security levels
available for the three SNMP • noAuth: Authenticates a packet by a string match of the
security models:
username or community string
• auth: Authenticates a packet by using either the Hashed
Message Authentication Code (HMAC) with Message Digest 5
(MD5) method or Secure Hash Algorithms (SHA) method.
• Priv: Authenticates a packet by using either the HMAC MD5
or HMAC SHA algorithms and encrypts the packet using the Data
Encryption Standard (DES), Triple DES (3DES), or Advanced
Encryption Standard (AES) algorithms.
2.3.4.5 This page shows the steps to
activate an SNMP trap receiver.
2.3.5.1 Describe two ways to set date and
time on a Cisco router. Manually edit the date and time
Configure Network Time Protocol
2.3.5.2 Describe the process of setting
date and time on Cisco routers • Devices are given the IP address of NTP masters. In an NTP
using NTP:
configured network, one or more routers are designated as the
master clock keeper (known as an NTP Master) using the ntp
master global configuration command.
• NTP clients either contact the master or listen for messages
from the master to synchronize their clocks. To contact the
server, use the ntp server ntp-server-address command.
• In a LAN environment, NTP can be configured to use IP
broadcast messages instead, by using the ntp broadcast client
command.
Fatma Ali – H00084658 05-March-11 10
CCNA Security Chapter 2
Securing Network Devices
2.3.5.3 Describe the security features of
NTP: - An encrypted authentication mechanism such as offered by NTP
version 3 or higher
-
2.3.5.3 This page shows the configuration
steps for CLI based NTP
authentication:
2.4.1.2 Describe some of the practices that
help ensure that a network device • Disable unnecessary services and interfaces
is secure: • Disable and restrict commonly configured management services,
such as SNMP
• Disable probes and scans, such as ICMP
• Ensure terminal access security
• Disable gratuitous and proxy Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
• Disable IP-directed broadcast
2.4.1.3 What is best way to determine and
fix the vulnerabilities that exist with Initiated from CLI and executes a script. The AutoSecure feature
a current configuration?
first makes recommendations for fixing security vulnerabilities, and
then modifies the security configuration of the router.
2.4.1.4 What actions does the Security
Audit wizard in Cisco Security • Shut down unneeded servers
Device Manager (SDM) perform?
• Disable unneeded services
• Apply the firewall to the outside interfaces
• Disable or harden SNMP
• Shut down unused interfaces
• Check password strength
• Enforce the use of ACLs
2.4.2.1 Differentiate between the Management plane:
management plane and the The MPP feature in Cisco IOS software provides the capability to
forwarding plane of a Cisco router:
restrict the interfaces on which network management packets are
allowed to enter a device. The MPP feature allows a network operator
to designate one or more router interfaces as management
interfaces. Device management traffic is permitted to enter a device
through these management interfaces. After MPP is enabled, no
interfaces except designated management interfaces will accept
network management traffic destined to the device. Restricting
management packets to designated interfaces provides greater
Fatma Ali – H00084658 05-March-11 11
CCNA Security Chapter 2
Securing Network Devices
control over management of a device. The MPP feature is disabled by
default. When you enable the feature, you must designate one or
more interfaces as management interfaces and configure the
management protocols that will be allowed on those interfaces. The
feature does not provide a default management interface. Using a
single CLI command, you can configure, modify, or delete a
management interface.When you configure a management interface,
no interfaces except that management interface will accept network
management packets destined to the device. When the last
configured interface is deleted, the feature turns itself off.
Forwarding plane:
a router is designed to minimize the state information on individual
packets. The main purpose of a router is to connect multiple
networks and forward packets destined either for its own networks
or other networks. A router is considered a Layer 3 device because
its primary forwarding decision is based on the information in the
Layer 3 IP packet, specifically the destination IP address. This
process is known as routing. When each router receives a packet, it
searches its routing table to find the best match between the
destination IP address of the packet and one of the network
addresses in the routing table. Once a match is found, the packet is
encapsulated in the layer 2 data link frame for that outgoing
interface. A router does not look into the actual data contents that
the packet carries, but only at the layer 3 addresses to make a
forwarding decision, plus optionally other information in the header
for hint on, for example, QoS. Once a packet is forwarded, the
router does not retain any historical information about the packet,
but the forwarding action can be collected into the statistical data,
if so configured
2.4.3.2 Describe the features of Cisco
AutoSecure that are not • SNMP is disabled but will not configure SNMPv3
implemented or are implemented
• SSH is enabled and configured with images that support
differently in Cisco SDM one-step
lockdown: this feature.
• Secure Copy Protocol (SCP) is not enabled--unsecure FTP is.
Fatma Ali – H00084658 05-March-11 12
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Guide: SUSE Linux Enterprise Server For SAP Applications 15 SP1Dokument110 SeitenGuide: SUSE Linux Enterprise Server For SAP Applications 15 SP1Surjeet Singh SaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab #3Dokument13 SeitenLab #3Trần Mỹ LinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCA19Dokument201 SeitenMCA19Bhushan AkolkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duty Cycle Control For Low-Power-Listening MAC ProtocolsDokument14 SeitenDuty Cycle Control For Low-Power-Listening MAC ProtocolspavanterdalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of Each Part & LED Status Display: Sleep (Power Saving) ButtonDokument2 SeitenName of Each Part & LED Status Display: Sleep (Power Saving) ButtonDedi Setiawan100% (1)
- Which Network Topology Has The LEAST Physical Connections Per HostDokument5 SeitenWhich Network Topology Has The LEAST Physical Connections Per Hostyekta10Noch keine Bewertungen
- New CCNA - New Questions 1: October 2nd, 2013Dokument176 SeitenNew CCNA - New Questions 1: October 2nd, 2013luismexxNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenStack NVM 2021Dokument120 SeitenOpenStack NVM 2021AtharvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global WCF Configuration GuideDokument56 SeitenGlobal WCF Configuration GuideAn le100% (1)
- A Seminar ReportDokument13 SeitenA Seminar Reportkeyurbz100% (1)
- Antares Introduction New - 3-06-2022Dokument86 SeitenAntares Introduction New - 3-06-2022aswar agusNoch keine Bewertungen
- WNG R2.1 Product GuidesDokument552 SeitenWNG R2.1 Product GuidesParesh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- The United Republic of Tanzania: Vacancies AnnouncementDokument48 SeitenThe United Republic of Tanzania: Vacancies AnnouncementAnonymous 3QQW2A6vyyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ViciBox v8 1-InstallDokument8 SeitenViciBox v8 1-InstallDen NisNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA4 Exploration: Accessing The WAN (Guided Case Study)Dokument13 SeitenCCNA4 Exploration: Accessing The WAN (Guided Case Study)Patrice AlabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Host Configuration ProtocolDokument19 SeitenDynamic Host Configuration ProtocolarunkraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9618 Cs Cambridge SpecificationDokument44 Seiten9618 Cs Cambridge SpecificationAl-Sami MashrafeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet Vs Books: Preference of Grade 12 Gas Students of Asian College Senior HGH School Quezon City The Problem and Its BackgroundDokument4 SeitenInternet Vs Books: Preference of Grade 12 Gas Students of Asian College Senior HGH School Quezon City The Problem and Its BackgroundPj ChavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- APS-3 With FIELDGenius v1.01Dokument74 SeitenAPS-3 With FIELDGenius v1.01Diyan Purnama PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 9Dokument43 SeitenChapter 1 9Mohammad Fahmi FirdausNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOPAC MP Hardware Guide Unprotected PDFDokument227 SeitenBIOPAC MP Hardware Guide Unprotected PDFPastravanu MariusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lu300 Hevc: Powerful Compact Hevc Field Unit For On-The-Go Live StreamingDokument2 SeitenLu300 Hevc: Powerful Compact Hevc Field Unit For On-The-Go Live StreamingPaul ShepherdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overcurrent Protection-Relay Testing With RTDS HardwareDokument6 SeitenOvercurrent Protection-Relay Testing With RTDS HardwareBitacora InternautaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Parking System (SPS) Architecture Using Ultrasonic DetectorDokument9 SeitenSmart Parking System (SPS) Architecture Using Ultrasonic Detectordecsa putraNoch keine Bewertungen
- It Solution Providers in IndiaDokument23 SeitenIt Solution Providers in IndiacubixtechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wano BR P Wano-Brochure 20150921Dokument8 SeitenWano BR P Wano-Brochure 20150921alfasukarnoNoch keine Bewertungen
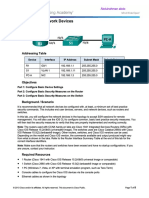
- 11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesDokument8 Seiten11.2.4.6 Lab - Securing Network DevicesSer SarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2600 MagazineVolume 29, Number 4 Winter 2012-2013Dokument34 Seiten2600 MagazineVolume 29, Number 4 Winter 2012-2013Kasi XswlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet - SRX3400,3600 PDFDokument12 SeitenData Sheet - SRX3400,3600 PDFPankajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konica Minolta Bizhub 554e DatasheetDokument4 SeitenKonica Minolta Bizhub 554e Datasheetpdy2Noch keine Bewertungen