Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Reading 18
Hochgeladen von
cfalevel10 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
107 Ansichten2 SeitenLR supply curve slopes upwards and LRAC curves shift downwards. SR supply curve is flat. More elastic = less steep in the SR, supply curves slope downwards and LRAC curves shift upwards. In the LR, economic profits in the industry will be zero. Entry and plant expansion increase supply and lower price and profit Exit and downsizing decrease supply and raise price and profit.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenLR supply curve slopes upwards and LRAC curves shift downwards. SR supply curve is flat. More elastic = less steep in the SR, supply curves slope downwards and LRAC curves shift upwards. In the LR, economic profits in the industry will be zero. Entry and plant expansion increase supply and lower price and profit Exit and downsizing decrease supply and raise price and profit.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
107 Ansichten2 SeitenReading 18
Hochgeladen von
cfalevel1LR supply curve slopes upwards and LRAC curves shift downwards. SR supply curve is flat. More elastic = less steep in the SR, supply curves slope downwards and LRAC curves shift upwards. In the LR, economic profits in the industry will be zero. Entry and plant expansion increase supply and lower price and profit Exit and downsizing decrease supply and raise price and profit.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Reading 18 - Perfect Competition
Friday, August 29, 2008
3:17 PM
Perfectly Competitive Market
o Many firms selling identical products
o Each firm produces only small portion of total supply
o Firms are price takers since they have no leverage to influence the market
price via any actions
o Perfectly elastic demand curve(horizontal straight line) and = Market Price
• But market elasticity is > 0 and less than infinity
o Firm's revenue is linear
Maximizing Profits in PC
o Produce up to the point where MC = MR = Price
o When MR > MC increase in output increases economic profit
o When MR < MC increase in output causes an economic loss. When Price = MR
< MC, firm temporarily shuts down. But when firm is covering its fixed costs,
continue operating
o an increase in industry demand will increase equilibrium price and output. At the
higher price, firms will earn positive economic profits in the short run because the
higher price will exceed average total cost
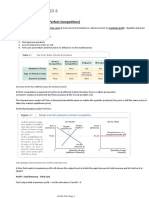
Short Run Supply Curve
o Portion of MC curve that lies at or above the minimum value of the AVC
and always slopes upward
o In the long run, firms will adjust their plant sizes until it maximizes profits
which is the size with the lowest SRAC curve. All firms in PC will operate with
the most efficient(lowest cost) plant size
o Over the LR, the supply curve is typically more elastic(flatter) than in the SR.
This is because they have more capacity to adjust their production scale and
methods over the LR vs the SR.
In PC in the LR, economic profits in the industry will be zero.
• Entry and plant expansion increase supply and lower price and profit
• Exit and downsizing decrease supply and raise price and profit.
• Industry as a whole outputs less but remaining firms output more
• This means the firms are just profitable enough to compensate them for the
risks taken on their capital. NPV = 0
Increasing Cost Industries - experience external diseconomies of scale. LR supply
curve slopes upwards and LRAC curves will shift upwards
Decreasing Cost Industries - experience external economies of scale(benefits of
technology and specialization). LR supply curves slope downward and LRAC curves
shift downwards
Constant Cost Industries - LR supply curve is flat.
More elastic = less steep
In the SR, the economic profit of a firm can be +, - or 0 but in LR it will always be
zero.
Quizzing Notes
• Watch for questions that try to make a supplier seem like a monopoly when it's
really facing PC which means it's a price taker.
• To find max production level, calculate where MC = MR. Also remember that
supply curve will - MC curve portion above AVC.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Employability Skills: Brush Up Your Business StudiesVon EverandEmployability Skills: Brush Up Your Business StudiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting, Maths and Computing Principles for Business Studies V11Von EverandAccounting, Maths and Computing Principles for Business Studies V11Noch keine Bewertungen
- 212 f09 NotesB Ch9Dokument20 Seiten212 f09 NotesB Ch9RIchard RobertsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ2011-Chapter 8: Competitive Markets (Perfect Competition)Dokument10 SeitenEcon2011-Chapter 8: Competitive Markets (Perfect Competition)RosemaryTanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-3 - Perfect Competition EcoDokument13 SeitenUnit-3 - Perfect Competition EcojinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect CompetitionDokument22 SeitenPerfect CompetitionVega AnelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Profit Maximization &cmptitive SupplyDokument92 SeitenChapter 8 Profit Maximization &cmptitive Supplysridhar7892Noch keine Bewertungen
- Market Structures IIDokument31 SeitenMarket Structures IIjarinak924Noch keine Bewertungen
- Average & Marginal Cost SchedulesDokument18 SeitenAverage & Marginal Cost SchedulesnehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IVDokument53 SeitenUnit IVS1626Noch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect CompDokument19 SeitenPerfect CompRishi Kant TamangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect CompititionDokument35 SeitenPerfect CompititionAheli Mukerjee RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 16 Market Structures-Perfect CompetitionDokument41 SeitenLecture 16 Market Structures-Perfect CompetitionDevyansh GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco 111 Principles of Economics - 014352Dokument6 SeitenEco 111 Principles of Economics - 014352ebubeeke846Noch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium of The Firm and Industry Under Perfect CompetitionDokument37 SeitenEquilibrium of The Firm and Industry Under Perfect CompetitionMOHIT SIGIRISETTYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5 MarketsDokument39 SeitenLesson 5 MarketsiitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect Competition 2Dokument3 SeitenPerfect Competition 2Aakash MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Firms Competitive 2022Dokument41 Seiten9 Firms Competitive 2022Pletea GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 6.1Dokument17 SeitenChap 6.1Annie DuolingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect CompetitionDokument41 SeitenPerfect CompetitionPrashantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Powerpoint Slides-2Dokument33 SeitenChapter 8 Powerpoint Slides-2Goitsemodimo Senna100% (1)
- Perfect CompetitionDokument24 SeitenPerfect CompetitionEmon ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit VII Pricing and Output Decisions: Perfect Competition and MonopolyDokument36 SeitenUnit VII Pricing and Output Decisions: Perfect Competition and MonopolyIshan PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium of The Firm Under Perfect CompetitionDokument14 SeitenEquilibrium of The Firm Under Perfect CompetitionShikha kushwahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hul211 Unit2e MKT PCDokument25 SeitenHul211 Unit2e MKT PCTanayJohariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profit MaximizationDokument284 SeitenProfit MaximizationNIKILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap009 Final 21Dokument17 SeitenChap009 Final 21MD TARIQUE NOORNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microeconomics I - Chapter FiveDokument36 SeitenMicroeconomics I - Chapter FiveGena DuresaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco101 Lec 14Dokument16 SeitenEco101 Lec 14Lulu LemonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competitive Markets: B 2 B MarketingDokument46 SeitenCompetitive Markets: B 2 B MarketingShikha TiwaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect Competition: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDokument12 SeitenPerfect Competition: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleValarmathy SankaralingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopoly MarketDokument5 SeitenMonopoly Marketkevinkoladiya43Noch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect Competition (Part 1)Dokument18 SeitenPerfect Competition (Part 1)Wasif KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 09Dokument8 SeitenChap 09Thabo MojavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microeconomics Chapter 5Dokument8 SeitenMicroeconomics Chapter 5Alejandra jpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microeconomics AssignmentDokument16 SeitenMicroeconomics Assignmentjamila mufazzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Markert Structures 2019Dokument85 SeitenMarkert Structures 2019Criss JasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- (6-5) /5 (131-131) /131 1 0 or Simply Alpha or Infinity SymbolDokument7 Seiten(6-5) /5 (131-131) /131 1 0 or Simply Alpha or Infinity SymbolMaria Emarla Grace CanozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 - Perfect Competition - PPMDokument33 Seiten6 - Perfect Competition - PPMShashwat JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC 2 RIGHTDokument65 SeitenPC 2 RIGHTAnuradha SaikiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect CompetitionDokument31 SeitenPerfect CompetitionAnand ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.5-2 Theory of The Firm and Market Structures HL Only - MS 2Dokument94 Seiten1.5-2 Theory of The Firm and Market Structures HL Only - MS 2Shuchun YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Price and Output DeterminationDokument26 SeitenPrice and Output DeterminationJiss George Mancherikalam0% (1)
- Economics HelpsDokument3 SeitenEconomics HelpssahilsureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 8 Firms CompetitiveDokument47 SeitenLecture 8 Firms CompetitiveKhan ArafatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 - Monopolistic CompetitionDokument22 Seiten8 - Monopolistic CompetitionShashwat JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented By:: Arpita Tripathy Gayatri Kumari Sahu Koustav Mohapatra Pritish Kumar Panda Guided By: DR - Ashamayee MishraDokument28 SeitenPresented By:: Arpita Tripathy Gayatri Kumari Sahu Koustav Mohapatra Pritish Kumar Panda Guided By: DR - Ashamayee MishraBhagyalaxmi sahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Firms in Competitive MarketsDokument34 SeitenFirms in Competitive MarketsRomeo DupaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic Module 7Dokument8 SeitenEconomic Module 7PatrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Diagrams A2 Business EconomicsDokument16 SeitenKey Diagrams A2 Business EconomicsEl Niño SajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Profit Maximisation and Competitive SupplyDokument26 SeitenChapter 8 Profit Maximisation and Competitive SupplyRitesh RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Structures HandoutDokument10 SeitenMarket Structures HandoutSuzanne HolmesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imperfect Comp. - Monopolistic CompetitionDokument12 SeitenImperfect Comp. - Monopolistic CompetitionPPE-T-3757 Hrushikesh TetwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Report. Perfect CompetitionDokument31 SeitenGroup Report. Perfect CompetitionMary Ann Manalo PanopioNoch keine Bewertungen
- MGMT-5245 Managerial Economics: Market Power: MonopolyDokument22 SeitenMGMT-5245 Managerial Economics: Market Power: MonopolyYining LiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopoly Oligopoly Monopolistic Competition Perfect CompetitionDokument8 SeitenMonopoly Oligopoly Monopolistic Competition Perfect CompetitionDerry Mipa SalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium of The Firm and IndustryDokument4 SeitenEquilibrium of The Firm and IndustryJoe EgwuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect CompetitionDokument15 SeitenPerfect CompetitionS1626Noch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Economics: Monopoly Profit MaximizationDokument13 SeitenManagerial Economics: Monopoly Profit MaximizationPrajwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopoly Profit MaximizationDokument29 SeitenMonopoly Profit MaximizationArmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LC To DC Sensitivity GammaLCDokument2 SeitenLC To DC Sensitivity GammaLCcfalevel1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reading 30Dokument1 SeiteReading 30cfalevel1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reading 24Dokument1 SeiteReading 24cfalevel1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reading 20Dokument2 SeitenReading 20cfalevel1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reading 17Dokument1 SeiteReading 17cfalevel1Noch keine Bewertungen
- CFA L1 Study PlanDokument2 SeitenCFA L1 Study Plancfalevel167% (3)
- Reading 16Dokument3 SeitenReading 16cfalevel1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reading 1&2 - Code of Ethics and SPC: ProfessionalismDokument7 SeitenReading 1&2 - Code of Ethics and SPC: Professionalismcfalevel1100% (1)
- Reading 7Dokument3 SeitenReading 7cfalevel1100% (1)
- Readings 3&4Dokument2 SeitenReadings 3&4cfalevel1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management Accounting Concepts and Techniques PDFDokument310 SeitenManagement Accounting Concepts and Techniques PDFvishnupriya100% (1)
- Bad Loans and E Ciency in Italian BanksDokument51 SeitenBad Loans and E Ciency in Italian BanksBishop PantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Economics-Q3-Module-5Dokument20 SeitenApplied Economics-Q3-Module-5manuel advincula71% (7)
- Strategic Business Plan - Shake Shack Burger PDFDokument21 SeitenStrategic Business Plan - Shake Shack Burger PDFShamsa Al Jaradi100% (4)
- Soal OSK-Inggris 2015-2020Dokument24 SeitenSoal OSK-Inggris 2015-2020NAWANG SASI NURUL NAWANG SASI NURULNoch keine Bewertungen
- MarketingDokument28 SeitenMarketingSaksham ChhabraNoch keine Bewertungen
- A3 Cola WarsDokument29 SeitenA3 Cola WarsBharatSubramonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2020Dokument20 SeitenMark Scheme (Results) January 2020samin3shohel0% (1)
- ECO120 Final Assessment Part B (40 Marks) SR11704 Mac-Aug21Dokument4 SeitenECO120 Final Assessment Part B (40 Marks) SR11704 Mac-Aug21Arif LoqmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC1301 Monoploy Practise QuestionsDokument32 SeitenEC1301 Monoploy Practise QuestionsKelly MerieNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChapterDokument50 SeitenChapterShital VaghasiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Challenges of Effective Cash Management in Nigerian Super Markets (A Study of Chime Super Market, Ishiagu)Dokument40 SeitenChallenges of Effective Cash Management in Nigerian Super Markets (A Study of Chime Super Market, Ishiagu)MajestyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaserch MethdologyDokument132 SeitenReaserch Methdologymelanawit100% (1)
- Marathon As BusinessDokument27 SeitenMarathon As Businessmm1ashanshahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study QuestionsDokument2 SeitenCase Study QuestionsІнна ЗорянськаNoch keine Bewertungen
- CitibankDokument12 SeitenCitibankshubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BUAD 805 SummaryDokument5 SeitenBUAD 805 SummaryZainab IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Percentage Questions For CATDokument17 SeitenPercentage Questions For CATStartup SkillsNoch keine Bewertungen
- FCI-Management Discipline QuestionsDokument9 SeitenFCI-Management Discipline QuestionsAnnie AnzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pie Kelompok 3Dokument15 SeitenPie Kelompok 3Marsha HafizhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - Part 1Dokument17 SeitenChapter 8 - Part 1dylanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrzysuskiM BerryRatioPaperDokument10 SeitenPrzysuskiM BerryRatioPapersuperandrosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCM CycleDokument45 SeitenSCM CycleMuhammad DuraidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profit TheoryDokument21 SeitenProfit TheoryWaseem KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus BA - Economics HONS I To III Sem - 2011-12 PDFDokument15 SeitenSyllabus BA - Economics HONS I To III Sem - 2011-12 PDFDipankar SardarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic Foundations of StrategyDokument57 SeitenEconomic Foundations of StrategyqunNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMB 541 CASE Marketing Heads Conundrum R PDFDokument9 SeitenIMB 541 CASE Marketing Heads Conundrum R PDFs4shivendra100% (1)
- Overview of The Module Purpose of The ModuleDokument11 SeitenOverview of The Module Purpose of The ModuleJulia Rosauro BalsamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitalism: Meaning, Stages, Features, Merits, De-Merits and ConclusionDokument12 SeitenCapitalism: Meaning, Stages, Features, Merits, De-Merits and ConclusionAnand RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oman Limited Liability CompanyDokument9 SeitenOman Limited Liability Companyadeel asgharNoch keine Bewertungen