Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Self-Locating Projection Weld Nuts Bulletin
Hochgeladen von
igtepOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Self-Locating Projection Weld Nuts Bulletin
Hochgeladen von
igtepCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SELF-LOCATING PROJECTION WELD NUTS
BULLETIN
WN
710
SELF-LOCATING PROJECTION WELD NUTS
PEM weld nuts (Types WN/WNS) provide load-bearing threads in metal sheets too thin to tap, and permit faster assembly. PEM brand weld nuts overcome many problems associated with other weld nuts burn-outs, complicated electrodes and pilots, tedious time-consuming indexing and re-tapping to remove weld spatter. Their design, based on the experience of hundreds of users of weld nuts, speeds production using standard equipment, thereby reducing labor costs. PEM stainless steel weld nuts offer the added advantage of resisting corrosion. You may specify steel or stainless steel for your requirements and be sure you are getting the weld nuts that are easiest to install. A variety of welding equipment is suitable for installation of PEM weld nuts. Best results have been obtained with a 50KVA press-type, spot-welding machine whose upper welding head moves vertically in a straight line with the lower electrode. Flat-faced electrodes with tip diameters .125 / 3.2 mm larger than the E dimension of the PEM weld nut should be used.
Self-locating shanks of PEM weld nuts eliminate the need for pilots and complex electrodes. The self-locating shanks not only properly position the weld nuts but they also protect threads from weld spatter and thereby eliminate secondary operations such as retapping to remove spatter.
Round head of PEM brand weld nuts eliminates tedious, timeconsuming indexing. Compact PEM weld nuts fit on narrow flanges.
The engineered projections of PEM weld nuts prevent burnouts in thin sheets
Look for the PEM trademark on all cataloged sizes.
PART NUMBER DESIGNATION
WN S 632 WN 632
Type Thread Code
0 0
CU
Finish Code: None on stainless steel nuts CU on steel nuts (standard)
Fastener Material Code S = 300 series stainless steel None = Carbon steel
Shank Code
WN-2 PennEngineering www.pemnet.com
SELF-LOCATING PROJECTION WELD NUTS
A
FASTENER MATERIAL: Type WN Carbon Steel Type WNS 300 Series Stainless Steel FINISH: Type WN CU - Copper Flash Type WNS Passivated and/or tested per ASTM A380 THREADS: Internal, ASME B1.1, 2B / ASME B1.13M, 6H
E
All dimensions are in inches.
Thread Size .112-40 (#4-40) .138-32 (#6-32) .164-32 (#8-32) .190-24 (#10-24) .190-32 (#10-32) .250-20 (1/4-20)
UNIFIED
Type Steel WN WN WN WN WN WN Stainless Steel WNS WNS WNS WNS WNS WNS
Thread Code 440 632 832 024 032 0420
Shank Code 0 0 0 0 0 0
A (Shank) Max. .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .048
Min. Sheet Thickness .030 .030 .030 .030 .030 .048
Hole Size In Sheet +.004 -.000 .173 .193 .218 .250 .250 .316
C Max. .172 .192 .217 .249 .249 .315
E +.000 -.010 .308 .341 .371 .440 .440 .522
T .004 .065 .094 .108 .156 .156 .186
Min. Dist. HoleC/L To Edge .154 .171 .186 .220 .220 .261
All dimensions are in millimeters.
Thread Size x Pitch
METRIC
Type Steel WN WN WN WN Stainless Steel WNS WNS WNS WNS
Thread Code M3 M4 M5 M6
Shank Code 0 0 0 0
A (Shank) Max. 0.77 0.77 0.77 1.22
Min. Sheet Thickness 0.77 0.77 0.77 1.22
Hole Size In Sheet +0.1 4.39 5.53 6.35 8.02
C Max. 4.36 5.5 6.32 7.99
E 0.25 7.82 9.42 11.17 13.25
T 0.1 1.49 2.58 3.78 4.56
Min. Dist. HoleC/L To Edge 3.91 4.71 5.59 6.63
M3 x 0.5 M4 x 0.7 M5 x 0.8 M6 x 1
INSTALLATION
1. With a PEM weld nut inserted in the properly sized hole (see above), bring the electrode force up sufficiently to clamp the projections of the fastener firmly against the sheet without embedding any portion of the projections. Be sure the electrodes are centered, and that the electrode faces are flat so that the force is applied evenly to all three projections. 2. Set the current or heat regulator on the low side and adjust along with the weld time until a good weld is produced. For mild steel, which has a medium electrical resistance, there is a wide range of adjustments possible. For austenitic stainless steel, which has a high electrical resistance, the range is narrow at low heat. 3. Adjust squeeze time so that there is adequate time for the electrodes to close and develop proper forces (suggested initial setting 35 cycles). The weld period should be established by starting with the settings suggested in the tables on page WN-4. As indicated above for current adjustments, a wide range of time is possible with mild steel, but there is a limited range with stainless steel. If weld time starts too soon, and proper welding is not achieved, the squeeze time should be lengthened. Also, the electrodes should be moved closer together so that they require less travel time to close on the work. Longer squeeze times will have no effect on the quality of the weld. However, they do affect productivity and decrease the number of weld nuts that can be installed per hour. Hold time is set long enough to permit cooling and solidification of the weld before removing the electrodes. Start with 15 cycles and lengthen if necessary.
PennEngineering www.pemnet.com
WN-3
SELF-LOCATING PROJECTION WELD NUTS
PERFORMANCE DATA
Type Thread Code
440 632 832 032 0420 440 632 832 032 0420
(1)
SETTING GUIDES FOR PEM WELD NUTS IN .030/0.77 MM TO .063/1.6 MM SHEETS
Type Thread Code
440 632 832 032 0420 440 632 832 032 0420
Test Sheet Material .060 Cold-rolled Steel .060 302 Stainless Steel Pushout Torque-out Pushout Torque-out (lbs.) (in. lbs.) (lbs.) (in. lbs.)
500 640 760 880 1000 N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a 13 22 33 56 185 N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a 680 800 850 900 1000 N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a 13 28 45 110 200
Cold-rolled Steel
Test Sheet Material 302 Stainless Steel
Electrode (A) Secondary (B) Ram Force Current (lbs.) Amps 500 Weld Time (C) Cycles/Sec.
Electrode (A) Secondary (B) Weld Ram Force Current Time (C) (lbs.) Amps 500 Cycles/Sec.
WN
WN
WNS
WNS
450-500 450-500 450-500 500-550 550-600 N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a
17,000 17,000 17,000 18,000 20,000 N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a
6 / 0.10 6 / 0.10 6 / 0.10 10 / 0.17 10 / 0.17 N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a
N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a 450-500 450-500 500-550 550-600 650-700
N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a 16,500 16,500 16,500 18,500 20,000
N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a 6 / 0.10 6 / 0.10 6 / 0.10 6 / 0.10 6 / 0.10
UNIFIED
Type
Thread Code
M3 M4 M5 M6 M3 M4 M5 M6
Test Sheet Material 1.5 mm Cold-rolled Steel 1.5 mm 302 Stainless Steel Pushout Torque-out Pushout Torque-out (N) (Nm) (N) (Nm)
2220 3380 3910 4445 N/a N/a N/a N/a 1.4 3.7 6.3 20.9 N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a 3020 3780 4000 4445 N/a N/a N/a N/a 1.4 5 12.4 22.5
UNIFIED
Test Sheet Material Type Thread Code
M3 M4 M5 M6 M3 M4 M5 M6
Cold-rolled Steel
Electrode (A) Ram Force (N) Secondary (B) Weld Current Time (C) Amps 500 Cycles/Sec.
302 Stainless Steel
Electrode (A) Ram Force (N) Secondary (B) Weld Current Time (C) Amps 500 Cycles/Sec.
METRIC
METRIC
WN
WN
WNS
WNS
2000-2220 2000-2220 2220-2440 2440-2670 N/a N/a N/a N/a
17,000 17,000 18,000 20,000 N/a N/a N/a N/a
6 / 0.10 6 / 0.10 10 / 0.17 10 / 0.17 N/a N/a N/a N/a
N/a N/a N/a N/a 2000-2220 2220-2440 2440-2670 2890-3110
N/a N/a N/a N/a 16,500 16,500 18,500 20,000
N/a N/a N/a N/a 6 / 0.10 6 / 0.10 6 / 0.10 6 / 0.10
N/A Not Applicable. (1) The values reported are averages when all installation specifications and procedures are followed. Performance testing of this product in your application is recommended. We will be happy to provide samples for this purpose.
N/A Not Applicable. (A) Electrode Force is the force exerted by the electrodes on the fastener and sheet to clamp them together and ensure good electrical contact. Electrode force also sets the weld nut down flush on the sheet as the projections melt during the welding period. Insufficient electrode force may result in flashing, spitting, burning, spatter, and discoloration. On the other hand, excessive electrode force may flatten the fastener projections before proper welding temperature is reached or may imbed the projections of the cold fastener into the sheet. Excessive electrode force can also distort threads during the weld cycle. (B) Secondary Current determines the heat applied to the PEM weld nut and sheet. Heat is in direct proportion to weld time, resistances of the materials, and the square of the current. Current should not be set so high as to cause flashing or spattering or excessive heat which will distort the threads. Low currents may produce good looking welds but pushout and torque-out strengths will not be satisfactory. (C) Timing Cycle for projection welding comprises four periods. (1) the squeeze time in which the electrodes move into position and develop the required force; (2) the weld time when the current is applied; (3) the hold time while the weld congeals and cools; and (4) the off time for positioning the work for the next weld nut. NOTE: The setting guides shown in the above charts are for reference only and may differ for your welding equipment.
GUIDES TO BETTER WELDING
Electrodes, weld nuts, and panels must be clean and free of grease, rust, and metal burrs. When welds appear satisfactory on installed nut, but pushout values are low, one or more of the following may be the cause: (1) Ram pressure too high. (2) Current too low. (3) Panel not clean. (4) Weld nuts not centered under electrodes. (5) Hold time not long enough to allow proper cooling. (6) Pressure regulator on welding equipment drifts. If installed threads are distorted, the following singly or in combination may be the cause: (1) Weld time too long. (2) Current too high. (3) Ram pressure too high. Should it be impossible to produce a proper weld because weld time starts before electrodes close on the work, shorten the gap between the electrodes so that they take less time to move into position and/or lengthen the squeeze time.
RoHS compliance information can be found on our website. 2010 PennEngineering.
Specifications subject to change without notice. Check our website for the most current version of this bulletin.
WN-4
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Resistance WeldingDokument13 SeitenResistance Weldingpavithra222Noch keine Bewertungen
- Split Second Brochure V3Dokument4 SeitenSplit Second Brochure V3houstonhimselfNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Consumables 309-320Dokument12 Seiten8 Consumables 309-320Márcio FerreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- WOWLibrary-Fundamentals MMA WeldingDokument9 SeitenWOWLibrary-Fundamentals MMA WeldingRahul BalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strain Gage Soldering Techniques: Strain Gages and InstrumentsDokument6 SeitenStrain Gage Soldering Techniques: Strain Gages and InstrumentsMuayad HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contact Welders GuideDokument13 SeitenContact Welders GuideValvemakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding InstructionsDokument12 SeitenWelding Instructionsrahman asadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correct Arc Length, Correct Travel Speed and Correct Electrode AngleDokument6 SeitenCorrect Arc Length, Correct Travel Speed and Correct Electrode AngleFelix MilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding Guide BrochureDokument4 SeitenWelding Guide BrochureAnonymous 6aGAvbNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stud WeldingDokument5 SeitenStud Weldingvinamap27Noch keine Bewertungen
- AN101 TO220 GuidelinesDokument4 SeitenAN101 TO220 GuidelinesBayangan MautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spot WeldingDokument8 SeitenSpot Weldingtoyota952Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resistance WeldingDokument7 SeitenResistance WeldingCristian GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistance WeldingDokument45 SeitenResistance WeldingAntony SiregarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEM Self Clinching Flush FastenersDokument4 SeitenPEM Self Clinching Flush FastenersAce Industrial SuppliesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper From SDI (Structural Deck Institute) WWDokument9 SeitenPaper From SDI (Structural Deck Institute) WWkiss_59856786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arc Welding - Basic Steps ReadingDokument12 SeitenArc Welding - Basic Steps Readingaddayesudas100% (1)
- Welding Lecture and OrientationDokument57 SeitenWelding Lecture and OrientationHenry SyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Ii Resistance Welding ProcessesDokument49 SeitenUnit Ii Resistance Welding ProcessesparthibankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipelines Welding HandbookDokument64 SeitenPipelines Welding HandbookSixto GerardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spot Welding, Types, Applications, Advantages and DisadvantagesDokument6 SeitenSpot Welding, Types, Applications, Advantages and DisadvantagesM ZahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spot Welding Process LabDokument4 SeitenSpot Welding Process Labjunaid gujratiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 MANGO 1 - Weld ProcedureDokument4 Seiten01 MANGO 1 - Weld ProcedureOPAZOSCNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB Welding-English PDFDokument20 SeitenTB Welding-English PDFdanghpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site Welding Instruction Sheet (SWIS) HandbookDokument36 SeitenSite Welding Instruction Sheet (SWIS) HandbookNuwan RanaweeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reinforcing Bar CouplersDokument9 SeitenReinforcing Bar CouplersAWAKSEORANGNoch keine Bewertungen
- FSW Technical HandbookDokument27 SeitenFSW Technical HandbookAnand Kumar MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control of Cracks in 9Cr-1Mov (P91) Material: Jacob Mathew and Sanu NakulanDokument8 SeitenControl of Cracks in 9Cr-1Mov (P91) Material: Jacob Mathew and Sanu NakulanSadhasivam VeluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistance WeldingDokument13 SeitenResistance WeldingAashishSethiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical To Quality in Welding-1Dokument29 SeitenCritical To Quality in Welding-1aadmaadmNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 TMSS 02 R0Dokument0 Seiten15 TMSS 02 R0renjithas2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resistance Seam WeldingDokument31 SeitenResistance Seam Weldingaiman87_uitm100% (3)
- Essential Variables of SmawDokument7 SeitenEssential Variables of SmawAbdallah Mansour100% (6)
- Non-Arc Welding ProcessesDokument30 SeitenNon-Arc Welding ProcessesKhalid El MasryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 320102cB SMAW-B - 1Dokument32 Seiten320102cB SMAW-B - 1Syaifur RohmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weldingfixtures 140919075513 Phpapp02Dokument28 SeitenWeldingfixtures 140919075513 Phpapp02VJ SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AJM & NDT - Module - 1Dokument35 SeitenAJM & NDT - Module - 1Naveen S BasandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEM Self Clinching Self Locking FastenersDokument4 SeitenPEM Self Clinching Self Locking FastenersAce Industrial SuppliesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cast Iron Welding AlloysDokument4 SeitenCast Iron Welding AlloysKhin Aung ShweNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESAB - PipelinesDokument65 SeitenESAB - PipelinesLigia114100% (2)
- Q1, Module 1, Lesson1Dokument9 SeitenQ1, Module 1, Lesson1Jerome A. GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welders Training Program ManualDokument140 SeitenWelders Training Program ManualAlmario Sagun100% (1)
- Atmospheric Corrosion Resisting SteelDokument10 SeitenAtmospheric Corrosion Resisting SteelCarlos PadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding: IntrdutionDokument10 SeitenWelding: IntrdutionJoseph George KonnullyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample WPS SMAW Stainless SteelDokument7 SeitenSample WPS SMAW Stainless Steeldaemsal100% (4)
- Assignment CE561Dokument2 SeitenAssignment CE561Karen Mae TingNoch keine Bewertungen
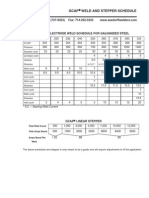
- Weld SchedulesDokument7 SeitenWeld SchedulesadamzlametNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spot Welding Interview Success: An Introduction to Spot WeldingVon EverandSpot Welding Interview Success: An Introduction to Spot WeldingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesVon EverandWeld Like a Pro: Beginning to Advanced TechniquesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- Farm and Workshop Welding: Everything You Need to Know to Weld, Cut, and Shape MetalVon EverandFarm and Workshop Welding: Everything You Need to Know to Weld, Cut, and Shape MetalBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Soldering Electronic Components 2nd EditionVon EverandSoldering Electronic Components 2nd EditionBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- How to prepare Welding Procedures for Oil & Gas PipelinesVon EverandHow to prepare Welding Procedures for Oil & Gas PipelinesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Welding the Inconel 718 Superalloy: Reduction of Micro-segregation and Laves PhasesVon EverandWelding the Inconel 718 Superalloy: Reduction of Micro-segregation and Laves PhasesNoch keine Bewertungen
- YellowGate Catalog v1 PDFDokument68 SeitenYellowGate Catalog v1 PDFOswaldo GuerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM W Welding CatalogDokument80 SeitenCM W Welding CatalogigtepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokument593 SeitenHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokument593 SeitenHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokument593 SeitenHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Weva4 4085Dokument6 SeitenWeva4 4085igtepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog 100Dokument100 SeitenCatalog 100igtepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lors Catalog 2010-3Dokument1 SeiteLors Catalog 2010-3igtepNoch keine Bewertungen
- TFM-561U: Quick Installation GuideDokument9 SeitenTFM-561U: Quick Installation GuideigtepNoch keine Bewertungen
- WD Mybook Essential User Guide EnglishDokument77 SeitenWD Mybook Essential User Guide Englishmatfox2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Durco Pressure Leaf Sulfur FiltrationDokument3 SeitenDurco Pressure Leaf Sulfur FiltrationBhusarapu SrinivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Record of Welder or Welding Operator Qualification TestsDokument1 SeiteRecord of Welder or Welding Operator Qualification TestsBalkishan DyavanapellyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wrought Ferritic, Ferritic/Austenitic, and Martensitic Stainless Steel Piping FittingsDokument7 SeitenWrought Ferritic, Ferritic/Austenitic, and Martensitic Stainless Steel Piping Fittingsiron manNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Simulation of Petcoke Steam GasificationDokument18 SeitenDesign and Simulation of Petcoke Steam Gasificationsaahikrishna8100% (1)
- H 99 Sec 2 BmaterialsDokument4 SeitenH 99 Sec 2 BmaterialsAxel MalusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Drilling OperationsDokument18 SeitenOverview of Drilling Operationsali nahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Denso Tank Base Protection System SpecDokument2 SeitenDenso Tank Base Protection System SpecmniteshpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete TechnologyDokument14 SeitenConcrete TechnologyShraddha DateyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScrewJack Assembly DocumentationDokument2 SeitenScrewJack Assembly DocumentationMDM19B034 BAKSHI ANUPAMA SAINoch keine Bewertungen
- ANDRE - Poland - Abrasive MaterialsDokument2 SeitenANDRE - Poland - Abrasive MaterialsRaja Sekhar Reddy PaluruNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWP Course NotesDokument320 SeitenAWP Course Notesduniaadnan100% (3)
- Zem CoatDokument1 SeiteZem Coatjcedricaquino0% (1)
- Donner Case Operations ManagementDokument3 SeitenDonner Case Operations Managementleeladon0% (1)
- Asme Section Ii A-2 Sa-995Dokument4 SeitenAsme Section Ii A-2 Sa-995Anonymous GhPzn1xNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gatekeeper Inert Gas Purifier EsiteDokument4 SeitenGatekeeper Inert Gas Purifier EsiteMarcos MedranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet Metal ShopDokument18 SeitenSheet Metal ShopAnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASPINWALL - Profiled Superabrasive Grinding Wheels For The Machining of A Nickel Based SuperalloyDokument4 SeitenASPINWALL - Profiled Superabrasive Grinding Wheels For The Machining of A Nickel Based SuperalloyLuis Fillipe Lopes TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molybdenum ProcessingDokument4 SeitenMolybdenum Processingkingysaint123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On Corrugated Boxes (Automatic Plant)Dokument6 SeitenProject Report On Corrugated Boxes (Automatic Plant)EIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wrapping Coating ProcedureDokument5 SeitenWrapping Coating Procedureshantanu kumar100% (1)
- Unit - I: Electron Beam WeldingDokument15 SeitenUnit - I: Electron Beam Weldingapi-271354682Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ips C Pi 410Dokument13 SeitenIps C Pi 410ali1860Noch keine Bewertungen
- PART 149 What Is Fusion WeldingDokument2 SeitenPART 149 What Is Fusion Weldingravindra_jivaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily ReportDokument3 SeitenDaily ReportJoseph AbousafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Vessel Manual-M.asgaRZADEGANDokument79 SeitenPressure Vessel Manual-M.asgaRZADEGANH BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat Bpe PDFDokument57 SeitenCat Bpe PDFJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNC Programmer ResumeDokument3 SeitenCNC Programmer Resumenaunit3666Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ovr Dossier.Dokument93 SeitenOvr Dossier.suria qaqcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Danh Sách Tiêu Chuẩn HesDokument2 SeitenDanh Sách Tiêu Chuẩn HesanhthoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09D 22 00 A3 Sheet 01Dokument1 Seite09D 22 00 A3 Sheet 01RobsNoch keine Bewertungen