Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Resumo de Inglês
Hochgeladen von
Luana AndradeOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Resumo de Inglês
Hochgeladen von
Luana AndradeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
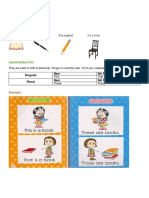
Resumo de ingls Book 1 Definite article: The student is Canadian.
The is used to identify a definite noun, and can be used with singular and plural nouns. Indefinite Articles: This is a pen This is an eraser. The indefinite article is used before singular countable nouns. A is used before consonant sounds and An is used before vowel sounds. Demonstrative Pronouns: This and that are used only with singular nouns. Ex: This is a dog That is a house.
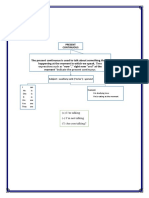
Plural forms; These an Those. Ex Those baseball bats are cheap. Possessive Case: to form the possessive case we add s to a singular noun, indicating the possessor . Possessor are only people or animals. Ex: Jean is Daniels sister. To form the possessive of the plural noun which ends in s, only the apostrophe () is used. Ex: That is my neighbors house. Interrogative pronouns : Who: is used to people . What is used to animals and objects. Adverbs of place: Here; There. Ex: The girls are here and the boys are there. Interrogative adverb: Where. Ex: Where is Click Possessive Adjectives: My, Your, His , Her,Its, Our, Your, Their. EX: This is the Stricklands House . This is their house. Interrogative Adjective: Whose. Ex: Whose dog is this Its Daniels. Whose brother is he Hes Jeans brother. The present tense of the verb TO BE
Singul ar
Affirmative
Interrogat ive Am i. Are you Is he. Is she. Is it.. Are we
Negative
I am or Im You are or youre He is or hes She is or shes It is or its plural We are or were You are or youre They are or theyre
Im not Youre not He isnt
She isnt It isnt We arent
Are you
You arent
Are they.
They arent
Ex: We arent afraid of water. There is: ( singular) used to say that something exists. There is a notebook here you can use it. Is there a book at your table. There are(plural): used to say that something exists. Ex: there are three boys. Interrogative expression of quanlity: how many: is used with plural (countable) nous. Ex: how many sandwiches, Johnny Just one, please. How much:is use with uncountable noun. Ex: How much milk is there, How much is this video game Determiners of indefinite quantity: Some and Any
Some: affirmative sentences. Ex there are some doughnuts in that box. Any: Interrogative or negative sentences. Ex there arent any sausages today. The present continuous tense: is use to describe an action that is in progress at the moment on is speaking: We are talking Book 3 The future with will can be use to express the future. Ex: I will be there at 5. Expressing probability- must: is use to express what we think is probably right, based on facts we have. Never use an infinitive with to after must. Ex: Its 11:00 Bobs still working. He must be really tired. The simple past tense of the verb to be singul ar Affirmati ve I was You were He was She was Interrogati ve Was i Were you Negative
I wasnt You werent He wasnt She wasnt It wasnt We werent You werent They werent
Was he Was she
It was plural We were
Was it Were we
You were They were
Were you
Were they.
Ex: Joe wasnt here yesterday.
There was, there were are used to say that something existed. Affirmative: there was and there were Interrogative: Was there or Were there Negative: There wasnt or there werent. Ex: Was there a party at your school on Friday The simple past tense of some regular verbs: to form the simple past tense of a regular verb in the affirmative form add ed.Ex: I visited Washington in January. To form interrogative of regular verb in the simple past tense , place DID before the subject and drop the ed from the end of the verb. Ex: Did they visit Washington on January To form the negative of a verb in the simple past tense pace DID NOT before the verb and drop the ed from the end od the verb. Ex: they didi not visit Washington in January. Book 4 Prepositions : into , in, out of Interrogative pronoun WHO: when a question begins with who, and who refers to the subject, the auxiliaries do,does or did are not used: who scared Ana Joe did Subject When a question begins with who, and who refers to the object, the auxiliaries, do, does or did are used. Who did Joe scared Joe scared Ana. Subject Object Indirect speech practice: We use indirect speech to tell someone what another person said, without repeating that persons exact words. Use the past tense of the verb if original statements was in the present tense Ex: Mr. Clark said, Peter lives in London.( Direct speech) Mr. Clark said that Peter lived in London ( Indirect speech) In indirect speech, we use he or she when used I or you in the original statementEx: (a) I think bob has a class at 2. (b) youre right. By using
indirect speech: Mrs Wilson said that she thougth Bob had a class at 2 (b) Mrs. Brown said that she was right. In indirect speech we use that when this was used in the original statement and use they when we or you were used in the original statement .Ex The salesperson said, This is the only black purse we have The salesperson said that that was the only black purse they had. In indirect speech we use asked instead of said when we are reporting a question; the word if is used when we are introducing a yes or no question, that is, a question whose answer begins with yes or no.Ex: Pam said Is your brother traveling around Europe, Bob. Pam asked Bob if his brother was traveling around Europe. We use his or her when my or your was used in the original statement; we use the past continuous tense when the present continuous tense was used in the original statement. We use those when these was used in the original statement;we use him or her when me or you was used in the original statement. Ex: Mr. Hasek said Are these boobs for me Mr. Hasek asked if those books were for him The comparative form: adjectives of 3 or more syllables, is used to compare two inems. Ex: San Francisco is more interesting than L.A. The superlative form-adjectives of 3 or more syllables: we use the superlative when we are comparing on item to the rest of a group .Ex: San Francisco is the most interesting city in California. Comparative form- Adjectives of one or two syllables. Ex: This coat is newer than my coat. Note: if a one-syllable adjective ends in or is formed by a consonant+ vowel+ consonant, we double the final consonant and add er to form comparative of the adjective; if the adjective ends in a consonant+y, we drop the y and add ier to form the comparative; if the adjective ends in e, just add r to form the comparative. The superlative form- adjectives of one or two syllables. Ex: This is the quietest street in the neighborhood Note: with one syllable adjectives that end in or are formed by consonant+ vowel+ consonant, we double the final consonant and add est to form the superlative; if the adjective ends in consonant +Y, we drop the y and add iest to form the superlative; if the adjective ends in e, we just add st to form the superlative.
The past continuous tense: When two actions, one longer than the other, occur at the same time in the past, the longer action is expressed in the use past continuous tense and the shorter action is expressed in the simple past tense. Ex: I was talking to Sue when Bob Arrived COULD is the past tense of can and is used for all persons ( singular or Plural) Ex: Tina coul read when she was four Could Tina rea when she was four My grandfather could not hear very well. WOUL LIKE: when asking for something, its more polite to use I woul like than I want Ex: I would like a steak or Id like a steak Would she like a steak I would not like to live in a big city. (If+ Present)Will: when we talk about something that may happen in the future if certain condition is met, that is, a possible future occurrence, we use the simple present tense in the part of the sentence that express condition, and the simple future tense in the part that says what may happen. If I have the money, I will travel to Europe. (If+ Past).Would: when we want to talk about an unreal or imaginary situation in the present, we use the past tense in part of the sentence that expresses conditions and conditional (would+ infinitive without to) in the part which express what would happen if that condition were met. When we use if+ the past tense of the verb to be, we have to use were for all persons If I had the money, I would buy a new car. If Mary were here, shed know what to do. Book 5 In indirect speech we use their when your or our was used in the original statement; use would when will was used in the original statement .ex: Sandra said Your mother will love this kitten Sandra told Paul and Met that their mother would love that kitten. In indirect speech , use them when us or you (pl) was used in the original statement. Ex: Lucy asked her father Is grandmother going to stay
with us using indirect speech: Lucy asked her father if her grandmother was going to stay with them. Use the next day or the following day when tomorrow was used in the original statement. Ex: The teacher said Ill talk to you about your test grade tomorrow The teacher told Harry that she would talk to him about his test grad the next day. In indirect speech , the formule (if+present)Will becomes (if+ past) would. Ex: Mary told Peter, If Greg is home, I will invite him over for dinner Mary told Peter that if Greg were home, she would invite him over for dinner May: we use to talk about the possibility of something happening She may have to work late tonight. I may not go to the party The formation of the present perfect tense: we use the verb to have in the present and the past participle of the main verb. One of the uses of the present perfect tense is when we want to talk about something that happened in the past without saying exactly when it happened Ex: Daniel has traveled around the States. Has Daniel traveled around the States Daniel has not traveled around the States. Like and alike: we use to compare people, things, places and situations that are like each other in some way. We use like between the items being compared and alike after the items being compared. Ex: Ray looks like his brother Jo. ; ray and his Brother Jo look alike. Different is use after the items being compared and different from between the items being compared. Ex: Lilys sunglasses are different from Danas sunglasses.; Lily sunglasses and Danas Sunglasses are different. To be able: is equivalent to can. It means to have the necessary power, ability or qualifications to do something. Ex: Are you able to speak german Book 6 Using have got or has got: mean the same thing as have and has Ex: I have Jims telephone number. Ive got Jims telephone number
Using have got to and has got to: mean the same thing as have to and has to, we usually use to make affirmative statements .Ex:I have got to get some glue pens It takes or it took are used to describe how much time is necessary to do a certain activity and it takes or it took+ person are used to describe how much time is or was necessary for someone to do a certain activity Ex: I takes a long time to go downtown during the rush hour; Does it take.;it usually tackes Vick a long time to get ready for a date. Many is used with plural contable noun and its more common to use it to make negative statements , a few means some or small number and Its is use with plural countable number an few means not many and is use with plural countable nouns. There arent many places to go at night in this town. Give me a few more day to think about your offer Few students earn black belt in karate It will take: it will take about an hour to get to the superstore As far as and up to are used to talk about distance. As far as generally means to a certain point and no further. Up to implies the idea of moving further north from where you are.Ex: I can take you as far as Mayberry; Im living Miami tonight and going up to Orlando We use until to talk abou time. Up to can also be uses to talk about time, but its not common.Ex: the stores open until 9 or the stores open up to 9. Might: to talk about the possibility of something happening in the present or future, dont use to after might.Ex: I might go to the beach to play volleyball tomorrowcc
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Final Assignment of English: Pysiotherapy Academi of St. Lukas Tomohon 2010Dokument12 SeitenFinal Assignment of English: Pysiotherapy Academi of St. Lukas Tomohon 2010cbxfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of speech, conditional sentences, and adverb rulesDokument10 SeitenParts of speech, conditional sentences, and adverb rulesBalach M. TheboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb To Be in The PastDokument12 SeitenVerb To Be in The PastAdalberto Jiménez100% (1)
- Pronouns: Types and FunctionsDokument44 SeitenPronouns: Types and FunctionsAsad ullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Preposition Describes A Relationship Between Other Words in A SentenceDokument13 SeitenA Preposition Describes A Relationship Between Other Words in A SentenceUriel Montes de OcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Guide for Students 6-19Dokument8 SeitenGrammar Guide for Students 6-19Orlando BloominNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present TenseDokument47 SeitenSimple Present TensealaiapramestipasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past ContinuousDokument3 SeitenPast ContinuousMarcelo Choque ApazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Been' Is The Past Participle of 'Be', Just Like 'Gone' Is The Past Participle of 'Go', and It Is Used in Precisely The Same WayDokument8 SeitenBeen' Is The Past Participle of 'Be', Just Like 'Gone' Is The Past Participle of 'Go', and It Is Used in Precisely The Same WayGubat Mystic Martial ArtsNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Tenses: Simple Past TenseDokument5 SeitenEnglish Tenses: Simple Past TenseHasnaoui DiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Think There'd Be A Lot of Children Who'd Love To Have A Climbing Wall in SchoolDokument11 SeitenI Think There'd Be A Lot of Children Who'd Love To Have A Climbing Wall in SchoolEmil FejzagićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Was WereDokument8 SeitenUse of Was WererishigivingawayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn English Grammar with ExamplesDokument16 SeitenLearn English Grammar with ExamplesAmitPandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideVon EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingles Practica 1-3Dokument19 SeitenIngles Practica 1-3juan pintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- English TensesDokument13 SeitenEnglish Tenseslog1alexNoch keine Bewertungen
- VERB TENSESDokument11 SeitenVERB TENSESJacqueline VunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pronouns: Be Careful: Make Sure The Listener Knows The Subject or Object Is Before You Start Using PronounsDokument10 SeitenPronouns: Be Careful: Make Sure The Listener Knows The Subject or Object Is Before You Start Using PronounsZahid AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- InglesDokument19 SeitenInglesBrian ShawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Compilation Dexway Vs Ioc 1ab2ab Levels PDFDokument49 SeitenGrammar Compilation Dexway Vs Ioc 1ab2ab Levels PDFmizquitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present ContinuousDokument12 SeitenPresent ContinuousCristian Ramirez RodasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approfondimenti Grammaticali Corso Inglese ECMDokument26 SeitenApprofondimenti Grammaticali Corso Inglese ECMAntonio PiazzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of VerbDokument6 SeitenTypes of VerbAdeel Raza100% (1)
- Learn English Is FunDokument71 SeitenLearn English Is Funika_nikanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5 Grammar ReviewDokument58 SeitenLesson 5 Grammar ReviewKai Jo-hann BrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qué Debo SaberDokument14 SeitenQué Debo SaberMaria Angelica Moreno O.100% (1)
- Gramaticade InglesDokument10 SeitenGramaticade InglesArianda Zarate ZarateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unidad 13Dokument40 SeitenUnidad 13Juan HermidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present: Does He Play Tennis?Dokument6 SeitenSimple Present: Does He Play Tennis?lopes martinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- GuideDokument28 SeitenGuideEmmanuel Martínez ApáezNoch keine Bewertungen
- VOICE AND NARRATIONDokument15 SeitenVOICE AND NARRATIONSukhwinder SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Present Perfect With Ever' and Never'Dokument9 SeitenThe Present Perfect With Ever' and Never'Yaina Ivanova100% (1)
- GRAMMARDokument19 SeitenGRAMMARcheng09Noch keine Bewertungen
- English Compendium 2Dokument16 SeitenEnglish Compendium 2Erick Mendiola TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Possessive Pronouns and AdjectivesDokument35 SeitenPossessive Pronouns and AdjectivesMutzda L IfahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wh-words in noun clausesDokument7 SeitenWh-words in noun clauseslusyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Zero Octavo Enero 2020. Taller.Dokument14 SeitenUnit Zero Octavo Enero 2020. Taller.Johana CamposNoch keine Bewertungen
- Changing Active Sentences to Passive VoiceDokument4 SeitenChanging Active Sentences to Passive VoiceBernadette NarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Changing Sentences in The Simple Present Tense Into PassiveDokument4 SeitenChanging Sentences in The Simple Present Tense Into PassiveBernadette NarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendices: Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean CleanDokument5 SeitenAppendices: Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean CleanDiego Alejandro MunguíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCSE French Complex Structures Corrected VersionDokument56 SeitenGCSE French Complex Structures Corrected VersionifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive and ActiveDokument7 SeitenPassive and Activeapi-304729893Noch keine Bewertungen
- Names: Sabrina e Tainá Class: 215Dokument11 SeitenNames: Sabrina e Tainá Class: 215Parameswari PerumalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main uses of the verb "to haveDokument3 SeitenMain uses of the verb "to havePatricia SandovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Direct and Indirect 3 Pages OnlyDokument4 SeitenLecture Direct and Indirect 3 Pages OnlyJuliet Orabiles MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 7 Verbs and TensesDokument11 SeitenBab 7 Verbs and TensesDwi TobingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transitive and intransitive verbs explainedDokument3 SeitenTransitive and intransitive verbs explainedRajeev RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GrammarDokument9 SeitenGrammarp4cvmx5cjzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding the Use of Articles (A, An, TheDokument20 SeitenUnderstanding the Use of Articles (A, An, ThePushpanathan ThiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modulo 7 Grammar ReferencesDokument19 SeitenModulo 7 Grammar ReferencesLEMMY RICHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sažeta Gramatika Engleskog JezikaDokument10 SeitenSažeta Gramatika Engleskog JezikaKristina StojanovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of Speech 2 Verbs, Articles & PronounsDokument28 SeitenParts of Speech 2 Verbs, Articles & PronounsKgomotso ShibamboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conditional Sentence Without If-1Dokument9 SeitenConditional Sentence Without If-1Ketua EE 2021 AndrianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Tenses PDFDokument6 SeitenEnglish Tenses PDFRizwan GhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special BeginnerDokument15 SeitenSpecial BeginnerabdulhakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrepositionsDokument28 SeitenPrepositionsMINI MATHEWNoch keine Bewertungen
- GuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarVon EverandGuíaBurros: Spanish Grammar Cheat Sheet: A quick and easy guide to Spanish GrammarBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- What Is The Objective Case?Dokument11 SeitenWhat Is The Objective Case?Ikra MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Confusing Words, Including Heteronyms; Or Why English is Difficult to LearnVon EverandConfusing Words, Including Heteronyms; Or Why English is Difficult to LearnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Langmuir Kinetics A Theorical Study PDFDokument3 SeitenLangmuir Kinetics A Theorical Study PDFJuan Pablo Castiblanco ZambranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Bet Isotherms PDFDokument19 SeitenIntroduction To Bet Isotherms PDFLuana AndradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Third ConditionalDokument0 SeitenThird ConditionalGregorio RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrio de Fase LLDokument9 SeitenEquilibrio de Fase LLLuana AndradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHT I 00introDokument15 SeitenCHT I 00introLuana AndradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Desulfurization of Heavy Oils and ResiduaDokument402 SeitenThe Desulfurization of Heavy Oils and ResiduaLuana AndradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Explorer Repetytorium Do GimnazjumDokument213 SeitenExam Explorer Repetytorium Do Gimnazjumedytkab86100% (1)
- Turning Direct Speech Into Reported SpeechDokument1 SeiteTurning Direct Speech Into Reported SpeechcrissNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported Speech: Statements, Questions, Commands and RequestsDokument10 SeitenReported Speech: Statements, Questions, Commands and RequestsKhumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- English 9 Syllabus GuideDokument6 SeitenEnglish 9 Syllabus GuideRùa RùaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported Speech GRAM BMDokument1 SeiteReported Speech GRAM BMJose GabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspect Ответы SBDokument369 SeitenAspect Ответы SBАйжан100% (3)
- TA 8 - 2 SGV - OlDokument140 SeitenTA 8 - 2 SGV - OlMưa Rào100% (1)
- Grammar - Notes of Reported SpeechDokument7 SeitenGrammar - Notes of Reported SpeechGhost GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported Speech GuideDokument15 SeitenReported Speech Guideawa polloNoch keine Bewertungen
- ағылшын т, педагогика тест 4 нұсқаDokument7 Seitenағылшын т, педагогика тест 4 нұсқаNazym100% (1)
- Welcome To Our Group Hope You Have A Nice LessonDokument18 SeitenWelcome To Our Group Hope You Have A Nice LessonTrọngNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGLISH 7 - Table of SpecificationsDokument2 SeitenENGLISH 7 - Table of SpecificationsJaver DegorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indirect Speech VIIIDokument5 SeitenIndirect Speech VIIIMadalina DumitrutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Widgb3 Ak PtestDokument4 SeitenWidgb3 Ak PtestkyrylNoch keine Bewertungen
- NDA - English For All in WordsDokument1 SeiteNDA - English For All in Wordsadityabhosale29200Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Communicative English-Class NotesDokument61 SeitenEffective Communicative English-Class Notesraj pandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 7 MELCs and Sub-Skills for EnglishDokument8 SeitenGrade 7 MELCs and Sub-Skills for EnglishNiña Anne Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 Appendix 2 Grammar SummaryDokument17 Seiten08 Appendix 2 Grammar SummaryRamona RaduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported Speech 4th CSEDokument4 SeitenReported Speech 4th CSEMoi PnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expressing Beliefs on a Filipino Wedding TraditionDokument7 SeitenExpressing Beliefs on a Filipino Wedding TraditionCheska Mary BarceloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differences between direct and indirect speechDokument21 SeitenDifferences between direct and indirect speechRizki AmaliyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported SpeechDokument1 SeiteReported Speechvuckovicpetra2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Direct and Indirect Speech RulesDokument9 SeitenDirect and Indirect Speech RulesSri DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Talk GrammarDokument237 SeitenReal Talk GrammarOmar yoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported Speech RulesDokument18 SeitenReported Speech RulesAnonymous vqzyDYXkNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Verb: Present SimpleDokument4 SeitenThe Verb: Present SimpleAna Maria IovescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narration: PersonDokument5 SeitenNarration: Personshafait MasumNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Grammar – Direct and Indirect Speech ExplainedDokument49 SeitenEnglish Grammar – Direct and Indirect Speech ExplainedShaunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indirect Speech RulesDokument5 SeitenIndirect Speech RulesKristine GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- WB - 9a2 - Semester 4 - TBDokument117 SeitenWB - 9a2 - Semester 4 - TBDiệu Thúy CaoNoch keine Bewertungen