Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Summary of NDT Methods
Hochgeladen von
mullanjiOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Summary of NDT Methods
Hochgeladen von
mullanjiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SUMMARY OF NDT METHODS
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.
Visual Testing (VT) Penetrant Test (PT) Magnetic Particle (MT) Eddy Current (ET) Ultrasonic (ET) Vibration Analysis (VA) Acoustic Emission (AE) Radiographic Testing (RT)
VISUAL Testing (VT)
APPLICATIONS
Surface discontinuities:
Cracks, porosity, slag misalignment, warpage, incorrect size or number.
COMMENTS
Should always be the first method applied.
VISUAL Testing (VT)
ADVANTAGES
Inexpensive; fast; simple; apply during processing. Can eliminate need for other methods.
LIMITATIONS
Surface only; variable and poor resolution; eye fatigue; distractions. Need good illumination.
PENETRANT (PT)
APPLICATIONS
Surface discontinuities:
Cracks, porosity, seams, laps, leaks.
COMMENTS
Messy; need good ventilation.
PENETRANT (PT)
ADVANTAGES
Inexpensive; easy to apply; more sensitive than visual alone; use on most materials; rapid; portable.
LIMITATIONS
Surface only; not useful on hot, dirty, painted, or very rough surfaces. Requires some technique.
MAGNETIC PARTICLE (MT)
APPLICATIONS
Surface and near surface discontinuities:
Cracks, voids, porosity, inclusions, seams, laps.
COMMENTS
Messy. Can cause defects.
MAGNETIC PARTICLE (MT)
ADVANTAGES
Low cost; fast; more sensitive to tight cracks than PT; can do near subsurface; portable.
LIMITATIONS
Material must be ferromagnetic; surface must be clean; part may be demagnetized; alignment of field is important. Requires operator technique.
EDDY CURRENT (ET)
APPLICATIONS
Surface and near surface discontinuities:
Seams, composition, thickness, eccentricity, surface condition.
COMMENTS
Requires good standards.
EDDY CURRENT (ET)
ADVANTAGES
Extremely rapid; can be automated; very sensitive; surface contact not necessary; permanent record.
LIMITATIONS
Shallow penetration; conductive materials only; may require special equipment; sensitive to geometry; difficult interpretation sometimes.
ULTRASONIC (UT)
APPLICATIONS
Surface and deep subsurface discontinuities:
Cracks, laminations, porosity, lack of fusion, inclusions, thickness.
COMMENTS
Need good standards. Frequently used method.
10
ULTRASONIC (UT)
ADVANTAGES
Rapid if automated but manual is slow; applicable to very thick specimens; can give location and size of discontinuity; good sensitivity; inspect from one side; portable.
LIMITATIONS
Couplant required; thin complex shapes are difficult; orientation of discontinuity important; very operator-dependent.
11
DYNAMIC TESTING VIBRATION ANALYSIS
APPLICATIONS
System abnormalities:
Misalignment, lack of bonding, missing or worn components, loose parts.
COMMENTS
Should begin with installation of system and test at regular intervals.
12
DYNAMIC TESTING VIBRATION ANALYSIS
ADVANTAGES
Useful in predictive or preventative maintenance; identify problem areas or parts; indicate severity in-service; test; portable.
LIMITATIONS
Special equipment; experience required; some systems are too complex.
13
ACOUSTIC EMISSION (AE)
APPLICATIONS
Surface and subsurface discontinuities:
Crack initiation and growth, leaks, boiling and cavitations, phase changes.
COMMENTS
Indications and usually checked by other methods. Use is growing rapidly.
14
ACOUSTIC EMISSION (AE)
ADVANTAGES
Remote and continuous surveillance, location, severity, permanent record. Tests an entire vessel or system.
LIMITATIONS
Contact with system; may need many contact points; complex interpretation; system must be stressed; usually expensive; some systems are too complex.
15
RADIOGRAPHY (RT)
APPLICATIONS
Subsurface discontinuities:
Cracks, voids, inclusions, thickness variation, lack of fusion, incomplete penetration, corrosion, missing components, composition>
COMMENTS
One of the most frequently used methods.
16
RADIOGRAPHY (RT)
ADVANTAGES
Easily understood permanent record; usually moderate cost; can be portable; applicable to a wide range of materials.
LIMITATIONS
Cannot detect laminations; radiation hazard and regulations; access to both sides can be high cost; requires trained operators.
17
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ex StickersDokument3 SeitenEx StickersmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSI Pipe Lengths: Size Standard LengthDokument2 SeitenANSI Pipe Lengths: Size Standard LengthmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tainjin Haigang Steel Co. Ltd. (Made in China)Dokument2 SeitenTainjin Haigang Steel Co. Ltd. (Made in China)mullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hindi English Masala TranslationDokument10 SeitenHindi English Masala TranslationmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection Check ListDokument3 SeitenInspection Check ListmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Details ASTM A53Dokument4 SeitenProduct Details ASTM A53mullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Galvanized (Round Pipes) NPS Wall Thickness (MM) 1.5 1.8 2 3 3.2 Weight (KG/M) Outside DiameterDokument1 SeitePre-Galvanized (Round Pipes) NPS Wall Thickness (MM) 1.5 1.8 2 3 3.2 Weight (KG/M) Outside DiametermullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Specification Levels for PipesDokument14 SeitenProduct Specification Levels for PipesmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm 500Dokument4 SeitenAstm 500mullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zinc MTC PDFDokument1 SeiteZinc MTC PDFmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NPT Thread DetailsDokument1 SeiteNPT Thread DetailsmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- API 5l Details From My SideDokument14 SeitenAPI 5l Details From My SidemullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BPV Stencil MarkingDokument2 SeitenBPV Stencil MarkingmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSI Coupling Weight Chart by SizeDokument1 SeiteANSI Coupling Weight Chart by SizemullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection Check ListDokument3 SeitenInspection Check ListmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee training recordsDokument10 SeitenEmployee training recordsmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al-Jazera Steel Factories API 5L Pipe SpecificationsDokument22 SeitenAl-Jazera Steel Factories API 5L Pipe Specificationsmullanji50% (2)
- CSWIP-WI-6-92 14th Edition April 2017Dokument17 SeitenCSWIP-WI-6-92 14th Edition April 2017mullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Analysis UpdatedDokument15 SeitenStandard Analysis UpdatedmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zinc MTCDokument1 SeiteZinc MTCmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NoiceDokument2 SeitenNoicemullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supplier List: Supplier Name & Address Vendor Code Product / Services StatusDokument2 SeitenSupplier List: Supplier Name & Address Vendor Code Product / Services StatusmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro Test Pressure As Per UL 852 (Sprinkler Pipes) IsDokument1 SeiteHydro Test Pressure As Per UL 852 (Sprinkler Pipes) IsmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance of Galvanized Steel ProductsDokument16 SeitenPerformance of Galvanized Steel ProductsAndy ChongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 46 RegionalMaterialsDokument8 Seiten46 RegionalMaterialsmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe ThreadsDokument11 SeitenPipe Threadsanac_mathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oznake ČelikaDokument8 SeitenOznake ČelikaSamra DukićNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS 1387/1985 Standard for Black and Galvanized Steel TubesDokument2 SeitenBS 1387/1985 Standard for Black and Galvanized Steel TubesmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work at Height Safety GuideDokument1 SeiteWork at Height Safety GuidemullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1 - 2 Welding Symbols and DrawingsDokument13 SeitenM1 - 2 Welding Symbols and DrawingsmullanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 486d283e69 Bok-SupercondDokument560 Seiten486d283e69 Bok-SupercondМихаил Дзюба100% (1)
- Normen Englisch Stand 09 2013Dokument9 SeitenNormen Englisch Stand 09 2013jmunjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project: Proposed Development of 242 Units of 27 Storeys Condominium (Phase 1A-Rc3)Dokument8 SeitenProject: Proposed Development of 242 Units of 27 Storeys Condominium (Phase 1A-Rc3)pakbilal1100% (1)
- Fatigue Life of Double Angle Tension MembersDokument10 SeitenFatigue Life of Double Angle Tension MembersalbertoxinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared By: - Yasmeen Bsharat - Abeer Saleh: Dr. Abdul Razzaq TouqanDokument49 SeitenPrepared By: - Yasmeen Bsharat - Abeer Saleh: Dr. Abdul Razzaq Touqanvuxuandung84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 7: Rockwell Hardness TestDokument11 SeitenExperiment 7: Rockwell Hardness TestDaniel Naoe Festin0% (2)
- Effects of Waste Polypropylene Fibers On The Mechanical Behavior of Fiber Reinforced Concrete An Experimental StudyDokument4 SeitenEffects of Waste Polypropylene Fibers On The Mechanical Behavior of Fiber Reinforced Concrete An Experimental StudyEditor IJTSRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Failure Analysis of W e L D Repaired Turbine RotorDokument6 SeitenFailure Analysis of W e L D Repaired Turbine RotorAli AlyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yielding of Brass Case Walls in The ChamberDokument29 SeitenYielding of Brass Case Walls in The ChamberDrew BrewerNoch keine Bewertungen
- TS 500-2000 Ex001Dokument4 SeitenTS 500-2000 Ex001Erik VelasteguíNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Excellent Chemistry Assignment The Solid StatesDokument5 Seiten2-Excellent Chemistry Assignment The Solid StatesSachin B SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar PustakaDokument6 SeitenDaftar PustakaEgyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bondek Design & Construct ManualDokument131 SeitenBondek Design & Construct ManualAkuma.Gokai7328100% (12)
- FEM Tables PDFDokument3 SeitenFEM Tables PDFAisyah NadhirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bs ClausesDokument3 SeitenBs ClausesTobin T Kunnath100% (1)
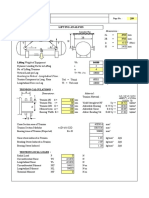
- Lifting analysis of vessel equipmentDokument1 SeiteLifting analysis of vessel equipmentshaishav100% (2)
- Homework 3Dokument8 SeitenHomework 3Alferid ShifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design 1st Partial Equation SheetDokument2 SeitenMachine Design 1st Partial Equation SheetRoberto Adrian Martinez ValverdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three Dimensional Nonlinear Finite Element Model for Analysis of Masonry Arch BridgesDokument10 SeitenThree Dimensional Nonlinear Finite Element Model for Analysis of Masonry Arch BridgesSA ArminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fermi Surface: Notes By: Shahzaib ShahidDokument7 SeitenFermi Surface: Notes By: Shahzaib ShahidShazaib MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- J & K All PapersDokument104 SeitenJ & K All PapersCgpscAspirantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Does Non-Linear Geometry Effects (NLgeom ON) Effect The Reaction Forces in ABAQUSDokument3 SeitenDoes Non-Linear Geometry Effects (NLgeom ON) Effect The Reaction Forces in ABAQUSMrk BrkngNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECCC - RECOMMENDATIONS-2014-Vol6 - 3Dokument5 SeitenECCC - RECOMMENDATIONS-2014-Vol6 - 3IndraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double-Layer Gadolinium Zirconate/Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Thermal Barrier Coatings Deposited by The Solution Precursor Plasma Spray ProcessDokument12 SeitenDouble-Layer Gadolinium Zirconate/Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Thermal Barrier Coatings Deposited by The Solution Precursor Plasma Spray ProcessDragomirescu AlinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardcarb - WearplatesDokument32 SeitenHardcarb - WearplatesJimit ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Somaloy-3p Material-Data June 2018 2273hog PDFDokument11 SeitenSomaloy-3p Material-Data June 2018 2273hog PDFvineethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm d412 Pdqv6897Dokument13 SeitenAstm d412 Pdqv6897Nayth Andres GalazNoch keine Bewertungen
- TTT DiagramDokument17 SeitenTTT DiagramGAURAV SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weld DesignDokument51 SeitenWeld DesignJoseph Booker100% (1)
- Lesson 12 - Hardness RockwellDokument6 SeitenLesson 12 - Hardness Rockwell4gen_5Noch keine Bewertungen