Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mathematics: Problem Solving in Mathematics
Hochgeladen von
Redzuan SaidiOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mathematics: Problem Solving in Mathematics
Hochgeladen von
Redzuan SaidiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
T I P S
PROBLEM SOLVING IN MATHEMATICS
Problem solving is the main focus in the teaching and learning of mathematics. Therefore the teaching
and learning process must include problem solving skills which are comprehensive and cover the whole
curriculum. The development of problem solving skills need to be emphasized so that students are able to
solve various problems effectively.
The skills involved are:
Understanding the problem
Devising a plan
Carrying out the plan; and
Looking back at the solutions
UNDERSTAND THE KEYWORDS
NO. KEYWORD WHAT IS ITS IMPLICATION ?
1 Hence Usually you have to use the answer obtained from the previous
section in your calculation.
2 Express No numerical answer is required. Answers are usually given in terms
of variables.
3 Prove, Show The answer is usually given. You are required to show clearly the
steps how you arrive at the answer. In this type of question, you must
be familiar with the mathematical formulas, rules and laws.
4 Write, State The answer can be worked out mentally. Hence, you can write down
the answer without showing the working.
5 Solve Find the root(s) of a given equation
6 Estimate For example, estimate the median from an ogive. A certain range of
answers is acceptable.
7 Calculate,fnd,determine Obtain the answer by showing proper steps of working.
8 Draw ( a graph ) Prepare a table of values, plot the points on a graph paper using a
suitable scale and then join the points using a straight line ( or a
smooth curve )
9 Sketch ( a graph ) A graph paper is not required. The accuracy of the graph is
negligible. The important factors are the shape of the graph and the
position of the graph with respect to the axes.
MATHEMATICS
T I P S
IMPORTANT FORMULAE
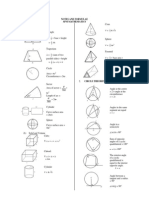
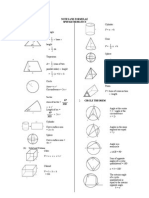
RELATION SHAPES AND SPACE
|
|
.
|
\
|
a c
b d
bc ad
A
1
1
P(A) =
( )
( ) S
A
P(A
/
) = 1 P(A)
Distance = ( ) ( )
2
1 2
2
1 2
y y x x +
Midpoint (x,y) = |
.
|
\
| + +
2
,
2
2 1 2 1
y y x x
Average speed = distance traveled
Time taken
Mean = sum of data
Number of data
Pythagoras
/
Theorem
c
2
= a
2
+ b
2
gradient , m =
1 2
1 2
x x
y y
ercept x
ercet y
m
int
int
=
Scale factor , k =
PA
PA
/
Area of image = k
2
x area of object
Sum of interior angles of a polygon
= ( n 2 ) x 180
0
Volume of right pyramid
=
3
1
x base area x height
Volume of sphere =
3
3
4
r I
Volume of cone = h r
2
3
1
I
Volume of cylinder = h r
2
I
Volume of right prism
= cross sectional area x length
Surface area of sphere =
2
4 r I
Curved surface area of cylinder = rh I 2
Area of circle =
2
r I
Circumference of circle = r d I = I 2
Area of trapezium
=
2
1
x sum of parallel sides x height
T I P S
1. Sentence of the truth is known is a statement.
2.
) ( 1 , ,
) (
/
A P A P
S
B A
B and A P
S
B A
B or A P
3. Range difference between the smallest value and the largest value.
4. m = tan T , where T is the angle made by the line with the horizontal and
measured in an anticlockwise direction.
5. Equation of the straight line: y = mx + c where m = gradient and c = y-intercept
at y intercept , x = 0 and x intercept , y = 0
The x-intercept and the y-intercept are not written in the form of coordinates.
6. A compound statement containing `` if and only if`` can be written as two
implications.
Implication 1 : If p then q
Implication 2 : If q then p
7. The number of subsets = 2
n
, where n is the number of elements in the set.
8. Standard form , A x 10
n
where 1 < A < 10 and n is an integer.
9. To factorise ax
2
+ bx = x ( ax + b ) , To factorise a
2
x
2
b
2
= (ax b )( ax + b )
10. In a unit circle, the value of sin T = y coordinate , cos T = x coordinate ,
tan T =
coordinate x
coordinate y
11. Cumulative frequency the total of the frequencies of the class interval and all the
classes before it.
12. The intersection of two straight lines is found by solving simultaneous equations.
13. If the lines are parallel then m
1
=m
2
else m
1
z m
2
14. A statement is a sentence which is either true or false. A sentence is not a statement if
we cannot determine whether it is true or false.
15. The mode and mean of grouped data:
(a) The modal class is the class with the highest frequency
(b) The midpoint of a class =
2
1
( upper class limit + lower class limit )
(c) Mean = Sum of ( midpoint of class x frequency )
Sum of frequency
SMART NOTES
T I P S
MISCONCEPTION CORNER
QUESTIONS INCORRECT CORRECT
1. Factorise 16k
2
- 25 16k
2
25
= ( 4k 5 )
2
(4k)
2
5
2
= ( 4k 5)(4k + 5 )
2. Solve y
2
2y = 3 y ( y 2 ) = 3
y = 3 0r y 2 = 3
y = 5
y
2
2y 3 = 0
( y 3)( y +1 ) = 0
y = 3 , y = - 1
3. Round off 7951 correct
to two significant figures.
7951 = 80 7951 = 8000
4. Determine if the
following mathematical
sentence is a statement or
not. Give a reason for your
answer.
`` 7 + 3 = 21 `
7 + 3 = 21 is not a
statement.
7 + 3 = 21 is a statement
because it is false.
Find the gradient of the
straight line y 3x = 7
y 3x = 7
Therefore, the gradient
is - 3
y 3x = 7
y = 3x + 7
Compare this equation with
y = mx + c
Therefore, the gradient
is 3 .
Given that L = { }
and M = { , find
5 , 4 , 3 , 2 , 1
} 6 , 5
( ) M L
( )
( ) 7 2 5
2 5 ) (
= + =
= =
M L
M and L { }
( ) 6
6 , 5 , 4 , 3 , 2 , 1
=
=
L K
L K
Complete the following
argument.
Premise 1 : ___________
Premise 2 : p - 3 = 10
Conclusion : p 13 =
If p - 3 = 10 , then p = 13 If p = 13 , then p - 3 = 10
Express
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
5
3
2
1
4
as a single matrix.
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
12
16
3
4
4
5 2
3 1
4
5
3
2
1
4
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
+
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
3
7
5 8
3 4
5
3
8
4
5
3
2
1
4
T I P S
MISCONCEPTION CORNER
QUESTIONS INCORRECT CORRECT
Find the values of
(a) sin 160
0
(b) tan 290
0
(a) sin 160
0
= sin ( 160
0
90
0
)
= sin 70
0
= 0.9397
(b) tan 290
0
= - tan ( 290
0
270
0
)
= - tan 20
0
= - 0.3640
(a) sin 160
0
= + sin (180
0
160
0
)
= sin 20
0
= 0.3420
(b) tan 290
0
= - tan ( 360
0
290
0
)
= - tan 70
0
= - 2.7474
6. Find the gradient of a
straight line passing
through P(2,3) and
Q ( 4,6 )
Gradient PQ
2
3
4 2
3 6
=
=
Gradient PQ
2
3
2 4
3 6
=
=
Find the difference in
longitudes between points
P ( 45
0
N, 87
0
E ) and
Q ( 45
0
N, 33
0
W )
Difference in longitudes
= 87
0
33
0
= 54
0
Difference in longitudes
= 87
0
+ 33
0
= 120
0
A box contains 3 yellow
and 5 white balls. Two
balls are selected at
random, one after another,
with replacement. Find the
probability that the selected
balls are of different
colours.
Let Y and W be the events of
selecting a yellow ball and a
white ball respectively.
P ( different colours )
= P ( yellow and white )
= P ( Y W )
=
8
5
8
3
=
64
15
Let Y and W be the events
of selecting a yellow ball
and a white ball
respectively.
P ( different colours )
= P ( Y W ) + P (WY)
32
15
8
3
8
5
8
5
8
3
=
|
.
|
\
|
+ |
.
|
\
|
=
7. A bag contains 3 black
and 2 green marbles.
Find the sample
space S
S = { } G B, S={ }
2 1 3 2 1
, , , , G G B B B
T I P S
CONSTRUCTION REQUIREMENT
KNOWLEDGE SKILL
1. Express ( 3x - 1)( 2x + 5 ) in the simplest
form.
1. Solve the equation
( 2y 1)( y + 3) = 2 (y + 1 )
2. Factorise each of the following:
(a) p q
2
p (b) 3x
2
5x 2
2. Using matrices, find the values
of x and y that satisfy the
following simultaneous equations.
3x + 4y = 5
4x 3y =
2
5
3. Explain why the mathematical sentence
` 2
3
+ 1 = 7 ` is a statement.
3. Make a general conclusion by
Induction for the number
sequence 5 , 9 , 13, 17, .
5 = 4(2) 3
9 = 4(3) 3
13 = 4(4) 3
17 = 4(5) - 3
T I P S
CLONE SPM QUESTIONS ( PAPER 1 )
ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS
1. 2 ( h 3k )
2
+ 3 hk =
A - 2h
2
+ 15hk + 18k
2
C - 2h
2
+ 15hk 18k
2
B - 2h
2
+ 9hk 18k
2
D - 2h
2
9hk + 18 k
2
Answer : C
Solution :
- 2 ( h 3k )( h 3k ) + 3hk
= - 2 ( h
2
6hk + 9k
2
) + 3hk
= - 2h
2
+ 12hk 18k
2
+ 3hk
= - 2h
2
+ 15hk 18k
2
LINEAR EQUATIONS
2. Given that
5
1
3
3
k k
, find the value of k .
A 6 B 9 C
4
1
D
4
3
Answer: B
Solution :
5k 15 = 3k + 3
5k 3k = 3 + 15
2k = 18 , k = 9
NUMBER BASES
3. Given that x
5
= 44
10
, then x =
A 34 B 43 C 134 D 431
Answer : C
5 44 Remainder
5 8 4
5 1 3
0 1
T I P S
ALGEBRAIC FRACTIONS
4. Express
2
12
5 2
6
1
p
p
p
as a single fraction in its simplest form.
2 2 2 2
12
1 3
12
5
12
3
3
1
p
p
D
p
C
p
p
B
p
A
Answer : C
Solution :
( )
( )
( )
( )
2 2
2
2
2
12
5
12
5 2 2
12
5 2 2
12
5 2
6 2
2 1
12
5 2
6
1
p p
p p
p
p p
p
p
p p
p
p
p
p
=
+
=
=
EARTH AS A SPHERE
5. P ( 30
0
N, 70
0
E ) and Q are two points on the surface of the earth such that PQ is a
diameter of the earth. State the location of Q.
A ( 30
0
N, 70
0
W ) B ( 30
0
N,110
0
B) C ( 30
0
S, 110
0
E)
D ( 30
0
S , 110
0
W )
Answer: D
Location of P P ( 30
0
N, 70
0
E )
Location of Q Q ( 30
0
S , 110
0
W )
FORMULAE
7 Given that 7
5
3
=
k
n
, then k =
( ) 5
7
3
5
7
3
5 7 5 49
2 2
2 2
+ |
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
n
D
n
C n B n A
Answer: C
T I P S
TYPE OF QUESTION
LEVEL OF DIFFUCULTY
LOW
1. Express 8
2
+ 5 as a number in base 8.
2. Given that
1
2
h
h
k , express h in terms of k .
3. Express 3.71 x 10
5
as a single number.
4. Find the difference in longitude between each pair of meridians given.
(i) 37
0
E and 78
0
E (ii) 43
0
E and 59
0
W
5. If K = ^ , determine the number of possible subsets. ` 7 , 5 , 4 , 3 , 2 , 1
MEDIUM
1. Calculate the values of m and n that satisfy the following simultaneous equations:
- m + n = 11 , 2m + 3n = 8
2. List all the integers y that satisfy the inequalities 4y 11 < y 2 < 3y + 2 .
3. There are 180 red, yellow and green marbles in a bag. 60 of them are red.
If a marble is picked at random from the bag, the probability of picking a
green marble is
4
1
. How many yellow marbles are there in the bag ?
HIGH
1. Express
2
10
4 2
5
3
m
m
m
as a single fraction in its simplest form.
2. Simplify 3m
0
x m
5
x ( 2m )
3
3.
8 2
7 3
0 1
6 4
4. Given that
k
k
3 2
1 2
9
1
9
, find the value of k .
T I P S
CRITICAL AND CREATIVE THINKING SKILLS (CCTS )
1. Express 4107
8
as a number in base two.
( Contexts Number Base , Difficulty level - Low )
2. Factorise k ( h 3 ) + 4 ( 1 h ) completely.
( Contexts Algebraic Expressions, Difficulty level Low )
3. P and Q are two points on the equator. The difference in longitude between
P and Q is 26
0
. Find the distance, in nautical miles, between P and Q
measured along the equator.
( Contexts Earth as a Sphere , Difficulty level Medium )
4. There are two lorries with 2.4 x 10
6
kg and 8.3 x 10
5
kg of flour respectively.
Find the difference of mass, in kg, between the two lorries.
( Contexts Standard Form , Difficulty level - Medium )
5. Calculate the values of h and k that satisfy both of the following equations:
2h + k = - 2 , - 6h 4k = 2
( Contexts Simultaneous Equations , Difficulty level - High )
EXAMPLES AND MARKING SCHEME OF PAPER 2
1. Solve the quadratic equation
2
1
3
5 2
2
k
k
( 4 marks )
Answer: 4k
2
3k 10 = 0 ( 1 mark )
(4k + 5)(k 2 ) = 0 ( 1 mark )
k = 2 ,
4
5
( 1 mark)( 1 mark )
2. Find the value of v and of w that satisfy the simultaneous linear equation below.
3 v 4 w = - 2 dan 13 2
2
1
w v ( 4 marks )
Answer:
v + 4w = 26 or equivalent ( 1 mark )
4v = 24 or equivalent ( 1 mark )
v = 6 ( 1 mark )
w = 5 ( 1 mark )
3. A straight line PQ is parallel to line y = - 2x + 5 and passes through point ( 4,-2 )
Find
(a) the gradient of the straight line PQ
(b) the equation of the straight line PQ and hence, state its y intercept.
( 5 marks )
Answer:
(a) - 2 ( 1 mark )
(b) - 2 = - 2(4) + c ( 1 mark )
c = 6 ( 1 mark )
y = - 2x + 6 ( 1 mark )
y intercept = 6 ( 1 mark )
4. (a) Determine whether the following is a statement or not. Give a reason to
you answer.
0 121 121
(b) Rewrite the following statement by inserting the word `` not `` into the
original statement. State the true value of your new statement.
`` 6 is the factor of 72 ``
(c) Construct a false statement using a suitable quantifier for the given object and
the property.
Object : Triangles
Property : Have a right angle
( 5 marks )
Answer:
(a) Statement. ( 1 mark )
False statement. ( 1 mark )
(b) 6 is not a factor of 72. ( 1 mark )
False. ( 1 mark )
(c) All triangles have a right angle ( 1 mark )
5 . Eleven cards bearing the letters of the word `` MATHEMATICS`` are
well shuffled and placed in a bag. Two cards are picked at random from
the bag, one after the other, and are not replaced. Calculate the probability that
(a) the first card bears letter A but the second card does not bear the
same letter A
(b) both cards bear the same letter ( 5 marks )
Answer :
(a) P ( first A and second not A )
mark
mark
1
55
9
1
10
9
11
2
u
(b) P ( both of the same letter )
= P ( AA or MM or TT )
T I P S
( 5 marks )
Answer:
(a) - 2 ( 1 mark )
(b) - 2 = - 2(4) + c ( 1 mark )
c = 6 ( 1 mark )
y = - 2x + 6 ( 1 mark )
y intercept = 6 ( 1 mark )
4. (a) Determine whether the following is a statement or not. Give a reason to
you answer.
0 121 121
(b) Rewrite the following statement by inserting the word `` not `` into the
original statement. State the true value of your new statement.
`` 6 is the factor of 72 ``
(c) Construct a false statement using a suitable quantifier for the given object and
the property.
Object : Triangles
Property : Have a right angle
( 5 marks )
Answer:
(a) Statement. ( 1 mark )
False statement. ( 1 mark )
(b) 6 is not a factor of 72. ( 1 mark )
False. ( 1 mark )
(c) All triangles have a right angle ( 1 mark )
5 . Eleven cards bearing the letters of the word `` MATHEMATICS`` are
well shuffled and placed in a bag. Two cards are picked at random from
the bag, one after the other, and are not replaced. Calculate the probability that
(a) the first card bears letter A but the second card does not bear the
same letter A
(b) both cards bear the same letter ( 5 marks )
Answer :
(a) P ( first A and second not A )
mark
mark
1
55
9
1
10
9
11
2
u
(b) P ( both of the same letter )
= P ( AA or MM or TT )
( )
( ) mark
marks
1
55
3
2
10
1
11
2
10
1
11
2
10
1
11
2
=
+ + =
6. P ( 50
0
N, 40
0
E) , Q ( 50
0
N, 100
0
E ) and R are three points on the
surface of the earth such that QR is the diameter of the parallel of
latitude 50
0
N.
(a) State the longitude of point R
(b) Calculate, nautical miles,
(i) the shortest distance from R to Q via the North Pole
(ii) the distance from P to R due west along the parallel
of latitude 50
0
N
(c) Given that the point W is 5100 nautical miles due south of P,
calculate the latitude of W . (12 marks)
Answer : (a) Longitude of R = ( 180 100 ) W = 80
0
W (2 marks)
(b) (i) Distance from R to Q via the North Pole
= 60 x 80 (2 marks)
= 4800 n.m (1 marks)
(ii) Distance from P to R along latitude 50
0
N
= 60 x 120 x cos 50
0
(3 marks)
= 4628 n.m (1 mark)
(c) 85
60
5100
or POW = Z (1 mark)
Latitude of W = ( 85 50 ) S (1 mark)
= 35
0
S (1 mark)
7. (a) The inverse matrix of is
|
|
.
|
\
|
4 1
8 3
|
|
.
|
\
|
3 1
4
1
k
m
Find the values of m and k .
(b) Using matrices, calculate the values of x and y that satisfy the
following simultaneous linear equations.
3x + 8y = 3
x + 4y = - 1 (7 marks)
Answer:
(a) k = - 8 ( 1 mark ) , m = 4 (2 marks)
(b) ( ) mark
y
x
1
1
3
4 1
8 3
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
T I P S
( )
( ) mark
marks
1
55
3
2
10
1
11
2
10
1
11
2
10
1
11
2
=
+ + =
6. P ( 50
0
N, 40
0
E) , Q ( 50
0
N, 100
0
E ) and R are three points on the
surface of the earth such that QR is the diameter of the parallel of
latitude 50
0
N.
(a) State the longitude of point R
(b) Calculate, nautical miles,
(i) the shortest distance from R to Q via the North Pole
(ii) the distance from P to R due west along the parallel
of latitude 50
0
N
(c) Given that the point W is 5100 nautical miles due south of P,
calculate the latitude of W . (12 marks)
Answer : (a) Longitude of R = ( 180 100 ) W = 80
0
W (2 marks)
(b) (i) Distance from R to Q via the North Pole
= 60 x 80 (2 marks)
= 4800 n.m (1 marks)
(ii) Distance from P to R along latitude 50
0
N
= 60 x 120 x cos 50
0
(3 marks)
= 4628 n.m (1 mark)
(c) 85
60
5100
or POW = Z (1 mark)
Latitude of W = ( 85 50 ) S (1 mark)
= 35
0
S (1 mark)
7. (a) The inverse matrix of is
|
|
.
|
\
|
4 1
8 3
|
|
.
|
\
|
3 1
4
1
k
m
Find the values of m and k .
(b) Using matrices, calculate the values of x and y that satisfy the
following simultaneous linear equations.
3x + 8y = 3
x + 4y = - 1 (7 marks)
Answer:
(a) k = - 8 ( 1 mark ) , m = 4 (2 marks)
(b) ( ) mark
y
x
1
1
3
4 1
8 3
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
( )
( )
( ) mark y
mark x
y
x
mark
y
x
1
2
3
1 5
2
3
5
1
1
3
3 1
8 4
4
1
=
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
8.
BOX NUMBER OF PENS NUMBER OF PENCILS
R 2 1
S 4 2
T 5 4
The table shows the number of pens and pencils in three boxes, R , S and T . The
probability of Hafiz choosing any of the boxes is the same. Calculate the probability that
Hafiz
(i) choose R or S (ii) chooses a pen from box T
(iii) chooses a pencil
(6 marks)
Answer :
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( )
( ) ( )
27
10
2
9
4
3
1
6
2
3
1
3
1
3
1
1
27
5
1
9
5
3
1
1
3
2
3
1
3
1
=
+ +
=
= +
marks iii
mark
mark ii
mark i
9. Transformation U represents the translation . Transformation V represents
|
|
.
|
\
|
2
3
the represents the reflection in the line x = 2. State the coordinates of image of point
( -1,2) under the following transformations.
(i) V (ii) U
2
(iii) VU (5 marks)
Answer: (i ) ( 5,2 ) (ii) ( 5,-2 ) (iii) ( 2,0 )
T I P S
( )
( )
( ) mark y
mark x
y
x
mark
y
x
1
2
3
1 5
2
3
5
1
1
3
3 1
8 4
4
1
=
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
8.
BOX NUMBER OF PENS NUMBER OF PENCILS
R 2 1
S 4 2
T 5 4
The table shows the number of pens and pencils in three boxes, R , S and T . The
probability of Hafiz choosing any of the boxes is the same. Calculate the probability that
Hafiz
(i) choose R or S (ii) chooses a pen from box T
(iii) chooses a pencil
(6 marks)
Answer :
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( )
( ) ( )
27
10
2
9
4
3
1
6
2
3
1
3
1
3
1
1
27
5
1
9
5
3
1
1
3
2
3
1
3
1
=
+ +
=
= +
marks iii
mark
mark ii
mark i
9. Transformation U represents the translation . Transformation V represents
|
|
.
|
\
|
2
3
the represents the reflection in the line x = 2. State the coordinates of image of point
( -1,2) under the following transformations.
(i) V (ii) U
2
(iii) VU (5 marks)
Answer: (i ) ( 5,2 ) (ii) ( 5,-2 ) (iii) ( 2,0 )
( )
( )
( ) mark y
mark x
y
x
mark
y
x
1
2
3
1 5
2
3
5
1
1
3
3 1
8 4
4
1
=
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
8.
BOX NUMBER OF PENS NUMBER OF PENCILS
R 2 1
S 4 2
T 5 4
The table shows the number of pens and pencils in three boxes, R , S and T . The
probability of Hafiz choosing any of the boxes is the same. Calculate the probability that
Hafiz
(i) choose R or S (ii) chooses a pen from box T
(iii) chooses a pencil
(6 marks)
Answer :
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( )
( ) ( )
27
10
2
9
4
3
1
6
2
3
1
3
1
3
1
1
27
5
1
9
5
3
1
1
3
2
3
1
3
1
=
+ +
=
= +
marks iii
mark
mark ii
mark i
9. Transformation U represents the translation . Transformation V represents
|
|
.
|
\
|
2
3
the represents the reflection in the line x = 2. State the coordinates of image of point
( -1,2) under the following transformations.
(i) V (ii) U
2
(iii) VU (5 marks)
Answer: (i ) ( 5,2 ) (ii) ( 5,-2 ) (iii) ( 2,0 )
T I P S
10. On the graph, OPQR is a parallelogram. O is the origin.
Find
(a) the equation of the straight
line PQ
(b) the x intercept of the straight
line RQ .
( 5 marks )
0
y
P (2,6)
Q
R (4,2)
x
Answer: (a)
4 0
2 0
0 4
0 2
or m
OR
( 1 mark )
c 2
2
1
6 or c = 5 ( 2 mark )
y =
2
1
x + 5 ( 1 mark )
(b) - 10 ( 1 mark )
11.
Time ( s )
22
16
u
0 8 12 18
Speed (ms
-1
)
The diagram shows the speed-time graph
of a particle over a period of 18 seconds.
Calculate
(i) its accelerations during the first
8 seconds.
(ii) the value of u , if the distance
traveled during the last 10 seconds
is 132 m .
( 5 marks )
Answer :
(i)
4
3
or - 0.75 ( 2 marks )
(ii)
2
1
x4x(16+u) +
2
1
x u x 6 = 132 ( 2 marks )
u = 20 ( 1 mark )
10. On the graph, OPQR is a parallelogram. O is the origin.
Find
(a) the equation of the straight
line PQ
(b) the x intercept of the straight
line RQ .
( 5 marks )
0
y
P (2,6)
Q
R (4,2)
x
Answer: (a)
4 0
2 0
0 4
0 2
or m
OR
( 1 mark )
c 2
2
1
6 or c = 5 ( 2 mark )
y =
2
1
x + 5 ( 1 mark )
(b) - 10 ( 1 mark )
11.
Time ( s )
22
16
u
0 8 12 18
Speed (ms
-1
)
The diagram shows the speed-time graph
of a particle over a period of 18 seconds.
Calculate
(i) its accelerations during the first
8 seconds.
(ii) the value of u , if the distance
traveled during the last 10 seconds
is 132 m .
( 5 marks )
Answer :
(i)
4
3
or - 0.75 ( 2 marks )
(ii)
2
1
x4x(16+u) +
2
1
x u x 6 = 132 ( 2 marks )
u = 20 ( 1 mark )
T I P S
12 cm
P
Q
R 12. The diagram shows a solid cylinder with a
hemispherical PQR hole removed from one
circular end. Both the cylinder and
hemisphere have the same diameter of 10 cm.
Using
7
22
, calculate
the volume of the remaining solid.
(4 marks)
Answer :
mark
mark I
mark j I
mark t j I
SOLID
CAL HEMISPHERI
CYLINDER
1 96 . 680
1 5
7
22
3
2
12 5
7
22
1 5
7
22
3
2
3
4
2
1
1 12 5
7
22
3 2
3 3
2 2
u u u u
u u u
u u
13.
142 145 147 148 158 153 155 157 159 152
157 160 164 148 161 169 150 153 158 143
159 165 163 156 167 162 156 151 154 149
Table 1
Table 1 shows the distribution of heights of 30 plants.
(a) State the size of the class interval. (1 mark)
(b) Copy and complete Table 1. (4 marks)
(c) From the frequency table
(i) state the modal class
(ii) calculate the mean height (4 marks)
Answer :
(a) 5 (1 mark)
(b)
Column 1 Column 2 Column 3
Height (cm ) Frequency Midpoint
140 144 2 142
145 149 5 147
150 154 6 152
155 159 9 157
160 164 5 162
165 - 169 3 167
Table 1
Column 1 (1 mark), Column 2 (2 marks), Column 3 (1 mark)
(c) (i) 155 159 ( 1 mark )
12 cm
P
Q
R 12. The diagram shows a solid cylinder with a
hemispherical PQR hole removed from one
circular end. Both the cylinder and
hemisphere have the same diameter of 10 cm.
Using
7
22
, calculate
the volume of the remaining solid.
(4 marks)
Answer :
mark
mark I
mark j I
mark t j I
SOLID
CAL HEMISPHERI
CYLINDER
1 96 . 680
1 5
7
22
3
2
12 5
7
22
1 5
7
22
3
2
3
4
2
1
1 12 5
7
22
3 2
3 3
2 2
u u u u
u u u
u u
13.
142 145 147 148 158 153 155 157 159 152
157 160 164 148 161 169 150 153 158 143
159 165 163 156 167 162 156 151 154 149
Table 1
Table 1 shows the distribution of heights of 30 plants.
(a) State the size of the class interval. (1 mark)
(b) Copy and complete Table 1. (4 marks)
(c) From the frequency table
(i) state the modal class
(ii) calculate the mean height (4 marks)
Answer :
(a) 5 (1 mark)
(b)
Column 1 Column 2 Column 3
Height (cm ) Frequency Midpoint
140 144 2 142
145 149 5 147
150 154 6 152
155 159 9 157
160 164 5 162
165 - 169 3 167
Table 1
Column 1 (1 mark), Column 2 (2 marks), Column 3 (1 mark)
(c) (i) 155 159 ( 1 mark )
(ii) marks 2
30
4655
= 155.17 ( 1 mark )
14. In diagram below, OHKM is a quadrant with the centre O and OMKL is a
semicircle with the centre M.
Given that OH= 14 cm. Using
7
22
, calculate
(a) the area, in cm
2
, of the shaded region
(b) the perimeter, in cm, of the whole diagram.
( 7 marks ) K
60
0
O
H
L
M
N
Answer:
(a) Area of sector OHK = mark 1 14 14
7
22
360
90
u u u
Area of sector ONM = mark 1 7 7
7
22
360
60
u u u
u u u 14 14
7
22
360
90
mark 1 7 7
7
22
360
60
u u u
= mark 1
3
1
128
(b) Arc HK = mark KLO Arc or 1 7
7
22
2
360
180
14
7
22
2
360
90
u u u u u u
= mark 1 14 7
7
22
2
360
180
14
7
22
2
360
90
u u u u u u
= 58 ( 1 mark )
15. (a) Copy and complete the following table 2 of values for y = - 2x
2
+ 4x + 7
T I P S
(ii) marks 2
30
4655
= 155.17 ( 1 mark )
14. In diagram below, OHKM is a quadrant with the centre O and OMKL is a
semicircle with the centre M.
Given that OH= 14 cm. Using
7
22
, calculate
(a) the area, in cm
2
, of the shaded region
(b) the perimeter, in cm, of the whole diagram.
( 7 marks ) K
60
0
O
H
L
M
N
Answer:
(a) Area of sector OHK = mark 1 14 14
7
22
360
90
u u u
Area of sector ONM = mark 1 7 7
7
22
360
60
u u u
u u u 14 14
7
22
360
90
mark 1 7 7
7
22
360
60
u u u
= mark 1
3
1
128
(b) Arc HK = mark KLO Arc or 1 7
7
22
2
360
180
14
7
22
2
360
90
u u u u u u
= mark 1 14 7
7
22
2
360
180
14
7
22
2
360
90
u u u u u u
= 58 ( 1 mark )
15. (a) Copy and complete the following table 2 of values for y = - 2x
2
+ 4x + 7
T I P S
(ii) marks 2
30
4655
= 155.17 ( 1 mark )
14. In diagram below, OHKM is a quadrant with the centre O and OMKL is a
semicircle with the centre M.
Given that OH= 14 cm. Using
7
22
, calculate
(a) the area, in cm
2
, of the shaded region
(b) the perimeter, in cm, of the whole diagram.
( 7 marks ) K
60
0
O
H
L
M
N
Answer:
(a) Area of sector OHK = mark 1 14 14
7
22
360
90
u u u
Area of sector ONM = mark 1 7 7
7
22
360
60
u u u
u u u 14 14
7
22
360
90
mark 1 7 7
7
22
360
60
u u u
= mark 1
3
1
128
(b) Arc HK = mark KLO Arc or 1 7
7
22
2
360
180
14
7
22
2
360
90
u u u u u u
= mark 1 14 7
7
22
2
360
180
14
7
22
2
360
90
u u u u u u
= 58 ( 1 mark )
15. (a) Copy and complete the following table 2 of values for y = - 2x
2
+ 4x + 7
x - 3 - 2.5 - 1.5 - 1 0 1 2 3 4
y - 23 - 3.5 1 7 9 7 - 9
Table 2 ( 2 marks )
(b) Using a scale of 2 cm to represent 1 unit on the x-axis and 2 cm to
Represent 5 units on the y-axis, Draw the graph of y = - 2x
2
+ 4x + 7
for . 4 3 d d x
(3 marks)
(c) Draw a suitable straight line on the graph to find the values of x where
which satisfy the equation 2 x 2x . 4 3 d d x
2
= 0 .
State these values of x.
(4 marks)
(d) On the same axes, draw the graph of 3y = - 7x + 21 and y = - 2 .
Hence, shade the region defined by the following inequalities:
. 2 21 7 3 , 0 ! d t y dan x y x
(3 marks)
Answer :
(a)
x - 2.5 3
y - 15.5 1
(2 marks)
(b) Draw a graph (3 marks)
(c) 2 x 2x
2
= 0 .
- 2x
2
x + 5x + 2 + 5 = 0 + 5x + 5
y = 5x + 5 (1 mark)
In this case, the suitable straight line that should
be drawn is y = 5x + 5 (1 mark)
From the graph, x = .., x = . (2 marks)
(d) (3 marks)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsVon EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Add MathsDokument40 SeitenAdd MathsJoseph TingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes and Formulae MathematicsDokument9 SeitenNotes and Formulae MathematicsNurAinKhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsVon EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Notes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryDokument9 SeitenNotes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometrySharmini RajagopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageVon EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasDokument9 SeitenFormula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasPurawin Subramaniam100% (11)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topper Sample Paper - 4 Class Xi - Mathematics Questions Time Allowed: 3 Hrs Maximum Marks: 100Dokument17 SeitenTopper Sample Paper - 4 Class Xi - Mathematics Questions Time Allowed: 3 Hrs Maximum Marks: 100guptafamily1992Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aieee 2012 Paper 1Dokument32 SeitenAieee 2012 Paper 1Ravi LorventNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Model Test Paper For Summative Assessment - 1Dokument13 SeitenMaths Model Test Paper For Summative Assessment - 1Apex InstituteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsVon EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Answer Technique MM 2Dokument34 SeitenAnswer Technique MM 2Lä HäNäNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM 2012 - FullDokument27 SeitenSPM 2012 - FullWong Weng SonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aieee Paper 2008Dokument30 SeitenAieee Paper 2008Ravi LorventNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics SPM 2011.powerpointDokument55 SeitenMathematics SPM 2011.powerpointuzai88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Mathematics Conclusion Proposition ProofDokument12 SeitenMathematics Conclusion Proposition ProofPrasen RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5 Additional Maths NoteDokument10 SeitenForm 5 Additional Maths NoteEric WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 - 12 Class X - Ag-3 (Cbse)Dokument6 Seiten01 - 12 Class X - Ag-3 (Cbse)Umesh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Calculus: Credit Hour: 3Dokument39 SeitenApplied Calculus: Credit Hour: 3bigbangmelvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 - 2007 - Module - Terengganu - Additional Mathematics - 03Dokument10 SeitenForm 4 - 2007 - Module - Terengganu - Additional Mathematics - 03Zacky MhdNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- AP - Math Sample Paper-1-Solution For Class 10Dokument12 SeitenAP - Math Sample Paper-1-Solution For Class 10Firdosh KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryDokument9 SeitenNotes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryJarnice Ling Yee ChingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leep 214Dokument23 SeitenLeep 214Koyal Gupta100% (1)
- Trial SPM 2014 Melaka P1 & P2 PDFDokument65 SeitenTrial SPM 2014 Melaka P1 & P2 PDFrusleenaosman790% (1)
- MIT Multivariable Calculus Exam A SolutionsDokument16 SeitenMIT Multivariable Calculus Exam A Solutions15klaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel GCE: Monday 16 January 2006 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDokument4 SeitenEdexcel GCE: Monday 16 January 2006 Time: 1 Hour 30 Minutesalphamale173Noch keine Bewertungen
- ACT Coordinate GeometryDokument25 SeitenACT Coordinate GeometryaftabNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Canadian Mathematical SocietyDokument18 SeitenThe Canadian Mathematical Societyสฮาบูดีน สาและNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metrobank Math Challeng Solution 2013Dokument5 SeitenMetrobank Math Challeng Solution 2013Kurth Maquiza100% (2)
- AM Paper 1 Set 3Dokument11 SeitenAM Paper 1 Set 3Nurallia AjeeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teknik Menjawab Matematik Spm2009Dokument25 SeitenTeknik Menjawab Matematik Spm2009adeksam72Noch keine Bewertungen
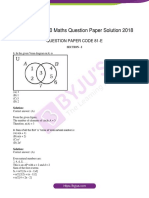
- Kseeb Class 10 Maths Question Paper Solution 2018Dokument23 SeitenKseeb Class 10 Maths Question Paper Solution 2018Raghav L NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 365 Sample ExamsDokument13 SeitenMath 365 Sample ExamsNab Tor100% (1)
- GR 10 Math Test 1 SolutionDokument13 SeitenGR 10 Math Test 1 SolutionParamNoch keine Bewertungen
- K.V. JMO 2014 SolutionsDokument11 SeitenK.V. JMO 2014 SolutionsPremMehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 46 THE POINT DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDokument22 Seiten46 THE POINT DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDVishal VjNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMC Fourth Year SolutionsDokument113 SeitenMMC Fourth Year SolutionsHermann Dejero LozanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- K.V. JMO 2014 SolutionsDokument11 SeitenK.V. JMO 2014 SolutionsPremMehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test Papers 1 To 14 EDokument35 SeitenPractice Test Papers 1 To 14 Essjatav128Noch keine Bewertungen
- All Form4 QuestionsDokument371 SeitenAll Form4 QuestionsArivananthanMarimuthuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 2 MathDokument10 SeitenForm 2 MathLywee NeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Year Form 4 P1Dokument9 SeitenMid Year Form 4 P1ahchin5Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Notes & Formulae MathematicsDokument9 SeitenSPM Notes & Formulae MathematicsPatrick PhuahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Form 4 Pap1 2013 - Paper 1Dokument13 SeitenMath Form 4 Pap1 2013 - Paper 1Kz FarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topical Test 4: Matrices: Ujian Topikal 4: MatriksDokument10 SeitenTopical Test 4: Matrices: Ujian Topikal 4: Matriksysheng98Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cubic EquationsDokument11 SeitenCubic EquationsTrustful EyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- VectorDokument6 SeitenVectorRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometrical Constructions - Lesson PlanDokument8 SeitenGeometrical Constructions - Lesson PlanRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard FormDokument4 SeitenStandard FormRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Studypattern SequenceDokument1 SeiteLesson Studypattern SequenceRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Angles and Their MeasuresDokument4 Seiten2-Angles and Their MeasuresRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular MeasureDokument27 SeitenCircular MeasureRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loop Game Fractions Decimals PercentagesDokument2 SeitenLoop Game Fractions Decimals PercentagesRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 1 Indices Revision Test 1.1: 40 Minutes Are Allowed. DO NOT Use A CalculatorDokument9 SeitenUNIT 1 Indices Revision Test 1.1: 40 Minutes Are Allowed. DO NOT Use A CalculatorRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gambar KucingDokument2 SeitenGambar KucingRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 - DifferentiationDokument27 SeitenChapter 9 - DifferentiationsazfizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Indices 1Dokument51 Seiten5 Indices 1Redzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intervensi Add Math BPKDokument58 SeitenIntervensi Add Math BPKRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Note 1.1 Functions Exercise 1.1: F (0) - 3 and F (6)Dokument12 SeitenNote 1.1 Functions Exercise 1.1: F (0) - 3 and F (6)Redzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extra Exercises - Express and SpecialDokument9 SeitenExtra Exercises - Express and SpecialRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intervensi Add Math BPKDokument58 SeitenIntervensi Add Math BPKRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Laws of Indices GREENDokument6 SeitenBasic Laws of Indices GREENRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching NotesDokument6 SeitenTeaching NotesRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FunctionsDokument15 SeitenFunctionsRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activities - Notes and SolutionsDokument1 SeiteActivities - Notes and SolutionsRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 1 Indices Mental Tests: Test 1.1 Test 1.2 Test 1.3 Test 1.4Dokument1 SeiteUNIT 1 Indices Mental Tests: Test 1.1 Test 1.2 Test 1.3 Test 1.4Redzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Indices 1Dokument51 Seiten5 Indices 1Redzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Log Bases Etc CardsDokument2 SeitenLog Bases Etc CardsRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Month Date Notes Activity/TopicDokument2 SeitenMonth Date Notes Activity/TopicRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30 Chapter30 546-561-1Dokument16 Seiten30 Chapter30 546-561-1Redzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Find The Midpoints of Each Side Connect Them in OrderDokument23 SeitenFind The Midpoints of Each Side Connect Them in OrderRedzuan Saidi0% (1)
- 16) Plotting Quadratic GraphsDokument10 Seiten16) Plotting Quadratic GraphsRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scale Drawing: Airil Ahmad SMK PerimbunDokument18 SeitenScale Drawing: Airil Ahmad SMK PerimbunRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebraic Formulae CG Redz: Sunday, July 10, 2016Dokument17 SeitenAlgebraic Formulae CG Redz: Sunday, July 10, 2016Redzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16) Plotting Quadratic GraphsDokument1 Seite16) Plotting Quadratic GraphsRedzuan SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tomas Claudio Colleges: Basic Education DepartmentDokument5 SeitenTomas Claudio Colleges: Basic Education DepartmentKristle R BacolodNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME45002 Aircraft SystemsDokument3 SeitenME45002 Aircraft Systemsvincent02hk_57881301Noch keine Bewertungen
- Communication StrategiesDokument36 SeitenCommunication StrategiesMarian CoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- At What Level Do I : Ncbts Domain 1. Social Regard For LearningDokument20 SeitenAt What Level Do I : Ncbts Domain 1. Social Regard For LearningDranrebz Regaspi0% (1)
- CV For Acadamic Jobs.Dokument5 SeitenCV For Acadamic Jobs.Sujee HnbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volume 28, Issue 1, 2008/2009Dokument17 SeitenVolume 28, Issue 1, 2008/2009LawLibNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Moe Corporate BrochureDokument48 SeitenMoe Corporate BrochurejhteoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week: 3 Class / Subject Time Topic/Theme Focus Skill Content Standard Learning Standard Learning ObjectivesDokument9 SeitenWeek: 3 Class / Subject Time Topic/Theme Focus Skill Content Standard Learning Standard Learning ObjectivesAlya FarhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Executive Master in Occupational Safety and Health ManagementDokument2 SeitenExecutive Master in Occupational Safety and Health ManagementMohamad Khalid B HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AAMPLE Company ProfileDokument19 SeitenAAMPLE Company ProfileAmrit VatsNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL - GEN CHEM 1 Week 2Dokument13 SeitenDLL - GEN CHEM 1 Week 2antonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- UB ULC SyllabusDokument3 SeitenUB ULC SyllabusclazgarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 9Dokument2 SeitenWeek 9api-314363504Noch keine Bewertungen
- 06-Ed-Dang Vu Hoai Nhan (45-53) 037Dokument9 Seiten06-Ed-Dang Vu Hoai Nhan (45-53) 037VũNhânNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus For Advanced Fluid Mechanics - ME-5442-01Dokument3 SeitenSyllabus For Advanced Fluid Mechanics - ME-5442-01vassaNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Newbs & Vets Exploration Guide RSD NationDokument8 SeitenFor Newbs & Vets Exploration Guide RSD NationfloredaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CT20151665101 JLDokument3 SeitenCT20151665101 JLAman KaushalNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Diploma in Language Teaching Management (Idltm)Dokument4 SeitenInternational Diploma in Language Teaching Management (Idltm)Syed Adnan RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Conference English Dept - ICFAI TechDokument2 SeitenNational Conference English Dept - ICFAI TechDena ElizabethNoch keine Bewertungen
- World03 02 16Dokument40 SeitenWorld03 02 16The WorldNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Use of Sand Paper Letters in Teaching The English AlphabetDokument8 SeitenThe Use of Sand Paper Letters in Teaching The English AlphabetGlobal Research and Development ServicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10th Promotion RegisterDokument1 Seite10th Promotion RegisterRaghu selvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loius I KahnDokument40 SeitenLoius I KahnMaliha Khan100% (2)
- Biotech Report of TourDokument15 SeitenBiotech Report of TourGagandeep MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in Math 3 Print NahDokument13 SeitenLesson Plan in Math 3 Print Nahapi-312373865Noch keine Bewertungen
- Matrix of Field Study 6: Subject Title Domain Competencies Units Professional Education SubjectDokument34 SeitenMatrix of Field Study 6: Subject Title Domain Competencies Units Professional Education SubjectDianne S. GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Division Als Festival of Skills and TalentsDokument9 Seiten2019 Division Als Festival of Skills and TalentsAlanie Grace Beron TrigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom Activities For MusicDokument2 SeitenClassroom Activities For Musicapi-237091625Noch keine Bewertungen
- Professional ResumeDokument2 SeitenProfessional Resumeapi-384455187Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorVon EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormVon EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeVon EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Von EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsVon EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldVon EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (80)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeVon EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingVon EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (21)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Von EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryVon EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)Von EverandParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeVon EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsVon EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (9)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- A Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathVon EverandA Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)