Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pathophysiology of Incomplete Abortion: Risk Factors and Management
Hochgeladen von
Claire Nimor VentulanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pathophysiology of Incomplete Abortion: Risk Factors and Management
Hochgeladen von
Claire Nimor VentulanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
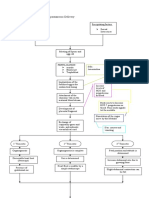
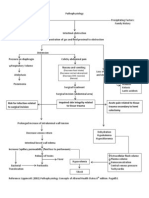
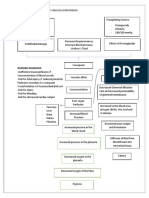
Pathophysiology of Incomplete Abortion RisK Factors: Fetal Factors: Abnormal development of zygote Maternal Factors: Infection Systemic disease
ase Exposure to radiation Reproductive system anomalies Drug ingestion Age Placental Factors: Abnormal placental implantation Premature separation of the normall implanted placenta Precipitating Factor: 8 weeks AOG( occurs during 1st Trimester of Pregnancy)
Implanted egg, slightly separates or tears from the uterus
Blood collects between the chorionic membrane( a membrane that develops around a fertilized egg) and the wall of the uterus
Blood leaks in the cervix
Mild uterine cramping on the lower abdomen with minimal vaginal spotting / bleeding ( 3-4 days ) Fetus is compromised Subsequently expelled from the uterus
Subchorionic hemorrhage
Severe subchorionic bleeding can lead to rupture of subchorionic membrane.
Disruption of blood flow, containing oxygen& nutrients to the developing fetus.
Fetus is compromised
subsequently expelled from the uterus
Patient now manifest signs and symptoms of a spontaneous abortion like: Heavy vaginal flow Severe uterine cramping Open cervix Passage of tissue Ultrasound reveals the absence of a viable fetus
Risk for miscarriage and threatened abortion
Incomplete abortion
Ultrasound shows that some of the products of conception are still inside the uterus
D and C
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyLiza MinonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABORTION PathophysiologyDokument3 SeitenABORTION PathophysiologyChiara FajardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pa Tho Physiology of Ectopic PregnancyDokument2 SeitenPa Tho Physiology of Ectopic Pregnancynelyang17100% (6)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY - Placenta PreviaDokument5 SeitenPATHOPHYSIOLOGY - Placenta PreviaFretzgine Lou Manuel100% (2)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Ectopic PregnancyDokument2 SeitenPa Tho Physiology of Ectopic Pregnancythediaber60% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Ruptured Ectopic PregnancyDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of Ruptured Ectopic PregnancyDan Kenneth Liban Llanto89% (9)
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDokument5 SeitenEctopic Pregnancy Pathophysiologyjoyrena ochondraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iii. Textbook Discussion A. Definition: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDokument3 SeitenIii. Textbook Discussion A. Definition: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsVianne ArcenioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incomplete AbortionDokument22 SeitenIncomplete AbortionAJ Dalawampu100% (2)
- Physiology Ectopic PregnancyDokument1 SeitePhysiology Ectopic Pregnancypinoynursetambay80% (5)
- Placenta Previa PathophysiologyDokument1 SeitePlacenta Previa Pathophysiologykathy85% (20)
- Pathophysiology PP FinalDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology PP FinalLouie Kem Anthony Babaran0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyPaul Vincent Alfonso100% (2)
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDokument1 SeiteEctopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- Case Study - Ectopic PregnancyDokument10 SeitenCase Study - Ectopic Pregnancykristine keen buanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incomplete Abortion MINI CASE STUDY (Group 3)Dokument22 SeitenIncomplete Abortion MINI CASE STUDY (Group 3)Twobee Evelyn Claire62% (21)
- Pathophysiology of Placenta PreviaDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Placenta PreviaJeffrey Calicdan Bucala100% (6)
- Nursing Care of Hydatidiform MoleDokument23 SeitenNursing Care of Hydatidiform MoleKristel Rivamonte100% (1)
- Patho PhysiologyDokument3 SeitenPatho PhysiologyKeith MadarangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study H MOLEDokument11 SeitenCase Study H MOLEmaori_martinez82% (11)
- Physiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDokument2 SeitenPhysiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliverySummer Rain100% (2)
- Abruptio Placenta PathophysiologyDokument4 SeitenAbruptio Placenta Pathophysiologyjamie carpioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incompetent Cervix Case Analysis Subgroup 2Dokument44 SeitenIncompetent Cervix Case Analysis Subgroup 2bunso padillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ectopic Pregnancy Nursing Care PlanDokument2 SeitenEctopic Pregnancy Nursing Care PlanKim GalamgamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Castillo H MoleDokument52 SeitenCase Study Castillo H MoleGodfrey Bag-ao100% (1)
- Incomplete Abortion Case StudyDokument40 SeitenIncomplete Abortion Case StudyLani Michelle BelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- H Mole PathoDokument1 SeiteH Mole PathoKyle AlmeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY HmoleDokument4 SeitenPATHOPHYSIOLOGY HmoleMonica Lyka Bancale100% (3)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYDokument2 SeitenPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYryeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of IntussusceptionDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of IntussusceptionJehazel Bastian100% (1)
- Placent Previa Case Study With Pa Tho PhysiologyDokument6 SeitenPlacent Previa Case Study With Pa Tho PhysiologyRey Deemsur Salvilla MolinosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Placenta Previa This Is It 1Dokument71 SeitenCase Study Placenta Previa This Is It 1Homework Ping100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDareRaymondNoch keine Bewertungen
- Placenta Previa Case StudyDokument59 SeitenPlacenta Previa Case StudyKen KenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of NSVDDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of NSVDLenjun83% (6)
- Abortion CaseDokument41 SeitenAbortion Casekaycee_delacruz60% (5)
- Cephalopelvic DisproportionDokument93 SeitenCephalopelvic Disproportionkyle cunanan100% (6)
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDokument19 SeitenAbnormal Uterine BleedingDelphy Varghese100% (1)
- BLEEDING IN EARLY PREGNANCYDokument36 SeitenBLEEDING IN EARLY PREGNANCYvictor onapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - Abortion or MiscarriageDokument43 Seiten5 - Abortion or Miscarriageasifdawar2011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ectopic Pregnancy and Abortion: DR - Shamim Rima MBBS, Dmu, FCGP M.PHL, Thesis Part Radiology & ImagimgDokument59 SeitenEctopic Pregnancy and Abortion: DR - Shamim Rima MBBS, Dmu, FCGP M.PHL, Thesis Part Radiology & Imagimgdr_shamimrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bleeding in Early Late PregnancyDokument46 SeitenBleeding in Early Late PregnancyAndrada Catrinoiu100% (2)
- Seminar G2 (Early Trimester Pregnancy Vaginal Bleeding)Dokument47 SeitenSeminar G2 (Early Trimester Pregnancy Vaginal Bleeding)Chalie MequanentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDokument4 SeitenBleeding in Early Pregnancynur1146Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abruptio PlacentaDokument3 SeitenAbruptio PlacentaNano KaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HemorrhageDokument19 SeitenHemorrhageNelly AstikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 High RDokument28 Seiten2 High RAbdurraouf SaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Hasil Tutorial Kelompok 10Dokument49 SeitenLaporan Hasil Tutorial Kelompok 10Ana Abadi Al IndNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbortionDokument16 SeitenAbortionGaurav TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topics Today: Normal Puerperium Diseases of Puerperium Ectopic Pregnancy AbortionDokument52 SeitenTopics Today: Normal Puerperium Diseases of Puerperium Ectopic Pregnancy AbortionBitto_Singh_5952Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDokument65 SeitenBleeding in Early PregnancyParthi ParthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abortion: L Sekhavat MD Ob & GynDokument38 SeitenAbortion: L Sekhavat MD Ob & GynNurulAqilahZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antepartum - AbortionDokument5 SeitenAntepartum - AbortionBench AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book Picture Patient PictureDokument22 SeitenBook Picture Patient PictureAnsiya K ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDokument32 SeitenBleeding in Early PregnancyPhuntsho OngmoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abortion TypesDokument19 SeitenAbortion TypesFany MaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDokument10 SeitenEctopic Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentXo Yem0% (1)
- High Risk PregnancyDokument10 SeitenHigh Risk PregnancyRoy Mujeres CabueñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submitted By: Diana M. Resultay A301/Group-3B Submitted To: Ms. ReyesDokument9 SeitenSubmitted By: Diana M. Resultay A301/Group-3B Submitted To: Ms. ReyesDiannetotz MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avulsed Wound Left FootDokument6 SeitenAvulsed Wound Left FootClaire Nimor VentulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstructive UropathyDokument5 SeitenObstructive UropathyClaire Nimor VentulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 25 Medical Terms You Need To KnowDokument2 SeitenTop 25 Medical Terms You Need To KnowClaire Nimor VentulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Medical AbbreviationsDokument16 SeitenList of Medical AbbreviationsClaire Nimor VentulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apgar ScoreDokument11 SeitenApgar Scorefaizura100% (1)
- List of Medical AbbreviationsDokument16 SeitenList of Medical AbbreviationsClaire Nimor VentulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Incomplete Abortion: Risk Factors and ManagementDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of Incomplete Abortion: Risk Factors and ManagementClaire Nimor Ventulan50% (4)
- Causes of MiscarriageDokument7 SeitenCauses of MiscarriageClaire Nimor VentulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetric Safety ProtocolsDokument10 SeitenObstetric Safety ProtocolsApril LilianNoch keine Bewertungen
- V3 Eng PDFDokument848 SeitenV3 Eng PDFaidhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Average Blood Loss Following Vaginal Delivery, Cesarean Delivery and Cesarean Hysterectomy Is 500 ML, 1000 ML and 1500 ML RespectivelyDokument11 SeitenThe Average Blood Loss Following Vaginal Delivery, Cesarean Delivery and Cesarean Hysterectomy Is 500 ML, 1000 ML and 1500 ML RespectivelypriyankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal AnatomyDokument60 SeitenMaternal AnatomyRaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of Female Genital Tract and Its AnomaliesDokument44 SeitenDevelopment of Female Genital Tract and Its AnomaliesSuresh KatakamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midwife Prometric Test1Dokument17 SeitenMidwife Prometric Test1Nesrine TrabelsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fpp-Obstetric & Gynaecology ProcedureDokument8 SeitenFpp-Obstetric & Gynaecology ProcedureNurul FarhanahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lecher Antenna Wave Lengths Printable ListDokument6 SeitenThe Lecher Antenna Wave Lengths Printable ListK P SiinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leopold's Maneuver Hand OutDokument2 SeitenLeopold's Maneuver Hand OutRain Marquez100% (2)
- Reproductive SystemDokument219 SeitenReproductive Systemtzushka_vipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purperal InfectionsDokument69 SeitenPurperal InfectionsBeulah DasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Male and Female Radiographic ProceduresDokument5 SeitenMale and Female Radiographic ProceduresKaye A. JardinicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal HysterectomyDokument23 SeitenAbdominal Hysterectomytata marethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of AbortionDokument22 SeitenTypes of AbortionMaritza BarriereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breech Presentation and Delivery GuideDokument27 SeitenBreech Presentation and Delivery GuideTrevor Uratel100% (1)
- MCN Midterm NotesDokument33 SeitenMCN Midterm NotesSHIELOU LOMODNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cupping Therapy in InfertilityDokument46 SeitenCupping Therapy in Infertilitymrcyber75% (8)
- Estimating Gestational AgeDokument2 SeitenEstimating Gestational AgeMharlynne Nezlou L. PoliranNoch keine Bewertungen
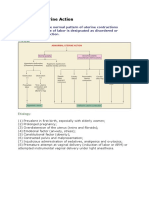
- Abnormal Uterine Contractions During LaborDokument9 SeitenAbnormal Uterine Contractions During LaborAnu ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do Organisms Reproduce - Class 10 Science SA2 NCERT Solutions Free PDF DownloadDokument11 SeitenHow Do Organisms Reproduce - Class 10 Science SA2 NCERT Solutions Free PDF Downloadmedi plusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cover Kacyiru 092633Dokument24 SeitenCover Kacyiru 092633Fulgence Umuhoza CleverstarNoch keine Bewertungen
- OBSTETRICS MIDTERM EXAM REVIEWDokument11 SeitenOBSTETRICS MIDTERM EXAM REVIEWJune Dumdumaya100% (2)
- Nursing Case Study TAHBSODokument17 SeitenNursing Case Study TAHBSOandymojer85% (13)
- MISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Dokument27 SeitenMISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Di VianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sejawat - Idn - Sistem Gastrointestinal, Urinaria, ReproduksiDokument91 SeitenSejawat - Idn - Sistem Gastrointestinal, Urinaria, ReproduksiAinaya Miftia Asy'aristaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Posterior Pituitary Gland Presentation - paraDokument40 SeitenPosterior Pituitary Gland Presentation - parahamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDokument14 SeitenAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemkukadiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Reproductive System FinalDokument16 SeitenThe Human Reproductive System FinalIlac Tristan BernardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akusherstvo (1) .Ru - enDokument103 SeitenAkusherstvo (1) .Ru - enPeprah OndibaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive DevelopmentDokument5 SeitenReproductive DevelopmentBela MillenaNoch keine Bewertungen