Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Common Reagents - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Hochgeladen von
Lily Li0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
246 Ansichten3 SeitenN-butyllithium Carbon disulfide Carbon tetrachloride an organolithium reagent; used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-styrenes (sbs) an organoaluminium compound; a reducing agent; converts esters and nitriles to aldehydes the diisopropyl ester
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenN-butyllithium Carbon disulfide Carbon tetrachloride an organolithium reagent; used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-styrenes (sbs) an organoaluminium compound; a reducing agent; converts esters and nitriles to aldehydes the diisopropyl ester
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
246 Ansichten3 SeitenCommon Reagents - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Hochgeladen von
Lily LiN-butyllithium Carbon disulfide Carbon tetrachloride an organolithium reagent; used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-styrenes (sbs) an organoaluminium compound; a reducing agent; converts esters and nitriles to aldehydes the diisopropyl ester
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
an organolithium reagent; used as a polymerization initiator in
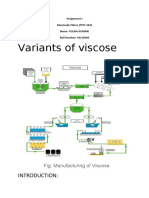
Common reagents n-Butyllithium the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia butadiene-styrene (SBS)
a non-polar solvent; used frequently as a building block in
This is a list of common inorganic and organic reagents often used in chemistry. Carbon disulfide
organic chemistry
toxic, and its dissolving power is low; consequently, it has been
Carbon tetrachloride
largely superseded by deuterated solvents
Contents often used for the coupling of amino acids for peptide synthesis
Carbonyldiimidazole
and as a reagent in organic synthesis
1 Synopsis
2 Reagent Compounds an inorganic compound; used as an oxidising agent in organic
Ceric ammonium nitrate
3 See also synthesis and as a standard oxidant in quantitative analysis
4 References Chloroform organic compound; a precursor to teflon
a strong and corrosive oxidising agent; an intermediate in
Chromic acid
chromium plating
Synopsis the acidic anhydride of chromic acid; mainly used in chrome-
Chromium trioxide
plating
Reagents are "substances or compounds that are added to a system in order to bring about a chemical reaction
Collins reagent used to selectively oxidize primary alcohols to an aldehyde
or are added to see if a reaction occurs." [1] Some reagents are just a single element. However, most processes
require reagents made of chemical compounds. Some of the most common ones are listed below. useful in a variety of applications ranging from organic
Copper(I) iodide
synthesis to cloud seeding
chemical reagent used to oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes
Reagent Compounds Dess–Martin periodinane
and secondary alcohols to ketones
Diborane the central organic synthesis reagent for hydroboration
Name General Discription
an organic compound; primary use is to couple amino acids
Acetic acid an organic acid; is one of the simplest carboxylic acids Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
during artificial peptide synthesis
Acetone an organic compound; simplest example of the ketones
a valuable reagent but also quite dangerous and explodes upon
a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne; widely used as a fuel Diethyl azodicarboxylate
Acetylene heating
and chemical building block
Diethyl ether organic compound; a common laboratory solvent
inorganic; the precursor to most nitrogen-containing
Ammonia a heterocyclic compound; used as a protecting group for
compounds; used to make fertilizer Dihydropyran
alcohols in organic synthesiss.[2][3]
aqueous ammonia; used in traditional qualitative inorganic
Ammonium hydroxide an organoaluminium compound ; a reducing agent; converts
analysis Diisobutylaluminium hydride
esters and nitriles to aldehydes
organic compound; often used as a foamer in plastics and rubber
Azobisisobutyronitrile the diisopropyl ester of azodicarboxylic acid; a reagent in the
and as a radical initiator Diisopropyl azodicarboxylate
production of many organic compounds
is an alkaline solution of potassium permanganate; used in
Baeyer's reagent organic chemistry as a qualitative test for the presence of the simplest ether; a useful precursor to other organic
Dimethyl ether
unsaturation, such as double bonds; compounds and an aerosol propellant
used in radical substitution and electrophilic addition reactions Dimethylformamide organic compound; a common solvent for chemical reactions
n-Bromosuccinimide
in organic chemistry organosulfur compound; used in petroleum refining and in
organic compound; similar solvent properties to acetone but has Dimethylsulfide petrochemical production processes; a reducing agent in
Butanone (methyl ethyl ketone) ozonolysis reactions
a significantly slower evaporation rate
a fat-soluble organic compound that is primarily used as an an organosulfur compound; an important polar aprotic solvent
Butylated hydroxytoluene Dimethyl sulfoxide
antioxidant food additive that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds
Dioxane a heterocyclic organic compound; classified as an ether
a powerful psychoactive drug; useed in alcoholic beverages, in aqua regia
Ethanol
thermometers, as a solvent, and as a fuel in organic synthesis, is widely used to oxidise alkenes to the
Osmium tetroxide
used to differentiate between water-soluble aldehyde and ketone vicinal diols
Fehling's reagent
functional groups used in organic synthesis for the preparation of acid chlorides
Oxalyl chloride
a solution of hydrogen peroxide and an iron catalyst that is used from the corresponding carboxylic acids
Fenton's reagent
to oxidize contaminants or waste waters a catalyst for many organic reactions by combining with many
Palladium(II) acetate
the simplest aldehyde; an important precursor to many other common classes of organic compounds to form reactive adduct
Formaldehyde chemical compounds, such as polymers and polyfunctional a powerful oxidizing agent; readily forms explosive mixtures;
alcohols Perchloric acid
mainly used in the production of rocket fuel
the simplest carboxylic acid; often used as a source of the a mineral acid with many industrial uses; commonly used in the
Formic acid Phosphoric acid
hydride ion laboratory preparation of hydrogen halides
the most common application is for alkylation of aldehydes and one of the most important phosphorus chlorides; a chlorinating
Grignard reagents Phosphorus pentachloride
ketones: [4] reagent
a phosphoramide; useful polar aprotic solvent and additive in Phosphorus tribromide used for the conversion of alcohols to alkyl bromides
Hexamethylphosphoramide
organic synthesis most important of the three phosphorus chlorides; used to
used as a foaming agent in preparing polymer foams; also a manufacture organophosphorus compounds; used to convert
Hydrazine Phosphorus trichloride
precursor to polymerization catalysts and pharmaceuticals primary and secondary alcohols into alkyl chlorides, or
used primarily for preservation of stock solutions, and as a carboxylic acids into acyl chlorides
Hydrazoic acid
reagent Phosphoryl chloride used to make phosphate esters such as tricresyl phosphate
Hydrochloric acid a highly corrosive, strong mineral acid with many industrial uses a common inorganic chemical reagent, most commonly used as
valued source of fluorine, precursor to numerous Potassium dichromate an oxidizing agent in various laboratory and industrial
Hydrofluoric acid applications
pharmaceuticals; higjly corrosive
Hydrogen peroxide an oxidizer commonly used as a bleach a strong base; precursor to most soft and liquid soaps as well as
Potassium hydroxide
numerous potassium-containing chemicals
an organic compound; this aromatic heterocyclic is a diazole
Imidazole a strong oxidizing agent; can be used to quantitatively determine
and is classified as an alkaloid
Potassium permanganate the total oxidisable organic material in an aqueous sample; a
simplest example of a secondary alcohol; dissolves a wide reagent for the synthesis of organic compounds
Isopropyl alcohol
range of non-polar compounds
used to oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes and secondary
a reducing agent in organic synthesis; used to prepare main Pyridinium chlorochromate
alcohols to ketones
Lithium aluminium hydride group and transition metal hydrides from the corresponding
metal halides Pyridinium dichromate (Cornforth
converts primary and secondary alcohols to ketones
reagent)
strong base used in organic chemistry for the deprotonation of
Lithium diisopropylamide an alternative catalyst for the hydrogenation of vegetable oils; in
weakly acidic compounds Raney nickel
organic synthesis, used for desulfurization
used as a pigment and as a precursor to other manganese
Manganese dioxide compounds; used as a reagent in organic synthesis for the Samarium(II) iodide (Kagan Reagent) a powerful reducing agent
oxidation of allylic alcohols used to prepare other silver compounds; in organic chemistry,
Silver oxide
Meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid used as an oxidant in organic synthesis used as a mild oxidizing agent
a gasoline additive; also used in organic chemistry as a precursor to many other silver compounds; commonly used in
Methyl tert-butyl ether Silver nitrate
relatively inexpensive solvent inorganic chemistry to abstract halides
an analytical reagent used to detect the presence of soluble used in the industrial production of indigo, hydrazine, and
Millon's reagent Sodium amide sodium cyanide[5] ; used for the drying of ammonia; used as a
proteins
strong base in organic chemistry
highly corrosive and toxic strong acid; used for the production
Nitric acid of fertilizers, production of explosives, and as a component of gas-forming component in airbag systems; used in organic
Sodium azide synthesis to introduce the azide functional group by
displacement of halides
References
a strong base; deprotonates ketones and esters to generate
Sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide
enolate derivative 1. ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version:
a versatile reducing agent; converts ketones and aldehydes to (1996) "Reactant (http://goldbook.iupac.org/R05163.html) ".
Sodium borohydride 2. ^ R. A. Earl L. B. Townsend (1990), "Methyl 4-Hydroxy-2-butynoate"
alcohols
(http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv7p0334) , Org. Synth.,
in organic synthesis, used for the oxidation of aldehydes to http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv7p0334; Coll. Vol. 7: 334
Sodium chlorite
carboxylic acids 3. ^ Arthur F. Kluge (1990), "Diethyl [(2-Tetrahydropyranyloxy)methyl]phosphonate"
Sodium hydride a strong base used in organic synthesis (http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv7p0160) , Org. Synth.,
http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv7p0160; Coll. Vol. 7: 160
strong base with many industrial uses; in the laboratory, used 4. ^ Haugan, Jarle André; Songe, Pål; Rømming, Christian; Rise, Frode; Hartshorn, Michael P.; Merchán, Manuela;
Sodium hydroxide with acids to produce the corresponding salt, also used as an Robinson, Ward T.; Roos, Björn O. et al. (1997), "Total Synthesis of C31-Methyl Ketone Apocarotenoids 2: The First
electrolyte Total Synthesis of (3R)-Triophaxanthin." (http://actachemscand.dk/pdf/acta_vol_51_p1096-1103.pdf) , Acta Chimica
Sodium hypochlorite frequently used as a disinfectant or a bleaching agent Scandinavica 51: 1096–1103, doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.51-1096 (http://dx.doi.org/10.3891%2Facta.chem.scand.51-
1096) , http://actachemscand.dk/pdf/acta_vol_51_p1096-1103.pdf, retrieved 2009-11-26
Sodium nitrite used to convert amines into diazo compounds 5. ^ Budavari, Susan, ed. (1996), The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (12th ed.),
strong mineral acid; major industrial use is the production of Merck, ISBN 0911910123
Sulfuric acid 6. ^ Allen, C. F. H.; Byers, Jr., J. R.; Humphlett, W. J. (1963), "Oleoyl chloride"
phosphoric acid
(http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv4p0739) , Org. Synth.,
used in a variety of oxidation processes; industrially, is used as http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv4p0739; Coll. Vol. 4: 739; Rutenberg, M. W.; Horning,
tert-Butyl hydroperoxide
a starter of radical polymerization E. C. (1963), "1-Methyl-3-ethyloxindole" (http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv4p0620) ,
one of the most polar ethers; a useful solvent; its main use is as Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv4p0620; Coll. Vol. 4: 620
Tetrahydrofuran
a precursor to polymers Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Common_reagents"
Tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0) a catalyst for palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions Categories: Chemistry lists | Reagents for organic chemistry
a quaternary ammonium salt; used as an anisotropic etchant of This page was last modified on 16 May 2011 at 13:30.
Tetramethylammonium hydroxide silicon; used as a basic solvent in the development of acidic Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may
photoresist in the photolithography process apply. See Terms of Use for details.
the simplest tetraorganosilane; a building block in Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
Tetramethylsilane
organometallic chemistry
an inorganic compound; used in chlorination reactions; converts
Thionyl chloride
carboxylic acids to acyl chlorides[6]
Thiophenol an organosulfur compound; the simplest aromatic thiol
an intermediate in the production of titanium metal and titanium
Titanium tetrachloride
dioxide
a chemical test most commonly used to determine whether a
Tollens' reagent known carbonyl-containing compound is an aldehyde or a
ketone
Triphenylphosphine used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds
See also
Reagent
Limiting reagent
Category:Reagents for organic chemistry
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- POISONOUS PLANTS: A GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING AND AVOIDING TOXIC SPECIESDokument34 SeitenPOISONOUS PLANTS: A GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING AND AVOIDING TOXIC SPECIESMohaiminu ArmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Vendedor de Goma Gum TechnologyDokument2 SeitenVendedor de Goma Gum Technologyalicia_brisanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Cubit Product ListDokument10 SeitenCubit Product ListShreedhar KadkolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- MiG AMMO Acrylic Paint ChartDokument2 SeitenMiG AMMO Acrylic Paint ChartPablo Maicá Machado50% (2)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Gluep Polymer Student InstructionDokument3 SeitenGluep Polymer Student InstructionWendy KangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- NODokument5 SeitenNODemang SatrioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- PK# RT Hit Compound Name Match R.Match CAS LibraryDokument11 SeitenPK# RT Hit Compound Name Match R.Match CAS LibraryGerson JoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Timber Lesson 6Dokument60 SeitenTimber Lesson 6Mohd Nizam ShakimonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- 98 GTU QuestionDokument3 Seiten98 GTU QuestionKushal RathodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- Astm D3878 23Dokument4 SeitenAstm D3878 23Hasan ÜyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- G&P Geotechnics SDN BHD Specification For Gabion Wall 1 August 2008Dokument4 SeitenG&P Geotechnics SDN BHD Specification For Gabion Wall 1 August 2008jinwook75Noch keine Bewertungen
- Protein StructureDokument16 SeitenProtein StructureAakash HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Handprint BlueDokument15 SeitenHandprint BluefrazNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Basement Water ProofingDokument35 SeitenBasement Water ProofingSCOA crewNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- RP 6 BananaDokument8 SeitenRP 6 BananaAKSHAT BENIWALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Elastomeric Impression MaterialsDokument45 SeitenElastomeric Impression MaterialsNetraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Composites For Structural ApplicationsDokument17 SeitenGreen Composites For Structural ApplicationsRamkumar RamaiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Test 05 Answer s2l6 PDFDokument2 Seiten12 Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Test 05 Answer s2l6 PDFShreyash KolekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textile Vocabulary Ch. 7-11Dokument7 SeitenTextile Vocabulary Ch. 7-11scribd101100% (2)
- Purchase Specification: Model No. 16-4 Double Check Detector AssemblyDokument3 SeitenPurchase Specification: Model No. 16-4 Double Check Detector Assemblyonin007Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- YASHICA Crease RecoveryDokument2 SeitenYASHICA Crease RecoveryYashica Gupta100% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Assignment 1 - Tulika (18110066)Dokument5 SeitenAssignment 1 - Tulika (18110066)Tarique RizwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProjectDokument12 SeitenProjectJoshi ParthNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Base For Final Exam PreparationDokument131 SeitenMCQ Base For Final Exam PreparationPurwa Rane100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Bosch Solenoid Valve PDFDokument16 SeitenBosch Solenoid Valve PDFdevdownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fenner Friction Belts BrochureDokument6 SeitenFenner Friction Belts BrochureAlexander SolomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conveyor Belt TestingDokument6 SeitenConveyor Belt TestingNorberto A. GhiggiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Data WoodDokument15 SeitenTechnical Data Woodwanda_hafizNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Court Rules Against Customs Forfeiture and Orders Release of GoodsDokument8 SeitenCourt Rules Against Customs Forfeiture and Orders Release of GoodsKirby MalibiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthetic Fifth Wheel & Open Gear CompoundDokument2 SeitenSynthetic Fifth Wheel & Open Gear CompoundBruce WappmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)