Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ABB Traction Rectifiers Brochure en
Hochgeladen von
iaiscan1009Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ABB Traction Rectifiers Brochure en
Hochgeladen von
iaiscan1009Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
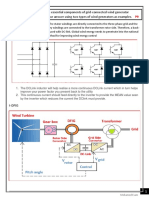
Traction Power Supply
ABB traction rectifiers
Diode rectifiers for DC traction substations
2 ABB traction rectifiers
Traction power supply is one of the
most important parts of the transport
infrastructure. It links the general AC
medium voltage supply system and
the DC supply line (catenary or third rail)
of the traction vehicles. For applications
in DC electric traction the naturally cooled
silicon diode rectifiers are the most
suitable because they combine simply
design, low maintenance, high overload
capacity and a long lifetime.
This short form technical catalogue
describes the main electrical, mechanical
and environmental features of the PD
family diode traction rectifiers.
ABB traction rectifiers 3
Introduction of railway infrastructure and municipal transport in Poland where
In practice, a three-phase power supply is the most often used the number of installed rectifiers reaches one thousand.
electricity source. Therefore, to be able to power trains using However, the most unique technological achievement so far
direct current, it is necessary to use an electronic power converter has been a design prepared for the underground transit system
(rectifier). A traction rectifier is the essence of two components in Brazilian São Paolo. The power system for the underground
of the modern technology: electronics and industrial power was designed in a manner enabling maximum use of electricity
engineering. Thanks to this element, railway and municipal surplus, returning it back to the municipal supply system after
tractions are able to convert alternate current into direct current conversion into alternate current. Such installations require
with power ensuring that hundred-tonne trains reach high speeds. application of the most advanced technologies, and so far only
ABB has a large experience in designing, construction and start-up several similar solutions have been used in public transport
of traction rectifiers, supported with many prestigious references. systems worldwide.
It is, among others, thanks to our solutions that the longest and Designers, engineers, as well as assemblers of ABB traction
most used London Underground line – Victoria – is able rectifiers are world-class specialists. Of course, their competence
to transport more than 200 million passengers a year. Also, is best proven by successfully completed contracts. Their actions
municipal transport systems in Belarus and Algeria could develop are also ranked very high in ABB Group, which is proven
and significantly increase capacities thanks to our engineers. by the fact that in 2010 a new factory will be open in Poland,
We cannot forget about ABB’s contribution in modernization which will start a new chapter in ABB traction rectifier history.
4 ABB traction rectifiers
ABB traction rectifiers 5
Example of short fully enclosed bus-bars duct between transformer and rectifier
General description and design
The PD rectifiers’ family is designed for the supply of DC traction PD rectifiers provide many variants of AC and DC connections.
loads like urban transport systems or main-line railways in ranges Standard design offers cable connection through the bottom
of following standard output voltages: or/and through the top.
– up to 825 V DC The bus-bars duct connection between transformer and rectifier is
– 1500-1650 V DC recommended for higher currents. ABB offers such enclosed bus-
– 3000-3300 V DC bars duct as an option even the transformer is ordered separately
PD rectifiers offer optimized for natural cooling power density (in this case customer has to provide all requested mechanical
(small footprint) and maintenance friendly mechanical design. data of transformer).
All types are type tested according to EN50328/IEC60146
and offers overload classes according to these standards. Individual silicon diodes are mounted on an air-cooled heat-
sink having adequate heat dissipation properties. Such diode
To minimize the harmonic distortion the PD rectifier consists of with double-side heat-sink creates a diode module. Each diode
two diode bridges connected in series or in parallel. Both bridges module is protected with RC circuit.
are prepared to be supplied from the two secondary windings All internal main circuit connections are made of copper busbars.
of the transformer, this solution provides 30o phase shift and The busbars cross section is adequate to the rectifier rating and
12-pulse influence on supply network. Two 12-pulse rectifiers natural cooling. Wherever it is necessary, flexible junction are used
supplied by two three windings transformers with +/-7.5o phase (e.g. bus-bar duct between transformer and rectifier).
shift of primary windings create 24-pulse rectifiers configuration. Auxiliary devices are separated from main circuit and located in
Single bridge 6-pulse rectifiers are available on request only. separate compartment inside main cubicle or in separate box
located on the side wall of rectifier’s cubicle.
The equipment should be installed indoors, otherwise it should All components are easily accessible from the front of rectifier’s
be requested and agreed during ordering (e.g.: the rectifier can cubicle. In case of low current rectifiers where AC and DC
be fitted with internal heater, higher IP class and other facilities). connections are made by cables, ABB offers front and rear
access cubicles also for easier maintenance.
The diode rectifiers are encased in steel sheet cubicles with As an option our cubicles could be equipped with interior lamps
welded or bolted internal frame. This internal structure frame and large windows in front doors to let customer’s staff examine
joining method depends on weight and environment conditions rectifier’s interior without deenergizing. Another very useful option
(e.g. earthquake immunity). In case of bolting PD rectifiers are from maintenance point of view is white colour painting
always equipped with welded bottom frame. of rectifier’s interior.
6 ABB traction rectifiers
1. Example of AC cables input through the top | 2. Terminal box of auxiliary connections | 3. Complete diode module (diode, heatsink and RC circuit)
4. Control box of the rectifier.
1. 2.
3. 4.
ABB traction rectifiers 7
Low power Input transformer requirements
3kV rectifier
Each rectifier always cooperates with its supply transformer.
This transformer provides adjustment the Medium Voltage (MV)
to the level required by the rectifier and its load.
The next very important function of the input transformer is
the output voltage regulation and short circuit current limitation.
Both of these things depend on impedance voltage of the
transformer and also on coupling factor of secondary windings
(in three winding transformer). Higher impedance voltage causes
higher voltage regulation and simultaneously lower short circuit
current. The correct output voltage characteristic inclination
provides appropriate load sharing between rectifiers supplying
the same load. The limitation of short circuit current value is
demanded by: supply network, DC switchgears or by rolling stock.
The input transformer has to provide also appropriate overload
ability, which corresponds to the overload class of the rectifier.
ABB offers input transformer parameters calculation and other
assistance even if transformer is ordered separately.
DC voltage versus DC current characteristic
Direct voltage
Real
no load
voltage Transformer power
for fundamental harmonic
No load
voltage Voltage
regulation
Voltage
at rated
current
(nominal
voltage)
Direct current
Rated
current
8 ABB traction rectifiers
Advantages and disadvantages of serial and parallel topology turns must be an integer. Due to the low secondary voltage
The most important advantage of parallel topology is decreasing the number of turns must be comparatively few. Hence a turn
of load losses (almost two times smaller than in serial ratio error is inevitable. The values of 5-th and 7-th harmonics are
configuration). It has an impact on the rectifier dimension, number a few times higher in case of parallel than in serial topology
of diodes and space required to dissipate heat produced by however they do not exceed allowable level and this difference
rectifier. exists mainly at low load.
However the turn ratio unbalances between the Y- and The conclusion is that a 12-pulse converter built up of two
D-windings of the converter transformer for 12-pulse converters parallel-connected six-pulse bridges is very sensitive to turn ratio
(built up of two six-pulse bridges connected in parallel) causes unbalances between the Y- and D-windings of the converter
discrepancies between theoretical and real harmonic level in transformer. A 12-pulse converter built up of two series connected
supply network (especially for the 5-th, 7-th, 17-th and 19-th six-pulse bridges is much less sensitive to this type of unbalance.
harmonics). To achieve the perfect balance the transformer The secondary windings of the transformer should be made as
windings connected to the rectifier bridges must generate exactly decoupled to decrease this effect significantly (coupling factor
the same voltage. The number of turns should then be √3 times < 0.2) or the output transition coil, which connects outputs of the
higher for the D-winding than for the Y-winding, but the number of parallel bridges, should be applied.
Parallel and serial configuration of rectifier’s bridges.
L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3
Option Option Option Option
Option Option Option Option Option Option
- - + + - - + +
ABB traction rectifiers 9
3.3kV, 1700A rectifier with redundancy option 750V,4000A rectifier with non standard DC out through sidewall
Protection Fuse and fuseless topology
The rectifier-transformer set is protected against short circuit The rectifier solution provides output short circuit immunity for at
at the DC output by MV circuit breaker. It is the main protection least 10 periods of supply network (200ms for 50Hz and 167ms
of the unit. for 60Hz). This time is long enough to break short circuit current
Protection against overload is provided by external protective relay by the circuit breaker on a primary side of transformer. For that
which is a part of MV breaker. This device protects transformer reason the main circuit is made as a fuseless solution. This
as well as rectifier. As an additional protection an overtemperature solution increases reliability of the rectifier significantly, because
relay could be used. The rectifier is equipped with two level the rectifier is able to withstand many short circuits, which appear
(ALARM and TRIP) overtemperature relays, which supervise during normal operation at DC supply line (the third rail) without
heatsink’s temperature. These devices could be considered as any deterioration of the rectifier’s components. Obviously
an additional overload protection. Moreover the rectifier could be the solution with fuses is also available on request.
equipped with an internal air temperature indicator as an option.
Protection against overvoltages is provided by RC circuit connected Redundancy
to the output terminals. As an option the surge arrester (metal-oxide ABB offers two possible solutions of redundancy: by fuses
arrester POLIM series) could be installed in the rectifier. or by additional serial diode.
Protection against internal short circuit is also provided by The redundancy by fuse consists of two or more diodes
MV circuit breaker. If there is no Ultra Rapid (UR) DC breaker (maximum four) in each arm of the bridge in parallel connection
between the rectifier and DC line, fuse topology of the rectifier has and each of them is provided with UR fuse.
to be chosen to avoid supplying of shorted rectifier by other units The faulty (shorted) diode is selectively separated by fuse so
connected to the same DC line. the rectifier remains in operation. If only one diode fuse is blown
10 ABB traction rectifiers
Test Field for non standard combined test of transformer and rectifier groups
(in one arm), the rectifier shall still be able to meet the rating
specified at nominal plate. The operation of the fuse is transferred
by potential free contact to rectifier’s diagnostic system.
The redundancy by additional serial diode consists in serial
connection of two or more diodes in each arm of the bridge.
In case of diode failure (internal breakdown) its resistance is close
to zero in both directions so it can be considered as a conductor.
The rectifier remains in operation if other diodes in arm have big
enough reversal voltage strength. Obviously this solution causes
higher losses during normal operation (higher voltage drop across
arm) however it can be economically motivated in 3.3kV DC
rectifiers (high voltage fuses are very expensive).
750V,
4000A rectifier
with DC out
through the top
ABB traction rectifiers 11
1. Diagnostics
The main task of the diagnostics circuit is monitoring of diodes.
It helps staff to find faulty diode without additional measurement.
Obviously this circuit is also able to generate the trip command to
the superior system (or directly to the MV circuit breaker) however
the rectifier-transformer unit has to be protected by MV circuit
breaker independently from diagnostics.
The diagnostics sensors solution applicable in the rectifier
depends on rectifier topology. If there is no serial connection
of diodes in one arm, the magnetic field sensors are used. If arm
of the rectifier bridge is created by two or more diodes connected
in series, the reversal voltage across diode is monitored. In case
where the fuses are used, the fuses micro-switches work as
sensors.
2. The magnetic field sensors detect direction of current flow.
If pulsating current in at least one sensor doesn’t appear in correct
direction when output current exceeds certain level of nominal
current (10-20% depending of rectifier’s power), an alarm signal
is generated within 200ms. If a current appears in wrong direction
in at least one sensor, trip signal is generated immediately
independently from the level of output current. Sensors are
mounted directly on the diode’s busbars. In one non dismountable
enclosure are placed two single directional field sensors and
testing coil. This solution provides galvanic insulation from the
main circuit and also allows testing of all diagnostics devices
(sensors, wires, boards and displays).
The reversal voltage diode sensors are mounted directly at
the heat-sink of the monitored diode. They generate pulse signal
when appropriate reversal voltage appears. If these pulses
3. disappear, it means that monitored diode is shorted. To avoid
unexpected operation of diagnostics when the main circuit supply
voltage is off, additional supply voltage sensor is used. To provide
appropriate insulation level between main and control circuit
the fibre optics are used. Each voltage sensor is connected to
the main control board of diagnostics panel via individual fibre
optic.
1. Magnetic field sensor | 2. Voltage sensor and RC circuit
details | 3. Diagnostics main board for voltage sensors.
12 ABB traction rectifiers
Diagnostics panel
The main board of diagnostics contains microprocessor based
logical circuit, which collects data from all sensors and stores
information about the failed element into memory, which has to be
cleared manually. This board provides self-test feature, which
generates FAULT signal in case of internal malfunction.
The diagnostics display consists of two color LED diodes
(one diode belongs to one power diode), which show condition
of power semiconductors. Three pushbuttons also exist on panel
surface: two to check diagnostics in both directions and one
to reset information about reason of failure from memory.
Diagnostics panel
The rectifier and transformer selection
To choose appropriate rectifier and transformer, correct input data
has to be known:
– rated requested DC power (or current),
– rated requested DC voltage,
– requested overload ability,
– requested topology (serial or parallel, fuse or fuseless)
– ambient conditions (IP requirements).
Having these data please contact the nearest ABB representative
and the most suitable rectifier will be selected by our staff as soon
as possible. In case of non standard requirements ABB is ready
to prepare tailor-made design also to fit to customer’s
requirements.
The table below shows main technical data of PD rectifiers.
Rated DC voltage [V] up to 750 1) 1500÷1650 3000÷3300
Max. output voltage [V] 900 1900 3800
Rated current [A] 800÷4800 800÷3000 300÷3000
Overload class VI according to EN50328/IEC60146
Efficiency [%] >99.5 >99.7 >99.7
>99.2 serial conf.
Max. ambient temp. [°C] 40 (up to 55 with derating)
Min. ambient temp. [°C] 0 (up to -20 as an option)
Max. installation altitude [m.a.s.l.] 1000 (up to 4000 with derating)
IP class (IEC60529) IP20÷IP21, IP30÷IP32, IP40÷IP45
Rated insulation voltage [kV] 0.9÷1.8 2.3÷3.0 3.6÷6.5
Power frequency withstand voltage [kV] 2.8÷4.6 5.5÷9.2 11.5÷23
Width [mm] 2) 830÷2400 1054÷2800 1054÷2800
Depth [mm] 2) 852÷1452 1054÷1452 1054÷1452
Height [mm] 2022÷2200 3)
Weight [kg] 4) 420÷2800 450÷1900 450÷1900
1) 825VDC available as an option
2) dimensions of rectifiers without redundancy
3) dimension of IP20, in case of higher IP class – up to 2600
4) weights refer to IP20
ABB traction rectifiers 13
The rectifier type code
1/2 P D – Product Type PD-diode rectifier
3/4 1 6 Current Rating in hundreds of amperes (rounded to full hundreds)
5 S / Bridges Topology S-serial, P-parallel, R-parallel with output inter-phase reactor, V-six pulse rectifier
6-8 7 5 0 – Nominal DC Voltage in volts (above 1kV in kV separated by dot eg. 3.3)
9 0 Redundancy
0-no redundancy without fuses 2-redundancy by add. serial diode
1-no redundancy with fuses 3-redundancy with fuses
10 0 Diagnostics
0-no diagnostics 2-diagnostics with voltage sensors
1-diagnostics with magnetic field sensors 3-diagnostics with fuses microswitches
11 0 Measuring instruments
0-no meters 2-ammeter and voltmeter
1-ammeter 9-version
12 0 – Auxiliary supply
0-no aux. voltage needed 2-230VAC
1-110VAC/DC 3-230VAC/220VDC
9-version
13 2 IP protection class (first digit – protection against solid objects)
14 0 IP protection class (second digit – protection against liquids)
15 1 AC input bars/cables terminals
0-top entry (typically IP-X0) 2-bottom entry
1-upper part sidewall entry 9-version
162 2 DC output bars/cables terminals
0-top entry (typically IP-X0) 2-bottom entry
1-upper part sidewall entry 9-version
17 0 – Enclosure Finish (0-standard, 9-version)
18 0 Non standard equipment
0-no additional equipment A-(1+2) F-(3+4) J-(1+2+3+4)
1-overtemperature protection B-(1+3) G-(1+2+3) 9-version
2-interior heater controlled by thermostat C-(1+4) H-(1+2+4)
3-internal lamp D-(2+3) G-(1+3+4)
4-door limit switch E-(2+4) H-(2+3+4)
14 ABB traction rectifiers
Output characteristic and energy recovery
In some applications it is necessary to have U=f(I) characteristic
other than natural characteristic offered by transformer and diode
rectifier unit. In such cases ABB suggests to use thyristor rectifiers
to create U=f(I) according to customer requirements. Such recti-
fiers are available in ABB’s portfolio for all voltage levels mentioned
in this catalogue.
If it is reasonable to send energy from braking trains to AC supply
network, ABB offers also thyristor inverters. These inverters could
cooperate with thyristor or diode rectifiers.
Example of 12-pulse thyristor rectifier
(inverter) for traction purposes.
ABB traction rectifiers 15
Contact us
ABB Sp z o.o.
4128PL219-W1-en. Edition 11.2009
Power Electronics
67/93 Aleksandrowska Str.
91-205 Lodz / Poland
tel.: +48/42 2993000
fax: +48/42 2993340
www.abb.com
We reserve the right to make technical changes
or modify the contents of this document without prior
notice. With regard to purchase orders, the agreed
particulars shall prevail. ABB does not accept any
responsibility whatsoever for potential errors
or possible lack of information in this document.
We reserve all rights in this document and in the
subject matter and illustrations contained therein.
Any reproduction, disclosure to third parties
or utilization of its contents – in whole or in parts – is
forbidden without prior written consent of ABB.
© Copyright 2009 ABB
All rights reserved
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Project Report of A Variable Power SupplyDokument21 SeitenProject Report of A Variable Power SupplyTalha Saeed100% (3)
- Project Report Regulated Power SupplyDokument36 SeitenProject Report Regulated Power SupplyPeerzada Wahid73% (11)
- Active Power Factor Correction Technique For Single Phase Full Bridge RectifierDokument6 SeitenActive Power Factor Correction Technique For Single Phase Full Bridge RectifierAnand KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionVon EverandAnalog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- Beng BenggsssDokument11 SeitenBeng BenggsssBeth PartozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buck ConverterDokument52 SeitenBuck Convertermayankrkl50% (2)
- Electronic Circuits Power Supply Electronic Basic Components AC Power Devices Like Home AppliancesDokument21 SeitenElectronic Circuits Power Supply Electronic Basic Components AC Power Devices Like Home AppliancesTushar GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridge Rectifier: Circuit Diagram & Its WorkingDokument12 SeitenBridge Rectifier: Circuit Diagram & Its WorkingChandra Sekhar CNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorDokument9 SeitenFirst Quadrant Single Phase Ac To DC Converter Semiconverter Separately Excited DC MotorzaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjustable DC Power Supply 0-30V: Laboratory Project Report Semiconductors Devices LabDokument5 SeitenAdjustable DC Power Supply 0-30V: Laboratory Project Report Semiconductors Devices LabMISHAL FATIMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode SDokument45 SeitenDiode SGanesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reduction of AC MainsDokument3 SeitenReduction of AC MainsFaizan NaeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Power Supply CircuitDokument7 SeitenDC Power Supply CircuitEhtasham Ul HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Improved AC-DC Single-Stage Full-BridgeDokument12 SeitenAn Improved AC-DC Single-Stage Full-BridgeAnonymous Z1RHn9ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonisolated Switch Mode DC DC ConvertersDokument81 SeitenNonisolated Switch Mode DC DC ConvertersRAJESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractDokument20 SeitenEmergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractAakash SheelvantNoch keine Bewertungen
- p185 PDFDokument24 Seitenp185 PDFதமிழன்Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 Linear DC Power SupplyDokument56 SeitenTopic 1 Linear DC Power SupplyKu AliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Processes: Analysis of A Series-Parallel Resonant Converter For DC Microgrid ApplicationsDokument14 SeitenProcesses: Analysis of A Series-Parallel Resonant Converter For DC Microgrid ApplicationsMohmed khaja HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEEN40197 Lecture Notes AJF PDFDokument46 SeitenEEEN40197 Lecture Notes AJF PDFAnonymous gVhwdk9ui9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lic Report 14 - 4 Final2Dokument12 SeitenLic Report 14 - 4 Final2Harshvardhan MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPTDokument32 SeitenPPTsingh vipulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Switched-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) CircuitsDokument10 SeitenIntroduction To Switched-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Circuits9chand3100% (1)
- Lab 2 Buck ConverterDokument3 SeitenLab 2 Buck ConverterShah VinodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijsrp p3178 PDFDokument11 SeitenIjsrp p3178 PDFJeannot MpianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 2 Wind0.02Dokument25 SeitenAss 2 Wind0.02Šämęh ËšśämNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Supply and Zener Diode (Canvas)Dokument95 SeitenPower Supply and Zener Diode (Canvas)Aaron Jacob ConcepcionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 3 Eng NaderDokument7 SeitenExperiment 3 Eng Naderياسر العويطيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Is The Constant Current Circuit ImportantDokument7 SeitenWhy Is The Constant Current Circuit ImportantjackNoch keine Bewertungen
- IE Mod 01 PowerSupplyDokument25 SeitenIE Mod 01 PowerSupplyRy AnNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Power SupplyDokument8 SeitenDC Power Supplyweaam raedNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Power SupplyDokument8 SeitenDC Power Supplyweaam raedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power SupplyDokument5 SeitenPower Supplyapi-19653075100% (1)
- Jpe 8-2-1Dokument12 SeitenJpe 8-2-1Jeevananthan SeenithangamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Fault DerivationDokument89 SeitenAnalog Fault DerivationSachidananda SwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation and Prototype Implementation of Phase Shift Full Bridge DC DC ConverterDokument4 SeitenSimulation and Prototype Implementation of Phase Shift Full Bridge DC DC ConverterjimmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Power Supply ReporDokument19 SeitenDC Power Supply ReporAbhay SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Level InverterDokument63 Seiten3 Level InverterThirumal ValavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Switch AC DC Cuk Converter For Power Factor and Efficiency EnhancementDokument5 SeitenSingle Switch AC DC Cuk Converter For Power Factor and Efficiency EnhancementInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Switched Mode Power SupplyDokument21 SeitenTheory of Switched Mode Power Supplyseahate100% (1)
- Effect of Source InductanceDokument25 SeitenEffect of Source InductanceSriram Anil Kumar Gandham100% (1)
- Analysis and Construction of Push Pull Converter - Noor Rulmuna Bt. Mohd Sarmin - TK7872.C8.N66 2006Dokument27 SeitenAnalysis and Construction of Push Pull Converter - Noor Rulmuna Bt. Mohd Sarmin - TK7872.C8.N66 2006Rizwan FaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class D Com FonteDokument29 SeitenClass D Com FontenicchioNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Project in PDF: Uilding A Power Supply For Most Electronic Projects Is Not Difficult and RatherDokument12 SeitenThis Project in PDF: Uilding A Power Supply For Most Electronic Projects Is Not Difficult and Ratherb3nyokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac-Dc ConvertersDokument7 SeitenAc-Dc ConvertersJessica PGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulated DC Power SupplyDokument15 SeitenRegulated DC Power SupplynalumilanimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer Based Resonant DC Inverter For Brushless DC Motor Drive SystemDokument7 SeitenTransformer Based Resonant DC Inverter For Brushless DC Motor Drive SystemStudents Xerox ChidambaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0-12v Variable Power SupplyDokument19 Seiten0-12v Variable Power Supplygirigtr2010100% (1)
- Diode ApplicationsDokument119 SeitenDiode ApplicationsFlorenzo Miguel AclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics NotesDokument2 SeitenPower Electronics Notesprasad357Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Phase Power Factor Correction, Using Vienna Rectifier ApproachDokument13 Seiten3-Phase Power Factor Correction, Using Vienna Rectifier Approachvdiaz1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Self Switching Power SupplyDokument20 SeitenSelf Switching Power SupplyPutra Purechk TokyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 2002Dokument12 SeitenPaper 2002Miguel VenzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power FactorDokument25 SeitenPower FactorSri Sai ComputersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsVon EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Von EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsVon EverandAnalog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (6)
- Acknowledgement: Er - Mila Shilpakar, Er - Aanand Kumar Mishra, Er - Suman Duwal, and Er. Ramesh BalaDokument19 SeitenAcknowledgement: Er - Mila Shilpakar, Er - Aanand Kumar Mishra, Er - Suman Duwal, and Er. Ramesh BalaSudip ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity Rates or TariffDokument10 SeitenElectricity Rates or TariffPVV RAMA RAONoch keine Bewertungen
- 663 - Cockcroft-Walton GeneratorDokument27 Seiten663 - Cockcroft-Walton GeneratorcassioalvarengaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paes 207 Rice Mill Methods of Test PDFDokument22 SeitenPaes 207 Rice Mill Methods of Test PDFEdsel Jay RaperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silent Generator TFN Type Specification Model YM6700T YM7700T YM9700T YM10000TDokument1 SeiteSilent Generator TFN Type Specification Model YM6700T YM7700T YM9700T YM10000TElvis Culma GallegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Code EEE-2310 EX-5Dokument3 SeitenCourse Code EEE-2310 EX-5Fardin ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Automation 1Dokument41 SeitenIndustrial Automation 1Chandan Chandan100% (2)
- RM8001Dokument2 SeitenRM8001shiauyunn.yeohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation Strategies For Three-Phase AC-DC Matrix Converters A ComparisonDokument7 SeitenModulation Strategies For Three-Phase AC-DC Matrix Converters A ComparisonSudip MondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 740 Professor Ali Keyhani Lecture #3: Ideal TransformersDokument11 SeitenEE 740 Professor Ali Keyhani Lecture #3: Ideal TransformersMohamed A. HusseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel Operation of GeneratorsDokument8 SeitenParallel Operation of GeneratorsTowfiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Power in India - WikipediaDokument9 SeitenWind Power in India - WikipediaTanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dunker Mae Katalog 2020 WebDokument92 SeitenDunker Mae Katalog 2020 Webgoran1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Footstep Power Generation Using Piezo Electric Transducer 1Dokument4 SeitenFootstep Power Generation Using Piezo Electric Transducer 1Subrat SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Olis Et Al. - 2013 - Feasibility Study of Economics and Performance of Solar Photovoltaics at The Snohomish County Cathcart Landfill Sit-AnnotatedDokument69 SeitenOlis Et Al. - 2013 - Feasibility Study of Economics and Performance of Solar Photovoltaics at The Snohomish County Cathcart Landfill Sit-AnnotatedLucas NascimentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LG47ln5400 Eletric Diagram LGP4750-13PL2-power+supply PDFDokument76 SeitenLG47ln5400 Eletric Diagram LGP4750-13PL2-power+supply PDFAri G LimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech Eng DSPDokument13 SeitenMech Eng DSPAnuar Angrac Lopez CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee 11Dokument17 SeitenEe 11Juphil PletoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safe and Reliable Photovoltaic Energy GenerationDokument48 SeitenSafe and Reliable Photovoltaic Energy Generationali hakan çolaker (Commissioning Engineer)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fulltext PDFDokument93 SeitenFulltext PDFD'há Santos RaúlNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4090-9005, - 9006 Suppression Release Peripheral Application and Installation InstructionsDokument10 Seiten4090-9005, - 9006 Suppression Release Peripheral Application and Installation InstructionsEliudNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB Surge Arrester POLIM-I - Data Sheet 1HC0075858 E01 ABDokument5 SeitenABB Surge Arrester POLIM-I - Data Sheet 1HC0075858 E01 ABRadu Sergiu CimpanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Lecture 4Dokument3 SeitenReport On Lecture 4Surajit SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Code EEE2310 EX-04Dokument4 SeitenCourse Code EEE2310 EX-04Fardin ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broadcrown CatalogueDokument28 SeitenBroadcrown CatalogueSerimNoch keine Bewertungen
- FP-ERL4. Oil Level Regulator.: Cooling TechnologiesDokument2 SeitenFP-ERL4. Oil Level Regulator.: Cooling TechnologiesChí Khang NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- K13 T1 SolDokument4 SeitenK13 T1 SolPriya Veer0% (1)
- Spring Operating Mechanism: For High Voltage Circuit-BreakersDokument8 SeitenSpring Operating Mechanism: For High Voltage Circuit-Breakersrimce77Noch keine Bewertungen
- (17-23) Vibration Analysis and Measurement - A Case StudyDokument7 Seiten(17-23) Vibration Analysis and Measurement - A Case StudyDilip KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 978 613 8 91055 8 PDFDokument309 Seiten978 613 8 91055 8 PDFEr Sayan ParamanikNoch keine Bewertungen