Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose
Hochgeladen von
Mark OrculloOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose
Hochgeladen von
Mark OrculloCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
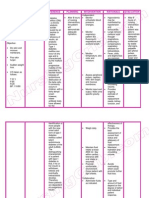
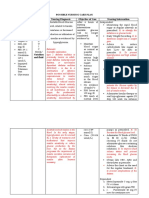
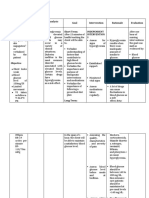
ASSESSMENT NONE
DIAGNOSIS Risk for unstable blood glucose related to deficient knowledge of diabetes
PLANNING SHORT TERM Patient will acknowledge factors that may lead to unstable glucose LONG TERM Maintain glucose in satisfactory range
INTERVENTION INDEPENDENT Determine individual factors that may contribute to unstable glucose Ascertain client s/SO s knowledge/understanding of condition and treatment needs Determine patient s awareness/ ability to be responsible for dealing with situation: age, maturity, and current health status, ability to provide own safety
RATIONALE
EVALUATION SHORT TERM
To assess risk/contributing factors
Patient acknowledged factors that may lead to unstable glucose LONG TERM Maintainedglucose in satisfactory range
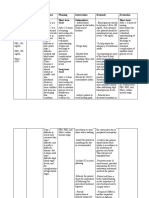
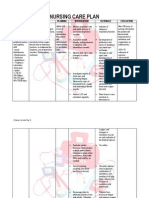
All available machines will Ascertain whether patient/SO are adept at operating patient s provide satisfactory reading if home glucose monitoring device properly used and maintained and routinely calibrated Provide information on balancing food intake, antidiabetic agents
Discuss home glucose monitoring according to individual parameters (ex. 6x/day for normal day and more frequently during times of stress)
To identify and manage glucose variations
Review patient s common situations that contribute to glucose instability on daily, occasional, and crisis basis
Multiple factors can play a role at anytime, such as missing meals, adolescent growth spurt, or infection
Review patient s diet, especially carbohydrate intake
Glucose balance is determined by the amount of carbohydrates consumed, which should be determined in needed grams/day
Encourage patient to read labels and choose foods described as having a low glycemic index, higher fiber and low fat content
These foods produce a slower rise in blood glucose
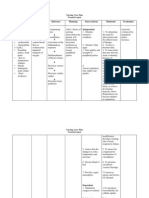
Discuss how patient s antidiabetic medications work
Drugs and combinations of drugs work in varying ways with different blood glucose control and side effects. Understanding drug actions can help patient avoid/reduce risk of potential for hypoglycemic reactions
Review types of insulin and delivery method
Affects timing of effects and provides clues to potential timing of glucose instability Insulin absorption can vary from day to day in healthy sites and is less absorbable lypohyperthropic tissues Children, adolescents, and elderly patients may forget injections or be unable to inject and may need reminders and supervisions
Check injection sites periodically
Ascertain that all injections are being given
COLLABORATIVE Consult with dietitian about specific dietary needs based on individual situation
Refer to appropriate community resources, diabetic educator, and/or support groups as needed.
For lifestyle modification, medical management, referral to insulin pump or glucose monitor, financial assistance for supplies, etc.
CHRISTIAN MARK ORCULLO
N412
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Nursing Diagnosis For DKADokument6 SeitenNursing Diagnosis For DKARhanne Bolante88% (24)
- Nursing Care Plan Diabetes Mellitus Type 1Dokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Diabetes Mellitus Type 1deric85% (46)
- Risk For Unstable Blood GlucoseDokument4 SeitenRisk For Unstable Blood GlucosehallegendNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements - Diabetes - NCPDokument5 SeitenImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements - Diabetes - NCPJulie Ann Jimenez Manlangit50% (4)
- Nursing Care PlanDokument10 SeitenNursing Care PlanZerica Andaca83% (6)
- Diabetes Mellitus NCPDokument7 SeitenDiabetes Mellitus NCPjfgnzls182892% (12)
- Fluid Volume ExcessDokument4 SeitenFluid Volume ExcessTamil Villardo100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Kenneth Regida)Dokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (Kenneth Regida)Kenneth Anthony Tiu Regida100% (8)
- NCP Risk For Unstable Blood GlucoseDokument2 SeitenNCP Risk For Unstable Blood GlucoseNathalie kate petallar75% (8)
- Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose (DM)Dokument4 SeitenRisk For Unstable Blood Glucose (DM)Ace Khiel Peralta50% (2)
- NCPDokument3 SeitenNCPGimcy Dela Fuente100% (6)
- Unstable Blood GlucoseDokument6 SeitenUnstable Blood Glucosetherese BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDokument2 SeitenRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose Related To Unhealthy Lifestyle.Dokument8 SeitenRisk For Unstable Blood Glucose Related To Unhealthy Lifestyle.eleinsamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition NCPDokument3 SeitenNutrition NCPMarielle Adrienne Bitancor100% (1)
- 3 Nursing Care Plan Diabetes MellitusDokument5 Seiten3 Nursing Care Plan Diabetes MellitusAnnisa Silvera II50% (2)
- NCP Tissue PerfusionDokument2 SeitenNCP Tissue PerfusionNiña Montejo Ealdama100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans For Diabetes MellitusDokument12 SeitenNursing Care Plans For Diabetes MellitusRaveen mayi85% (59)
- Care Plan 3Dokument3 SeitenCare Plan 3nyctotem50% (2)
- Fitzpatricks Dermatology in General Medicine 8ed 1Dokument10 SeitenFitzpatricks Dermatology in General Medicine 8ed 1ANTINNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsDokument4 SeitenNCP - Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsKaye Nicole Lugo80% (5)
- Risk For Unstable Blood GlucoseDokument24 SeitenRisk For Unstable Blood GlucoseFerreze Ann100% (1)
- NCP DMDokument4 SeitenNCP DMStef Bernardo67% (3)
- NCP DMDokument2 SeitenNCP DMAna Ramos LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPRachel PerandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Diabetes Mellitus Type IIDokument10 SeitenNCP - Diabetes Mellitus Type IIChristine Karen Ang SuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP FVDDokument2 SeitenNCP FVDMarlon AnryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lanjutan NCP DMDokument14 SeitenLanjutan NCP DMVera Andri YaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Possible Nursing Care Plan Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Nursing InterventionDokument12 SeitenPossible Nursing Care Plan Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Nursing InterventionClaire M. AuditorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pain NCPDokument1 SeiteAcute Pain NCPJed AvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument7 SeitenNCPChris Denver BancaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knowledge DeficitDokument3 SeitenKnowledge DeficitInigo Miguel DulayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes Mellitus NCPDokument5 SeitenDiabetes Mellitus NCPCazze SunioNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument2 SeitenNCPJanelle Cabida Supnad100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDharylle Cariño100% (3)
- NCP For DM1Dokument2 SeitenNCP For DM1Pau Hipol MadriagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For DM PatientDokument10 SeitenNursing Care Plan For DM PatientRainier Rhett Concha100% (5)
- Case Chronic Renal Failure Discharge PlanningDokument2 SeitenCase Chronic Renal Failure Discharge PlanningFatima Dorcas Roxas LabausaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument9 SeitenNCPTracy Camille EscobarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument12 SeitenNursing Care Plankeishaaa29100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan DM Type 2Dokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan DM Type 2Jay V. FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP RiskDokument3 SeitenNCP RiskMaricar Azolae MascualNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertension NCPDokument1 SeiteHypertension NCPj4royce100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAn-Imbalance NutritionDokument2 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAn-Imbalance NutritionJoan Parlan100% (1)
- Hydatidiform MoleDokument28 SeitenHydatidiform MoleRitamaria100% (7)
- NCP (Fatigue)Dokument1 SeiteNCP (Fatigue)student_019100% (1)
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPAndrea BroccoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan JaundiseDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan Jaundisearif aimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDokument2 SeitenImpaired Gas ExchangeAura Salve Ildefonso Allas100% (3)
- NCP HyperthermiaDokument2 SeitenNCP HyperthermiaKirby ContaoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Impaired Skin Integrity and Readiness For Enhanced PowerDokument3 SeitenRisk For Impaired Skin Integrity and Readiness For Enhanced PowerdanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP: Diabetes Mellitus Prepregnancy/GestationalDokument11 SeitenNCP: Diabetes Mellitus Prepregnancy/GestationalJavie85% (13)
- NCP For FT, SGADokument7 SeitenNCP For FT, SGAJule Santoya80% (5)
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM)Dokument1 SeiteDiabetes Mellitus (DM)Bheru LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For StrokeDokument4 SeitenNCP For StrokeJASON OGALESCONoch keine Bewertungen
- Independent: Actions/Interventions RationaleDokument8 SeitenIndependent: Actions/Interventions RationalePedro SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nurse ResponsibilitiesInterventionsDokument3 SeitenNurse ResponsibilitiesInterventionskarylle hilarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Askep B.inggrisDokument2 SeitenAskep B.inggrisVivi AuridaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TerapiDokument43 SeitenTerapiEva SinagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 NotesDokument5 SeitenDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 NotesAimee Kaye DetablanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook John Murtaghs General Practice Companion Handbook PDF Full Chapter PDFDokument67 SeitenEbook John Murtaghs General Practice Companion Handbook PDF Full Chapter PDFroberto.duncan209100% (27)
- Australian - 2008 - Maxillofacial Trauma in Major Trauma PatientsDokument6 SeitenAustralian - 2008 - Maxillofacial Trauma in Major Trauma Patientsووويويويةءتؤوبةين للاNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sacra Men To Medical Transportation ServicesDokument2 SeitenSacra Men To Medical Transportation ServicesSACPROS INC.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Neurone Disease: J GormallyDokument14 SeitenMotor Neurone Disease: J GormallyBambang SutrisnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vi. Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenVi. Nursing Care PlanJopaii TanakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewon Rabiesand VaccinesDokument23 SeitenReviewon Rabiesand VaccinesNimra Naveed ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contact Urticaria Syndrome: Occupational Aspects: Becky S. Li, Iris S. Ale, and Howard I. MaibachDokument34 SeitenContact Urticaria Syndrome: Occupational Aspects: Becky S. Li, Iris S. Ale, and Howard I. MaibachsaskiakonitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 4 3 2 1 Grounding Techniqueqspae PDFDokument2 Seiten5 4 3 2 1 Grounding Techniqueqspae PDFsheetcherry57Noch keine Bewertungen
- Antimicrobial Effect of Aqueous Banana Peel Extract, IraqDokument4 SeitenAntimicrobial Effect of Aqueous Banana Peel Extract, IraqLilis KhusnulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatology Research - 2023 - Yoshiji - Management of Cirrhotic Ascites Seven Step Treatment Protocol Based On The JapaneseDokument12 SeitenHepatology Research - 2023 - Yoshiji - Management of Cirrhotic Ascites Seven Step Treatment Protocol Based On The JapaneseSarah FaziraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diarrhoea Patient InformationDokument3 SeitenDiarrhoea Patient InformationIgor DemićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pacemakers - Fact SheetDokument7 SeitenPacemakers - Fact Sheettalha.k.rajpootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secondary Immunodeficiency in ChildrenDokument16 SeitenSecondary Immunodeficiency in Childrenryan20eNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Aid Maxilofacl SurgeryDokument94 SeitenFirst Aid Maxilofacl SurgerydoctorniravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Grade10 4th QuarterDokument40 SeitenHealth Grade10 4th QuarterYnjel HilarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrainsDokument19 SeitenDrainspaulineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sars-Cov-2 & Influenza AB & RSV Antigen Combo Test Kit (Self-Testing)Dokument2 SeitenSars-Cov-2 & Influenza AB & RSV Antigen Combo Test Kit (Self-Testing)Ignacio PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipcrf TemplateDokument57 SeitenIpcrf TemplateJeng SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chandy C. John - Advances in The Diagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric Infectious Diseases - 2013Dokument212 SeitenChandy C. John - Advances in The Diagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric Infectious Diseases - 2013Alla AlkateebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pregnancy ComplicationsDokument14 SeitenPregnancy Complicationsvienny kayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community Nursing Care PlanDokument6 SeitenCommunity Nursing Care Plantansincos93% (14)
- Alkaloids Physiological EffectsDokument25 SeitenAlkaloids Physiological EffectsGiang Lam100% (1)
- Seizure Disorders: Assessment and Diagnostic FindingsDokument3 SeitenSeizure Disorders: Assessment and Diagnostic FindingsBlessed GarcianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Re-Test SUBJECT-English Core Class - Xi Time: 2 Hrs. M.M: 50 General InstructionsDokument8 SeitenRe-Test SUBJECT-English Core Class - Xi Time: 2 Hrs. M.M: 50 General InstructionsSunilDwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Files PedsDokument54 SeitenCase Files PedsSam ZeezNoch keine Bewertungen
- "The Effects of Interpersonal Crime On Victims": Reporter: Michel O. Espinosa Bs-Psychology Code: 3175Dokument6 Seiten"The Effects of Interpersonal Crime On Victims": Reporter: Michel O. Espinosa Bs-Psychology Code: 3175Ezri Mariveles Coda Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- First Aid For The Usmle Step 1 2022-Mcgraw-Hill Education 2022Dokument1 SeiteFirst Aid For The Usmle Step 1 2022-Mcgraw-Hill Education 2022Beto RendonNoch keine Bewertungen
- March 2012Dokument28 SeitenMarch 2012Bill5199Noch keine Bewertungen
- Covid 19 WorksheetsDokument16 SeitenCovid 19 WorksheetsKarla Paola MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen