Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
1311 - As-Ad HW (Ans)
Hochgeladen von
Haifa Al-humayydOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1311 - As-Ad HW (Ans)
Hochgeladen von
Haifa Al-humayydCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Econ 1311 AS - AD & Business Cycle
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Over the business cycle, A) neither real GDP nor potential GDP fluctuate because they just grow smoothly along their trends. B) potential GDP fluctuates around its trend. C) only real GDP fluctuates around its trend and potential GDP remains equal to its trend. D) only potential GDP fluctuates around its trend and real GDP remains equal to its trend. E) real GDP fluctuates around its trend. E 2) A business cycle has two turning points, which are the A) recession and trough. B) peak and recession. C) peak and expansion. D) trough and peak. E) expansion and recession. D 3) The business cycle has two phases, A) recession and expansion. B) recession and trough. C) expansion and peak. D) peak and trough. E) expansion and trough. A 4) Identifying and dating business cycles is A) done by the government, at the Federal Reserve. B) done by the government, at the Commerce Department. C) impossible because the economy changes so much. D) done by a private organization, the NBER. E) done by people on Wall Street. D 5) Since 1854, the average length of an expansion phase in the United States is A) 120 months, about ten years. B) 35 months, about three years. C) 72 months, about six years. D) 48 months, about four years. E) 14 months, slightly more than a year. B 6) Moving along the potential GDP line, if the price level rises then A) there is no change in potential GDP. B) the quantity of GDP supplied increases. C) the potential GDP line shifts out to the right. D) the quantity of potential GDP supplied increases. E) the quantity of GDP supplied decreases. A 1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7) The real wage rate definitely falls if the money wage rate ________ and the price level ________. A) remains constant; rises B) remains constant; falls C) falls; falls D) rises; falls E) rises; rises A 8) A fall in the real wage rate ________ firms' profits and leads to ________ in the quantity supplied. A) lowers; an increase B) raises; a decrease C) raises; an increase D) lowers; a decrease E) does not change; no change C 9) Moving along the AS curve, when the price level increases the A) nominal wage rate falls and there is an increase in the quantity of real GDP supplied. B) real wage rate rises and there is a decrease in the quantity of real GDP supplied. C) real wage rate rises and there is an increase in the quantity of real GDP supplied. D) nominal wage rate rises and there is a decrease in the quantity of real GDP supplied. E) real wage rate falls and there is an increase in the quantity of real GDP supplied. E 10) A change in the price level A) shifts the potential GDP line. B) changes the quantity of real GDP supplied. C) shifts the aggregate supply curve leftward. D) shifts the aggregate supply curve rightward. E) shifts the aggregate demand curve leftward. B 11) If the nominal wage rate does not change, then if the price level increases, the real wage rate ________ and profits ________. A) rises; decrease B) rises; increase C) does not change; increase D) falls; increase E) falls; decrease D 12) The aggregate supply curve shifts rightward when A) the money wage rate rises. B) potential GDP decreases. C) government purchases increase. D) the money wage rate falls. E) income taxes increase. D 13) An increase in technology ________ potential GDP and ________ aggregate supply. A) increases; increases B) decreases; decreases C) decreases; increases D) does not change; does not change E) increases; decreases A
7)
8)
9)
10)
11)
12)
13)
14) Which of the following statements is correct? A) The lower the price level, the greater the quantity of real GDP demanded B) The lower the price level, the more the aggregate demand curve shifts leftward. C) The higher the price level, the more the aggregate demand curve shifts rightward. D) The price level does not effect the level of real GDP demanded. E) The lower the price level, the more the aggregate demand curve shifts rightward. A 15) At a price level of 100, John has savings equal to $20,000. If the price level increases to 130, the buying power of John's savings is approximately A) $26,000. B) $30,000. C) $12,780. D) $15,400. E) $20,000. D 16) A reason why an increase in the price level decreases the quantity of real GDP demanded is that A) the buying power of money increases. B) the inflation rate decreases. C) potential GDP decreases. D) the price of domestic goods and services increases relative to foreign goods and services. E) the real interest rate falls. D 17) Aggregate demand A) increases if the expected inflation rate increases. B) decreases if expected future income rises. C) increases if government expenditures decrease. D) increases if aggregate supply increases. E) increases if the exchange rate rises. A 18) Which of the following decreases aggregate demand and shifts the AD curve leftward? A) a decrease in potential GDP B) a decrease in government expenditures C) a decrease in the price of exported goods and services D) a tax cut E) a decrease in price level B 19) A tax increase A) decreases aggregate demand and the AD curve shifts leftward. B) does not shift or lead to a movement along the aggregate demand curve. C) increases aggregate demand and the AD curve shifts rightward. D) increases the quantity of real GDP demanded and there is a movement down along the AD curve. E) decreases the quantity of real GDP demanded and there is a movement up along the AD curve. A
14)
15)
16)
17)
18)
19)
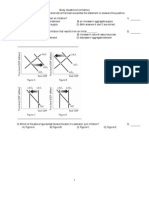
20) In the figure above, the shift in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 could be result of A) a decrease in the quantity of money. B) a rise in the price level. C) an increase in government expenditures on goods and services. D) an increase in taxes. E) a fall in the price level. C 21) In the figure above, the shift in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD3 could be the result of A) an increased expectation of a recession that lowers the expected rate of profit from investment. B) a decrease in the buying power of money. C) a decrease in the real interest rate. D) a decrease in the foreign exchange rate. E) an increase in the price level. A Price level (GDP deflator) 80 90 100 110 120 130 Real GDP demanded (trillions of 2000 dollars) 10 9 8 7 6 4 Real GDP supplied (trillions of 2000 dollars) 2 4 6 7 8 9
20)
21)
22) The above table gives aggregate demand and aggregate supply schedules. The equilibrium price level is A) 120. B) 110. C) 100. D) 90. E) 130. B
22)
23) The above table gives aggregate demand and aggregate supply schedules. If the price level is 120 then the aggregate quantity demanded is ________ than the aggregate quantity supplied and the price level ________. A) less; falls B) greater; rises C) less; rises D) greater; falls E) less; might fall, rise or not change depending on whether real GDP is more than, less than, or equal to potential GDP. A
23)
24) In the figure above, the economy is at an equilibrium with real GDP of $10 trillion and a price level of 110. As the economy moves toward its ultimate equilibrium, the ________ curve will shift ________. A) potential GDP; rightward B) aggregate supply; leftward C) aggregate supply; rightward D) aggregate demand; leftward E) aggregate demand; rightward B
24)
25) In the figure above, the economy is at an equilibrium with real GDP of $10 trillion and a price level of 110. At this point there is A) an inflationary gap. B) a recessionary gap. C) a full-employment equilibrium. D) price stability. E) an above full-employment equilibrium. B
25)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Macro Quiz 5 PDFDokument4 SeitenMacro Quiz 5 PDFcvofoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Questions 9 (Inflation and Phillips Curve)Dokument8 SeitenStudy Questions 9 (Inflation and Phillips Curve)Kiran KachhawahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The CorrectionDokument8 SeitenThe CorrectionDiamante GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflation (Multiple Choice Questions)Dokument16 SeitenInflation (Multiple Choice Questions)NickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 - KTEE203.1Dokument11 SeitenAssignment 1 - KTEE203.1Hà ChiếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fall Macro 2016-3.tst PDFDokument7 SeitenFall Macro 2016-3.tst PDFctyre34Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ad As Without AnsDokument5 SeitenAd As Without AnsnomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic GrowthDokument7 SeitenEconomic GrowthAhmed BahaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank 2Dokument6 SeitenTest Bank 2Nouran BakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics Canadian 8Th Edition Sayre Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument36 SeitenMacroeconomics Canadian 8Th Edition Sayre Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkevin.reider416100% (11)
- Macroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition Sayre Test Bank 1Dokument36 SeitenMacroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition Sayre Test Bank 1marychaveznpfesgkmwx100% (28)
- ECON 102 Midterm1 SampleDokument5 SeitenECON 102 Midterm1 SampleexamkillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled12 PDFDokument27 SeitenUntitled12 PDFErsin TukenmezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Sample QuestionsDokument11 SeitenFinal Exam Sample Questionsecobalas7100% (1)
- F22 Macro TermTest TF MCDokument8 SeitenF22 Macro TermTest TF MCjefferyliu791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 5Dokument6 SeitenProblem Set 5bus242Noch keine Bewertungen
- Economics Model GR12Dokument15 SeitenEconomics Model GR12Mamush kasimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 2 Sample MCQ (4-8)Dokument13 SeitenTest 2 Sample MCQ (4-8)gg ggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intermediate Microeconomics 2 Year Dr. Eman Gamal El-Din M. Chapter 4 Part 1Dokument31 SeitenIntermediate Microeconomics 2 Year Dr. Eman Gamal El-Din M. Chapter 4 Part 1Ceren Gökçe KeskinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapters 8,11 & 12Dokument9 SeitenChapters 8,11 & 12gg ggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ 3010 Final Exam Multiple Choice (100 Points)Dokument9 SeitenEcon 3010 Final Exam Multiple Choice (100 Points)westsiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baims-1644406705 13 MLF Altmaryn PDFDokument5 SeitenBaims-1644406705 13 MLF Altmaryn PDFShahadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 203 Sample Midterm2Dokument16 Seiten203 Sample Midterm2Annas GhafoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics 10th Edition Parkin Test BankDokument23 SeitenMacroeconomics 10th Edition Parkin Test Banklouisbeatrixzk9u100% (32)
- Macroeconomics 10th Edition Parkin Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument44 SeitenMacroeconomics 10th Edition Parkin Test Bank Full Chapter PDFcarlarodriquezajbns100% (11)
- Chapter 11 Aggregate Demand and SupplyDokument5 SeitenChapter 11 Aggregate Demand and SupplyPinaki MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics Practice Exam: FIGURE 24-1Dokument13 SeitenMacroeconomics Practice Exam: FIGURE 24-1adam jamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs With Solution For ECONS (Macro)Dokument38 SeitenMCQs With Solution For ECONS (Macro)DzifahManteau100% (1)
- Practice MCQ Set 1Dokument3 SeitenPractice MCQ Set 1coffeedance100% (1)
- Chapter 17 Questionnaire - AdjustedDokument11 SeitenChapter 17 Questionnaire - AdjustedNatalia Cabrera LazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QUIZ CH 23 Topik Economic Growth (Tanpa Jawaban)Dokument12 SeitenQUIZ CH 23 Topik Economic Growth (Tanpa Jawaban)mbevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock Exam Solutions FAPM Economics Feb 2016Dokument11 SeitenMock Exam Solutions FAPM Economics Feb 2016MbusoThabetheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument11 SeitenAssignment 1Anh LanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIN201 - Quiz - 2 - FA - 2022 - Nguyễn Đức Minh-HS173138Dokument12 SeitenFIN201 - Quiz - 2 - FA - 2022 - Nguyễn Đức Minh-HS17313828- Nguyễn Đức Minh - Chíp PơNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs Inflation Business Cycle - EditedDokument5 SeitenMCQs Inflation Business Cycle - EditedSadia IlyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 5 ECON 343Dokument7 SeitenAssignment 5 ECON 343Jack BNoch keine Bewertungen
- MT 2016Dokument9 SeitenMT 2016Ismail Zahid OzaslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Mocks P-1 RevisionDokument15 SeitenAs Mocks P-1 RevisionpretzNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 26 Ad & AsDokument25 SeitenCH 26 Ad & AsAli HussinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 Exam AP MacroeconomicsDokument25 Seiten2008 Exam AP MacroeconomicsJoanna Ip100% (6)
- Macroeconomics Chapter 8 Multiple ChoiceDokument3 SeitenMacroeconomics Chapter 8 Multiple ChoiceGene'sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ 101 Test #2Dokument10 SeitenEcon 101 Test #2overloaduser_10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fiscal Policy (Multiple Choice Questions)Dokument16 SeitenFiscal Policy (Multiple Choice Questions)NickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision 2 4 5 MICRODokument15 SeitenRevision 2 4 5 MICROahmad Al-SaggafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Study Quiz and Exercises Final 17 March 20113Dokument161 SeitenSelf Study Quiz and Exercises Final 17 March 20113markNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test BankDokument14 SeitenTest BankHossam EssamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econ 203 PRactice Final 2016Dokument15 SeitenEcon 203 PRactice Final 2016BOOMERBADNoch keine Bewertungen
- w10 112 v1Dokument22 Seitenw10 112 v1Rusty ButlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument8 SeitenAssignment 2Hà ChiếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 05 - 10ce - Macro-1-5Dokument5 SeitenChap 05 - 10ce - Macro-1-5shienalycabiles98Noch keine Bewertungen
- Macro - InteDokument7 SeitenMacro - InteHilary ChoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 203 Sample Midterm3 AnswersDokument13 Seiten203 Sample Midterm3 AnswersMarilyne JinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 ReviewDokument7 SeitenChapter 5 ReviewZahaAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.3 InflationDokument7 Seiten5.3 Inflationyiming peiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Exam!!!!Dokument22 SeitenSample Exam!!!!kbond93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Econ 2101 Sample Questions MacroDokument3 SeitenEcon 2101 Sample Questions MacroRafaPMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 MCBDokument6 SeitenChapter 8 MCBHunter KellettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of Development Economics, Third EditionVon EverandEssentials of Development Economics, Third EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Up SellingDokument4 SeitenUp SellingKhokha JamaliehNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAF 3 Activity Based Costing by Sir Saud Tariq ST AcademyDokument21 SeitenCAF 3 Activity Based Costing by Sir Saud Tariq ST Academyrana hassan aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEFA All Modules SolutionsDokument205 SeitenBEFA All Modules Solutions21951a2183Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Final Sample Econ12 F22Dokument1 SeiteExam Final Sample Econ12 F22Bri MinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Practice QuestionsDokument9 SeitenChapter 6 Practice QuestionsAbdul Wajid Nazeer CheemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kunci Jawaban Siklus Akuntansi (P1)Dokument30 SeitenKunci Jawaban Siklus Akuntansi (P1)Zulkarnain Zoel67% (3)
- TNERC Miscellaneous ChargesDokument86 SeitenTNERC Miscellaneous ChargesanandpurushothamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC No. 03 s.2017: Consolidated Schedule of Fees and ChargesDokument3 SeitenMC No. 03 s.2017: Consolidated Schedule of Fees and ChargesMae Richelle Dizon DacaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 7.palepuDokument13 SeitenCH 7.palepuRavi OlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tea at PeninsulaDokument4 SeitenTea at PeninsulaBilly GambalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Transportation?Dokument7 SeitenWhat Is Transportation?Geethu ParvathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer RetentionDokument7 SeitenCustomer RetentionDrKamal WarraichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Costing:: CSWPA-SM Certified SOLIDWORKS Professional - Advanced Sheet MetalDokument1 SeiteCosting:: CSWPA-SM Certified SOLIDWORKS Professional - Advanced Sheet MetalMech SathyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purchase Agreement: Contract Number: 004/BHS - SYRAKO/CPO/V/2017Dokument4 SeitenPurchase Agreement: Contract Number: 004/BHS - SYRAKO/CPO/V/2017Dian Pratama Putri100% (1)
- History of Anti DumpingDokument20 SeitenHistory of Anti DumpingOjantricNoch keine Bewertungen
- 900-kW Grid Connected Solar PV System: Technical and Commercial ProposalDokument8 Seiten900-kW Grid Connected Solar PV System: Technical and Commercial ProposalGulshana GajjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skoda AutoDokument36 SeitenSkoda Auto613450% (2)
- EMIS Insights - Colombia Real Estate and Construction Sector Report 2018 - 2019Dokument80 SeitenEMIS Insights - Colombia Real Estate and Construction Sector Report 2018 - 2019Giovanny Galvis HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Citation CJ4 - Operating Economics GuideDokument4 SeitenCitation CJ4 - Operating Economics Guidealbucur100% (1)
- Retailing: Promoting The Sale of Goods, Especially by Their Presentation in Retail Outlets. (New OxfordDokument4 SeitenRetailing: Promoting The Sale of Goods, Especially by Their Presentation in Retail Outlets. (New OxfordAbhishek ChaubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Promotion StrategiesDokument4 SeitenGlobal Promotion StrategiesPatricia MumbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate SupplyDokument8 SeitenAggregate Demand and Aggregate Supplytasleem1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bollore Logistics CanadaDokument17 SeitenBollore Logistics Canadadeepakshi0% (1)
- FinMan 12 IPO and Hybrid Financing 2015Dokument50 SeitenFinMan 12 IPO and Hybrid Financing 2015panjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPI Suggested June 2014Dokument25 SeitenCAPI Suggested June 2014Meghraj AryalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Compensation N RewardDokument52 SeitenModule 1 Compensation N RewardAnshul PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 39 Airbus vs. Boeing: Prepared byDokument13 SeitenCase Study 39 Airbus vs. Boeing: Prepared byShakir EbrahimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caso Biovail Corportation - RespuestasDokument6 SeitenCaso Biovail Corportation - RespuestasSergioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sách Economy TOEIC 4 - Phần Đọc PDFDokument278 SeitenSách Economy TOEIC 4 - Phần Đọc PDFCẩm ThạchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimating The Cost of The Proposed Reston VPAC: Construction and Operating Costs, December 8, 2022Dokument10 SeitenEstimating The Cost of The Proposed Reston VPAC: Construction and Operating Costs, December 8, 2022Terry MaynardNoch keine Bewertungen