Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Essay Form 5 Chapter 3 Review
Hochgeladen von
Tan YKCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Essay Form 5 Chapter 3 Review
Hochgeladen von
Tan YKCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
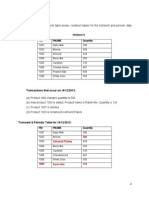
Essay Form 5 Chapter 3 Review 1. Diagram 9.1 shows a structure of a unit of a nephron.
Rajah 9.1menunjukkan struktur satu unit nefron.
=TYK=
Diagram 9.1 Rajah 9.1
(a) Explain the structure and the role of the nephron. Terangkan struktur dan peranan nefron. [6 marks] (b) Describe how urine is produced. Terangkan bagaimana air kencing dibentuk. [10 marks] (c) Explain the consequences of kidney failure. Jelaskan kesan kegagalan ginjal. [4 marks]
Marking Scheme Essay Form 5 Chapter 3 Review (a) Able to explain the structure and the role of the nephron : P1 - Nephron is the functional unit of a kidney. P2 - A nephron consists of 3 major parts : - Glomerulus and its associated vessels P3 - the Bowmans capsule P4 - a long narrow tube called the renal tubule, which is made up of the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubule. P5 - the distal convoluted tubules of several nephrons join to a common collecting duct. P6 the loop of Henle is a long hairpin-shaped region of the nephron that descends into the medulla and then returns to the cortex. Total 6m (b) Able to describe the formation of urine. F1 - Able to state three processes in urine formation E1 - Ultrafiltration, reabsorption and secretion. All 3 = 1m F2 P1 P2 P3 P4 Able to explain the ultrafiltration process Blood is under relatively high pressure when it reaches the nephron. The high blood pressure in the glomerulus, forces fluid to filter through the filtration membrane into the lumen of Bowmans capsule forming glomerular filtrate; contains water, glucose, amino acids, urea, mineral salts and other small molecules (Any 3) Max 3 Able to explain the reabsorption process The glomerular filtrate will flow into proximal convoluted tubule selective reabsorption occurs; all the glucose, amino acids, vitamins and many inorganic ions are reabsorbed back into the blood by active and passive transport forming a relatively high solute concentration in the peritubular capillaries thus a large volume of water is reabsorbed into the blood by osmosis and increase the concentration of urea in the convoluted tubule glomerular filtrate then flow into loop of henle and distal convoluted tubule more water and minerals being reabsorbed back into the blood (Any 4) Max 4
F3 P5 P6P7P8P9 P10P11P12-
F4 - Able to explain the secretion process P13 - takes place in the distal convoluted tubule P14 - urea/toxins/certain drugs / hydrogen ions/potassium ions/ammonia being secreted by passive diffusion and active transport from the blood capillary into the distal convoluted tubule
P15 - the filtrate reaches the collecting duct ; now called urine P16 - flows down the ureter, the bladder and the urethra and is finally excreted. (Any 2) Max 2 Total 10m (c) Able to explain the consequences of kidney failure : P1 - if both kidneys stop functioning, the blood osmotic pressure and blood volume cannot be maintained. P2 - the built up of toxic wastes in the body can result in life threatening conditions. P3 - they have to undergo haemodialysis P4 - another treatments for impaired kidney functions is the transplant of a healthy kidney from a donor to the patient. Total 4
TOTAL MARKS 20m
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Lab4 ActivityDiagram LatestDokument1 SeiteLab4 ActivityDiagram LatestTan YKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cseb114 CourseoutlineDokument3 SeitenCseb114 CourseoutlineTan YKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Database 2 DB2Dokument3 SeitenDatabase 2 DB2Tan YKNoch keine Bewertungen
- DataSec Lab2Dokument7 SeitenDataSec Lab2Tan YKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 1.1Dokument1 SeiteQuiz 1.1Tan YKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alice MyreportDokument1 SeiteAlice MyreportTan YKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human CloningDokument8 SeitenHuman CloningTan YKNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Nexus Undercarriage Cross Reference GuideDokument185 SeitenNexus Undercarriage Cross Reference GuideRomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEEPZ Special Economic ZoneDokument2 SeitenSEEPZ Special Economic ZonetarachandmaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affordable Care Act Tax - Fact CheckDokument26 SeitenAffordable Care Act Tax - Fact CheckNag HammadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHASE 2 - Chapter 6 Object ModellingDokument28 SeitenPHASE 2 - Chapter 6 Object Modellingscm39Noch keine Bewertungen
- Etp ListDokument33 SeitenEtp ListMohamed MostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5030si PDFDokument2 Seiten5030si PDFSuperhypoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leyte Geothermal v. PNOCDokument3 SeitenLeyte Geothermal v. PNOCAllen Windel BernabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easyjet Group6Dokument11 SeitenEasyjet Group6Rishabh RakhechaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proprietar Utilizator Nr. Crt. Numar Inmatriculare Functie Utilizator Categorie AutovehiculDokument3 SeitenProprietar Utilizator Nr. Crt. Numar Inmatriculare Functie Utilizator Categorie Autovehicultranspol2023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Storage Reservior and Balancing ReservoirDokument19 SeitenStorage Reservior and Balancing ReservoirNeel Kurrey0% (1)
- QDA Miner 3.2 (With WordStat & Simstat)Dokument6 SeitenQDA Miner 3.2 (With WordStat & Simstat)ztanga7@yahoo.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Namal College Admissions FAQsDokument3 SeitenNamal College Admissions FAQsSauban AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Czar Alexander IIDokument11 SeitenCzar Alexander IIMalachy ChinweokwuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review 5Dokument4 SeitenLiterature Review 5api-463653994Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oscar Ortega Lopez - 1.2.3.a BinaryNumbersConversionDokument6 SeitenOscar Ortega Lopez - 1.2.3.a BinaryNumbersConversionOscar Ortega LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolsas Transfer FKDokument7 SeitenBolsas Transfer FKBelèn Caridad Nelly Pajuelo YaipènNoch keine Bewertungen
- WPB Pitch DeckDokument20 SeitenWPB Pitch Deckapi-102659575Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tps65070X Power Management Ic (Pmic) With Battery Charger, 3 Step-Down Converters, and 2 LdosDokument98 SeitenTps65070X Power Management Ic (Pmic) With Battery Charger, 3 Step-Down Converters, and 2 Ldosmok waneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept, Types, Characteristics and ClassificationsDokument6 SeitenConcept, Types, Characteristics and ClassificationsCJ FaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evan Gray ResumeDokument2 SeitenEvan Gray Resumeapi-298878624Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Non Technical Part: Sample Interview Questions For Network EngineersDokument5 SeitenThe Non Technical Part: Sample Interview Questions For Network EngineersblablaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMDS Indoor/Outdoor Transmitter Manual: Chengdu Tengyue Electronics Co., LTDDokument6 SeitenMMDS Indoor/Outdoor Transmitter Manual: Chengdu Tengyue Electronics Co., LTDHenry Jose OlavarrietaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movie Review TemplateDokument9 SeitenMovie Review Templatehimanshu shuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Risk ManagementDokument29 SeitenQuality Risk ManagementmmmmmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structures Module 3 Notes FullDokument273 SeitenStructures Module 3 Notes Fulljohnmunjuga50Noch keine Bewertungen
- CONFLICT ManagementDokument56 SeitenCONFLICT ManagementAhmer KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hollow lateral extrusion process for tubular billetsDokument7 SeitenHollow lateral extrusion process for tubular billetsjoaopedrosousaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acceptance and Presentment For AcceptanceDokument27 SeitenAcceptance and Presentment For AcceptanceAndrei ArkovNoch keine Bewertungen
- S4H - 885 How To Approach Fit To Standard Analysis - S4HANA CloudDokument16 SeitenS4H - 885 How To Approach Fit To Standard Analysis - S4HANA Cloudwai waiNoch keine Bewertungen
- JWCh06 PDFDokument23 SeitenJWCh06 PDF007featherNoch keine Bewertungen