Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Neuro Review
Hochgeladen von
redmeatisgoodOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Neuro Review
Hochgeladen von
redmeatisgoodCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
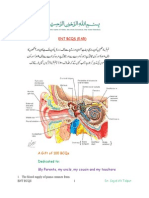
Cortex/thalamus/midbrain/pons/medulla/spinal cord Pyramidal voluntary motor (2 neuron system) CST: precentral gyrus (broadman 4) Coronoa radiate/Crus cerebri /Pons/medulla
85% decussate midline (lateral CST)/ synapse at gamma motor neuron other 15% form the anterior spinal tract Sensory info sensory fiber/ drg/ fasiculus gracilis (lower extrem) or fasic cuneutous (arm)/ internal arc fiber/ medial lemniscus/ VPL (in thalamus) -face: trigem to VPM to post-central gyrus Pain and Temp (crude touch and sexual sensation) Hand pain: Drg (1st order) Aa Ad C pain fibers/dorsal horn and synapses there at substantia gelatinosa (everything after is lissaurs tract) [also synapses directly w/A motor neuron to engage quick withdrawl reflex to move away from pain!) / decussate @ anterior white commissure / ascends as the STT / VPL of thalamus/ post central gyrus as it ascends, it also relays to the reticular formation (slow pain pathway)/ periaqueductal gray (endorphins and enkephlins) / intralaminar nuclei/ cortical regions and limbic system (emotions) CN8 enters at medullary/pontine juncton Auditory system Cochlea (organ of corti) CN8 in spiral ganglion/ synapse at dorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei (at outer edge of pons) / 2nd order neurons can go to MANY places (and decussate and ascend all over the place) superior olivary complex (either side)/ lateral lemniscus/ inferior colliculus / medial geniculate body (in thalamus) / projects to heschels gyrus (41 and 42) Visual pathway Retina/optic nerve/ optic chiasm/ optic tract (two options from here) a) : lateral geniculate nucleus/ optic radiation / visual cortex (lines calcerine sulcus) broadmans 17) and visual association 18, 19 b) brachium of the superior colliculus hits the superior colliculus/ pretectum/ NEW (CN3 and pregrang parasymps)/ cilliar ganglion (postgang symps)/ pupillary sphincter and the ciliary body allows for accomidation (areas 18 and 19 also contribute to this) Extra Pyr system This loop is required: motor cortex/basal gang/thalamus/back to motor cortex / to muscle to move
VA/VL are motor nuclei of the thalamus ST prob=hemibalism SN prob= parkinsons
Limbic System (papez circuit)memory/motivationties together primitive part of brain to the more higher order brain areas Gag reflex 10 causes input and 9 causes response at nucleus ambiguous Alternating hemianesthsia lateral medullary syndrome (PICA) Blink reflex: V1 (bilateral) and 7 Medial medullary plate: anterior spinal aa rupture, alternating hemiplegia, damage a bunch of stuff and a cn 12 too as it exits the stem (tongue moves to the same side as the lesion) MLF: connects 3,4,6,8 (allows you to hear/stay upright)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Tulane/UH New Orleans EM RotationDokument13 SeitenTulane/UH New Orleans EM RotationredmeatisgoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The Straight Razor ShaveDokument40 SeitenThe Straight Razor Shaveπετρακας πετρακαςNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Charting Outcomes 2011Dokument268 SeitenCharting Outcomes 2011sweetwskittlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Soap 1Dokument1 SeiteSoap 1redmeatisgoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Speech MechanismDokument5 SeitenThe Speech MechanismSittie HijaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Catch Up Friday Feb 29Dokument4 SeitenCatch Up Friday Feb 29leicatapangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Oriental Tongue DiagnosisDokument36 SeitenOriental Tongue Diagnosissai calder100% (2)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Lyphochek Immunoassay Plus Control Levels 1, 2 and 3: Revision Date 2023-09-25 Indicates Revised InformationDokument2 SeitenLyphochek Immunoassay Plus Control Levels 1, 2 and 3: Revision Date 2023-09-25 Indicates Revised InformationclinicalbiochemistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Biology PPT 11Dokument11 SeitenBiology PPT 11agarwalabhinav050Noch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- 'Dissertation - SynopsisDokument11 Seiten'Dissertation - SynopsisAjith SmileloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Biology Worksheet on the Excretory SystemDokument3 SeitenGrade 10 Biology Worksheet on the Excretory SystemDinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Internal Medicine,: Prof WBP Matuja Muhas/MnhDokument31 SeitenDepartment of Internal Medicine,: Prof WBP Matuja Muhas/MnhDanyu KibuguluNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Cholinergic ReceptorsDokument67 SeitenCholinergic ReceptorsShynne RPhNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Normal OcclusionDokument33 SeitenNormal OcclusionFatimah Az-ZahrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- 2 Seminal FluidDokument10 Seiten2 Seminal FluidShyne ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Dental Radiology for Age EstimationDokument5 SeitenDental Radiology for Age EstimationalyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tonsilopharyngitis and Adenoid Hypertrophy in Fadhli RajifDokument1 SeiteTonsilopharyngitis and Adenoid Hypertrophy in Fadhli RajifFadhli Rajif TangkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A HeartsDokument69 SeitenA Heartsapi-3703916Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kidney, Suprarenal Gland, Ureter and Bladder AnatomyDokument46 SeitenKidney, Suprarenal Gland, Ureter and Bladder AnatomyzahrazhfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision For Assessment II (Y8)Dokument33 SeitenRevision For Assessment II (Y8)Nan Hay Zun Naung LattNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Physiology Lab Report 10 - UrinalysisDokument19 SeitenPhysiology Lab Report 10 - Urinalysisbenamos100% (10)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Breast Anatomy Regions and Lymph Node DrainageDokument8 SeitenBreast Anatomy Regions and Lymph Node DrainagedrhendyjuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Aging On The Digestive SystemDokument3 SeitenEffects of Aging On The Digestive SystemShereen Manabilang100% (2)
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 10Dokument10 SeitenNcert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 10JollyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Materi Anatomi DR ElieserDokument49 SeitenMateri Anatomi DR ElieserAbhauasjsjjjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology NotesDokument58 SeitenImmunology Notespawnjabi100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Sevilla C. Yobueno, Ph.D. SPAMAST Malita Campus I. Cells, Tissues and MembranesDokument5 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Sevilla C. Yobueno, Ph.D. SPAMAST Malita Campus I. Cells, Tissues and MembranesReuben EscarlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Female Reproductive SystemDokument34 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of The Female Reproductive Systemruthpebbles100% (2)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- ENT BCQsDokument19 SeitenENT BCQsSajid AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease-Induced Thyroid Storm: Ase EportDokument4 SeitenGestational Trophoblastic Disease-Induced Thyroid Storm: Ase EportAhmad Harissul IbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan Skeletal SystemDokument9 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan Skeletal SystemVianney Madrazo Apolinario100% (1)
- BibliographyDokument332 SeitenBibliographyWali MahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estrogen DR DeanDokument8 SeitenEstrogen DR DeanMochammad Halim NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hema2 Lec 2 TransDokument159 SeitenHema2 Lec 2 TransJPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)