Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Assignment 1
Hochgeladen von
Niranjan MoreOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assignment 1
Hochgeladen von
Niranjan MoreCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assignment 1.
Name : Niranjan More Roll No : 127
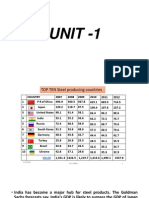
Michael Porters Five Forces Model Steel industry Introduction India occupies a central position on the global steel map, with the establishment of new state-of-the-art steel mills, acquisition of global scale capacities by players, continuous modernisation and upgradation of older plants, improving energy efficiency and backward integration into global raw material sources Steel production in India has increased by a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8 percent over the period 2002-03 to 2006-07. Going forward, growth in India is projected to be higher than the world average, as the per capita consumption of steel in India, at around 46 kg, is well below the world average (150 kg) and that of developed countries (400 kg). Indian demand is projected to rise to 200 million tonnes by 2015. Given the strong demand scenario, most global steel players are into a massive capacity expansion mode, either through brownfield or greenfield route. By 2012, the steel production capacity in India is expected to touch 124 million tonnes and 275 million tonnes by 2020. While greenfield projects are slated to add 28.7 million tonnes, brownfield expansions are estimated to add 40.5 million tonnes to the existing capacity of 55 million . Porters Five force analysis. 1. Entry Barrier:- High a) Capital Requirement: Steel industry is a capital intensive business. It is estimated that to set up 1 mtpa capacity of integrated steel plant, it requires between Rs 25 bn to Rs 30 bn depending upon the location of the plant and technology used.
b) Economies of scale: As far as the sector forces go,scale of operation does matter. Benefits of economies of scale are derived in the form of lower costs, R& D expenses and better bargaining power while sourcing raw materials. It may be noted that those steel companies, which are integrated, have their own mines for key raw materials such as iron ore and coal and this protects them for the potential threat for new entrants to a significant extent. c) Government Policy: The government has a favorable policy for steel manufacturers. However, there are certain discrepancies involved in allocation of iron ore mines and land acquisitions. Furthermore the regulatory clearances and other issues are some of the major problems for the new entrants.
2. Competition:- High The steel industry is truly global in terms of through aggressive exports. Steel, being a commodity it is, branding is not differentiation between competing products. Presence of a large number of players in the unorganized sector. High Competition due cost differentiation from companies like Adhunik , MUSCO, Kalyani Steels, JSW , Viraj It is medium in the domestic steel industry as cheaper products does exist. demand still exceeds the supply. India is a net importer of steel. However, a threat from dumping of common and there is little competition with large producing countries like China significantly influencing global prices
3. Bargaining power of suppliers: High The bargaining power of suppliers is low for the fully integrated steel plants as they have their own mines of key raw material like iron ore, coal for example Tata Steel. However, those who are non-integrated or semi integrated has to depend on suppliers. An example could be SAIL, which imports coking coal. Globally, the Top three mining giants BHP Billiton, CVRD and Rio Tinto supply nearly two-thirds of the processed iron ore to steel mills and command very high bargaining power. In India too, NMDC is a major supplier to standalone and nonintegrated steel mills. 4. Threat of substitutes: Low Plastics and composites pose a threat to Indian steel in one of its biggest markets automotive manufacture. For the automobile industry, the other material at present with the potential to upstage steel is aluminium. However, at present the high cost of electricity for extraction and purification of aluminium in India weighs against viable use of aluminium for the automobile industry. Steel has already been replaced in some large volume applications: railway sleepers (RCC sleepers), large diameter water pipes (RCC pipes), small diameter pipes (PVC pipes), and domestic water tanks (PVC tanks). The substitution is more prevalent in the manufacture of automobiles and consumer durables
5. Bargaining power of Customers: Mixed Some of the major steel consumption sectors like automobiles, oil & gas, shipping, consumer durables and power generation enjoy high bargaining power and get favorable deals. However, small and retail consumers who are scattered and consume a significant part do not enjoy these benefits.
Conclusion Industry unattractive because of high compitition and high entry barriers.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- JSW - FInal - 2Dokument10 SeitenJSW - FInal - 2Devika SinghaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Steel Policy 2017Dokument31 SeitenNational Steel Policy 2017Jagdish AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel and Iron Industry AnalysisDokument7 SeitenSteel and Iron Industry AnalysisRhutika KuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Steel IndustryDokument15 SeitenReport On Steel Industrysiddhesh4788Noch keine Bewertungen
- SWOT Analysis For JSW SteelDokument8 SeitenSWOT Analysis For JSW SteelPankaj Khannade75% (4)
- A Study of Electronic Data Storage Steel Factory in Mumbai11Dokument71 SeitenA Study of Electronic Data Storage Steel Factory in Mumbai11Thirupal Nk100% (3)
- A Study of Electronic Data Storage Steel Factory in Mumbai11 150218034403 Conversion Gate02Dokument51 SeitenA Study of Electronic Data Storage Steel Factory in Mumbai11 150218034403 Conversion Gate02NIKHIL CHAUHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logistics of Indian Steel IndustryDokument28 SeitenLogistics of Indian Steel Industryvishalchandu86% (7)
- Problem and Prospect of LSIDokument14 SeitenProblem and Prospect of LSIakky.vns2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On Comparative Analysis of Public and Private Sector Steel Companies in IndiaDokument48 SeitenProject Report On Comparative Analysis of Public and Private Sector Steel Companies in IndiaHillary RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tata Steel Strategic Management AssignmentDokument11 SeitenTata Steel Strategic Management AssignmentJj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Industry of BangladeshDokument3 SeitenSteel Industry of BangladeshMISHUM RAHMAN100% (1)
- CHAPTER 3 Steel Industry 12 Mini ProjectDokument18 SeitenCHAPTER 3 Steel Industry 12 Mini ProjectMilkey PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-3 Iron and Steel Industry SWOT Analysis A. Strength: Page - 1Dokument50 SeitenUnit-3 Iron and Steel Industry SWOT Analysis A. Strength: Page - 1Archana RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Scenario: Kushagra JadhavDokument12 SeitenSteel Scenario: Kushagra JadhavKushagra JadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precision Steel TubesDokument9 SeitenPrecision Steel TubesRam KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy Review - Tata SteelDokument20 SeitenStrategy Review - Tata SteelKen SekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Making NotesDokument22 SeitenSteel Making NotesVipin NandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Porter's Five Forces Analysis of the Indian Steel IndustryDokument4 SeitenPorter's Five Forces Analysis of the Indian Steel IndustrySwetabh2250% (2)
- Economics (Sree)Dokument45 SeitenEconomics (Sree)steevejan541Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problems of Iron and Steel Industry in India:: Swot Analysis StrengthDokument4 SeitenProblems of Iron and Steel Industry in India:: Swot Analysis StrengthAnonymous hmd3jXd4Noch keine Bewertungen
- India's Growing Steel Industry and Future OutlookDokument6 SeitenIndia's Growing Steel Industry and Future OutlookMonish RcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drgorad SM ProjectDokument10 SeitenDrgorad SM ProjectDeepak R GoradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iron and Steel in India Is Over 125 Year OldDokument7 SeitenIron and Steel in India Is Over 125 Year Olddharun1193Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report On IronDokument11 SeitenReport On IronammoosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iron and Steel Industry in IndiaDokument16 SeitenIron and Steel Industry in IndiaAnonymous gQyrTUHX38100% (1)
- Steel Market Oligopoly and Rising Indian DemandDokument6 SeitenSteel Market Oligopoly and Rising Indian Demandarchana783Noch keine Bewertungen
- ChapterDokument6 SeitenChapterMaria Sebastian ManjalyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper On Indian Steel IndustryDokument5 SeitenResearch Paper On Indian Steel Industryuziianwgf100% (1)
- Capstone Deliverable2 Group31Dokument11 SeitenCapstone Deliverable2 Group31Anju PuthanamkuzhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel IndustryDokument21 SeitenSteel IndustryBhupen YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Industry Overview ReportDokument92 SeitenSteel Industry Overview ReportAnkit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sub: Strategic Management: Steel IndustryDokument13 SeitenSub: Strategic Management: Steel IndustryRohit GhaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Industry in India: Project FinanceDokument32 SeitenSteel Industry in India: Project FinanceSharvil Vikram Singh100% (1)
- Shishir 2.1 To 2.4Dokument4 SeitenShishir 2.1 To 2.4Shishir KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Industry IntroductionDokument8 SeitenSteel Industry IntroductionAmitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sail ProjectDokument69 SeitenSail ProjectBhoomika SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnantaQUEST Tech Case Study FileDokument2 SeitenAnantaQUEST Tech Case Study FileDhanunjai IitbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tata Steel: Q1. Apply PESTLE, FIVE FORCES & SWOT Analysis On Following Tata BusinessDokument51 SeitenTata Steel: Q1. Apply PESTLE, FIVE FORCES & SWOT Analysis On Following Tata BusinessAnsh AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel IndustryDokument28 SeitenSteel Industryrohitmahato10Noch keine Bewertungen
- OTCM DriversDokument5 SeitenOTCM Driverslikith.focus25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Regression Analysis of Factors Affecting Steel Company SalesDokument18 SeitenMultiple Regression Analysis of Factors Affecting Steel Company SalesArun Kumar SatapathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iron and Steel Industry in IndiaDokument10 SeitenIron and Steel Industry in IndiaJordan SarasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industry Profile: Steel Industry Is Becoming More and More Competitive With Every Passing Day. During TheDokument19 SeitenIndustry Profile: Steel Industry Is Becoming More and More Competitive With Every Passing Day. During Thevinay8464Noch keine Bewertungen
- Future of Steel in IndiaDokument41 SeitenFuture of Steel in IndiaSatish TrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Five Forces AnalysisDokument4 SeitenFive Forces Analysisneekuj malikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Report 1 JindalDokument22 SeitenTraining Report 1 JindalPoonam vaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nezone FinalDokument61 SeitenNezone Finalvictor saikiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCI Iron and Steel Industry in IndiaDokument16 SeitenCCI Iron and Steel Industry in IndiaShubham KhattriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel IndustryDokument14 SeitenSteel IndustryRidhi BhanushaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- India's National Steel Policy 2005 Goals: Modern Steel Industry of 100 Million Tonnes by 2019Dokument15 SeitenIndia's National Steel Policy 2005 Goals: Modern Steel Industry of 100 Million Tonnes by 2019Yadav KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internship ReportDokument41 SeitenInternship ReportPankaj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industry and Company AnalysisDokument76 SeitenIndustry and Company AnalysisAnsu MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tata Steel's business strategy and growth plansDokument7 SeitenTata Steel's business strategy and growth plansshraddha_maheshwari6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Steel Industry Mini ProjectDokument6 SeitenChapter 1 Steel Industry Mini ProjectMilkey PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Institute of Management Bangalore Steel Industry AnalysisDokument23 SeitenIndian Institute of Management Bangalore Steel Industry AnalysisSylvia GraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iron & Steel IndustryDokument21 SeitenIron & Steel IndustryShejal SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TGM Metallurgy 010910 NK PDFDokument335 SeitenTGM Metallurgy 010910 NK PDFSiti Rabiatul AdawiyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- MY2200 Primary Metal 2002Dokument52 SeitenMY2200 Primary Metal 2002LTE002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrosteel Steel Plant Pre-Feasibility ReportDokument110 SeitenElectrosteel Steel Plant Pre-Feasibility ReportAbhinav SinglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing of SAIL By-Products via E-AuctionDokument8 SeitenMarketing of SAIL By-Products via E-AuctionShilpi AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- POSCO Brochure (플랜트소개용)Dokument27 SeitenPOSCO Brochure (플랜트소개용)German Jaramillo VillarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION: INVENTORY MANAGEMENTDokument51 SeitenCHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION: INVENTORY MANAGEMENTVettri VenthanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arvedi Brief Presentation Modernisation ProgrammeDokument30 SeitenArvedi Brief Presentation Modernisation ProgrammeKetnipha SukwannawitNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Steel BookDokument40 SeitenThe Steel BookFranklin GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparing Byproduct and Heat-Recovery CokemakingDokument9 SeitenComparing Byproduct and Heat-Recovery Cokemakingkselvan_1100% (1)
- Nucor Complete Guide 1Dokument101 SeitenNucor Complete Guide 1Hugo Rodriguez100% (2)
- Tata Steel PowerDokument37 SeitenTata Steel PowerChetana DiduguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Sector Motilal OswalDokument30 SeitenSteel Sector Motilal OswalBinod Kumar PadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACRJ-JSW Steel PDFDokument21 SeitenACRJ-JSW Steel PDFshiva12mayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clean Steel Making Initiatives in DRI / EAF ProcessDokument31 SeitenClean Steel Making Initiatives in DRI / EAF Processkar_kaushik20037144Noch keine Bewertungen
- IndustryDokument44 SeitenIndustryShumailaMumtazNoch keine Bewertungen
- PassionForProcesse en 04-13Dokument20 SeitenPassionForProcesse en 04-13Mutas MattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 017-Construction of Green Steel Manufacturing System For Shougang JingtangDokument8 Seiten017-Construction of Green Steel Manufacturing System For Shougang JingtangcornNoch keine Bewertungen
- W2 W3-302E Long Products Bulletin 2016Dokument120 SeitenW2 W3-302E Long Products Bulletin 2016bbcsteeltech LtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lavanya (20065-CH-009) VSP PPT-1Dokument21 SeitenLavanya (20065-CH-009) VSP PPT-1Yogesh BuradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epa Air ToxinsDokument220 SeitenEpa Air Toxinsnsavage1Noch keine Bewertungen
- DRI Report 2Dokument43 SeitenDRI Report 2FahmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cvs Dss FTP Project DescriptionDokument21 SeitenCvs Dss FTP Project Descriptionmetudgn100% (1)
- Vocational Training Report on Bhilai Steel PlantDokument29 SeitenVocational Training Report on Bhilai Steel PlantMohammad AfzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- VSP Industrial Training ReportDokument20 SeitenVSP Industrial Training ReportRohith KancherlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- R&D Roadmap Blast FurnaceDokument37 SeitenR&D Roadmap Blast FurnaceVishal JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Mill Ladle Weigihing System - SchenckDokument22 SeitenSteel Mill Ladle Weigihing System - SchenckBruno SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- TS-Compressed Air SystemDokument40 SeitenTS-Compressed Air SystemmishtinilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year Minimills 2010Dokument8 SeitenYear Minimills 2010mishtinilNoch keine Bewertungen
- QC Vision SAIL DurgapurDokument103 SeitenQC Vision SAIL DurgapurPratap Panda100% (1)