Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
0209 Case 2
Hochgeladen von
willygopeOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
0209 Case 2
Hochgeladen von
willygopeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00302.
x
COM FEBRUARY 2009 CASE 2 b pa _ 3 0 2 535..538
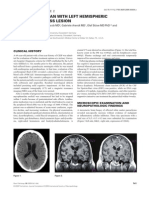
64-YEAR-OLD MAN WITH MULTIPLE CEREBRAL LESIONS bpa_302 535..538
Nicolas Dea MD2; Manuela Pelmus MD1; David Mathieu MD2; François Belzile MD3; Denis Bergeron MD3;
Sylvie Gosselin MD4; Ana-Maria Tsanaclis MD1
1
Department of Pathology, 2 Service of Neurosurgery, 3 Department of Neuroadiology, 4 Department of Neurology, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de
Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Québec, Canada.
angioplasty was performed for progression of the stenosis in the
CLINICAL HISTORY left common carotid artery, proximal to the initial stenotic stented
A 64 year-old man presented with multiple transient cerebral area. After an additional seven months of being asymptomatic, he
ischemic attacks progressing for a week consisting of right-sided presented, once again, with right hemiparesis. A head CT scan
hemiparesis. The patient had a history of squamous cell cancer of revealed multiple hyperdense lesions in the left carotid artery terri-
the pharynx managed by chemotherapy and radiotherapy 10 years tory. Contrast-enhanced MRI confirmed the presence of 15 hemor-
earlier. Six years ago, he had a lingual recurrence of his cancer, rhagic lesions restricted to that vascular territory (Figure 3). These
for which he underwent a partial glossectomy with left cervical lesions were hypointense on T1WI and T2WI with mild focal gado-
dissection. linium enhancement and showed no diffusion restriction. A carotid
Radiologic investigation revealed a subtotal stenosis of the left angiogram showed the patency of the left carotid axis. A FDG PET
internal carotid artery without cerebral infarction (Figure 1 and 2). scan revealed no active systemic neoplasm and hypometabolic
In view of his prior history of surgery and radiation in the left cerebral lesions.
cervical area, he was treated by percutaneous angioplasty and A left frontal open biopsy was performed and 3 grouped lesions
stenting. He was then asymptomatic for about 8 months when were removed and submitted for pathology.
ischemic episodes began to recur. Repeat percutaneous left carotid
PATHOLOGY
Gross examination of the specimen revealed dark brown fragments
of intermediate consistency. Histopathological examination
revealed a necrotic and hemorrhagic lesion formed by an irregular
set of vascular channels (Figure 4). These channels were lined by
highly anaplastic cells with marked pleomorphism and numerous
mitoses (Figure 5). The chromatin content of the nucleus was
Figure 1. Figure 2.
Brain Pathology 19 (2009) 535–538 535
© 2009 The Authors; Journal Compilation © 2009 International Society of Neuropathology
Correspondence
Figure 3.
highly variable. There was a voluminous vessel with endoluminal Tumor cells revealed a strong positive reaction for CD31 and
proliferation of neoplastic cells (Figure 6). The tumor cells rested CD34. The reaction for factor VIII was positive but more
on a conjunctive tissue stroma. In addition, there were macroph- delicate. Reticulin surrounded vascular channels and some actin
ages with hemosiderin-filled cytoplasm, indicating remote bleed- positivity was noted in the vessels walls. Immunostaining for
ing. The interface with the adjacent cerebral tissue was sharply GFAP, EMA, Melan-A and HMB-45 did not elicit any reaction. A
demarcated and this tissue showed a mild hypercellularity in the positive reaction for GFAP was noted in the peripheral reactive
form of a significant reactive gemistocytic astrocytosis. astrocytosis.
Figure 4.
536 Brain Pathology 19 (2009) 535–538
© 2009 The Authors; Journal Compilation © 2009 International Society of Neuropathology
Correspondence
Figure 5.
Figure 6.
Brain Pathology 19 (2009) 535–538 537
© 2009 The Authors; Journal Compilation © 2009 International Society of Neuropathology
Correspondence
REFERENCES
DIAGNOSIS
1. Ben-Izhak O, Vlodavsky E, Ofer A, Engel A, Nitecky S, Hoffman A
Cerebral angiosarcoma.
(1999) Epithelioid angiosarcoma associated with a Dacron vascular
graft. Am J Surg Pathol 23(11):1418–1422.
2. Fehrenbacher JW, Bowers W, Strate R, Pittman J (1981)
DISCUSSION Angiosarcoma of the aorta associated with a Dacron graft. Ann
Thorac Surg 32(3):297–301.
Angiosarcoma is a rare tumor accounting for less than one percent 3. Laskin WB, Silverman TA, Enzinger FM (1988) Postradiation soft
of all sarcomas (10). It occurs typically in the skin and soft tissues tissue sarcomas, an analysis of 53 cases. Cancer 62:2330–2340.
of the head and neck. It is a very malignant neoplastic proliferation 4. Liassides C, Katsamaga M, Deretzi G, Koutsimanis V, Zacharakis G
arising from vascular endothelial cells. Systemic metastasis at the (2004) Cerebral metastasis from heart angiosarcoma presenting as
time of diagnosis is reported to be as high as 80% (4). Central multiple hematoma. J Neuroimaging 14(1):71–73.
nervous system (CNS) involvement has been described, but is quite 5. Matsuno A, Nagashima T, Tajima Y, Sugano I (2005) A diagnostic
unusual. Only 17 cases of cerebral angiosarcoma primary to the pitfall: Angiosarcoma of the brain mimicking cavernous angioma. J
CNS have been reported in the English literature (5, 6). Cerebral Clin Neurosci 12(6):688–691.
6. Mena H, Ribas JL, Enzinger FM, Parisi JE (1991) Primary
metastases are also rare; only 21 cases have been described (for
angiosarcoma of the central nervous system. J of Neurosurg
references please go to: http://path.upmc.edu/divisions/neuropath/
75:73–76.
bpath/cases/case181/dx.html ). The typical primary site for meta- 7. Okada M, Takeuchi E, Mori Y, Ichihara S, Usui A, Ueda Y (2004) An
static cerebral angiosarcoma is the heart, accounting for 57% of autopsy case of angiosarcoma arising around a woven Dacron
cases. Other primary sites have been described, such as Dacron prosthesis after a Cabrol operation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg
aortic vascular grafts, aorta, pleura, skin, liver, penis, bone, pla- 127(6):1843–1845.
centa and the orbit. Cerebral metastases are multiple in 57.9% of 8. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AR (1948) Sarcomas
the cases. The described risk factors for the development of induced in rats by implanting cellophane. Proc Soc Exper Biol Med
angiosarcomas are radiation therapy, foreign object (8), chronic 67:33–34.
lymphedema associated with radical mastectomy, A-V fistulas and 9. Van der Laan BF, Baris G, Gregor RT, Hilgers FJ, Balm AJ (1995)
Radiation induced tumors of the head and neck. J Laryngol Otol
certain environmental carcinogens like vinyl chloride, arsenic and
109:346–349.
Thorotrast.
10. Weiss SW, Goldblum JR (1995) Malignant Vascular Tumors. In: Soft
In a series of 53 post-radiation sarcomas (3), Laskin and al. Tissue Tumors, chapter25, pp. 917–938, Mosby: London.
reported that the most frequent radiation-induced sarcoma was 11. Weiss WM, Riles TS, Gouge TH, Mizrachi HH (1991) Angiosarcoma
malignant fibrous histiocytoma (68%) and that an angiosarcoma at the site of a Dacron vascular prosthesis: a case report and literature
represented only one case (2%), on the thoracic wall. Another review. J Vasc Surg 14(1):87–91.
series (9) of 2500 patients treated for ENT cancer reported only 5
sarcomas in the irradiated zone. None were angiosarcoma.
Vascular prostheses, especially Dacron prostheses, also have the
ABSTRACT
potential to induce malignant mesenchymatous changes (1, 2, 7, A 64 year-old man, previously treated with radiotherapy for a pha-
11). We, however, did not find any cases that occurred after inser- ryngeal carcinoma, presented with multiple transient cerebral
tion of a vascular endoprosthesis. ischemic attacks. Investigations revealed subtotal stenosis of the
The histologic examination of this case shows typical features left internal carotid artery, for which he underwent angioplasty.
of angiosarcoma: atypical cells forming an irregular vascular Several months later he presented with multiple cerebral lesions
network. The positivity of these cells for endothelial markers con- confined to the vascular territory of the stented carotid artery.
firms the diagnosis. Immunohistochemistry for factor VIII was Histopathological examination of these lesions revealed highly
slightly positive but cases with poorly differentiated tumors are anaplastic cells forming irregular sets of vascular channels with
reported with equivocal positivity for this marker. endoluminal proliferation. Positive reaction for CD31 and CD34
We believe this patient had an angiosarcoma of the carotid artery confirmed the diagnosis of metastatic angiosarcoma. Considering
with distal tumor embolisms since all the lesions were restricted to the past history of radiation to the cervical area and the fact that
this vascular territory, and presented as stroke-like episodes. The these lesions were all confined to a single vascular territory, we
carotid stent might have contributed to the development of the believe this patient developed an angiosarcoma of the carotid
tumor in tissues already sensitized by the prior irradiation. The artery with distal tumor embolism. No other primary sources were
brain tumors may also be primary angiosarcomas, but in view of found despite extensive investigation. Angiosarcoma is a rare
the multiplicity of the lesions and the restriction to the vascular tumor with cerebral involvement being even more unusual. Only 17
territory of the left internal carotid artery, this hypothesis seems cases of primary cerebral angiosarcoma are described and only 21
less likely. Investigations did not reveal any other possible primary cases of cerebral metastases from other sites have been reported,
source. Unfortunately, even though a mass of tumoral cells was the heart being the single most often cited primary site. Radiation
identified inside one of the specimen’s vascular channels, we are therapy is a well known risk factor for this type of tumor. We
not able to ascertain that the primary site is the carotid artery, as the found no cases of post-radiotherapy carotid angiosarcoma in the
family of the patient refused the proposed autopsy. literature.
538 Brain Pathology 19 (2009) 535–538
© 2009 The Authors; Journal Compilation © 2009 International Society of Neuropathology
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 1208 Case 1Dokument2 Seiten1208 Case 1willygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0709 Case 2Dokument4 Seiten0709 Case 2willygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1109 Case 2Dokument4 Seiten1109 Case 2willygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1208 Case 2Dokument4 Seiten1208 Case 2willygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1009 Case 2Dokument4 Seiten1009 Case 2willygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma of The Infundibular-Hypothalamic Region: Case Report and Literature ReviewDokument6 SeitenEpithelioid Hemangioendothelioma of The Infundibular-Hypothalamic Region: Case Report and Literature ReviewcarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0909 Case 2Dokument2 Seiten0909 Case 2willygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy A Noninvasive Diagno - 2006 - Magnetic ResonancDokument3 SeitenMagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy A Noninvasive Diagno - 2006 - Magnetic Resonanctejas1578Noch keine Bewertungen
- A 45-Year Old Male With Left-Sided Hemihypesthesia: Clinical HistoryDokument4 SeitenA 45-Year Old Male With Left-Sided Hemihypesthesia: Clinical HistorywillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 5 5 Pontine Atypical Neurocytoma Case Report 副本Dokument8 Seiten5 5 5 Pontine Atypical Neurocytoma Case Report 副本singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Follicular Carcinoma of Thyroid Presenting As Brain MetastasisDokument3 SeitenFollicular Carcinoma of Thyroid Presenting As Brain MetastasisArif Susilo RahadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ochalski 2010Dokument5 SeitenOchalski 2010Felipe RohamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intracranial Hemorrhage With Cerebral Venous Sinus ThrombosisDokument2 SeitenIntracranial Hemorrhage With Cerebral Venous Sinus ThrombosisNeurologia homicNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Rare Case of Space Occupying Lesion of Brainstem in An Elderly Male PatientDokument3 SeitenA Rare Case of Space Occupying Lesion of Brainstem in An Elderly Male PatientInternational Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Research (IJCBR)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abdollahi Et AlDokument5 SeitenAbdollahi Et AlMarc DaouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calcified Pseudoneoplasm of The Neuraxis Capnon A Lesson Learnt From A Rare Entity PDFDokument3 SeitenCalcified Pseudoneoplasm of The Neuraxis Capnon A Lesson Learnt From A Rare Entity PDFKisspetre PetreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jhua16000143 PDFDokument3 SeitenJhua16000143 PDFsamiratumananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebellar Hemangioblastoma-A Rare EntityDokument10 SeitenCerebellar Hemangioblastoma-A Rare EntityJay LeheriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Intracranial Leiomyoma: A Case Report and Literature ReviewDokument3 SeitenPrimary Intracranial Leiomyoma: A Case Report and Literature ReviewcandiddreamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebral Edema Associated With MeningiomaDokument3 SeitenCerebral Edema Associated With MeningiomaEstefania Ramirez CardonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0309 Case 2Dokument4 Seiten0309 Case 2willygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1009 Case 1Dokument4 Seiten1009 Case 1willygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- En Plaque MeningiomaDokument3 SeitenEn Plaque Meningiomasilvia erfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acu Accident LumbarDokument2 SeitenAcu Accident Lumbarrswongym449Noch keine Bewertungen
- Demographics of Brain Metastasis: ANA E N TA ADokument8 SeitenDemographics of Brain Metastasis: ANA E N TA AhangryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurocytoma/rhabdomyoma (Myoneurocytoma) of The CerebellumDokument6 SeitenNeurocytoma/rhabdomyoma (Myoneurocytoma) of The CerebellumRafael Mujica OreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Displasia Cortical de TaylorDokument11 SeitenDisplasia Cortical de TaylorOscar F. Ochoa RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- M: Elaine Crystine Vieira de Paiva Rua Pedro I, 1.033 Centro 60035-101 - Fortaleza - CE - BrazilDokument2 SeitenM: Elaine Crystine Vieira de Paiva Rua Pedro I, 1.033 Centro 60035-101 - Fortaleza - CE - Brazilpruebaprueba321765Noch keine Bewertungen
- A 10-Year Old Girl With Neck Pain: Clinical HistoryDokument4 SeitenA 10-Year Old Girl With Neck Pain: Clinical HistorywillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- E - Uniform Round Tumour Cells With Small Nucleus and Clear Vacuolated CytoplasmDokument16 SeitenE - Uniform Round Tumour Cells With Small Nucleus and Clear Vacuolated CytoplasmAien LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 31-Year-Old Man With Balint'S Syndrome and Visual Problems: Clinical History and NeuroimagingDokument4 Seiten31-Year-Old Man With Balint'S Syndrome and Visual Problems: Clinical History and NeuroimagingwillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma With Metastasis To The OrbitDokument3 SeitenA Case of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma With Metastasis To The OrbitjamesyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vol-1, Issue-1 Prospective Study of Peripheral Nerve Tumors Over A Period of 2 YearsDokument4 SeitenVol-1, Issue-1 Prospective Study of Peripheral Nerve Tumors Over A Period of 2 YearsijhrmimsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Neurosurgery Cases and ReviewsDokument5 Seiten1 Neurosurgery Cases and ReviewsintodoieblissNoch keine Bewertungen
- White Matter Injury After Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic StrategiesDokument12 SeitenWhite Matter Injury After Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic StrategiesSerque777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Histopathological Changes in Acute Ischemic Stroke: R I G I N A L A P E RDokument13 SeitenHistopathological Changes in Acute Ischemic Stroke: R I G I N A L A P E RJosé Luis García MezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCS Current Concepts 2k18Dokument6 SeitenCCS Current Concepts 2k18Guna KalanjiyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 678 FullDokument5 Seiten678 Fullakram socisseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Image Fusion - Craniofacial SurgeryDokument4 SeitenImage Fusion - Craniofacial SurgeryMarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bedeschi 2006Dokument8 SeitenBedeschi 2006Modou NianeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apathy and Hypersomnia Are Common Features of Myotonic DystrophyDokument7 SeitenApathy and Hypersomnia Are Common Features of Myotonic DystrophyAnnisa HusainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tumores en CuelloDokument6 SeitenTumores en CuellokalixinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Neuroimages: Progressive Facial Hemiatrophy (Parry-Romberg Syndrome) With Ipsilateral Cerebral HemiatrophyDokument2 SeitenTeaching Neuroimages: Progressive Facial Hemiatrophy (Parry-Romberg Syndrome) With Ipsilateral Cerebral HemiatrophyRifky Budi TriyatnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Extraskeletal Ewing Sarcoma of The Sinonasal Tract - A Rare Case Report and Review of The LiteratureDokument7 SeitenPrimary Extraskeletal Ewing Sarcoma of The Sinonasal Tract - A Rare Case Report and Review of The LiteraturemohammadsayfooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain Imaging in Colloid CystDokument5 SeitenBrain Imaging in Colloid CystMohamed Farouk El-FaresyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tumefactive Demyelinating Lesions: Nine Cases and A Review of The LiteratureDokument9 SeitenTumefactive Demyelinating Lesions: Nine Cases and A Review of The LiteraturePS NeuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Middle and Posterior Fossa AspergillomaDokument4 SeitenMiddle and Posterior Fossa AspergillomamuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurohistiocytosis: Two Cases of A Rare DiseaseDokument8 SeitenNeurohistiocytosis: Two Cases of A Rare DiseaseIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging - 2010 - Kumar - Eccentric Target Sign in Cerebral Toxoplasmosis Neuropathological Correlate ToDokument4 SeitenMagnetic Resonance Imaging - 2010 - Kumar - Eccentric Target Sign in Cerebral Toxoplasmosis Neuropathological Correlate ToMartha OktaviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prion BrainDokument2 SeitenPrion BrainD SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malignant Myopericytoma: Report of A New Case and Review of The LiteratureDokument6 SeitenMalignant Myopericytoma: Report of A New Case and Review of The LiteratureRachel AutranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meningeal Solitary Fibrous Tumor: Jong-Myong Lee, M.DDokument3 SeitenMeningeal Solitary Fibrous Tumor: Jong-Myong Lee, M.DFerry TebeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolated Lesser Trochanter Fracture Associated With LeukemiaDokument3 SeitenIsolated Lesser Trochanter Fracture Associated With LeukemiaIndora DenniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Horners Syndrome Resulting From Agenesis of The Internal Carotid Artery: Report of A Third CaseDokument2 SeitenHorners Syndrome Resulting From Agenesis of The Internal Carotid Artery: Report of A Third CaseDanielle SangalangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syndromes of The Orbital Fissure, Cavernous Sinus, Cerebello-Pontine Angle, and Skull BaseDokument10 SeitenSyndromes of The Orbital Fissure, Cavernous Sinus, Cerebello-Pontine Angle, and Skull BaseMarlene Arbeu ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intracranial Epidermoid CystDokument3 SeitenIntracranial Epidermoid CystWildaHanimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neoplastic Cerebral Aneurysm From Metastatic Lung CarcinomaDokument3 SeitenNeoplastic Cerebral Aneurysm From Metastatic Lung CarcinomaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROCEEDINGS OF THE PAEDlATRlC NEURO-ONCOLOGY TUMOUR BOARDDokument9 SeitenPROCEEDINGS OF THE PAEDlATRlC NEURO-ONCOLOGY TUMOUR BOARDfriiday.qNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRI Findings in Susac SyndromeDokument6 SeitenMRI Findings in Susac SyndromeLeonardoBubackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry BasicsDokument2 SeitenGeometry BasicswillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A 45-Year Old Male With Left-Sided Hemihypesthesia: Clinical HistoryDokument4 SeitenA 45-Year Old Male With Left-Sided Hemihypesthesia: Clinical HistorywillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Tiling of The Plane With TrianglesDokument6 SeitenA Tiling of The Plane With TriangleswillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trig SubstitutionDokument13 SeitenTrig SubstitutionwillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chords RegionsDokument3 SeitenChords RegionswillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A 10-Year Old Girl With Neck Pain: Clinical HistoryDokument4 SeitenA 10-Year Old Girl With Neck Pain: Clinical HistorywillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 31-Year-Old Man With Balint'S Syndrome and Visual Problems: Clinical History and NeuroimagingDokument4 Seiten31-Year-Old Man With Balint'S Syndrome and Visual Problems: Clinical History and NeuroimagingwillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0610case1 Metastatic MelanomaDokument4 Seiten0610case1 Metastatic MelanomawillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1009 Case 1Dokument4 Seiten1009 Case 1willygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0909 Case 2Dokument2 Seiten0909 Case 2willygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A 7-Year-Old Boy Dying of Acute Encephalopathy: Case History Autopsy FindingsDokument4 SeitenA 7-Year-Old Boy Dying of Acute Encephalopathy: Case History Autopsy FindingswillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- References: American Society For Clinical Pathology 2006 Resident In-Service ExaminationDokument9 SeitenReferences: American Society For Clinical Pathology 2006 Resident In-Service ExaminationwillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0309 Case 2Dokument4 Seiten0309 Case 2willygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Item Descriptors Anatomical Pathology: American Society For Clinical Pathology 2006 Resident In-Service ExaminationDokument6 SeitenItem Descriptors Anatomical Pathology: American Society For Clinical Pathology 2006 Resident In-Service ExaminationwillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2006FallRISE ContentOutlineDokument1 Seite2006FallRISE ContentOutlinewillygopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Whats New PDFDokument74 SeitenWhats New PDFDe Raghu Veer KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Democracy in SomalilandDokument118 SeitenDemocracy in SomalilandAbdirahman IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 9:: What Did You See at The Zoo?Dokument11 SeitenUnit 9:: What Did You See at The Zoo?ARiFin MoHaMedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook Fulfilling Destiny As Demanded by GodDokument94 SeitenEbook Fulfilling Destiny As Demanded by GodIfeanyi OmeiheakuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teacher LOA & TermsDokument3 SeitenTeacher LOA & TermsMike SchmoronoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Network TOPCIT PDFDokument80 Seiten03 Network TOPCIT PDFJayson AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fairy Rebel PDFDokument2 SeitenFairy Rebel PDFSamuel0% (1)
- General Mathematics - Module #3Dokument7 SeitenGeneral Mathematics - Module #3Archie Artemis NoblezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gayatri Mantram SPDokument17 SeitenGayatri Mantram SPvaidyanathan100% (1)
- Physical Education: Learning Activity SheetDokument13 SeitenPhysical Education: Learning Activity SheetRhea Jane B. CatalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance ManagerDokument4 SeitenMaintenance Managerapi-121382389Noch keine Bewertungen
- SDS SheetDokument8 SeitenSDS SheetΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Market Making Agreement 31.03Dokument13 SeitenRevised Market Making Agreement 31.03Bhavin SagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- (154 Marks) : (1 Mark)Dokument40 Seiten(154 Marks) : (1 Mark)Manav NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter02 AnglesDokument40 SeitenChapter02 Angleslen16328100% (1)
- Electoral Politics Module-2, Hand Out 2, Class 9, Civics, Lesson-3, Electoral PoliticsDokument4 SeitenElectoral Politics Module-2, Hand Out 2, Class 9, Civics, Lesson-3, Electoral PoliticsSaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ComeniusDokument38 SeitenComeniusDora ElenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prejudicial QuestionDokument1 SeitePrejudicial QuestionlmafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Deformity in The Pueblo AreaDokument3 SeitenCranial Deformity in The Pueblo AreaSlavica JovanovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Scopes TrialDokument10 SeitenThe Scopes Trialapi-607238202Noch keine Bewertungen
- ShakespeareDokument12 SeitenShakespeareapi-510189551Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spanish Web PDFDokument36 SeitenSpanish Web PDFSergio SayagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Vagabond SongDokument4 SeitenA Vagabond SongLiLiana DewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDLSS Numerical Assignments - DOC FormatDokument3 SeitenHDLSS Numerical Assignments - DOC FormatNikhil UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies GENERAL CONTENT: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDokument21 SeitenNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies GENERAL CONTENT: Multiple-Choice Questionslisa voNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movie Review TemplateDokument9 SeitenMovie Review Templatehimanshu shuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filters SlideDokument17 SeitenFilters SlideEmmanuel OkoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIS Tutorial 4 AnswerDokument8 SeitenMIS Tutorial 4 AnswerChia Kong Haw0% (1)
- The "Write" Way: A Judicial Clerk's Guide To Writing For The CourtDokument92 SeitenThe "Write" Way: A Judicial Clerk's Guide To Writing For The Courtunknown07blackstarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Exercise: 8Dokument5 SeitenLab Exercise: 8Test UserNoch keine Bewertungen