Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Oscillating Spring
Hochgeladen von
Ibrahim BtOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Oscillating Spring
Hochgeladen von
Ibrahim BtCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
002 Oscillating Spring
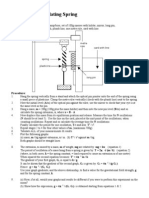
Apparatus:
Spring and cork, tall retort stand/clamp/boss, set of 100g masses with holder, mirror, long pin,
small piece of plasticine, stop watch, plumb line, one metre rule, card with line.
metre
rule
card with line
mirror
spring
plasticine
long pin
Procedure:
1. Hang the spring vertically from a stand and attach the optical pin pointer onto the end of the spring using
a small piece of plasticine. Clamp the metre ruler vertically (check with the plumb line) next to the spring.
2. Note the initial level (A/m) of the optical pin against the ruler, use the mirror to check that your eye is at
the same level as the pin.
3. Hang a mass, m = 200g (100g plus the mass holder) and then note the new pin level (B/m) and so
calculate the spring extension, x, where x = B - A
4. Now displace this mass from its equilibrium position and release. Measure the time for N oscillations
(N should be at least 5). Use the line on the card, placed at the mid-point of the oscillations, when
counting oscillations. Repeat and so calculate the average time for N oscillations.
Finally calculate the period for one oscillation, T/s and also T2 / s2.
5. Repeat stages 2 to 4 for four other values of m, (maximum 700g).
6. Tabulate ALL of your measurements & results.
7. Plot the following graphs:
(a) mass, m / kg against extension, x / m. (b) T2 / s2 against m / kg.
Both graphs should be straight lines.
8. The extension, x caused by a mass, m of weight, mg are related by: mg = kx (equation 1)
The period of oscillation of a mass hung from a spring is given by: T = 2π √ (m / k) (equation 2)
(where, in both cases, k = the spring constant, = load required to cause an extension x of one metre)
When squared the second equation becomes: T2 = 4π 2 m / k
The gradient of your first graph, G1 is equal to k / g.
It can be shown that the gradient of the second graph, G2 is given by: G2 = 4π 2 / (g G1 )
Hence: g = 4π 2 / (G1 G2)
Use your graph gradients, and the above relationship, to find a value for the gravitational field strength, g
and for the spring constant, k.
9. (a) How, if at all, would your graphs and results be different if you were to perform this experiment on the
moon?
(b) Show how the expression, g = 4π 2 / (G1 G2) is obtained starting from equations 1 & 2.
KT v. 4.2 17 May 2011
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Belt Friction Full ReportDokument8 SeitenBelt Friction Full ReportJoshua Reynolds73% (11)
- Senarai Amali Fizik SPM Ting 4Dokument52 SeitenSenarai Amali Fizik SPM Ting 4Hazrina Awang100% (3)
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (10)
- Solenoid Actuators: Theory and Computational MethodsVon EverandSolenoid Actuators: Theory and Computational MethodsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Basic Principles of Gravity MethodDokument78 SeitenBasic Principles of Gravity Methodرضوان المليكيNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Find Acceleration Due To Gravity Using Compound PendulumDokument7 SeitenHow To Find Acceleration Due To Gravity Using Compound PendulumMohid Khan100% (1)
- Simple Pendulum.Dokument13 SeitenSimple Pendulum.ab594100% (5)
- Ship Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesVon EverandShip Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- 6243-02 Jan 2009 MS (Unit 3 Old Syllabus)Dokument11 Seiten6243-02 Jan 2009 MS (Unit 3 Old Syllabus)Ibrahim Bt50% (2)
- ChartsDokument1 SeiteChartsravikumarmgowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY2061 Enriched Physics 2 Lecture Notes: Coulomb's LawDokument7 SeitenPHY2061 Enriched Physics 2 Lecture Notes: Coulomb's LawRavi Kanth M NNoch keine Bewertungen
- 002 Oscillating SpringDokument1 Seite002 Oscillating SpringRoshika Fernando Nirmani HabarawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6B Revision Notes ExtraDokument15 Seiten6B Revision Notes ExtraMoustafa Sohdy100% (7)
- F4 ExperimentsDokument52 SeitenF4 ExperimentsKiTTy94% (16)
- Understanding How Pendulum Length Affects PeriodDokument52 SeitenUnderstanding How Pendulum Length Affects PeriodSyafiq HazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practrical Sheets - Coll ADokument20 SeitenPractrical Sheets - Coll ADanialNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAG 10.3 - Comparison of Methods of Determining Spring StiffnessDokument5 SeitenPAG 10.3 - Comparison of Methods of Determining Spring StiffnessPootisNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAG 10.3 - Comparison of Methods of Determining Spring StiffnessDokument5 SeitenPAG 10.3 - Comparison of Methods of Determining Spring StiffnessjmsonlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiments Physics Form 4Dokument52 SeitenExperiments Physics Form 4cikgusya67% (3)
- Introduction To Physics: 1.1 PendulumDokument68 SeitenIntroduction To Physics: 1.1 Pendulumfahmi100% (1)
- Newton's Laws in ActionDokument48 SeitenNewton's Laws in ActionMarissa FreemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of Gravity MethodDokument77 SeitenBasic Principles of Gravity Methodرضوان المليكي100% (1)
- Hooke Law Experiment Determines Spring Constant Statically and DynamicallyDokument6 SeitenHooke Law Experiment Determines Spring Constant Statically and DynamicallyDiey LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual of Medical Physics PDFDokument48 SeitenManual of Medical Physics PDFAli AlengineerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 1 SPH 2170: Precision MeasurementsDokument29 SeitenPhysics 1 SPH 2170: Precision MeasurementsJuan SomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual of Medical PhysicsDokument18 SeitenManual of Medical Physicsأ. علي محمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pendulum Lab ReportDokument11 SeitenPendulum Lab ReportArlan DyussenovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqa A Level Physics - Required Practicals: JUNE 2017Dokument33 SeitenAqa A Level Physics - Required Practicals: JUNE 2017LouisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determine Moment of Inertia of Wooden PendulumDokument24 SeitenDetermine Moment of Inertia of Wooden PendulumafnanhananyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular Motion Lab: Centripetal ForceDokument5 SeitenCircular Motion Lab: Centripetal ForceJamkevin SariegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt 06 Centripetal Force LabDokument3 SeitenExpt 06 Centripetal Force Labsamruddhi1996Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exp03 GyroDokument4 SeitenExp03 GyrocooljseanNoch keine Bewertungen
- P and D LabDokument3 SeitenP and D LabTDxSWETZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1Dokument13 SeitenActivity 1Marving ZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy Report Exp2Dokument5 SeitenPhy Report Exp2audiliciousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honors Physics Tension LabDokument3 SeitenHonors Physics Tension Labpianoman3_1417750Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Physics Paper3 NotaDokument52 SeitenSPM Physics Paper3 Notanlweing100% (2)
- Lab ManualDokument25 SeitenLab ManualFarhan Khan NiaZi100% (1)
- Dynamics LabDokument14 SeitenDynamics LabDhiraj ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibrations Practical Lab Report 2Dokument25 SeitenVibrations Practical Lab Report 2Anonymous L7XrxpeI1zNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular Motion Experiment SubeshDokument6 SeitenCircular Motion Experiment SubeshSubesh ShanmugamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 3 PhyDokument4 SeitenExp 3 PhyShawn BrandonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresVon EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Experimental Determination of the Velocity of Light: Made at the U.S. Naval Academy, AnnapolisVon EverandExperimental Determination of the Velocity of Light: Made at the U.S. Naval Academy, AnnapolisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 421, January 26, 1884Von EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 421, January 26, 1884Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transport Phenomena in Micro- and Nanoscale Functional Materials and DevicesVon EverandTransport Phenomena in Micro- and Nanoscale Functional Materials and DevicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsVon EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Installations Technology: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionVon EverandElectrical Installations Technology: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringVon EverandWorkbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- DFMA Boothroyd Codes - EngineDokument1 SeiteDFMA Boothroyd Codes - EngineIbrahim BtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6CH08 Chemistry Jan 2012 MSDokument15 Seiten6CH08 Chemistry Jan 2012 MSIbrahim BtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Jun 2010 Mark Scheme Unit 3Dokument15 SeitenChemistry Jun 2010 Mark Scheme Unit 3dylandonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6CH07 Chemistry Jan 2012 MSDokument16 Seiten6CH07 Chemistry Jan 2012 MSIbrahim BtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel Analytical Chemistry (6CH07)Dokument7 SeitenEdexcel Analytical Chemistry (6CH07)Ibrahim BtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6CH04 Chemistry Jan 2012 MSDokument23 Seiten6CH04 Chemistry Jan 2012 MSIbrahim BtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6CH07 Jan 2011 QP+MSDokument12 Seiten6CH07 Jan 2011 QP+MSIbrahim BtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel Analytical Chemistry (6CH07)Dokument7 SeitenEdexcel Analytical Chemistry (6CH07)Ibrahim BtNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResistivityDokument1 SeiteResistivityIbrahim Bt100% (1)
- Youngs ModDokument10 SeitenYoungs ModgjosephidesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion Down A SlopeDokument1 SeiteMotion Down A SlopeIbrahim BtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Bulb and Diode CurvesDokument1 SeiteLight Bulb and Diode CurvesIbrahim BtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Fall Using Light GatesDokument2 SeitenFree Fall Using Light GatesIbrahim BtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Resistance of A BatteryDokument5 SeitenInternal Resistance of A BatteryIbrahim BtNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1 June 2008 MSDokument8 SeitenM1 June 2008 MSIbrahim BtNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCAP - Exam: Website: VCE To PDF Converter: Facebook: TwitterDokument14 SeitenPCAP - Exam: Website: VCE To PDF Converter: Facebook: TwitterChristian QCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam CADCAMFinal 2016FinalAnswersDokument10 SeitenFinal Exam CADCAMFinal 2016FinalAnswerskhalil alhatabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Representing Sequences Recursively and ExplicitlyDokument4 SeitenRepresenting Sequences Recursively and Explicitlytwitch tv caibingweiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scale Factors And: Discovering The Effect On The Volume of A Prism When Its Dimensions Are Multiplied by A Scale FactorDokument54 SeitenScale Factors And: Discovering The Effect On The Volume of A Prism When Its Dimensions Are Multiplied by A Scale FactorPort of Long Beach100% (4)
- Answers pt1 PDFDokument33 SeitenAnswers pt1 PDFJason SchellerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS6005 Advanced Database System UNIT III ADokument164 SeitenCS6005 Advanced Database System UNIT III Avenkatarangan rajuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Induction ConceptsDokument11 SeitenMathematical Induction ConceptsMehak ElahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circle the correct math answers quizDokument10 SeitenCircle the correct math answers quizShukri AidahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Calculus: Derivatives ExplainedDokument25 SeitenBasic Calculus: Derivatives ExplainedKrrje INoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative TechniquesDokument62 SeitenQuantitative TechniquesSteffanie GranadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3-Acceleration and Newton Second Law of MotionDokument58 SeitenChapter 3-Acceleration and Newton Second Law of Motionsarah2941100% (1)
- Supplementary Note335Dokument21 SeitenSupplementary Note335Syafiq ArtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1 PDFDokument8 SeitenExercise 1 PDFLeong Yue HanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business MathematicsDokument10 SeitenBusiness MathematicsDipesh Raj PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forecasting Aggregate Consumption in the Lower MainlandDokument51 SeitenForecasting Aggregate Consumption in the Lower MainlandVelina MilevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Chapter 3Dokument9 SeitenResearch Chapter 3Ashly MacandiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning With CaeDokument6 SeitenMachine Learning With CaeHarsha KorlapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1 (Activity Guide)Dokument3 SeitenActivity 1 (Activity Guide)Ronel AlbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Questions for Stephen Hawking about the UniverseDokument2 Seiten10 Questions for Stephen Hawking about the UniverseYihuan ZouNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADSL Line Driver Design Guide, Part 2Dokument10 SeitenADSL Line Driver Design Guide, Part 2domingohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparitive Study of Various Watermarking TechniquesDokument7 SeitenComparitive Study of Various Watermarking TechniquesHitanshi SachdevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SF-2200H Operating ManualDokument36 SeitenSF-2200H Operating ManualuripssNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.8 Index of Refraction LabDokument4 Seiten2.8 Index of Refraction LabsashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Unit 2 - AbsorptionDokument68 SeitenLearning Unit 2 - AbsorptionTshwarelo MahlakoaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Chemistry Intensive and Extensive PropertiesDokument23 SeitenPhysical Chemistry Intensive and Extensive PropertiesAdilla Rizka YonitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLS Point Cloud RegistrationDokument55 SeitenTLS Point Cloud RegistrationLipkowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Summary of PI and PID Controller Tuning Rules For Processes With Time Delay. Part 2: PID Controller Tuning RulesDokument7 SeitenA Summary of PI and PID Controller Tuning Rules For Processes With Time Delay. Part 2: PID Controller Tuning RulesAdrián BuenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unpacking PDFDokument15 SeitenUnpacking PDFNicole HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen